I’ll explain at the outset that Caheragh is (more or less) pronounced ‘corer’ (as in coring apples)! It’s a parish in West Cork that we have visited before. Have a look at my article on the Ilen River, here. This locality is brimming over with history and we go exploring as often as possible: there is always more to find. And – with wide views and cloud scapes in all directions from the high ground – it’s an uplifting place, especially when blessed with the August sun.

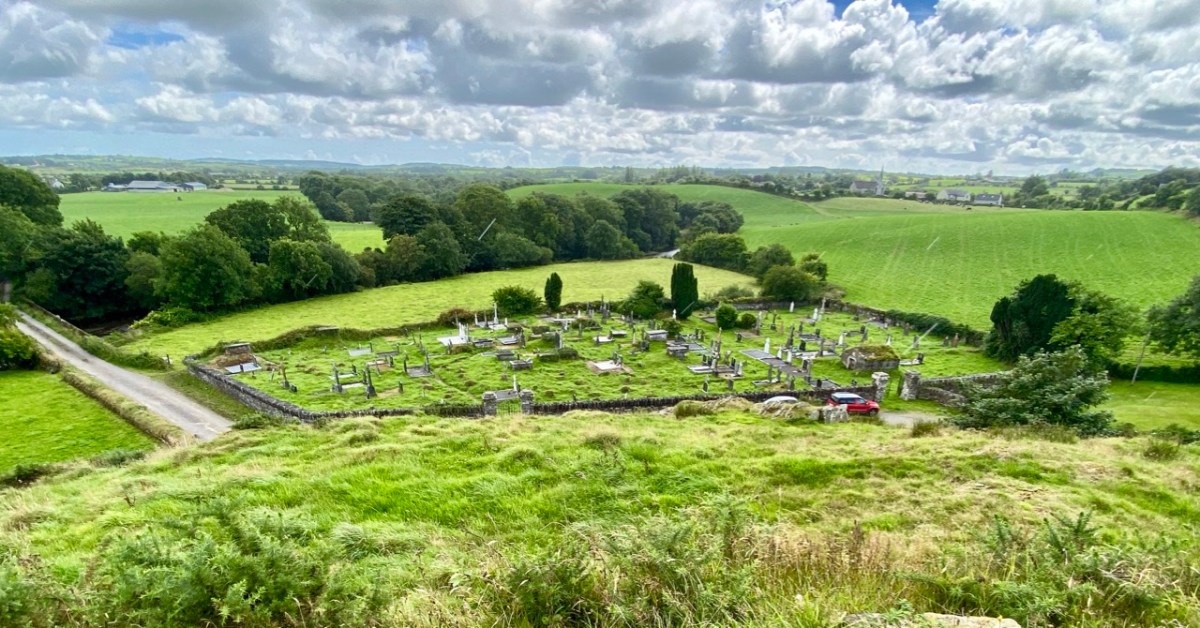
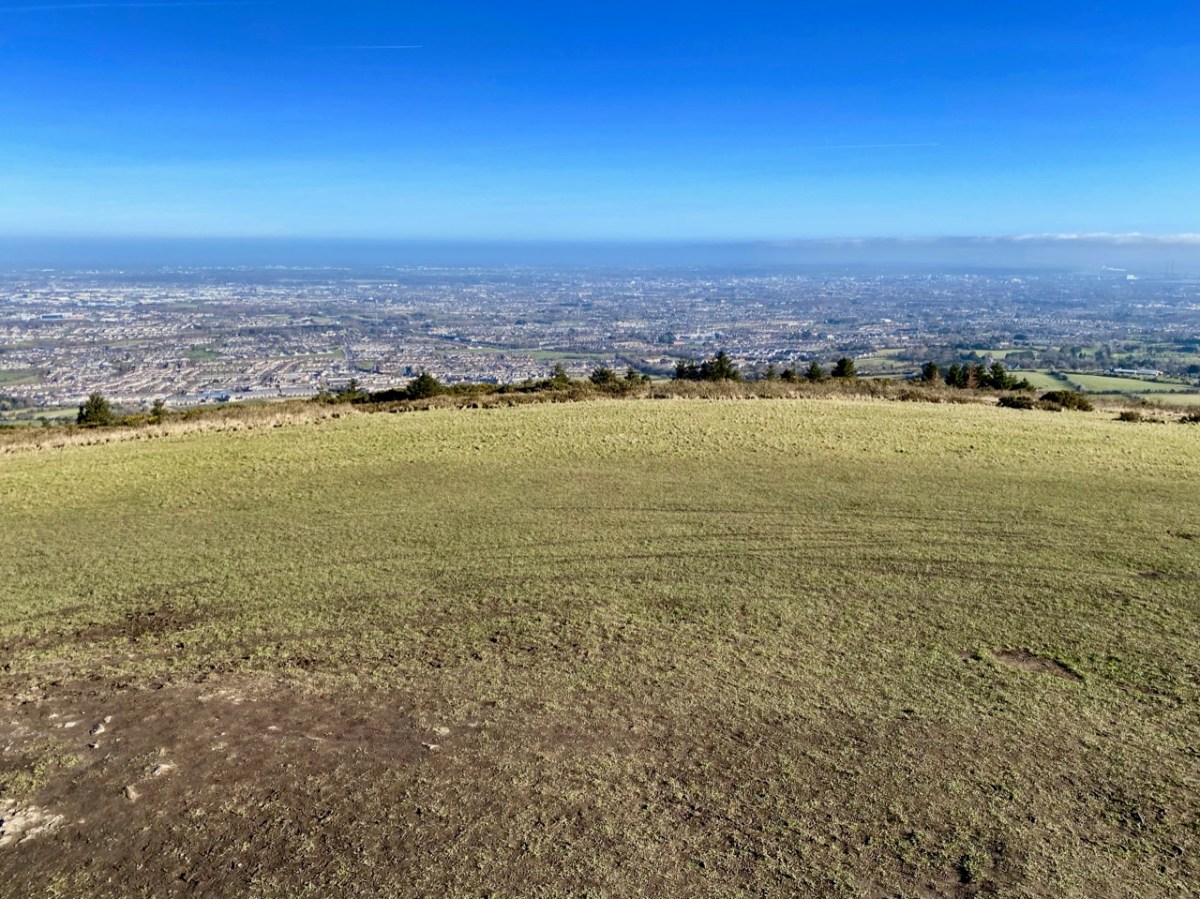
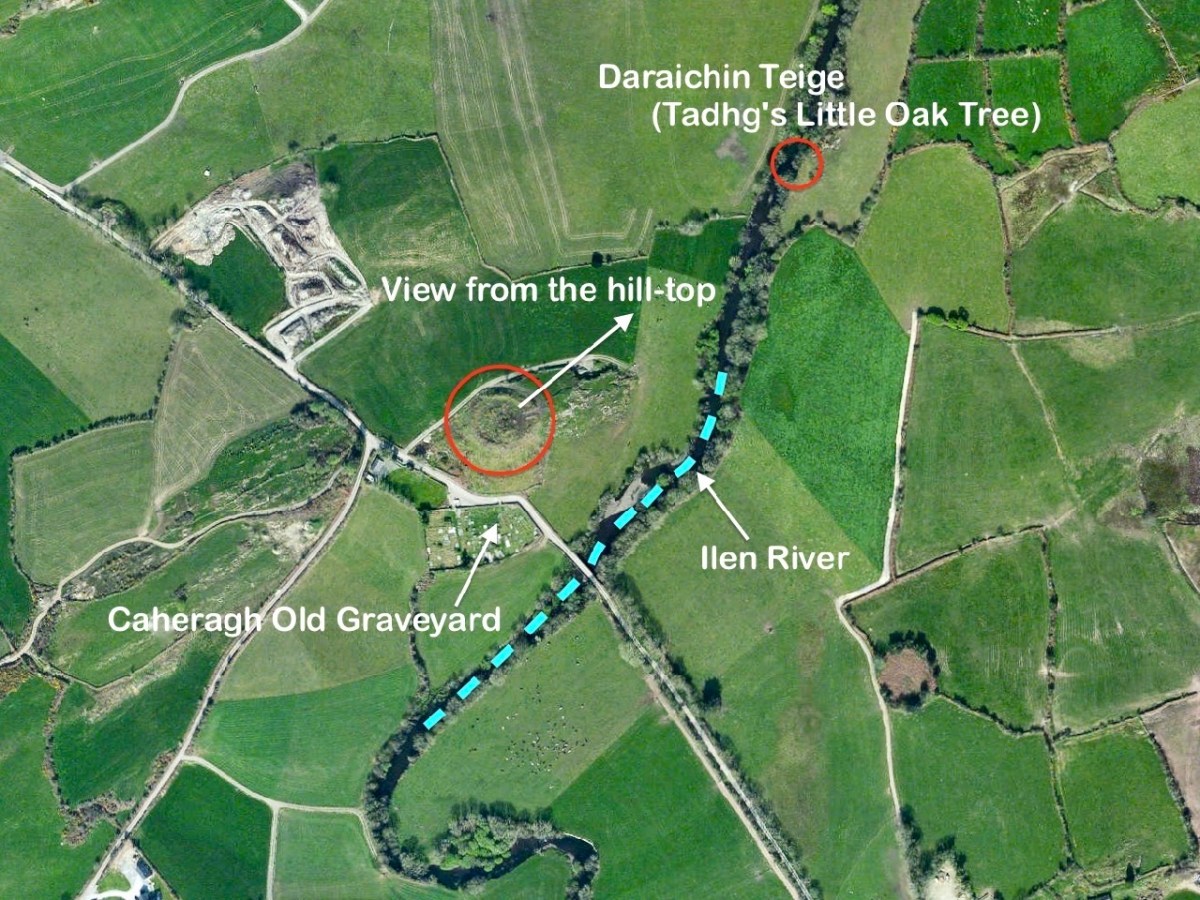
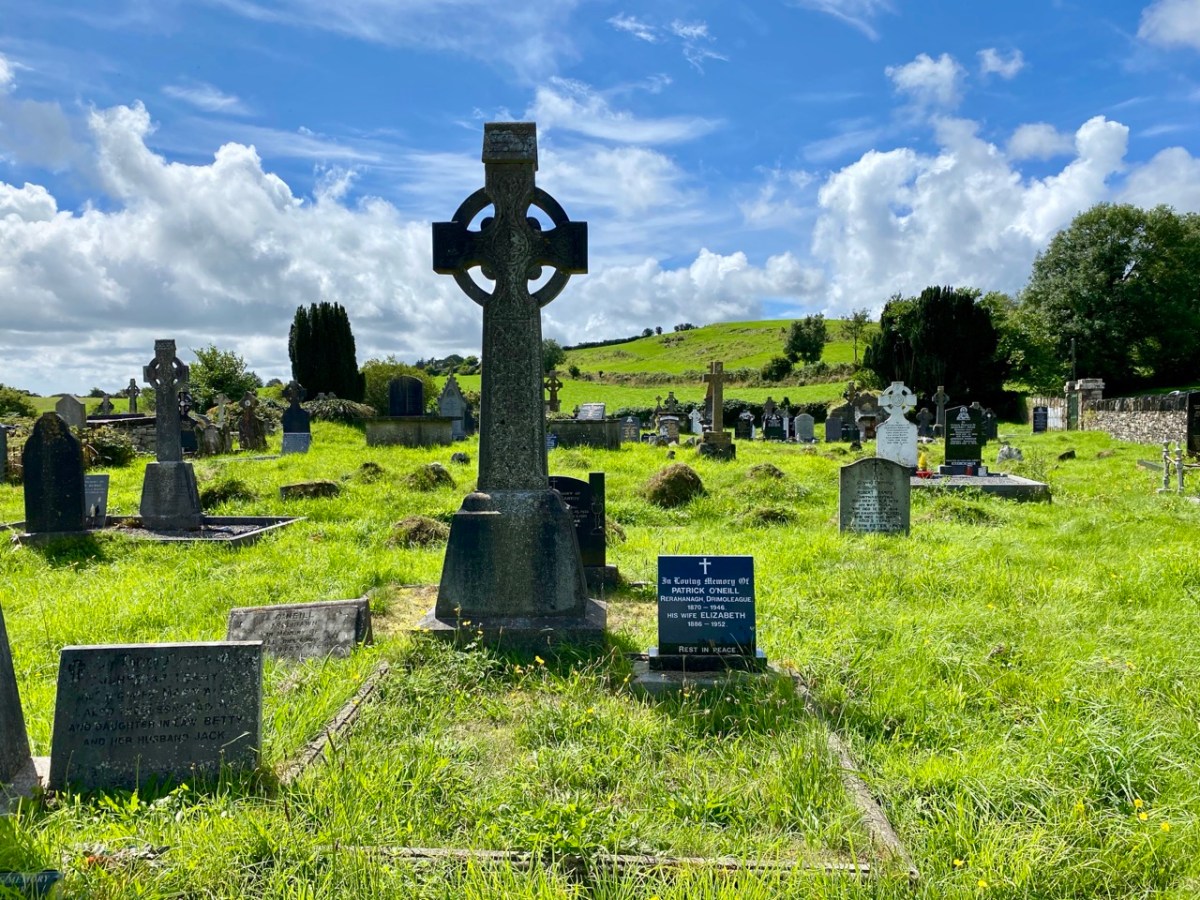
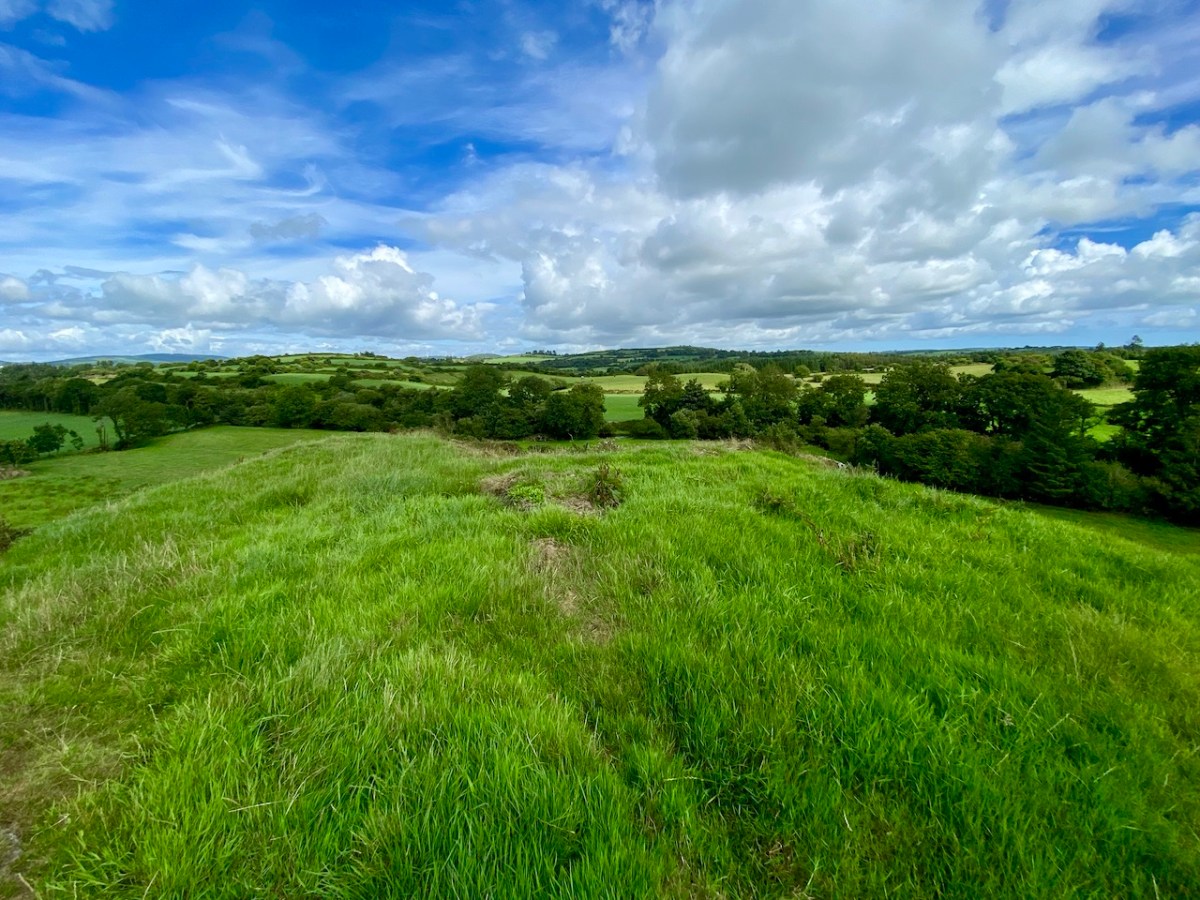
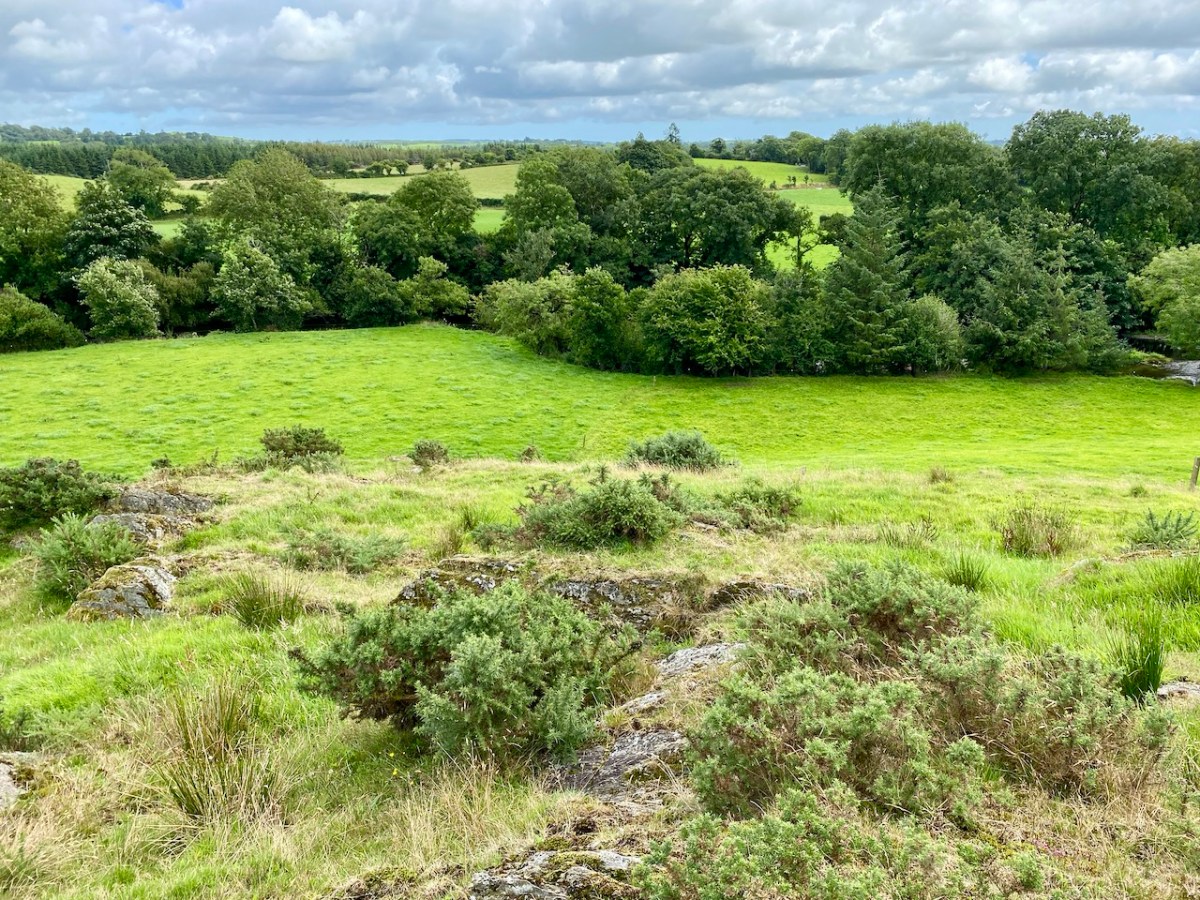
Here’s a vista to the north-east, from the top of the mound beside the graveyard that might just be a ring-fort, or possibly the site of a monastic centre dating from medieval times – more on that later. In the middle distance is the Ilen River with its wooded banks, heading out towards Castle Donovan and – eventually – to its source on Mullaghmesha (or, perhaps, Nowen Hill – we have yet to determine exactly where it rises. This post from the Sweet Ilen series covers the area). And that Donovan castle itself graces the cover of the latest Skibbereen Historical Journal (Volume 18, 2022), which you can get in bookshops locally, or online here. You will find a summary of some of my research on the Ilen River in this journal, together with many other fascinating and erudite articles.

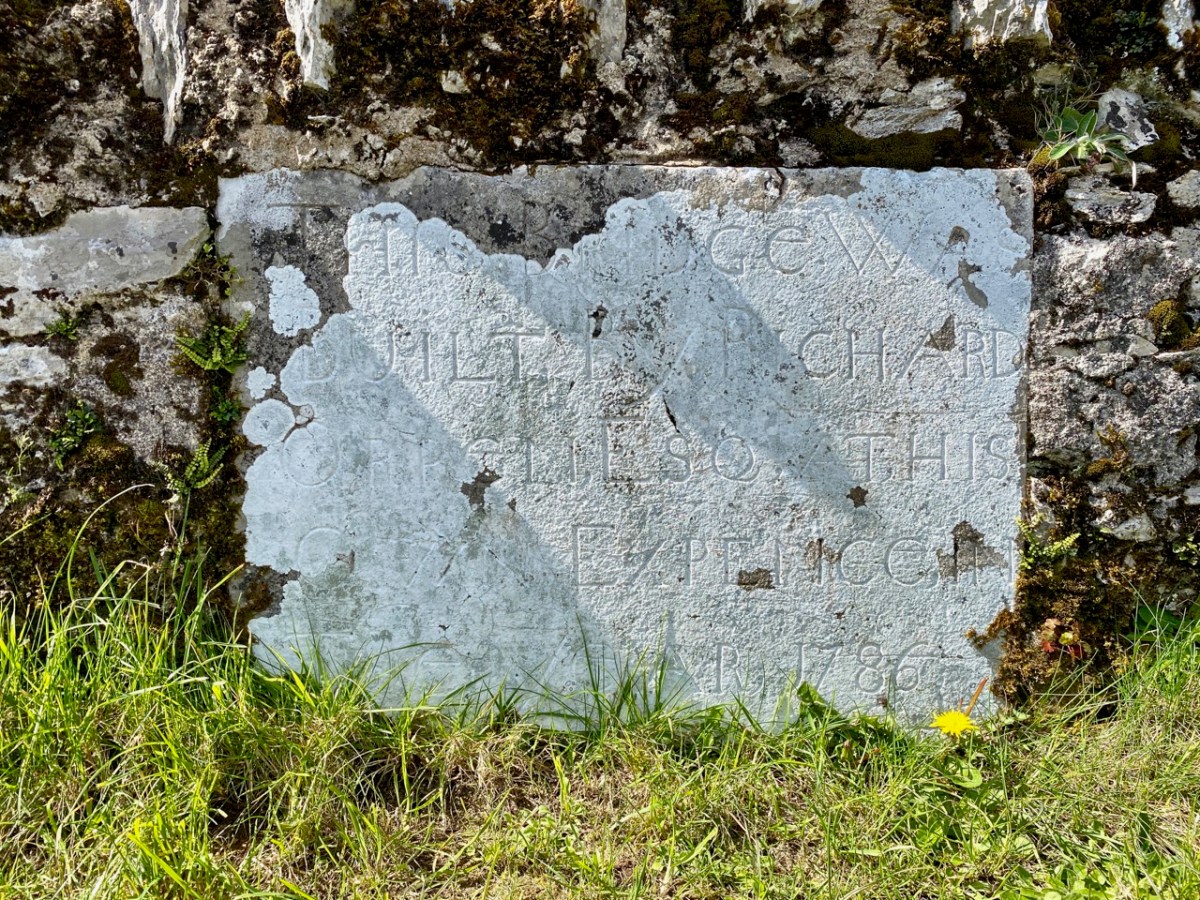
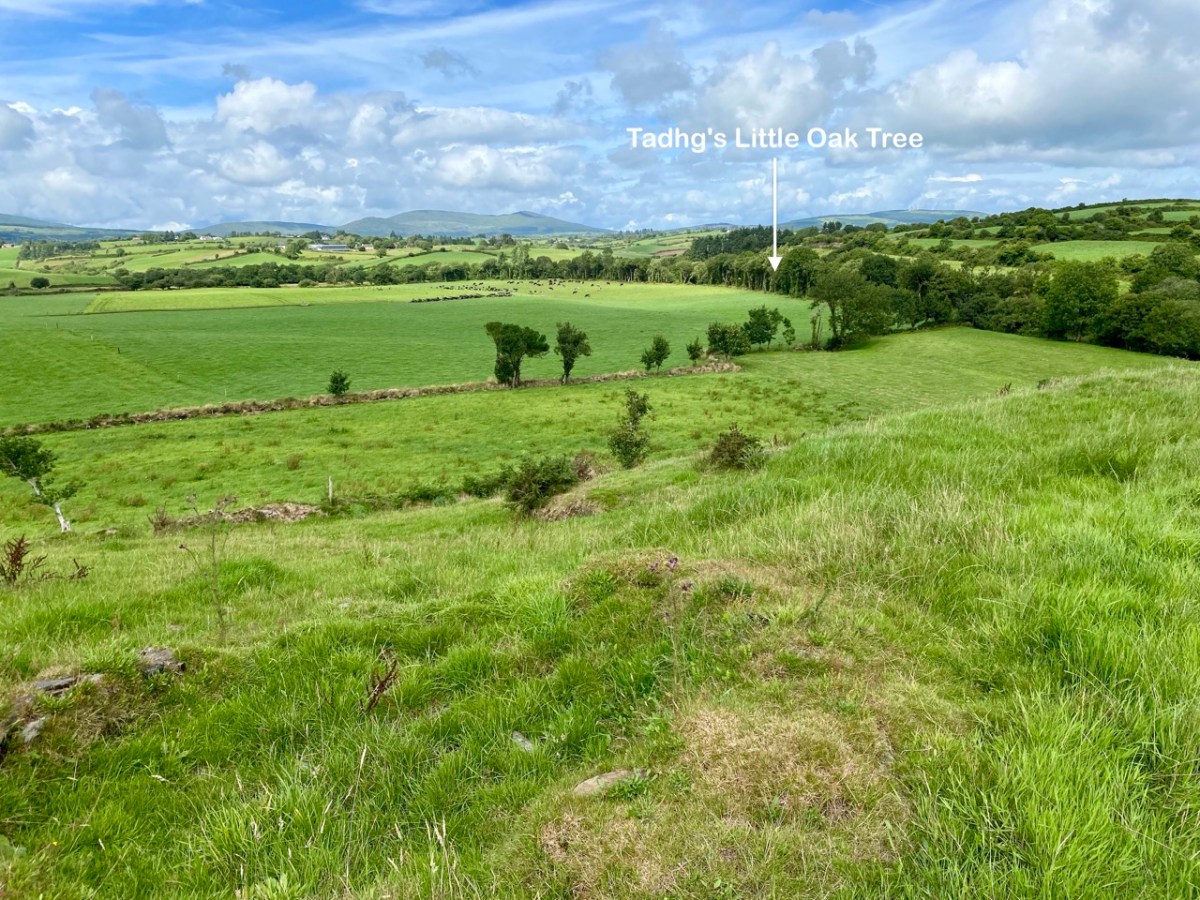
But, going back to that sunlit vista, you’ll notice Tadhg’s Little Oak Tree is indicated. I can’t resist quoting the story of this feature that appears as a ‘Redundant Record’ in the Historic Environment Viewer:
. . . On E bank of River Ilen. Site of tree, ‘Darriheen Teige’ or ‘Daraichin Teige’ (Tadhg’s little oak tree), where Tadhg O’Donovan, chieftain of Clan Cahill, was slain c 1560 by rival group of O’Donovan’s (O’Donoghue 1986, 55). Nearby is Poll a’ Daraichin (pool of the little oak) . . .
Archaeology.ie Historic Environment Viewer – Record CO132-066
Well, it seems strange that the ‘site of a tree’ is a recorded monument. In fact, if the oak was still flourishing (we couldn’t find it), it would probably be just one of only a few trees included in Ireland’s vast record of archaeological monuments!
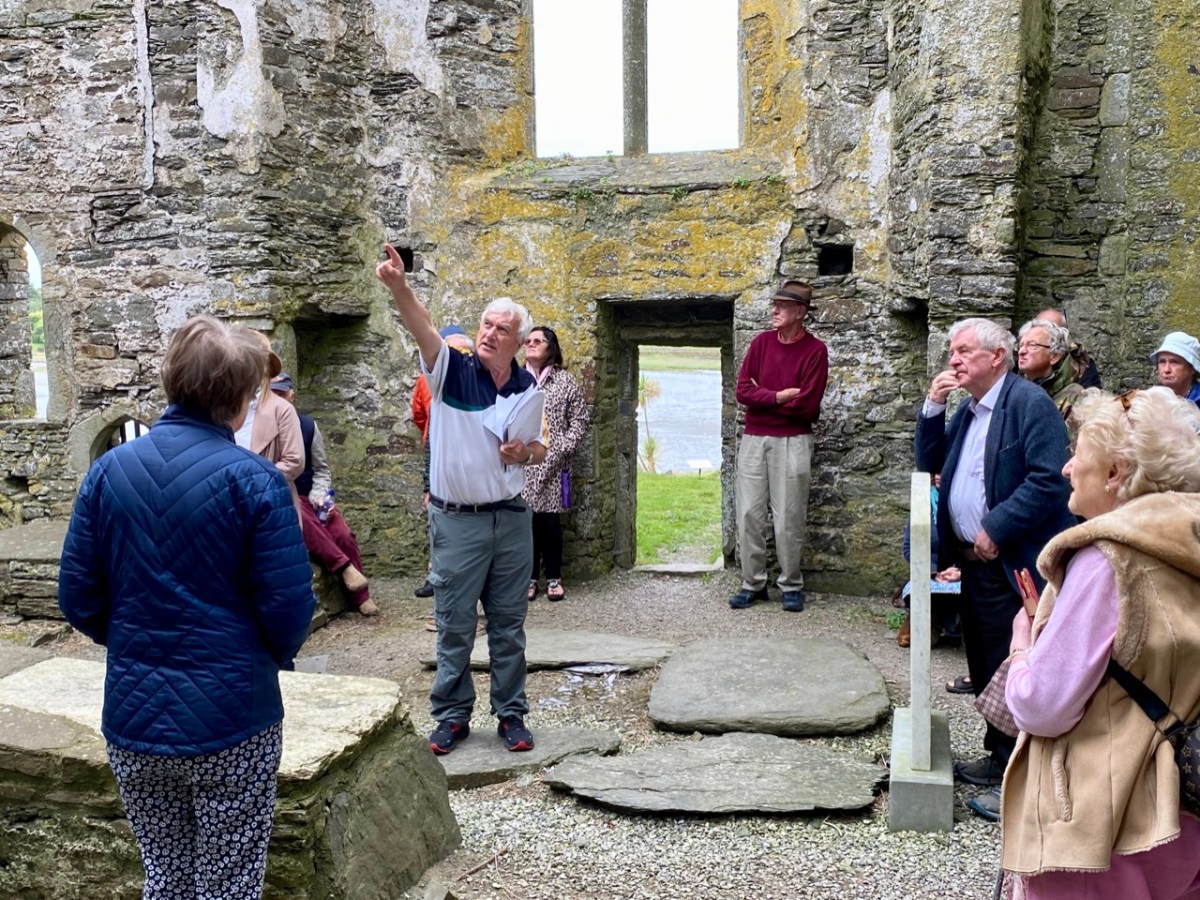
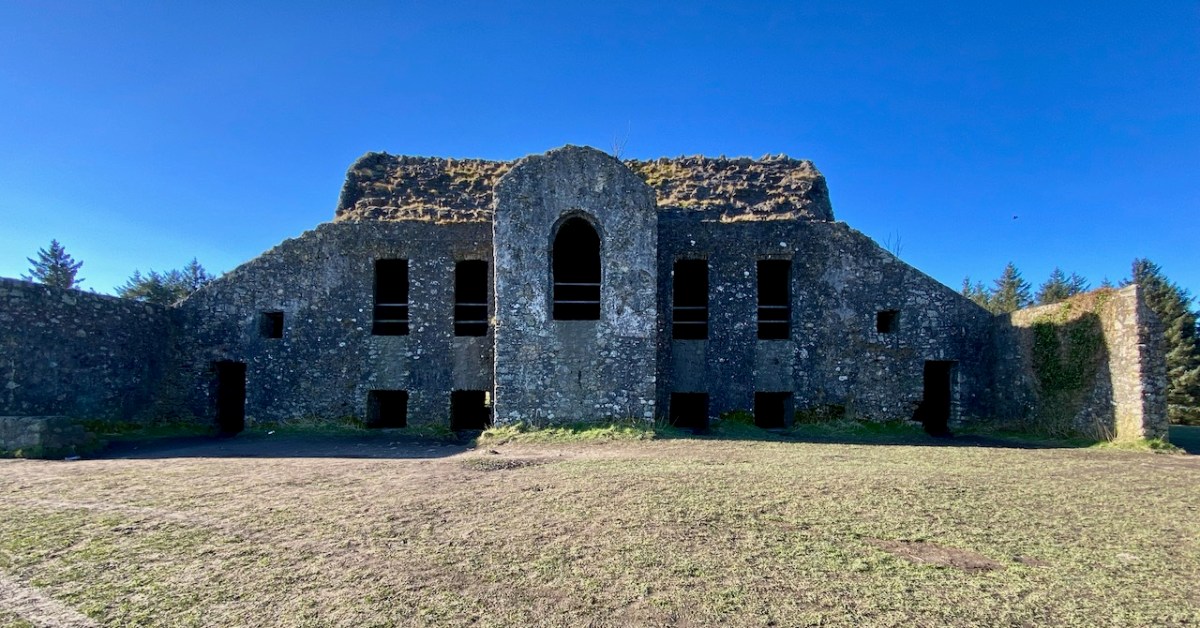
For today’s post I am indebted to our historian friend Pat Crowley, who directed us to a clip from The Southern Star newspaper dated January 12, 1929. It was a letter written to the newspaper by Captain Francis O’Neill, retired Chief of Police in Chicago and well-known prolific collector of traditional Irish music. O’Neill (1848-1936) was raised in his family home at Tralibane, in the parish of Caheragh. He has been mentioned in this journal, and I was fascinated to read his letter, which became a protracted discussion on the parish, the old graveyard, historic sites and archaeology in the area.
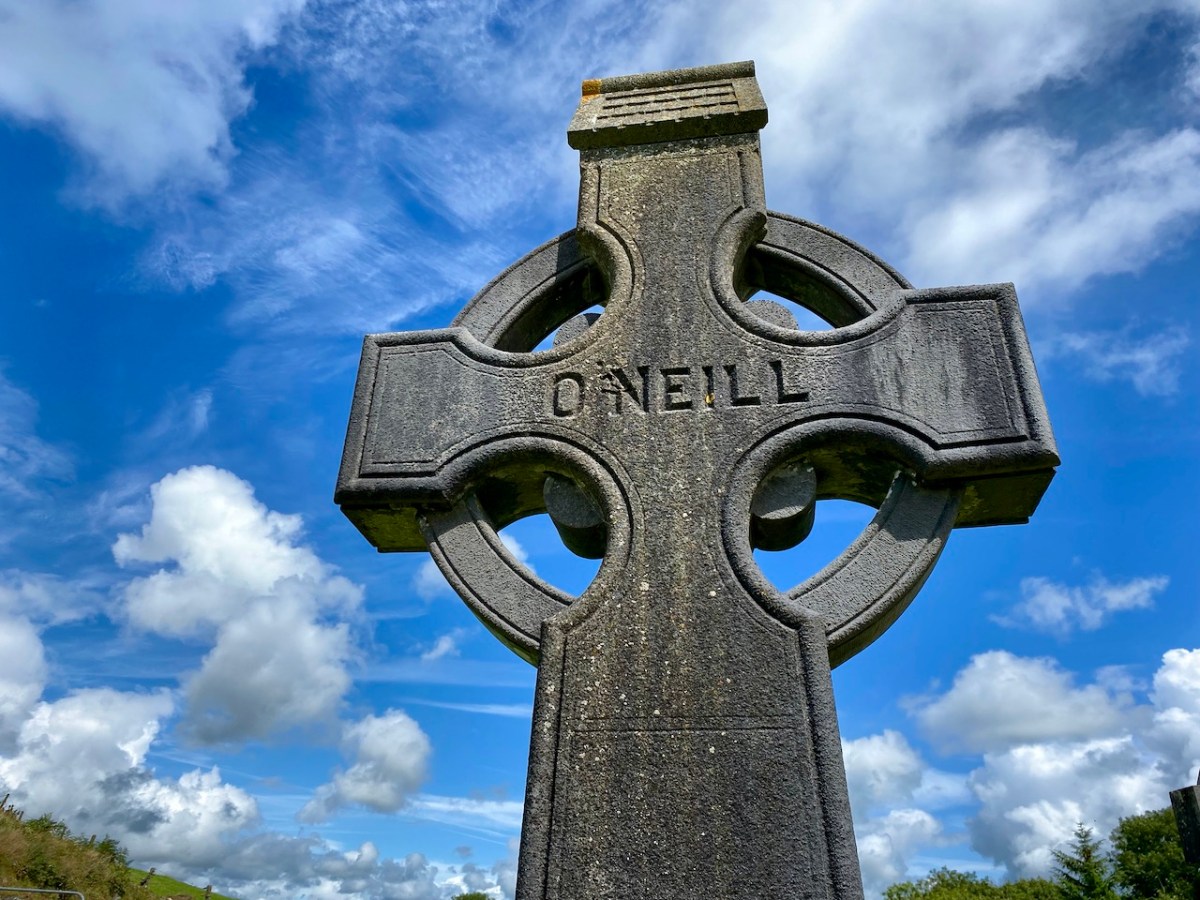

All this came about because Francis had returned from Chicago to West Cork in 1906 – after a long absence – ostensibly to visit the burial place of his parents, and to order a suitable monument to mark their graves (above).
. . . On my return to Ireland July 1906, after an absence of 41 years, I visited the bleak Caheragh graveyard, in which the remains of my parents, and O’Neill ancestors, were buried. There being nothing visible in the environment to indicate its origin as a cemetery, personal curiosity, abetted by that of the Downings of Tralibane – cousins of McCarthy Downing, MP – led to investigation . . . The result, somewhat disconnected and fragmentary, is herewith submitted for publication . . .
Southern Star 12.01.1929
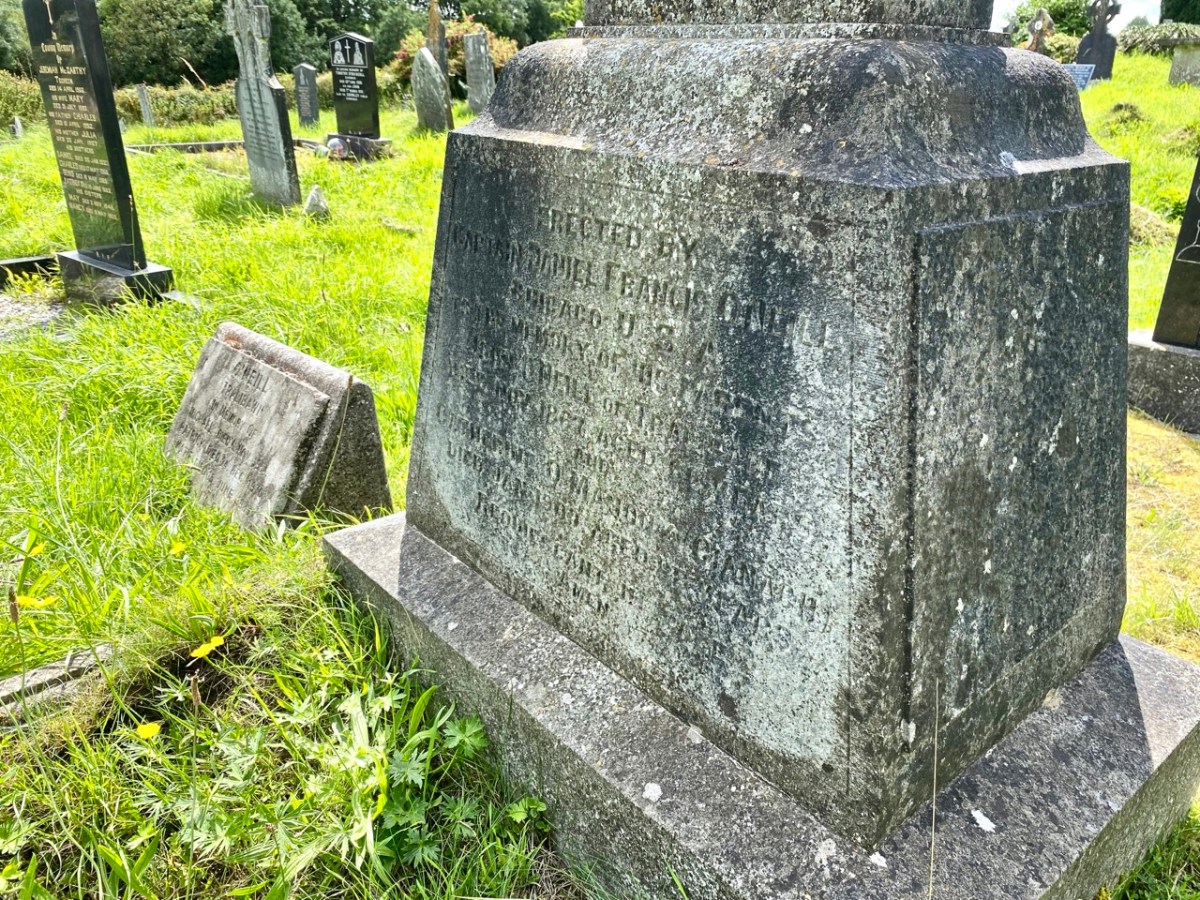


The O’Neill burial plot at Caheragh. Francis ordered the large cross to mark the graves of his parents. The inscription reads:
Erected By
Captain Daniel Francis O’Neill
Chicago USA
To the Memory of his Parents
John O’Neill of Tralibane
Died Nov 1867 Aged 66 Years
And
Catherine O’Mahoney (Cianach)
Died 1900 Aged 88 Years
Requiescant In Pace
Amen
Quoting again from Francis O’Neill’s letter to the Southern Star:
. . . All available authorities in my library have been consulted, and I find that references to the parish of Caheragh are both meagre and obscure… The earliest mention of this parish which has come to my notice, is in the report of Dive Downes, Episcopal Bishop of Cork and Ross, who made a trip on horseback to all parishes in his diocese in the years 1699 – 1702. Following is the entry: – “Caheragh Church, about two miles distant from Drommaleage Church to the SW lies close to the Island River (he means Ilen). On the west side of the river are 35.5 lowlands in this parish, of which 20 lie on the west side of the river, and 6.5 lie on the east side of the said river . . . There are about 12 Protestant families in this parish. ’Tis thought there are forty Papists for one Protestant in this parish . . . Will Gureheen, a very old man, is priest of this parish . . . The church is ruinous. The north side is down . . .”
Southern Star 12.01.1929
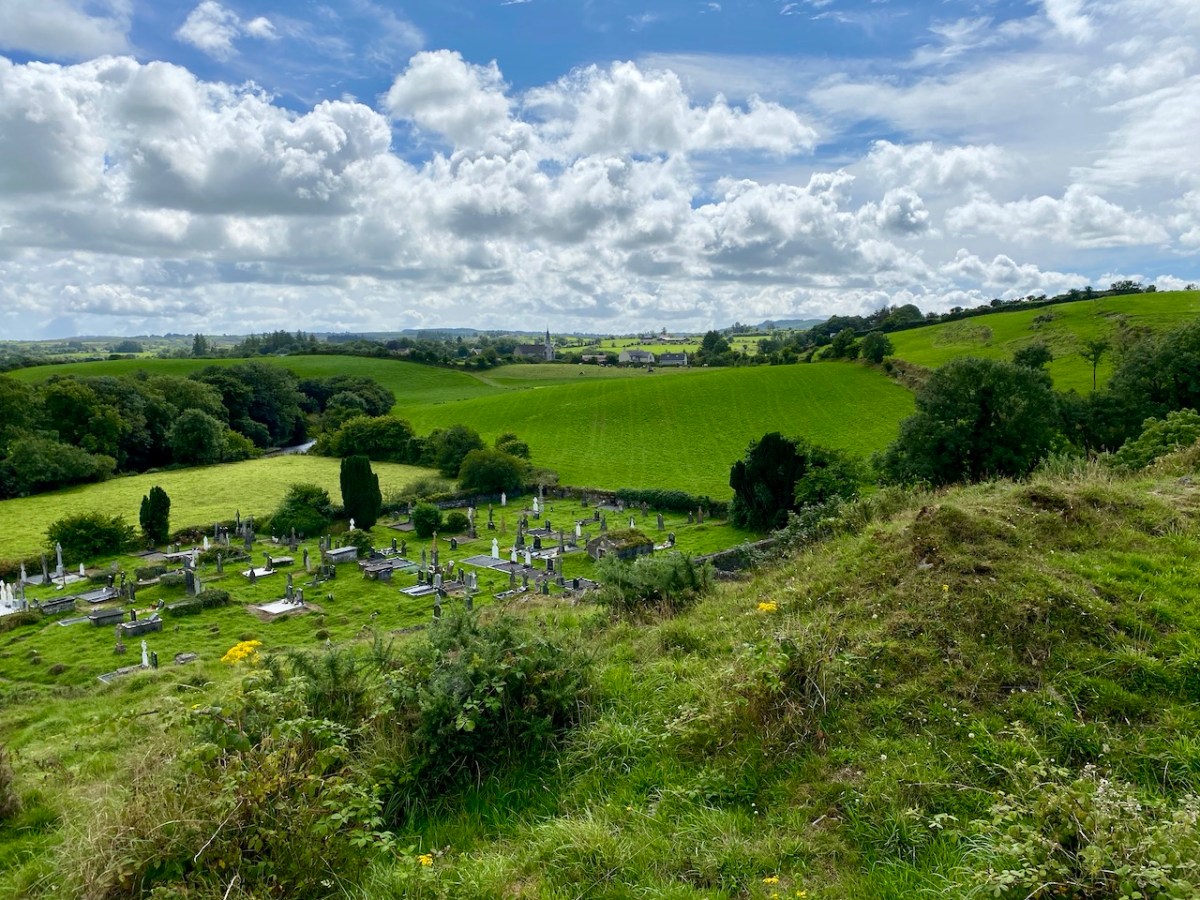

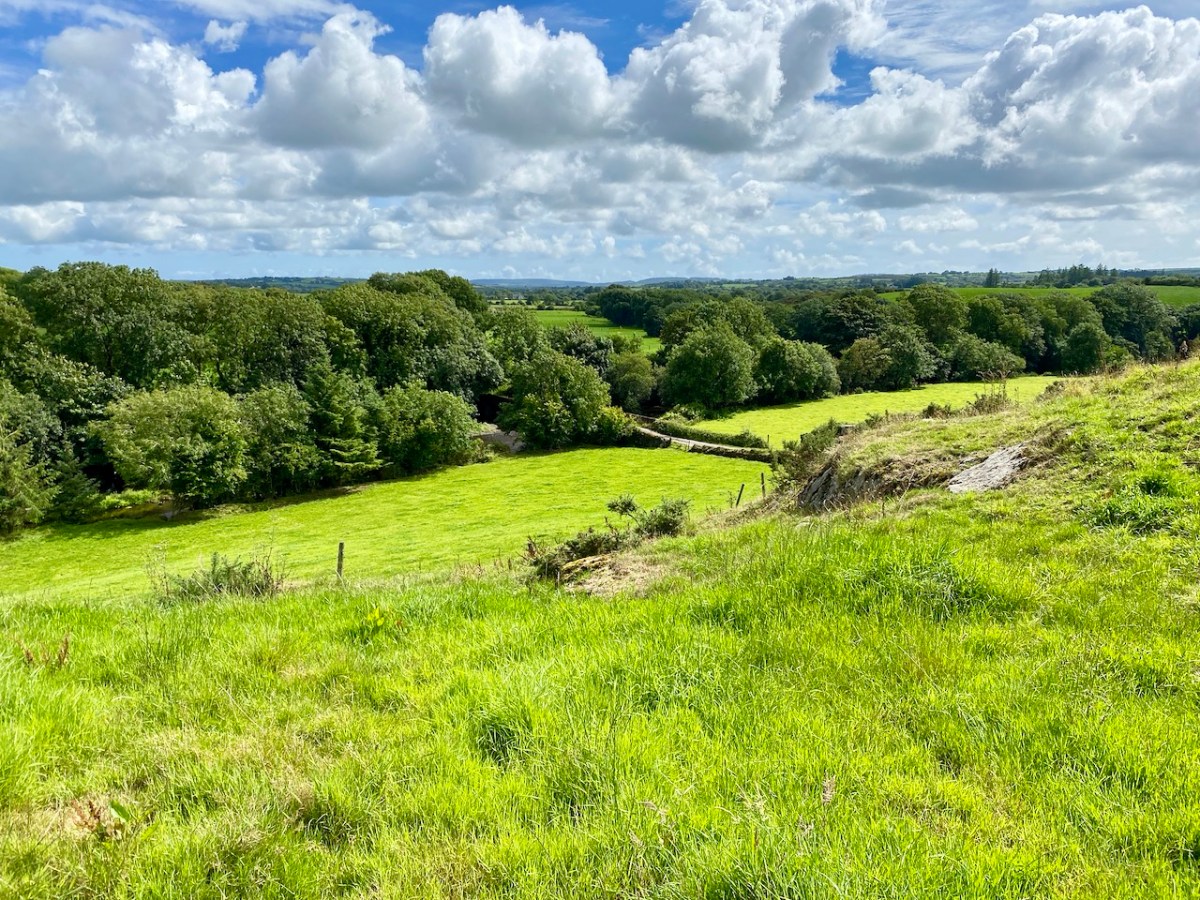
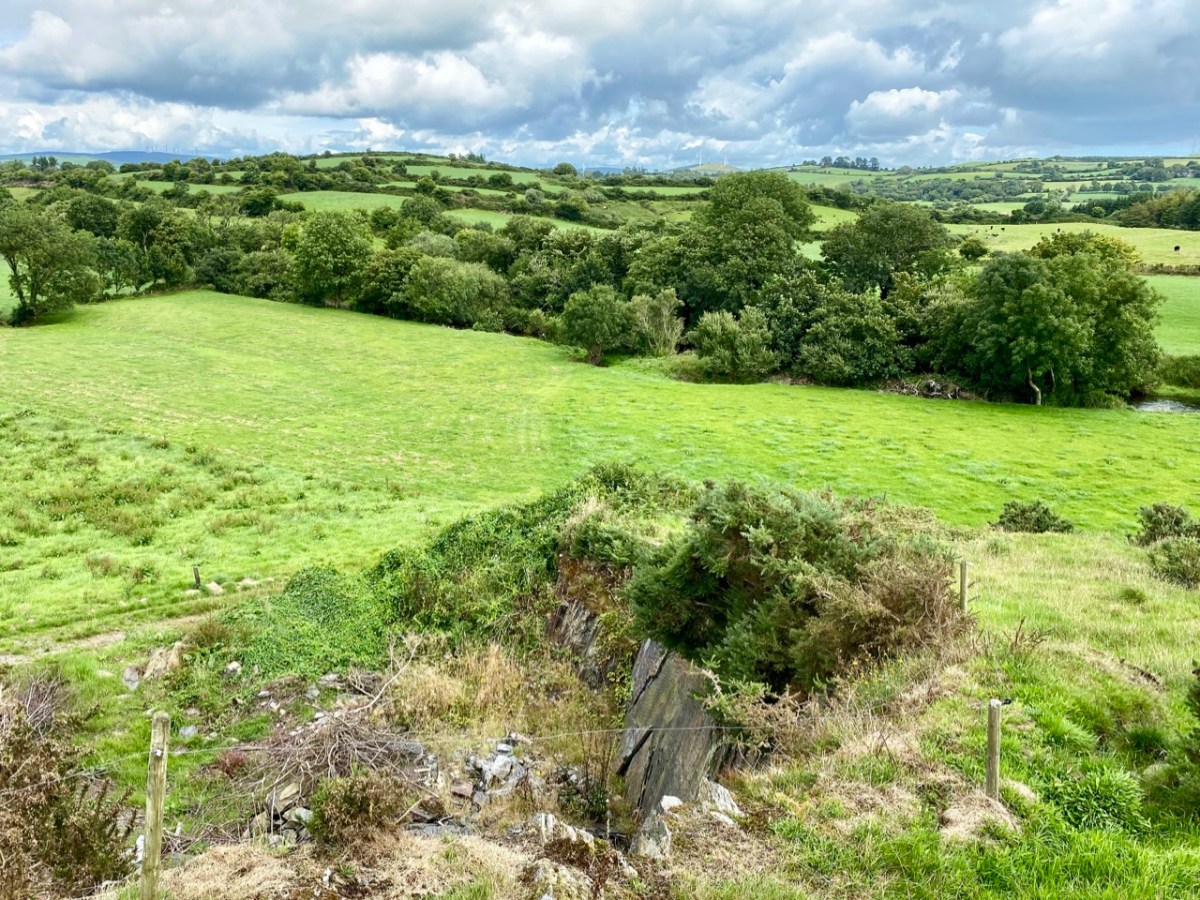
A vista to the west, from the top of the mound beside the graveyard. The present-day village of Caheragh is distant beyond the green pasture (a long way from this ‘Old Graveyard’ – why…?), identifiable through the spire of the 1963 Holy Family Church. O’Neill continues, now quoting from Samuel Lewis “A Topographical Dictionary of Ireland” published in London in 1837:
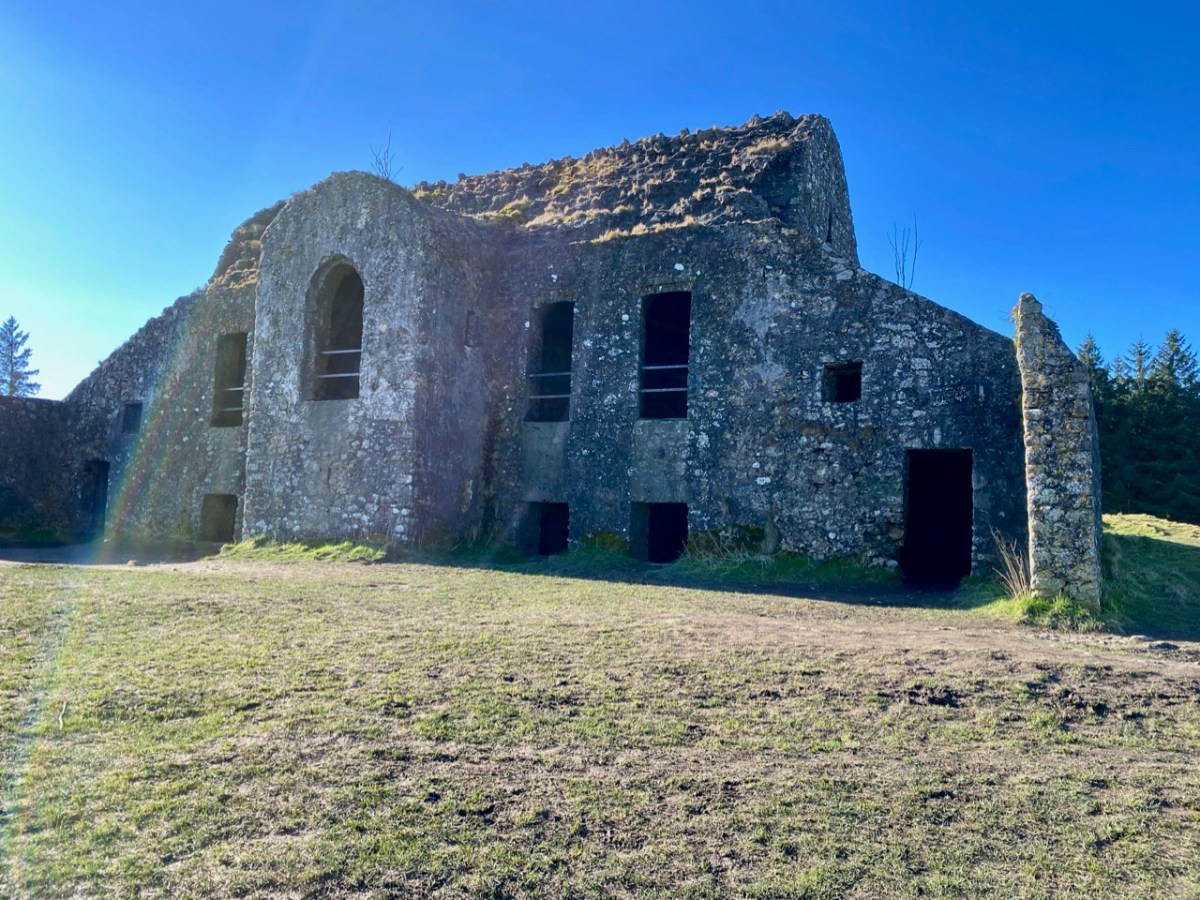
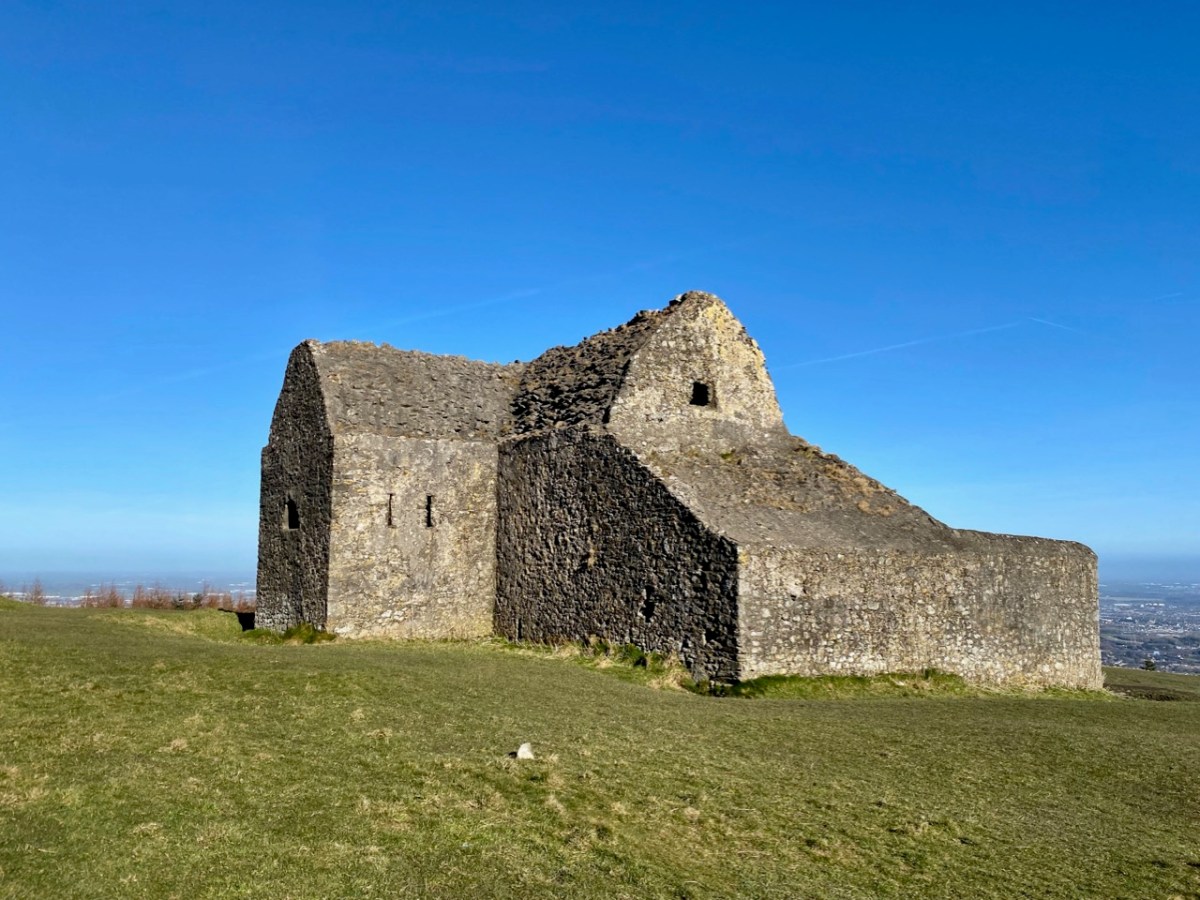
“Near Lisangle are the ruins of a strong castle, once the residence of McCarthy, King of Cork. The ruins of the old church also remain, which the people here call the ‘Abbey of Cahir” . . . The absence of ruins at Caheragh, which, by the way, seems to have never attracted the attention of historians or antiquaries, is easily accounted for. The stones, conveniently at hand, were utilised in the building of the walls which encompassed the graveyard . . .
Southern Star 12.01.1929
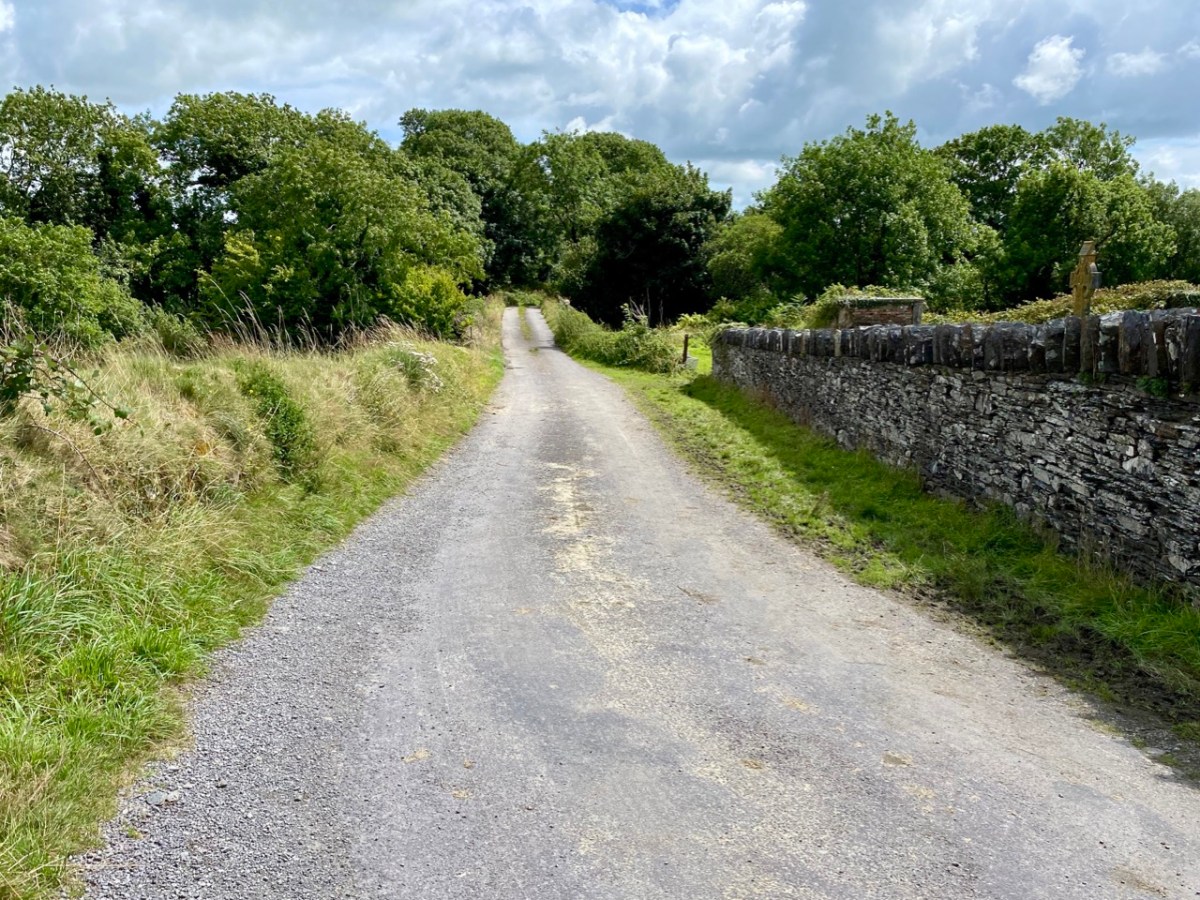

Above – the western boundary wall of Caheragh Old Graveyard. The small road continues over the Ilen River: the bridge here was built by the Congested Districts Board for Ireland in the early years of the twentieth century, to replace a ford, the stone flag bed of which can still be seen.


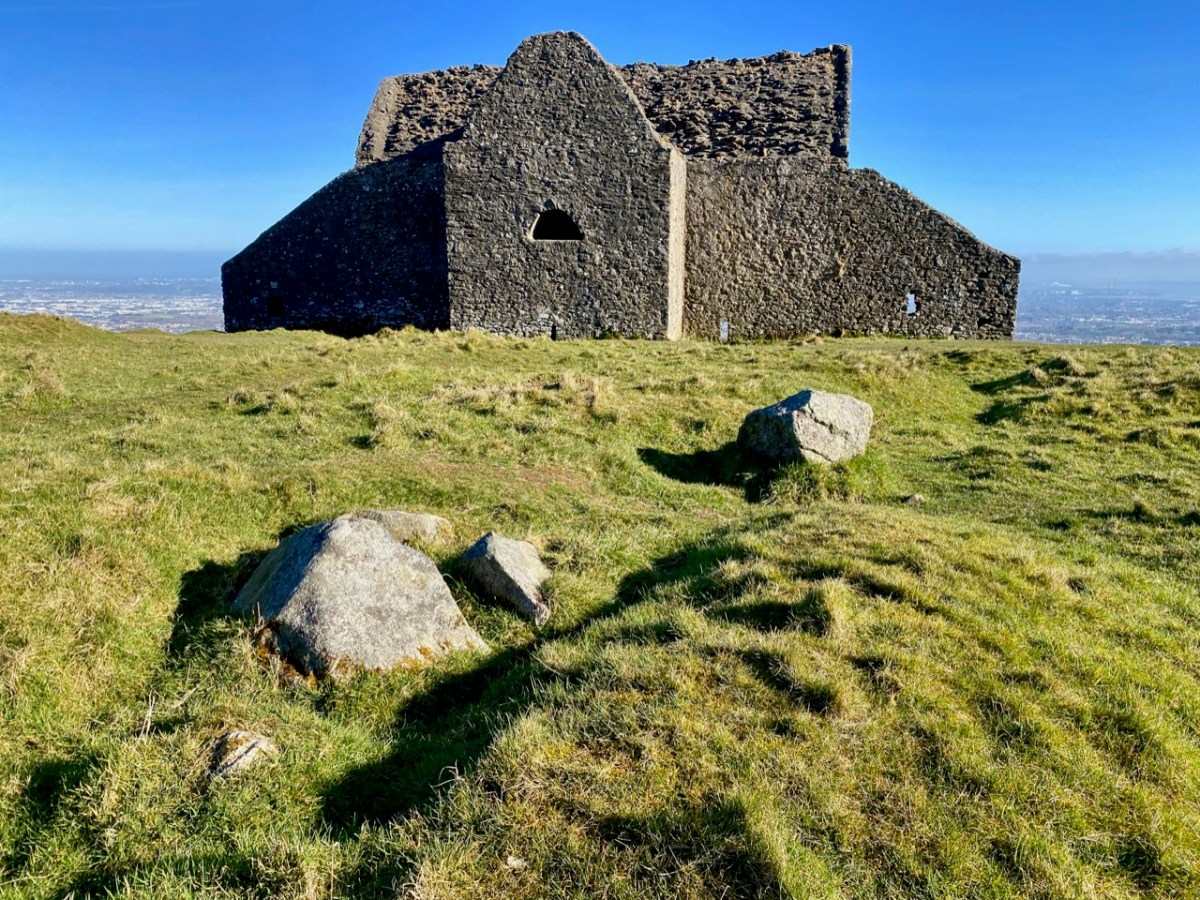
. . . The Irish word Cathair, spelled and pronounced in English Caher or Cahir, meant a circular stone fort, and therefore Caheragh, under any form of spelling, signifies the field of the stone fort. But where is the fort? one naturally asks. Remembering the descriptive nature of the Irish place names on my short call at Caheragh in 1906, I looked for something to justify the name and found it. In order to gain a vantage point, to view the country round about, I struggled through the thicket of furze to the top of the hill east of the road and, unexpectedly, to my great delight, found the outlines of the stone foundations of the Cahir, mostly covered with soil and grass, but quite distinct on the flat top. Again was the correctness of Irish topographical names vindicated . . .
Letter from Capt Francis O’Neill, Southern Star 12.01.1929
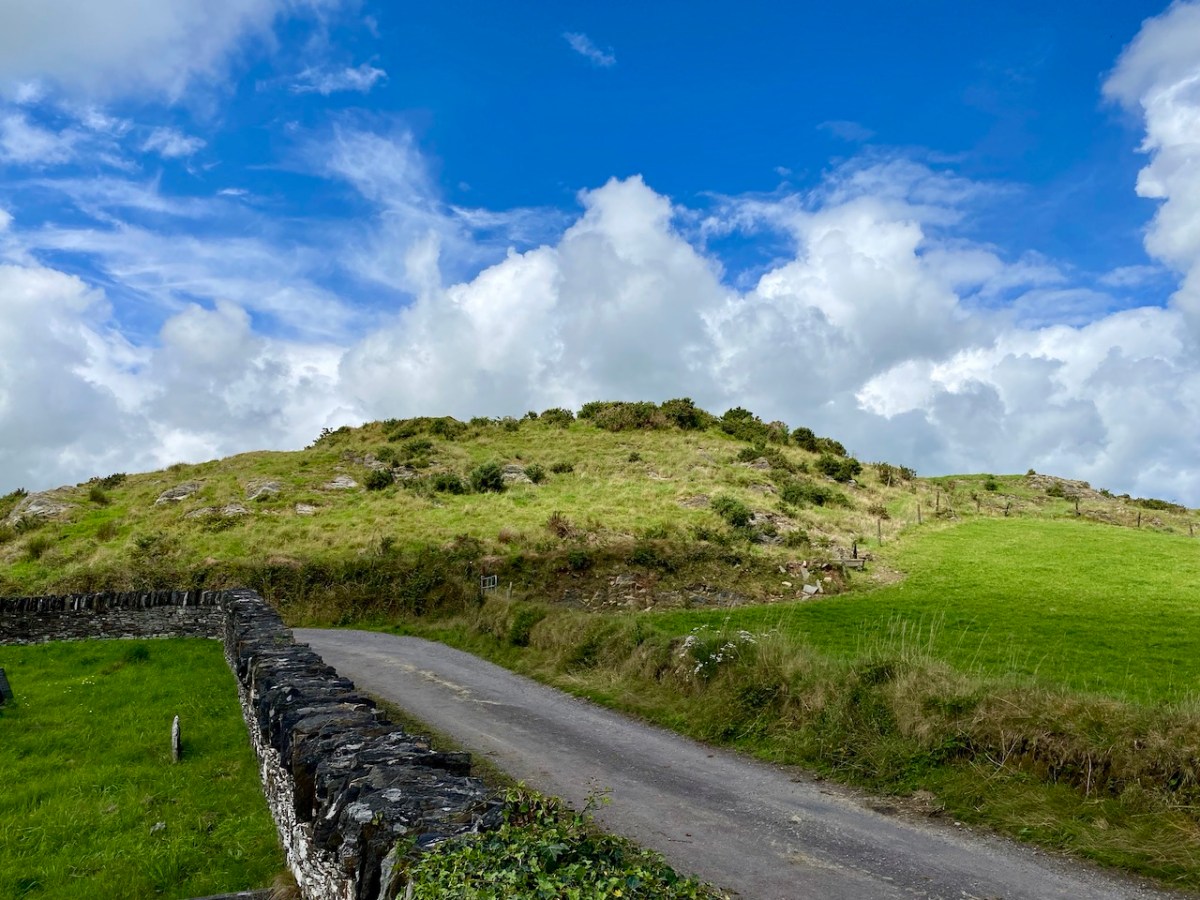
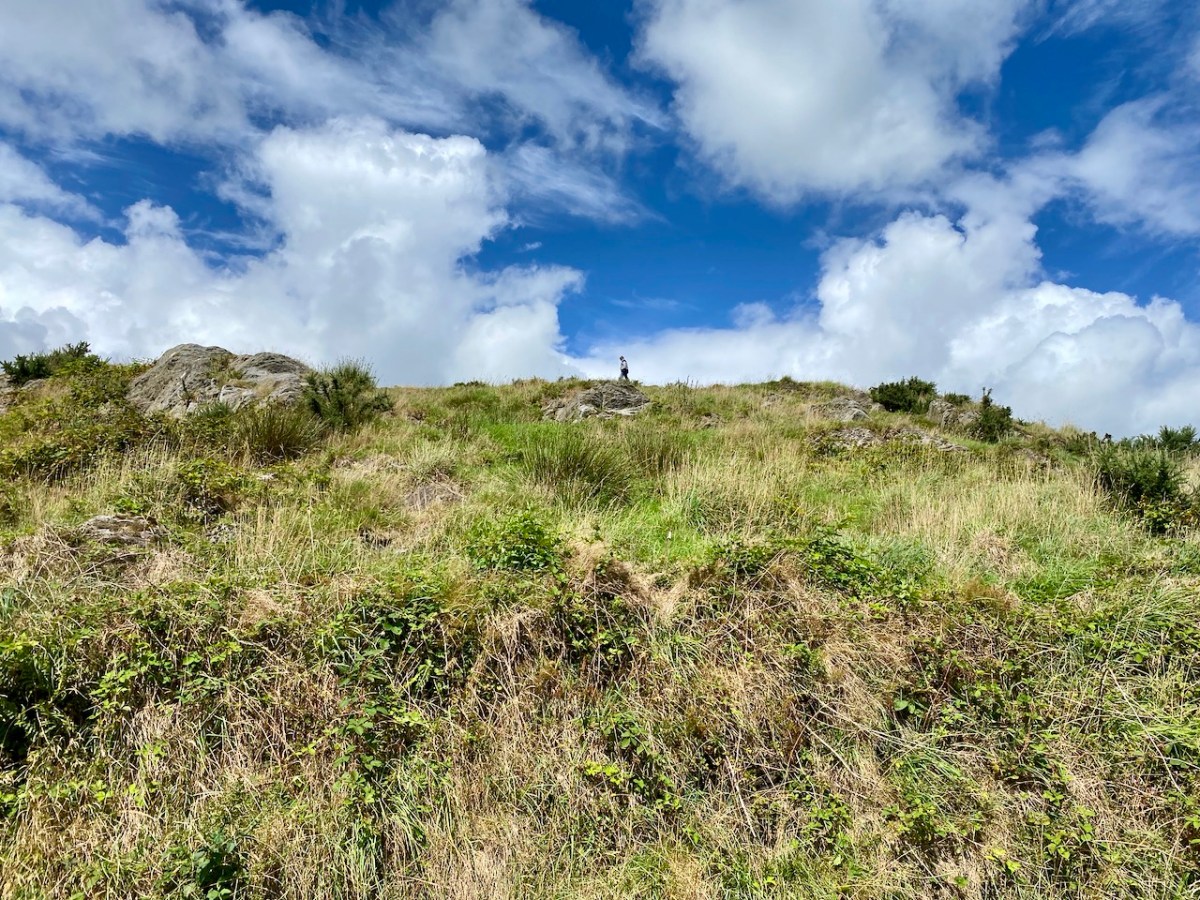


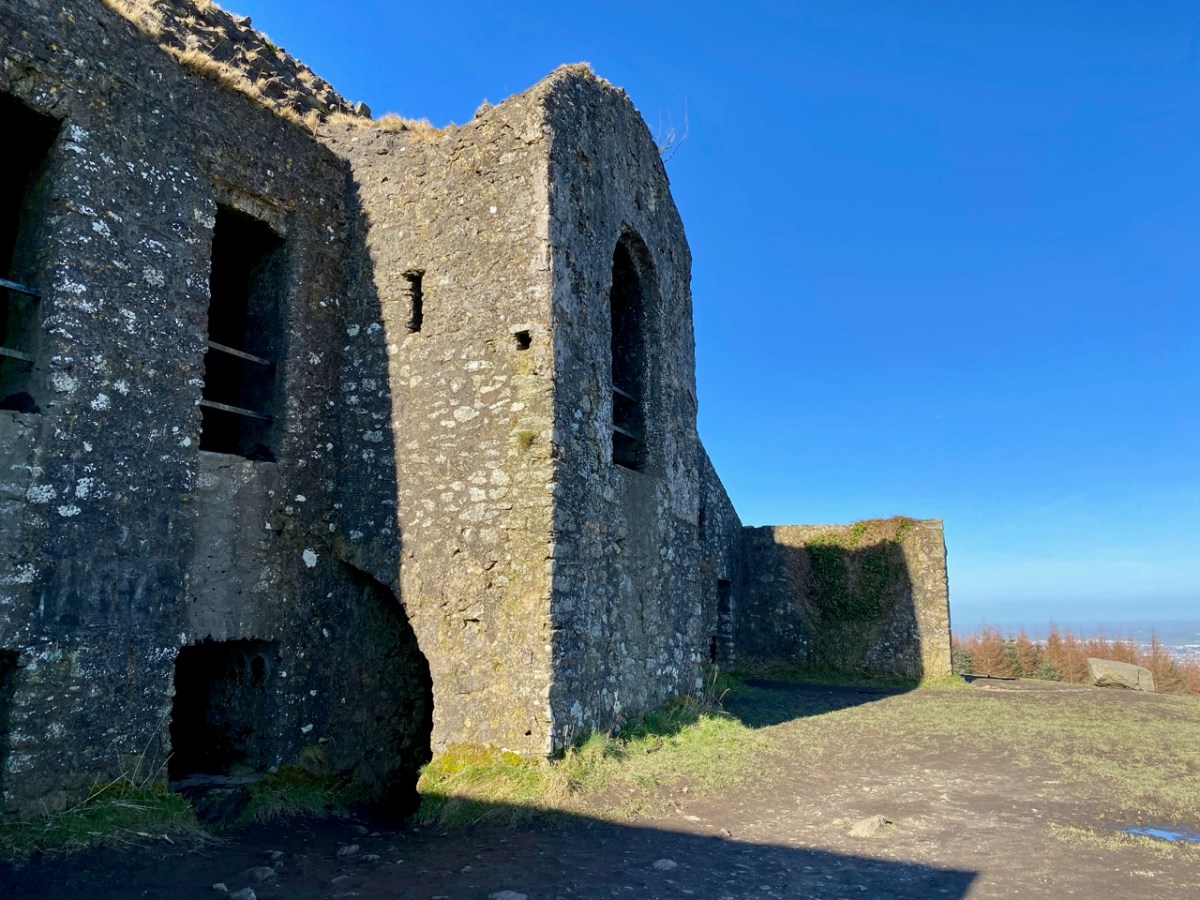
This feature (the two pictures above) is the hilltop referred to by O’Neill, where he claims to have found the ruins of the ‘Cahir’. Today it is recorded on the National Monuments Record as a ‘ringfort’ or ‘rath’:
CO132-017001-
Class: Ringfort – rath
Townland: CAHERAGH
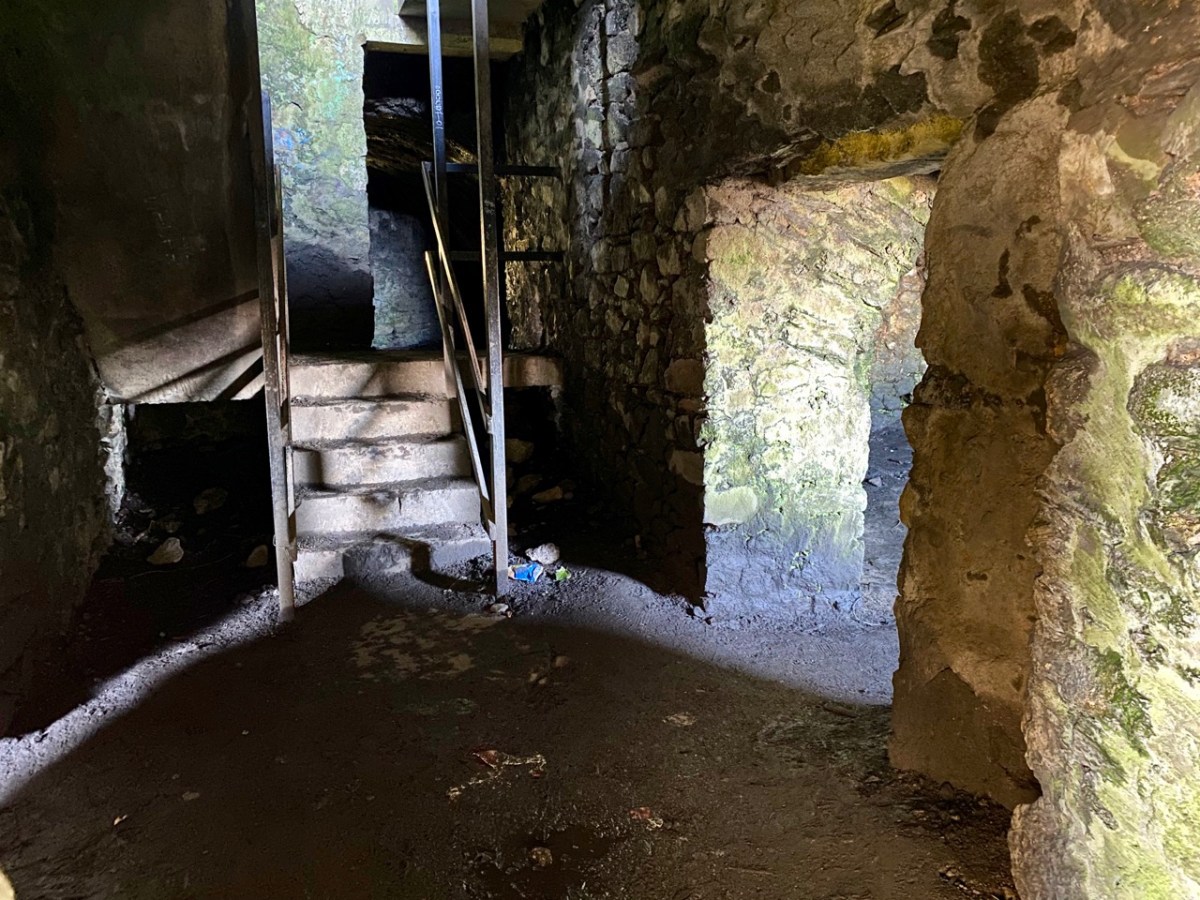
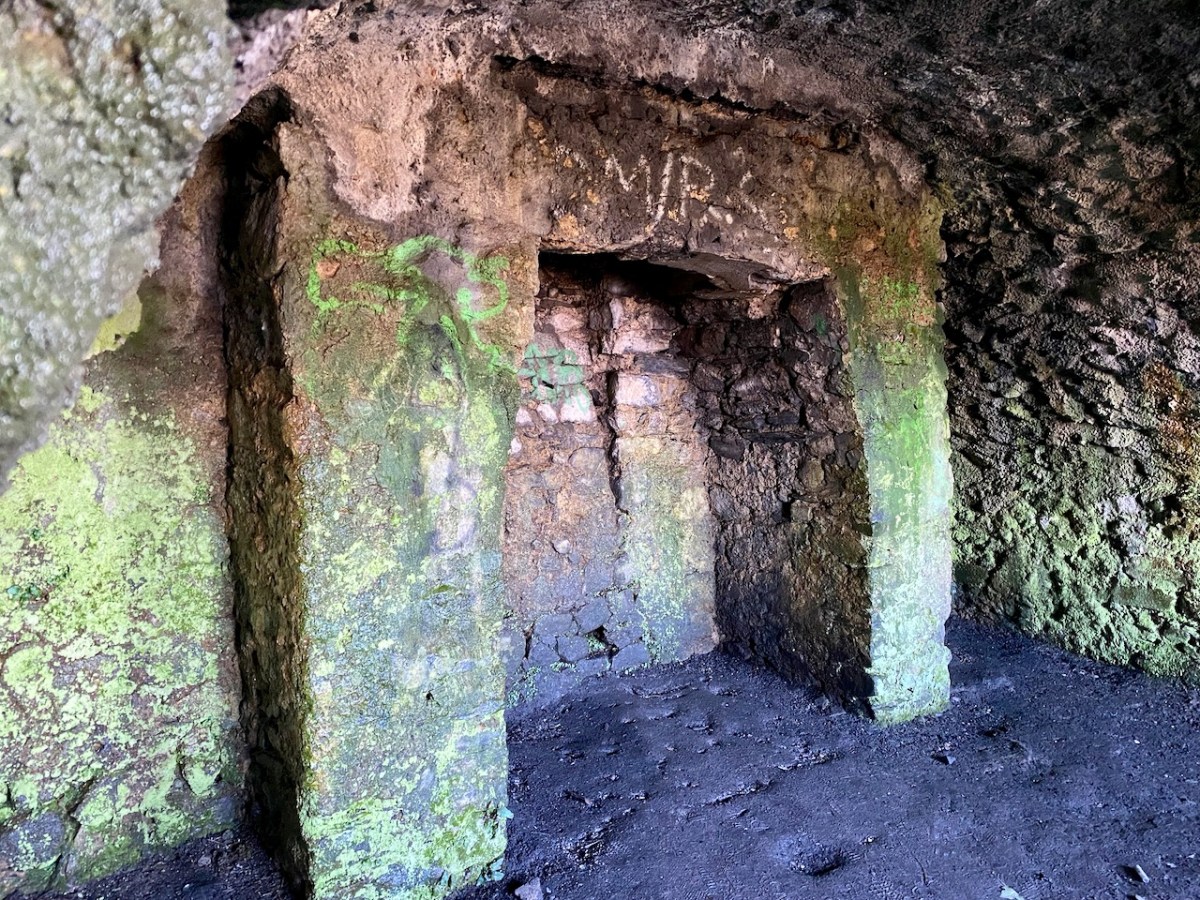
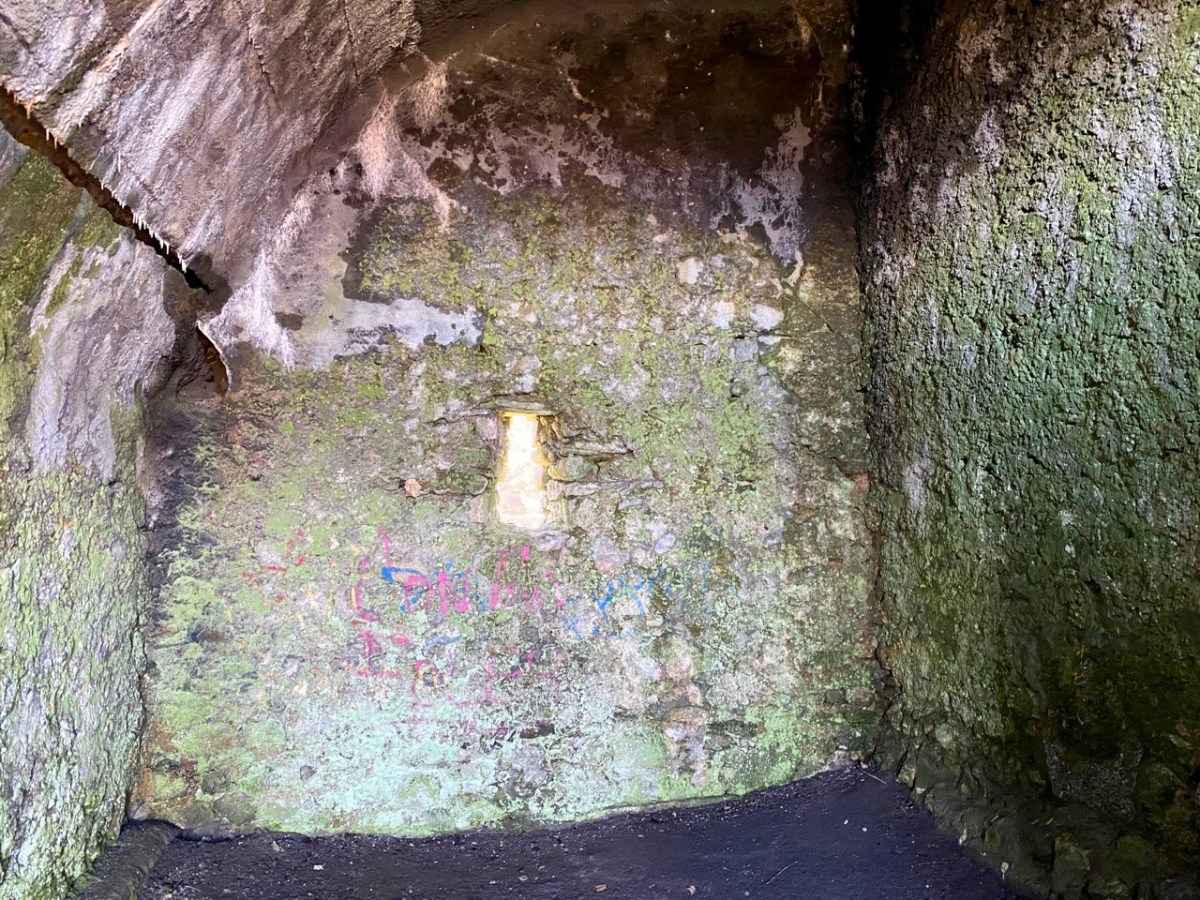
Description: In pasture, atop hillock broken by rock outcrop. Circular area (36.5m N-S; 37.5m E-W) enclosed by earthen bank (max H 3.8m). Break in bank to NNW (Wth 5m); and WSW (Wth 4m), where triangular feature adjoins inner bank face. Possible souterrain (CO132-017002-) in SW quadrant
Archaeology.IE National Monuments Record



Top: flat-topped mound with circular summit, very much in line with the expectation of a ringfort structure. Centre: stone embankment seen from the top of the ‘fort’. Lower: a defined ‘entrance’ through the ‘fort embankment’ on the summit of the mound. This could be ancient or modern: cattle use the fields in which this feature is located, and some of the topography could be shaped by this usage over centuries.
. . . The builders of Abbeys and Monasteries were wise in their day in the choice of locations for their establishment, and one essential desideratum was near to a plentiful supply of water, such as the banks of lakes and rivers, or adjoining never-failing springs. In this instance the River Ilen met all requirements, and taking everything into consideration, I am led to the conclusion that the graveyard at Caheragh was the site of the “Abbey of Cahir” mentioned by Lewis in the Topographical Dictionary of Ireland . . .
Letter from Capt Francis O’Neill, Southern Star 12.01.1929
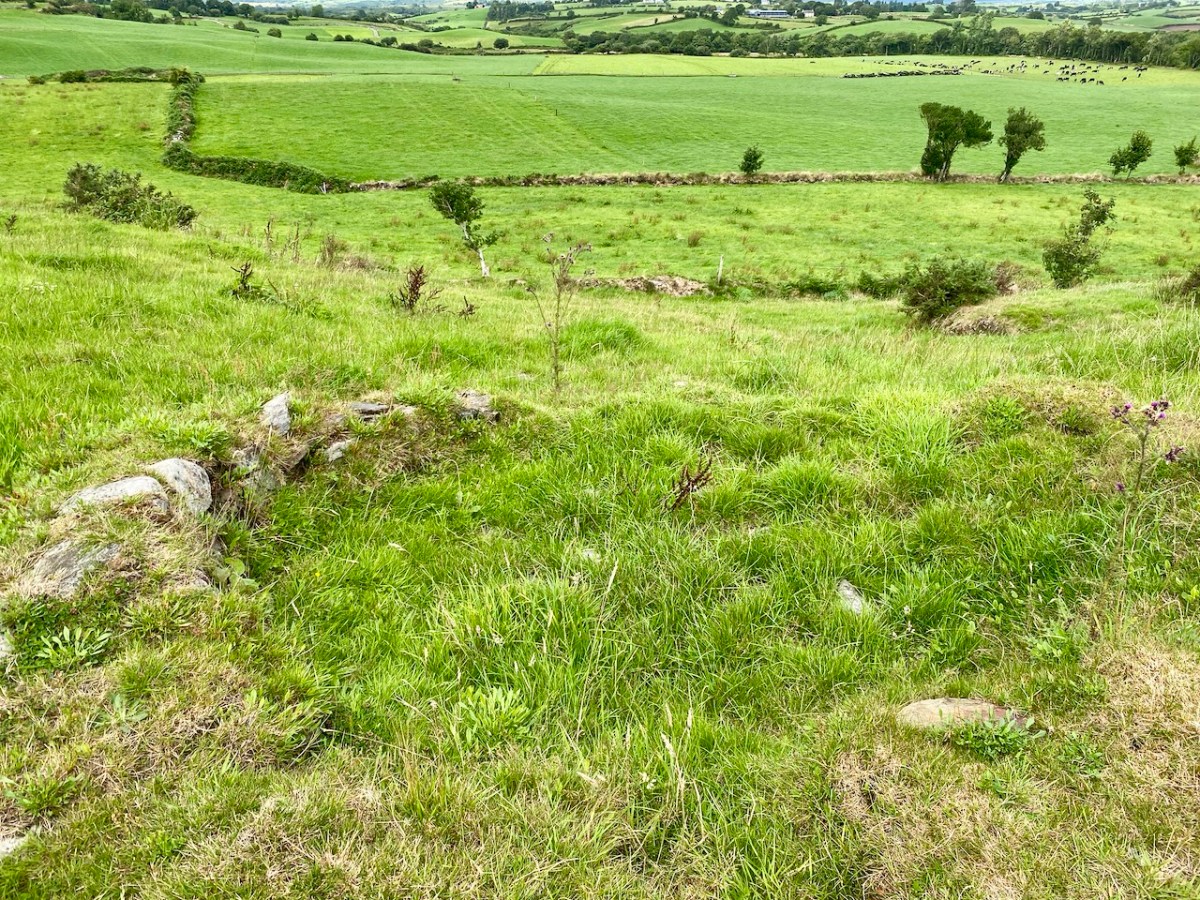

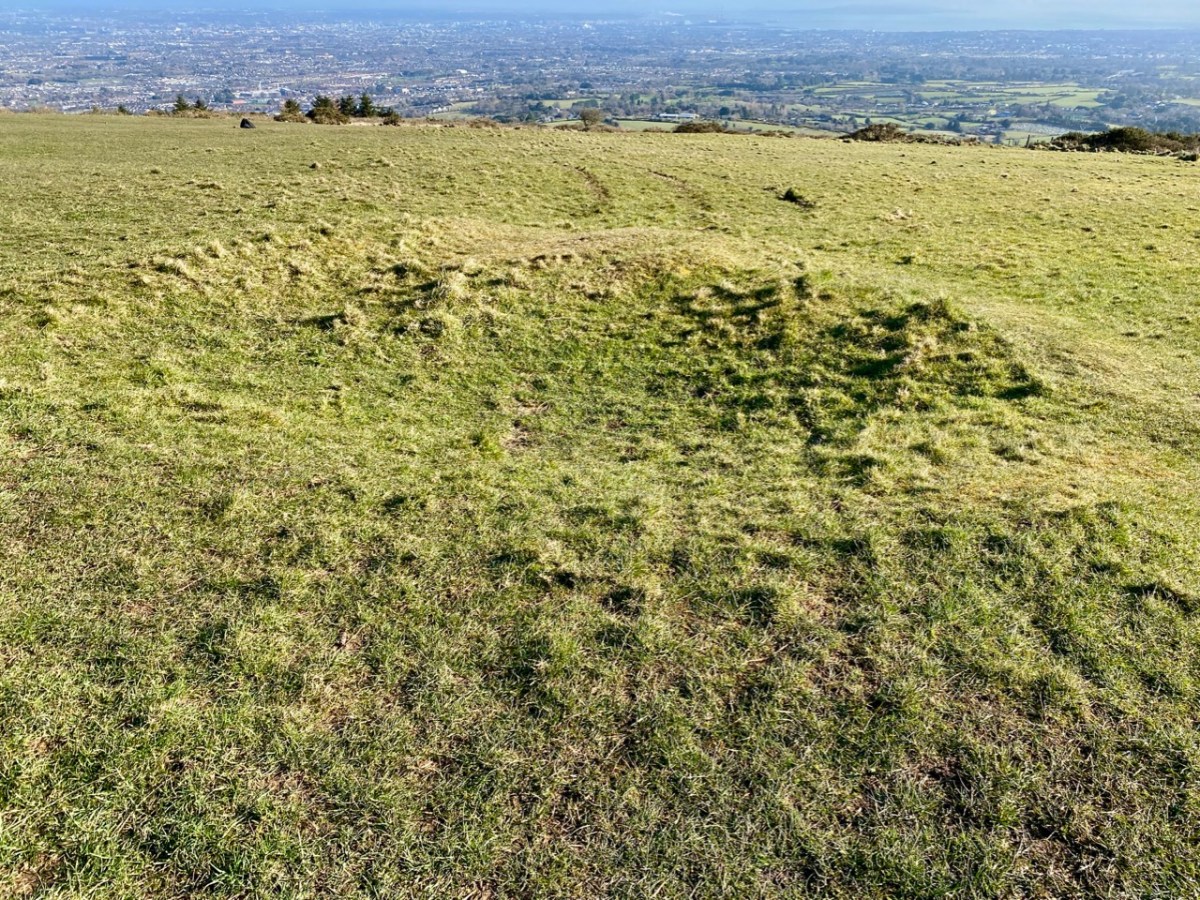
Above: evidence of built structures on the summit of the ‘ringfort’ mound at Caheragh. A significant circular foundation is clearly outlined. Perhaps, after all, there is some substance in the Captain’s musings on what occupied this site in earlier times? This account is from The county and city of Cork remembrancer; or, Annals of the county and city of Cork by Francis H Tuckey, Savage and Son, 1837:
. . . 1317 December 28, Geoffrey Fitz John de Cogan is presented by the King (by mandate to the Bishop of Cork), to the church of the Blessed Mary de Catheragh, in the King’s gift, by reason of his wardship of the lands and heir of John de Cogan . . . ‘Blessed Mary de Caheragh’ was a monastic site, said to be ‘situated on the hilltop commanding the view above the graveyard at Caheragh’ (possibly on the site of the ringfort). It was no doubt founded here because of the proximity of the watercourse . . .

So there – for your consideration – is the suggestion that the hill above Caheragh’s Old Graveyard (which may, in earlier times, have been a ringfort with a souterrain) was the monastic settlement Blessed Mary de Caheragh in medieval times. That’s quite a thought. My own opinion would be that the monastery would have been founded on the level ground close to the river: in fact where the graveyard is today. As the monastery declined, a church might have remained, eventually becoming a ruin. It was common for old churches and their environs to be used for burials and this might account for the comparative remoteness of this site from the village itself. Now – of course – there is no trace of a church ruin. This theory would hold good except for the annals quoted above, which state that a monastic site was situated on the hilltop overlooking what is now the graveyard.
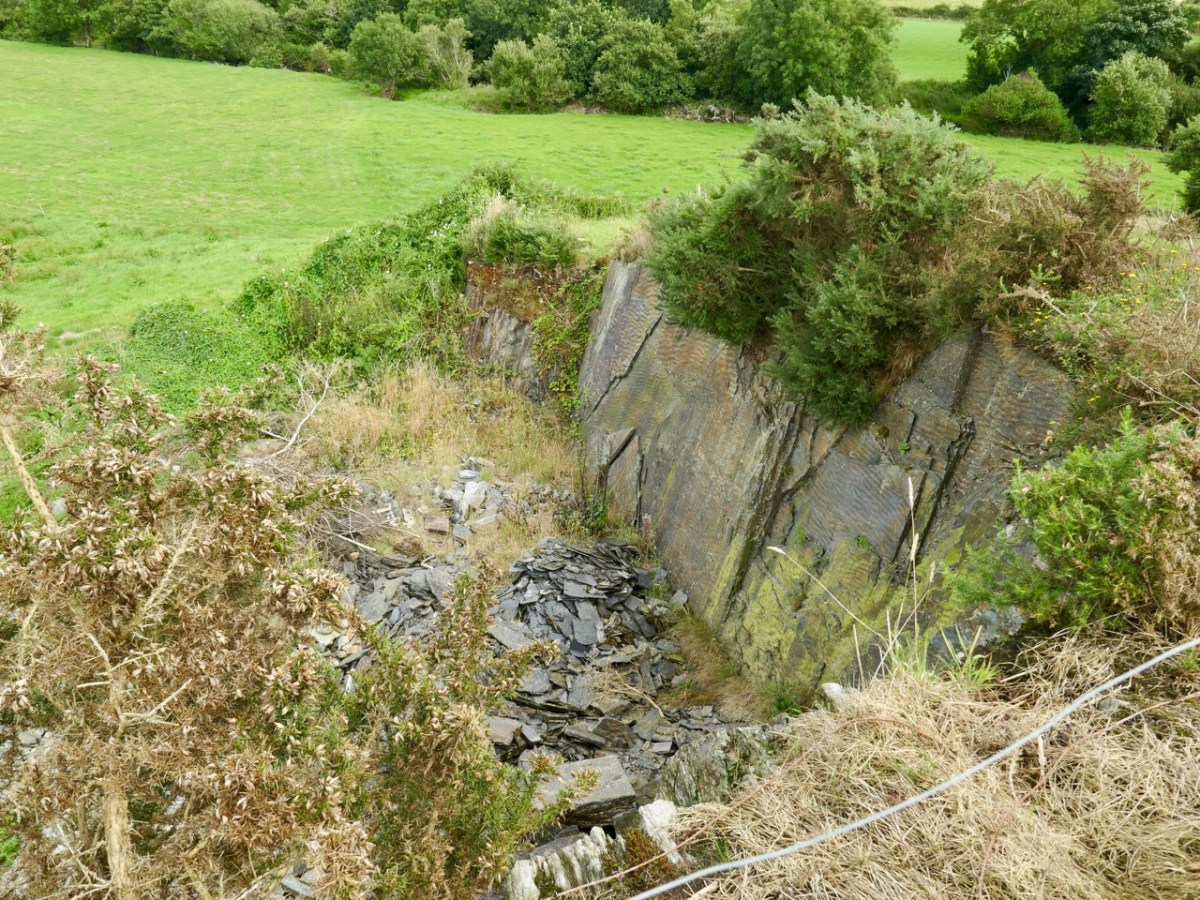


Evidence of stone quarries on the hillside suggest that significant quantities of stone has been used locally. Graveyard wall, field fences, or built structures? But the most challenging feature has to be the ringed foundation, or base, clear to see on the edge of the hill (below). Could it be a souterrain entrance – or, more fanciful, the base of a round tower?
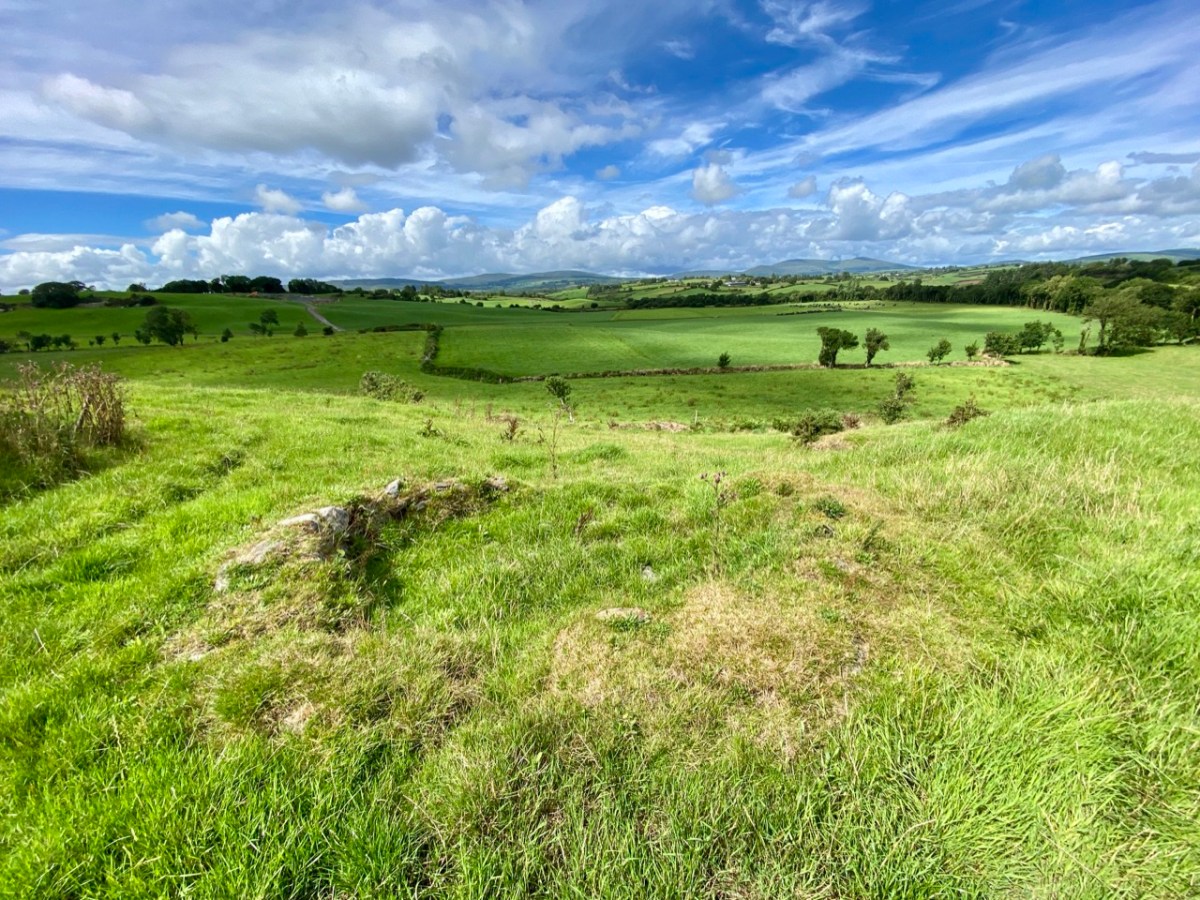

I’ll leave you with that conundrum (and my whimsical daydream below) for now, but we will continue with Francis O’Neill’s musings (which become even more complex) in a future post.