Ballinspittle, Co Cork: the Marian Grotto became a world news sensation
1954 was a great year for the construction of outdoor shrines and grottoes in Ireland. Pope Pius XII had designated it a special Marian Year to mark the centenary of the ‘dogma of the Immaculate Conception and Assumption’. The Marian Year was an international event, but apparently no other country embraced the idea with greater fervour than Ireland. The notion seemed to capture the imagination of a young republic suffering from serious recession, high unemployment and loss of population through emigration. Hundreds of projects were put in hand and today, on almost every road in the country – and in every community – you will see statues of the Blessed Virgin Mary, usually in well tended settings. They add to the colour and character of this green land: like the ancient holy wells, they are venerated and not forgotten.

Statue maker Maurice O’Donnell recalled that 1954 was a bonanza year for him: “…I was making so many at that time there was no time to dry them out before painting, so lots of statues in the shrines around the country are still unpainted. But that was in the Marian Year. The bottom has dropped out of the statues market since the Vatican Council…” Although many statues of the Virgin were painted later on, you will still see many unpainted (white) examples.
Marian Year shrine added on to the Holy Well at Keallkill, Co Cork
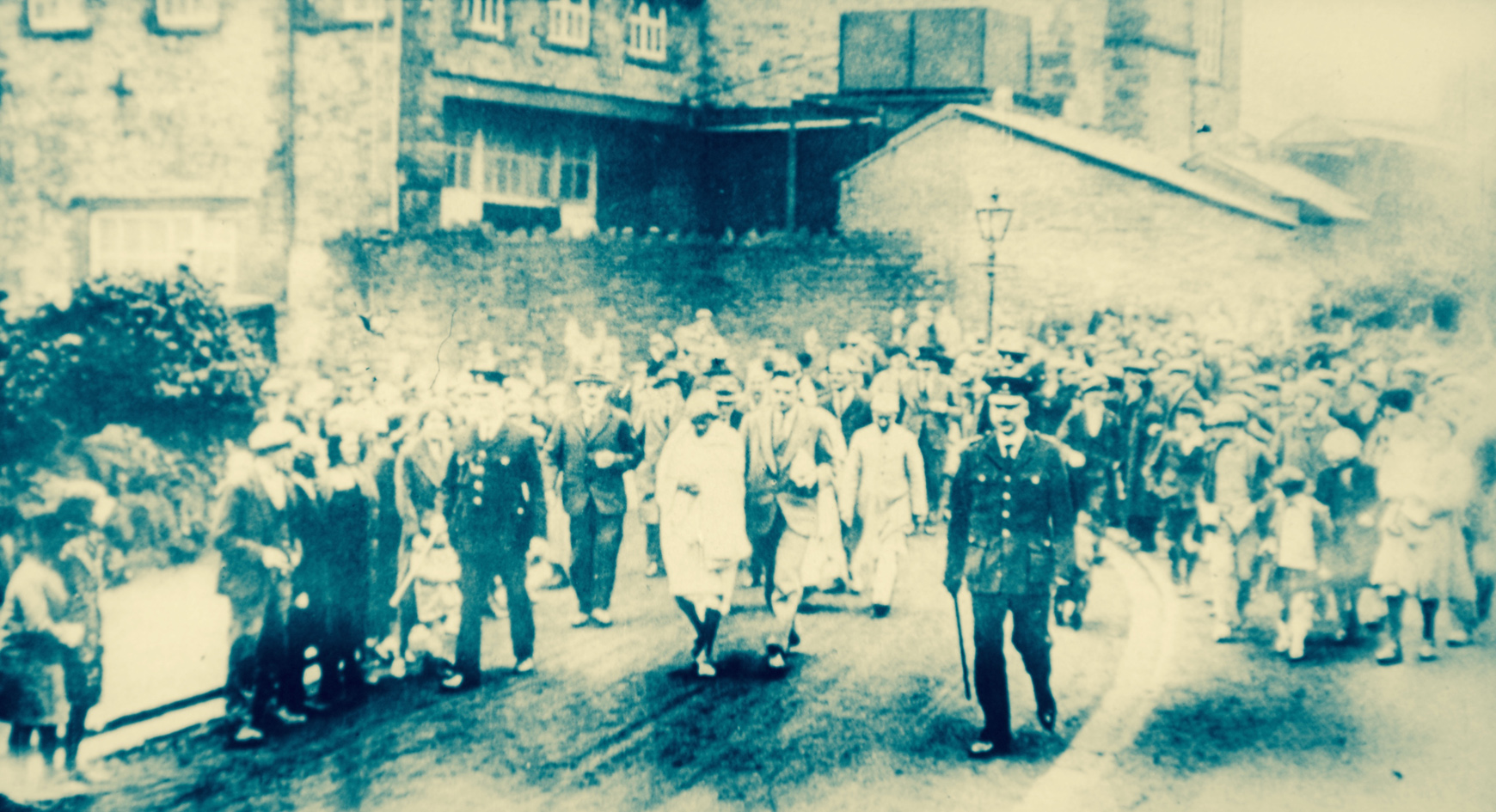
Exactly thirty years ago – on 26 July 1985 – the grotto at Ballinspittle jumped into the news headlines of the world because two local women witnessed the statue there moving while they were praying. The little Cork village suddenly found itself the centre of media attention and – during that summer – thousands of people came in bus loads from all over Ireland, either out of curiosity or anxiety to become part of a phenomenon. Many saw the statue move: a police sergeant (presumably a reliable observer) saw it rise into the air – while cures were claimed by sick people who visited the site.

Crowds at Ballinspittle 1985 – Evoke.ie
Strange events were not limited to Ballinspittle. Reports had already appeared elsewhere. Kerry got in first: in February of the same year 30 schoolchildren saw two statues moving in the church at Asdee, while in nearby Ballydesmond something similar happened soon after. Here’s a contemporary extract from RTE News – worth watching for the concise view of rural Ireland in the 1980s.

Over 10,000 people visited the Ballinspittle grotto every night throughout the summer. The Irish Times (6 August 1985) reported: ’…Ballinspittle’s claim to a moving statue was matched in no time at all by reports of similar occurrences in Dunmanway and Courtmacsherry. But too many people, including senior gardai, well-tried sceptics and some who registered what appeared to be genuine shock said they saw the statue move, so Ballinspittle has remained the premier place of pilgrimage…’

The Catholic Church distanced itself from these happenings. Bishop Michael Murphy of Cork warned that “…common sense would demand that we approach the claims made concerning the grotto in Ballinspittle with prudence and caution…” but he also relished the fact that “…crowds are gathering there in a great spirit of prayer…” A difficult stance, perhaps, as similar occurences from Lourdes and Knock in the 19th century led to the creation of huge religious centres and pilgrimage destinations.

The visions at Knock, witnessed in 1879
The moving statues was a story big enough to inspire Peter Mulholland of the National University of Ireland, Maynooth, to pen a lengthy monograph in 2009, Moving Statues and Concrete Thinking, available in full on line – and a fascinating read. Mulholland makes the point that from the 1950s to the 1980s the western world, including Ireland, was perceived to be under threat from the Cold War, ‘Nuclear Nightmare’ (from weapons and waste), Communism, the ‘permissive society’ – and, more locally, ‘The Troubles’ and increasing unemployment and emigrations; while in 1970 the Bishop of Galway said he thought ‘organized atheism’ was the source of the ‘most serious injury’ being done to the young people of Ireland. All this, says Mullholland, contributed to an underlying feeling of insecurity which created an atmosphere ripe for ‘cults’ (such as observers of moving statues) because of a high level of anxiety in the community. The monograph goes pretty deeply into the realms of psychology, quoting one researcher who “…argued that a certain kind of family structure ‘intensifies Oedipal desires in both sons and daughters, and so promotes Marian devotion’. He held that Marian ‘hallucinations’ are shaped not simply by Oedipal desires but also by other infantile and adult desires…”
Mulholland concludes: “…The moving statues were a modern manifestation of the kind of ‘magical devotionalism’ that sections of the Irish Catholic population have long been prone to resort to during periods of personal or collective distress… They were products of the kind of literalistic, magical-devotionalism that Irish clerics condemned in the 1950s and ‘60s as being ‘anti-intellectual’ and a ‘peasant religion’…”

Knock Shrine, early 20th century
Perhaps it’s just coincidence (and I haven’t seen anyone else mention this), but it is worth noting that the Air India Disaster occurred at Ahakista, on the coast of West Cork, less than a month before the first apparitions were seen at Ballinspittle. This terrorist event which killed over 300 innocent souls must have had some effect on the local – if not the national – psyche, and could certainly have enhanced feelings of anxiety and insecurity in a rapidly changing world.

1985 Air Disaster Memorial, Ahakista
Looking back from the 21st century to these events I feel a sense of – well, disappointment – that what comes across now in reports on the phenomenon is mainly disparagement. This is a country which, quite rightly, hangs on to its history and mythologies: as with the wandering bards of older times stories are kept alive at the fireside, in the pubs – wherever people gather. Stories of The Other Crowd, of old battles, of heroes – and of neighbours – are listened to eagerly, and will be repeated just as eagerly. I don’t hear people dismissing them or expressing cynicism about them, as they seem ready to do about moving statues. Such scepticism is understandable in modern Ireland but I will continue to listen with an open mind to all the stories of miraculous happenings that are cherished and passed on, and which underscore the ancient faith of the countryside.

It would be wrong not to finish the story of Ballinspittle. On 31st October (Samhain) 1985, when a group was gathered in prayer at the grotto a car pulled up and three men got out carrying hammers and axes. In front of the dismayed onlookers they smashed the statue of the Virgin and shouted abuse at the worshippers for “…adoring false Gods…” The men, who claimed to belong to an extremist fundamental Christian sect based in California, were later arrested and charged with ‘causing malicious damage in a place of divine worship’. Amazingly, at the trial the Judge stated that he had to be “…particularly zealous in guarding the rights of the three defendants…” and dismissed the case on the grounds that the Ballinspittle grotto is not, in fact, a place of divine worship. In March 1986 the perpetrators appeared on the popular Late Late Show, hosted by Gay Byrne on RTE Television. They cited the fourth and fifth commandments of the Old Testament as giving them divine sanction to smash all religious statues in Ireland, regardless of the rights and views of other people. Reporter Eoghan Corry stated in an article in the Sunday Press, “…there isn’t a safe statue in the country.” Fortunately, following further acts of vandalism they were duly convicted.
Links worth following for more on the Moving Statues:
Finola’s blog post Mary Mary
Radio Documentary from RTE in 1992
RTE TV documentary on Ballinspittle

Email link is under 'more' button.

 It was the high point (although not the culmination yet) of two months of Rossa commemorations in West Cork which has included lectures, a play, a walking tour, exhibitions and the unveiling of new monuments in several places including the impressive Skibbereen installation inaugurated by President Higgins.
It was the high point (although not the culmination yet) of two months of Rossa commemorations in West Cork which has included lectures, a play, a walking tour, exhibitions and the unveiling of new monuments in several places including the impressive Skibbereen installation inaugurated by President Higgins.