Aultagh Ogham Stone
One thing always leads to another – that’s something you can be sure of when we are on our archaeological adventures. A case in point was a recent expedition to have a look at Ballynacarriga Castle (not far from Dunmanway, County Cork: 16th century – notable for having a Sheela-na-gig carving built high up into the outer masonry wall, and some unusual carved inscriptions on the internal stonework).
Ballynacarriga Castle (left) with its Sheela-na-gig (right)
Perhaps these various stone scribings turned our minds to the subject of Rock Art (easily done). Our excellent guide on that morning, Margaret Murphy of the Skibbereen Heritage Centre, offered to show us an Ogham stone not too far away, in the townland of Aultagh. How could we refuse?
Assistance required in finding the stone!
Our goal was beside an ancient track in Aultagh Wood (Coil an Ailtaigh), approached from a private driveway. Margaret knew the owner who readily gave us permission to have a look. In fact, he provided sterling service after we had searched in vain for the elusive rock – opportunely arriving with a pole to clear the thick undergrowth, and soon revealing this modest boulder to our eager gaze.
Stone uncovered…
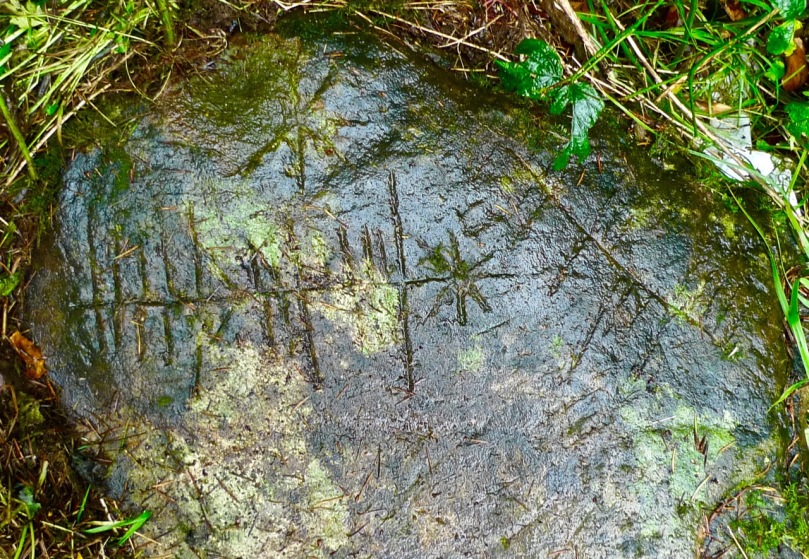
The stone lies close to a drainage ditch and has possibly arrived there from another location at some time in its history. In one area the surface of the rock has been damaged, affecting part of the scribings: it may be that it was once standing – now it is prone with carved marks clearly visible on the upper surface.
The Aultagh Ogham Stone in context
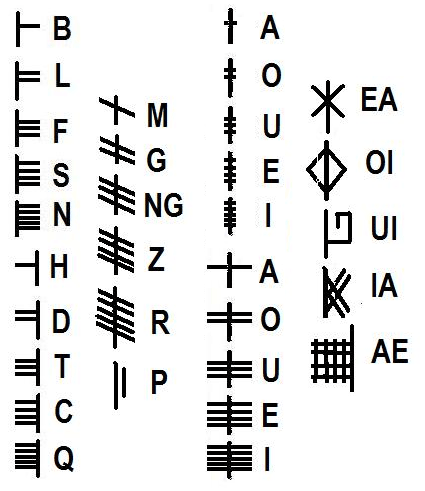
The last time I wrote a post about ogham (here it is) I gave a very general overview of the subject. Ogham stones are concisely described by the Irish National Monuments Service as:
…upright monoliths or recumbent slabs, onto which ogham script has been incised. Ogham script consists of groups of 1-5 parallel lines and notches cut along the side or across the edge of a stone to represent the sounds of the Irish language. It is usually read up the left angle. The inscription gives a person’s name (usually male) and immediate antecedent/s or tribal ancestor. The stones may have functioned as memorials, grave markers or territorial markers and date from the late 4th to the early 8th century AD.
Fine examples of ogham stones in Ireland
Here’s the entry in the National Monuments Service records for our Aultagh stone:
Description: On a W-facing slope, in Aultagh Wood. Fallen stone (L 1.1m; 0.7m x 0.3m) with inscription on flat face. According to Macalister (1945, 75) ‘fashioned by an illiterate artificer, copying by rote from a wooden model cut for his guidance’ and reading UBEDABO ALTASI.
 That’s quite a bald statement from Robert Alexander Stewart Macalister who was Professor of Celtic archaeology at University College Dublin from 1909 to 1943, during which time he compiled and edited the catalogue of all known ogham inscriptions from Britain and Ireland. Macalister’s theories on ogham are generally out of favour today (some commentators have claimed that his interpretations are gibberish) but he seems to accept the Aultagh stone as being within the early medieval ogham tradition. Yet it seems to me very different from many of the other stones we have seen: it is very sharply incised, obviously with a fine-tipped metal tool, whereas a majority of the traditional or ‘classic’ ogham stones are larger and more robustly carved.
That’s quite a bald statement from Robert Alexander Stewart Macalister who was Professor of Celtic archaeology at University College Dublin from 1909 to 1943, during which time he compiled and edited the catalogue of all known ogham inscriptions from Britain and Ireland. Macalister’s theories on ogham are generally out of favour today (some commentators have claimed that his interpretations are gibberish) but he seems to accept the Aultagh stone as being within the early medieval ogham tradition. Yet it seems to me very different from many of the other stones we have seen: it is very sharply incised, obviously with a fine-tipped metal tool, whereas a majority of the traditional or ‘classic’ ogham stones are larger and more robustly carved.
Possible ogham stone at Maulinward, West Cork (left) and others from the Stone Corridor at UCC
When you begin to delve into modern literature on ogham you realise how very many varieties of examples there are, and also how many differing interpretations there are of how to ‘read’ the script. This was monumental writing, labour intensive and time consuming to undertake. For this reason it is generally supposed that ogham was ostensibly reserved for marking important graves or places, and that the inscriptions are all names.
 Aultagh Ogham Stone – ‘classic’, ‘scholastic’ – or ‘fake’?
Aultagh Ogham Stone – ‘classic’, ‘scholastic’ – or ‘fake’?
There are suggestions that ogham inscriptions for more general – and less monumental – usage were once carved on wood, and might have been language primers for the bardic poets. Later inscriptions are sometimes termed ‘scholastic ogham’ deriving from the fact that the inscriptions are believed to have been inspired by manuscript sources, instead of being continuations of the original ‘monument’ tradition. Hallmarks of scholastic ogham are the median line and scribings being on the flat face of a stone (as at Aultagh) rather than on the edge. Ogham was occasionally used for notes in manuscripts down to the 16th century, and the burgeoning interest in all things antiquarian from the 18th century onwards led to a popular ogham revival. A typical example, from the graveyard in Ahenny, Co Tipperary, has an English inscription dated 1802 and this in ogham: FA AN LIG SO NA LU ATA MARI NI DHIMUSA O MBALLI NA GCRANIBH, interpreted as ‘Under this stone lies Mary Dempsy from Ballycranna’. Macalister takes the view that this inscription, and others like it, were written “with much more zeal than discretion”, while some scholars have suggested that this more modern usage of the scribing should be termed ‘fake ogham’.
My own drawing of the Aultagh inscribed stone – traced from detailed photographs
You may like to have a go at translating the inscription at Aultagh for yourself. Firstly you will need to select your decipherer: a quick internet search will show that there are many, and also a whole lot of inconsistencies. But perhaps this is all part of the head-scratching: and also part of the whole fascination of a historical subject where many of the elements can only be guessed at…












My old school teachers would laugh if I had to add Ogham to my list of failed attempts at learning a foreign language. My father took me to Ballynacarriga (he was from Dunmanway) many years ago and told me it was a McCarthy castle – probably a good guess due to the big crowd of McCarthys in West Cork.
LikeLiked by 1 person
Reblogged this on West Cork History.
LikeLike
A fascinating write up, after an action-packed day. It is a remarkable stone whatever. Have you had a go at deciphering yourself?
LikeLike
Yes – I am quite sure it translates as “Please do not disturb…”
LikeLiked by 1 person