The Hardiman Atlas*, held in the Digital Repository of Ireland, is a bound volume of maps all of which were collected by James Hardiman. An erudite Mayo man born in 1782, he spoke Irish as his first language, studied law but was an historian to his core. He wrote histories, including one of Galway, and collected songs and manuscripts. He eventually became the librarian at Queen’s College Galway (now the University of Galway) where the main library is named for him. I’ve used the Hardiman Atlas before, for my posts on Jobson’s work on Planning a Plantation Part 1 and Part 2.

In the Digital Repository description we find this information of the Hardiman Atlas:
IE TCD MS 1209 is the collection of maps held in the Library of Trinity College Dublin and made by George Carew (1555-1629) 1st Earl of Totnes and Lord President of Munster at the beginning of the 17th century. Presented to the Library of Trinity College Dublin in the late 1700s. It contains nearly 90 maps and plans and is one of the largest sets of original Tudor and early Stuart maps of Ireland surviving anywhere. They are known collectively as the ‘Hardiman atlas’ after their first cataloguer, James Hardiman. Hardiman (1782-1855) was born in Co. Mayo and trained as a lawyer. He was librarian in Queen’s College Galway. Quoting from J.H. Andrews (‘Maps and Atlases’, Treasures of the Library Trinity College Dublin ed., Peter Fox (RIA: Dublin, 1986)): These maps, which are ‘for the most part competently drawn and attractively coloured’ and which ‘display not one scale of latitude or longitude in the entire collection … are essentially the by-product of a military and political conquest. However, as well as forts, defended towns and troop movements, they are rich in placenames, territorial boundaries and a good deal of ordinary landscape detail. Carew is said to have wanted all his Irish papers to be deposited at Trinity … though as it turned out most of them finally came to rest at Lambeth Palace in London. Nobody knows when, how or why the maps became detached from the collection and found their way to Dublin. They simply turn up in the College records of the late eighteenth century …. It was a non-Trinity historian, James Hardiman of Galway, who first catalogued them in 1821, apparently on his own initiative, and after being bound into a single, large volume they became generally known as the Hardiman atlas … The credit for [the rediscovery of their true origin] belongs to a recent Keeper of Manuscripts William O’Sullivan, who put the issue beyond any doubt by identifying Carew’s hand on many of the Hardiman maps and by collating all their titles and subjects with the original early-seventeenth-century catalogue still at Lambeth’.
https://repository.dri.ie/catalog/sn00qn48t
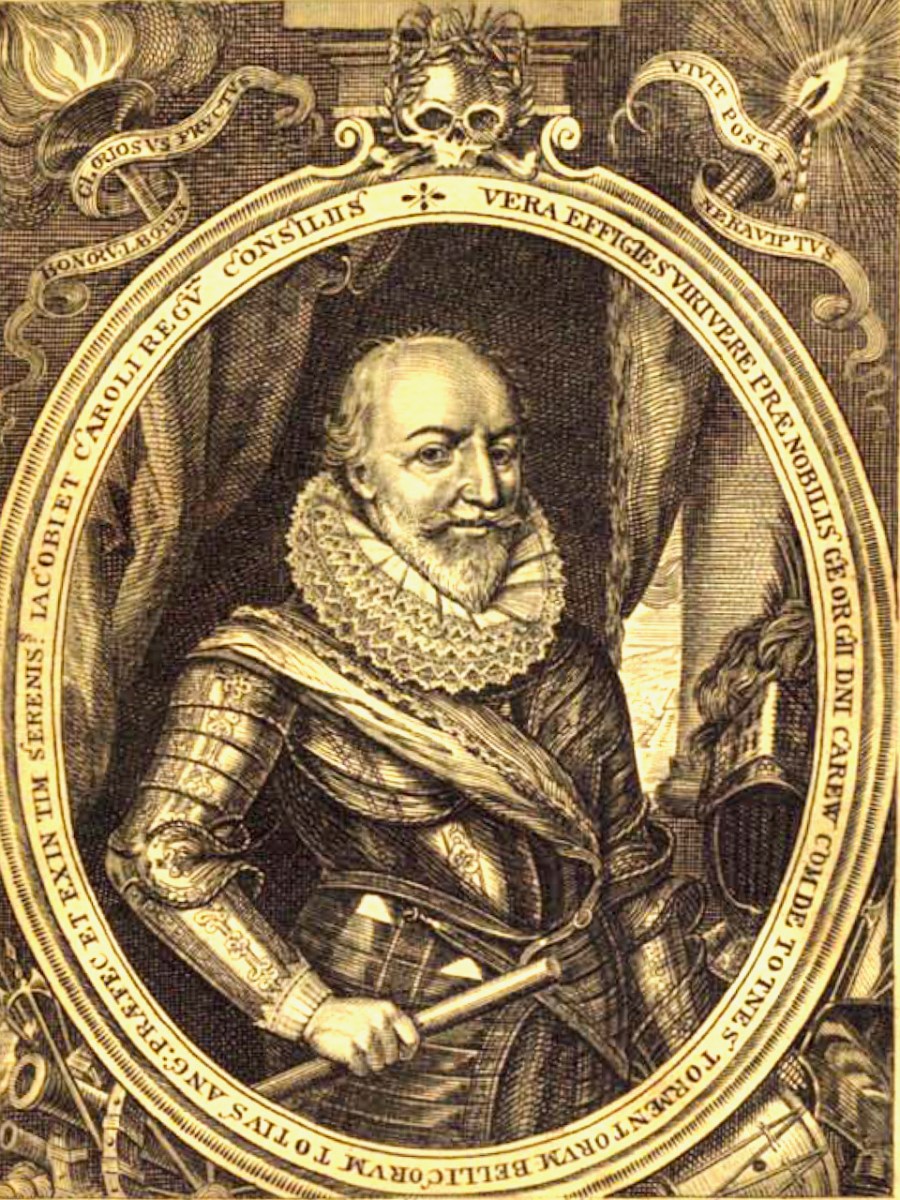
George Carew** collected anything that helped to support his claim to large tracts of land in Munster. But maps were also vital for him as one of the military leaders in charge of subduing Ireland before and after the Battle of Kinsale in 1601. Read all about Carew and his time in Ireland in this excellent entry by Terry Clavin in the Dictionary of Irish Biography. (You might want to take a blood-pressure tablet first.)

Back to the map! Familiar to us from other Elizabethan Maps, this one is oriented east/west, rather than north/south, meaning that we see Ireland lying on its side. By the way, I have to use a lower resolution for the blog, but you can view the map yourself in very high resolution in the Digital Repository.
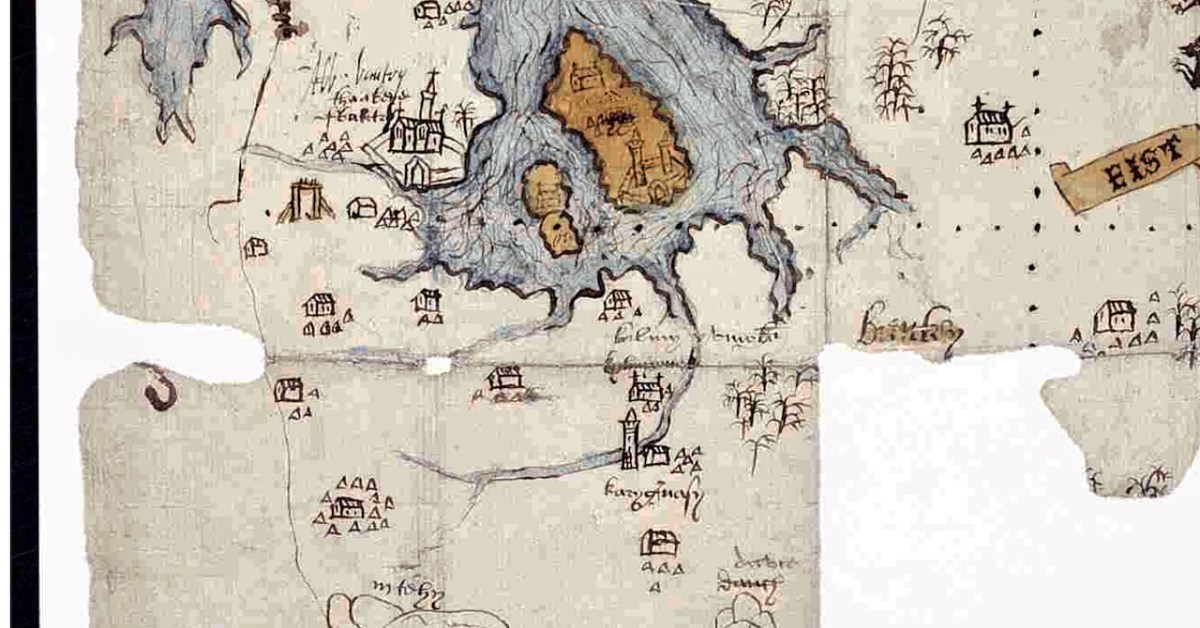
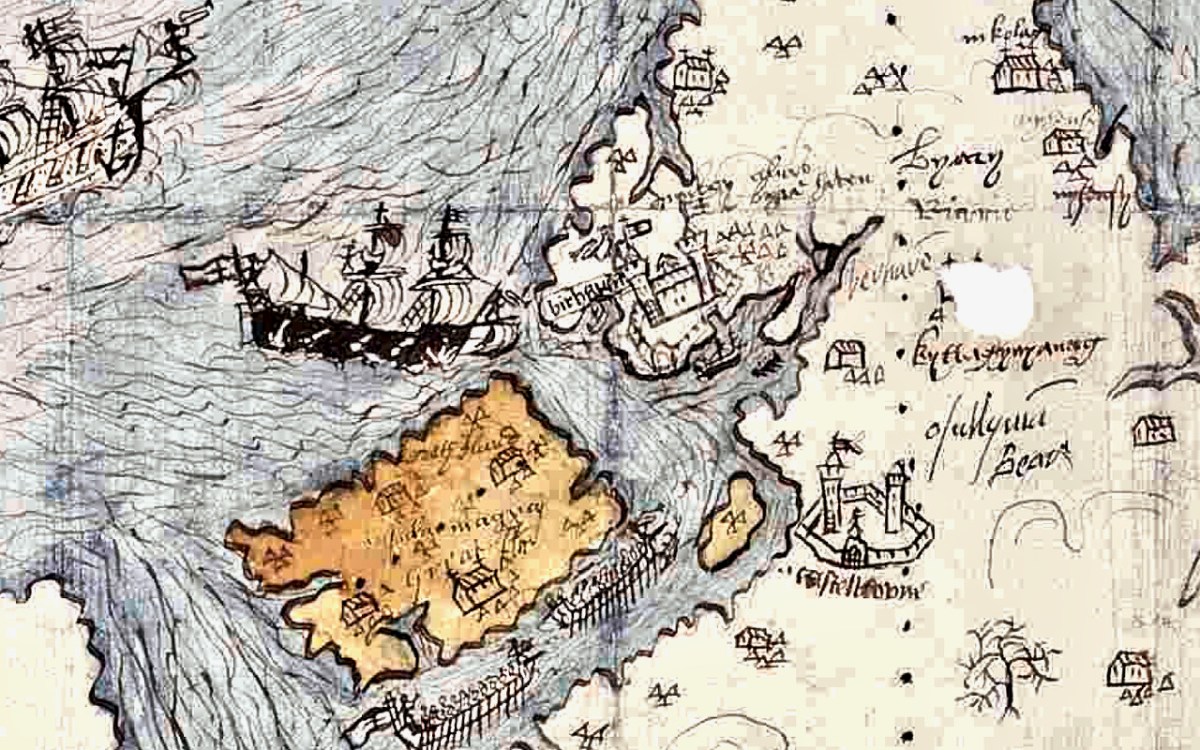
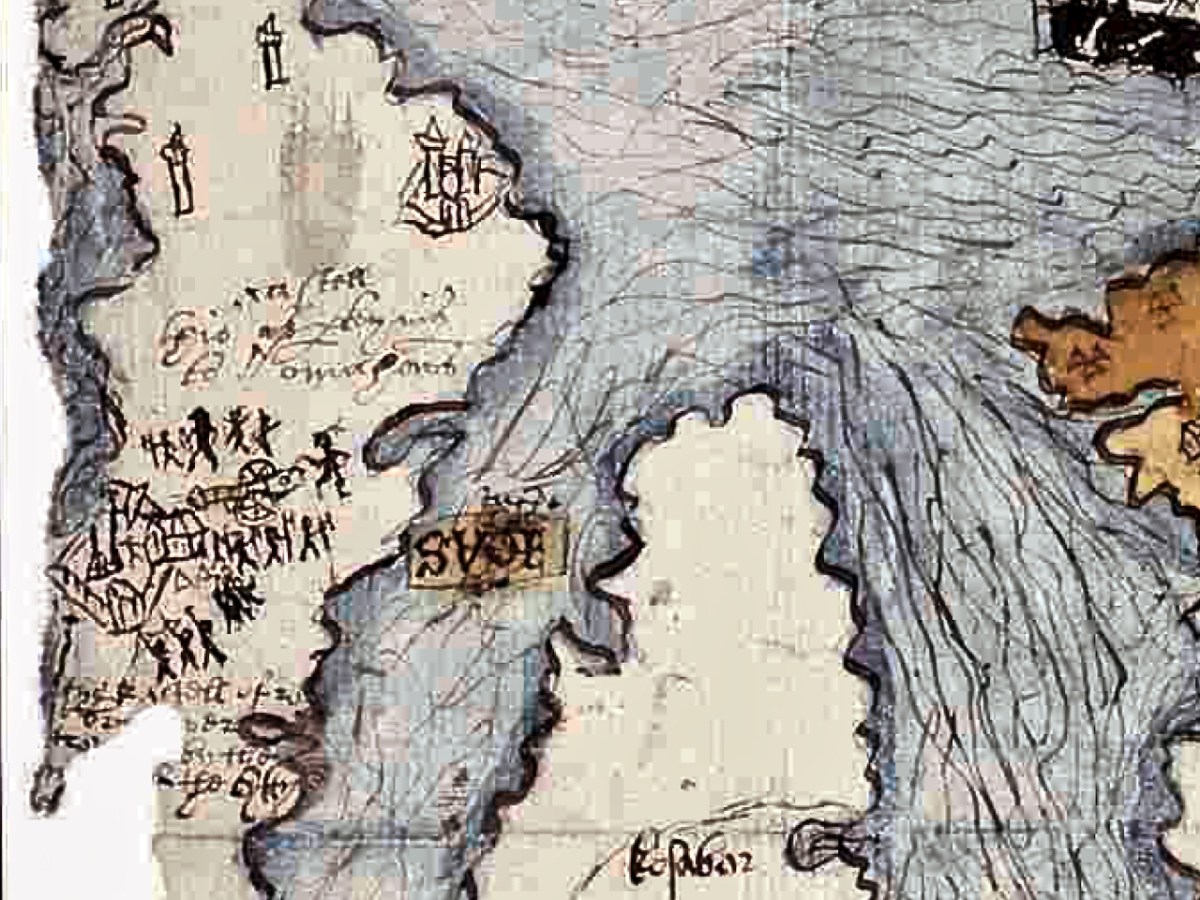
We don’t know who did this one, or when: The date is given as 1560-1620. It seems in some ways more basic than other maps of the period, and less exact. However, it still contains an extraordinary amount of information. The area it covers stretches from Bere Island to Waterford and from the sea to the Limerick and Tipperary borders. For ease, I have turned it rightside-up, so that West Cork is now as we expect to see it, on the bottom left of the map.
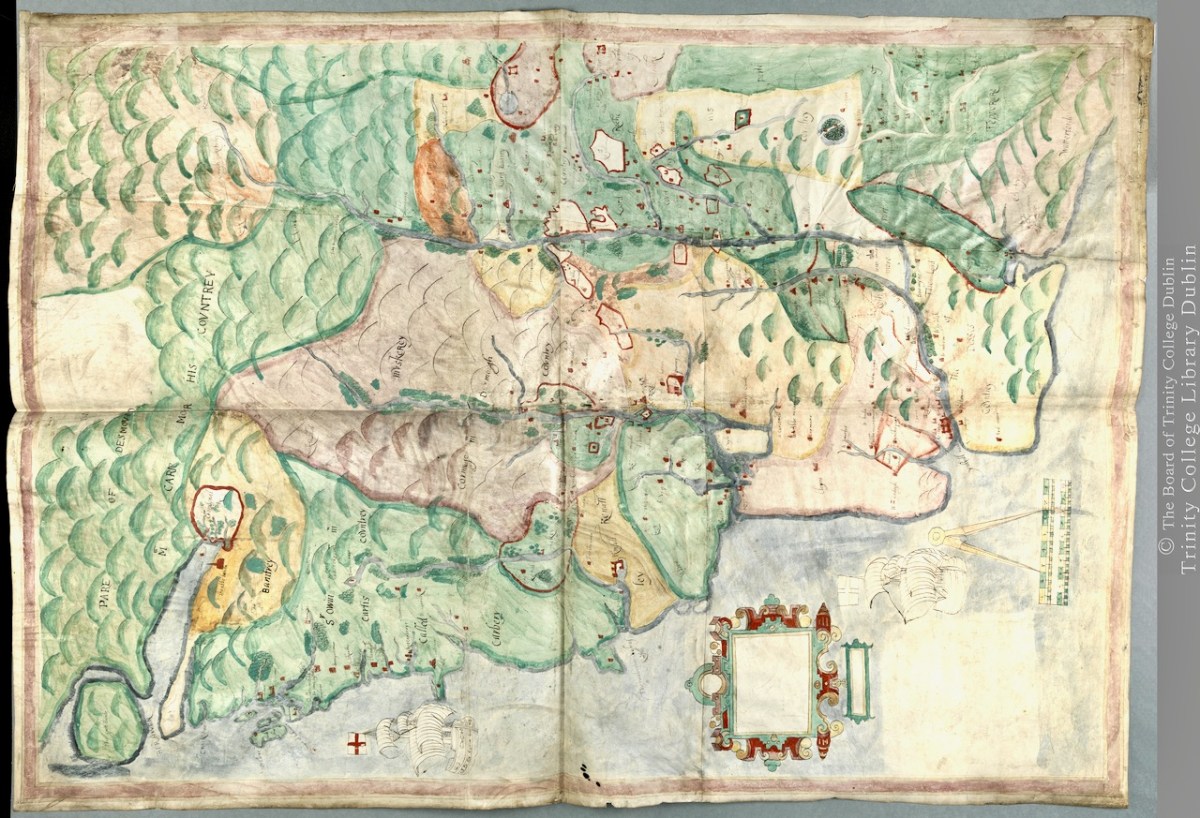
For this first post, I will concentrate on the area around Roaringwater Bay and west to Castlehaven, since this is my home turf, but we will explore further afield later. To put it in a little context, here’s a slightly broader view of the area (below). Note that it is labelled Sir Owen McCarthy’s Country called Carbery. There is also a large tract simply labelled Bantrey, of which the only feature is The Abbe Benita. Dunmanway, Donemenuye, is shown on an island at the head of the Bandon River. Berhaven, Croukhaven, Cape Clere, and The Haven of Boltimore are shown along the coast, along with a very fine warship in full sail, with cannons, a crow’s nest and an English flag.
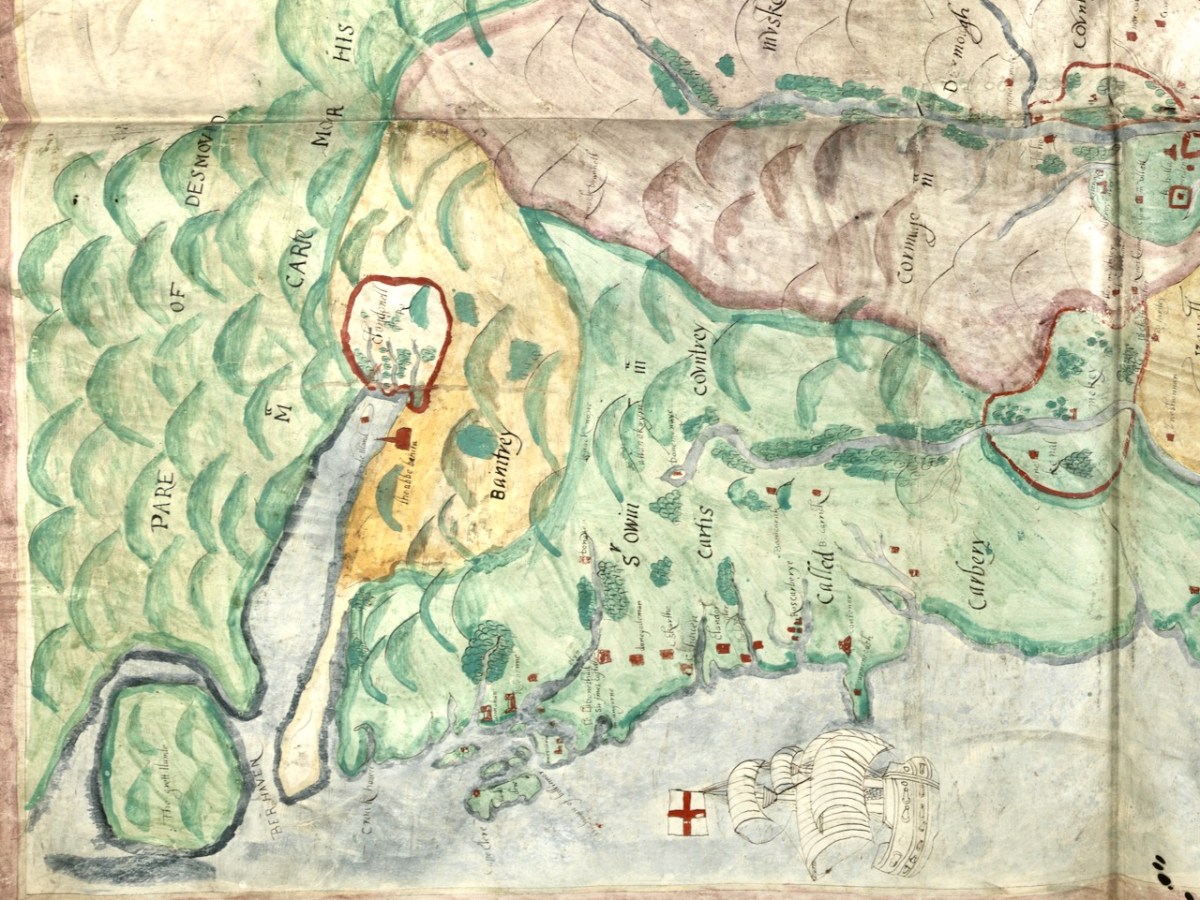
So you can further orient yourself, here is the 1880s map of the same area (more or less). The yellow dots indicate castles/tower houses as identified on the 1880s Ordnance Survey Map as part of the National Monuments Service.
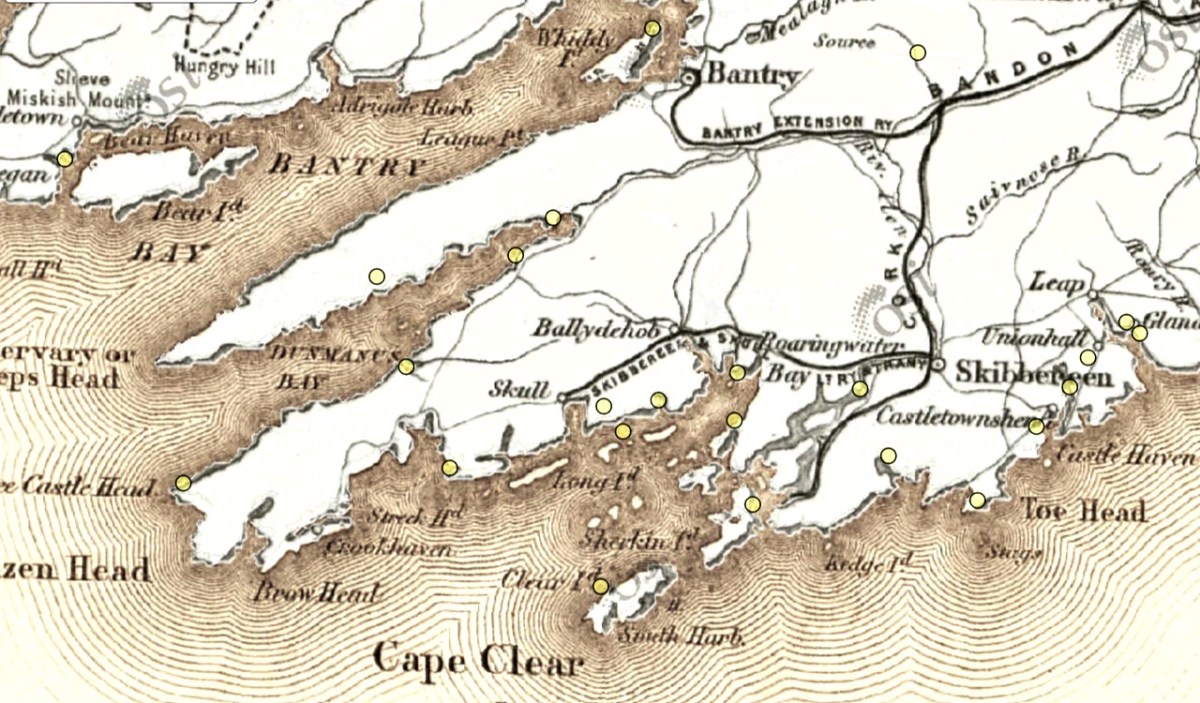
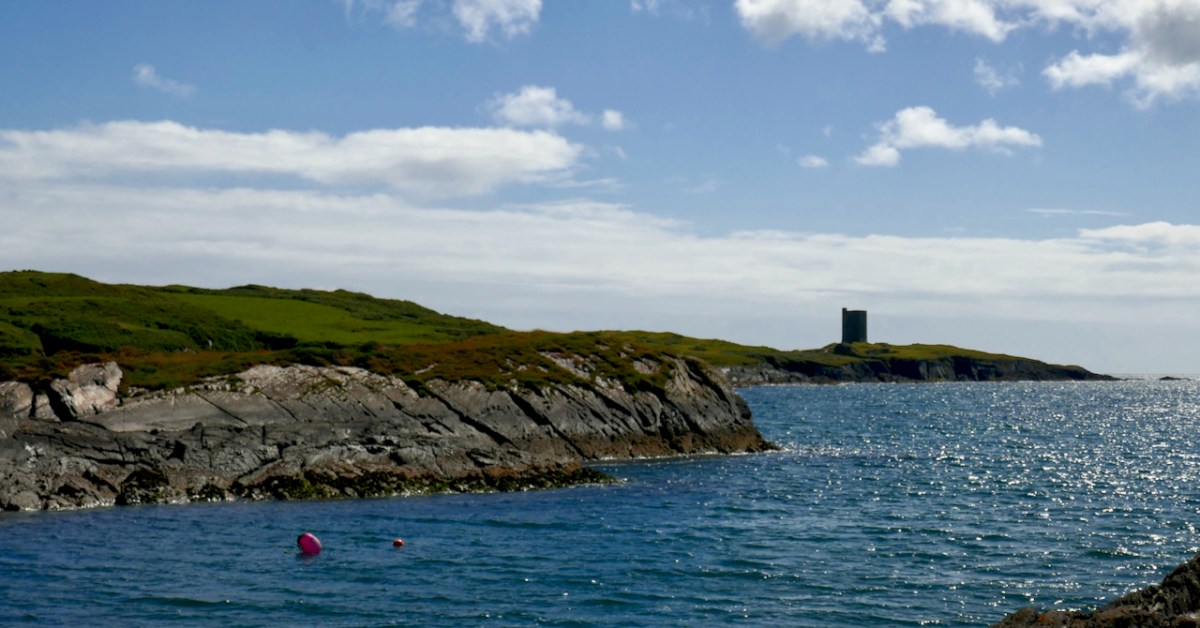
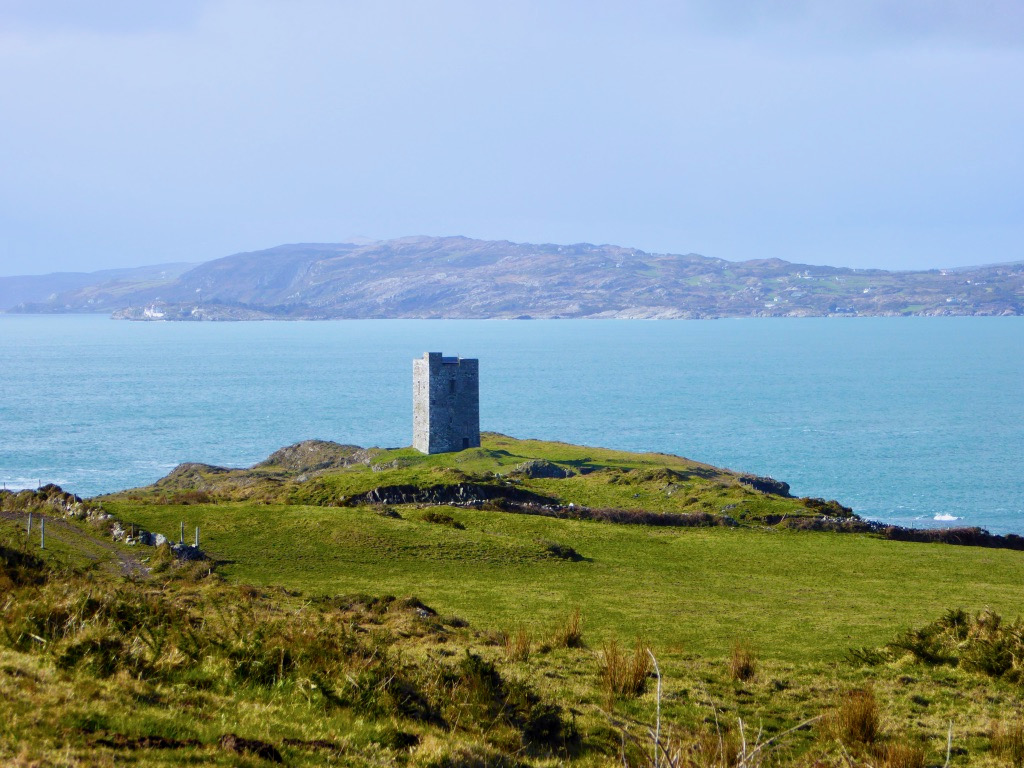
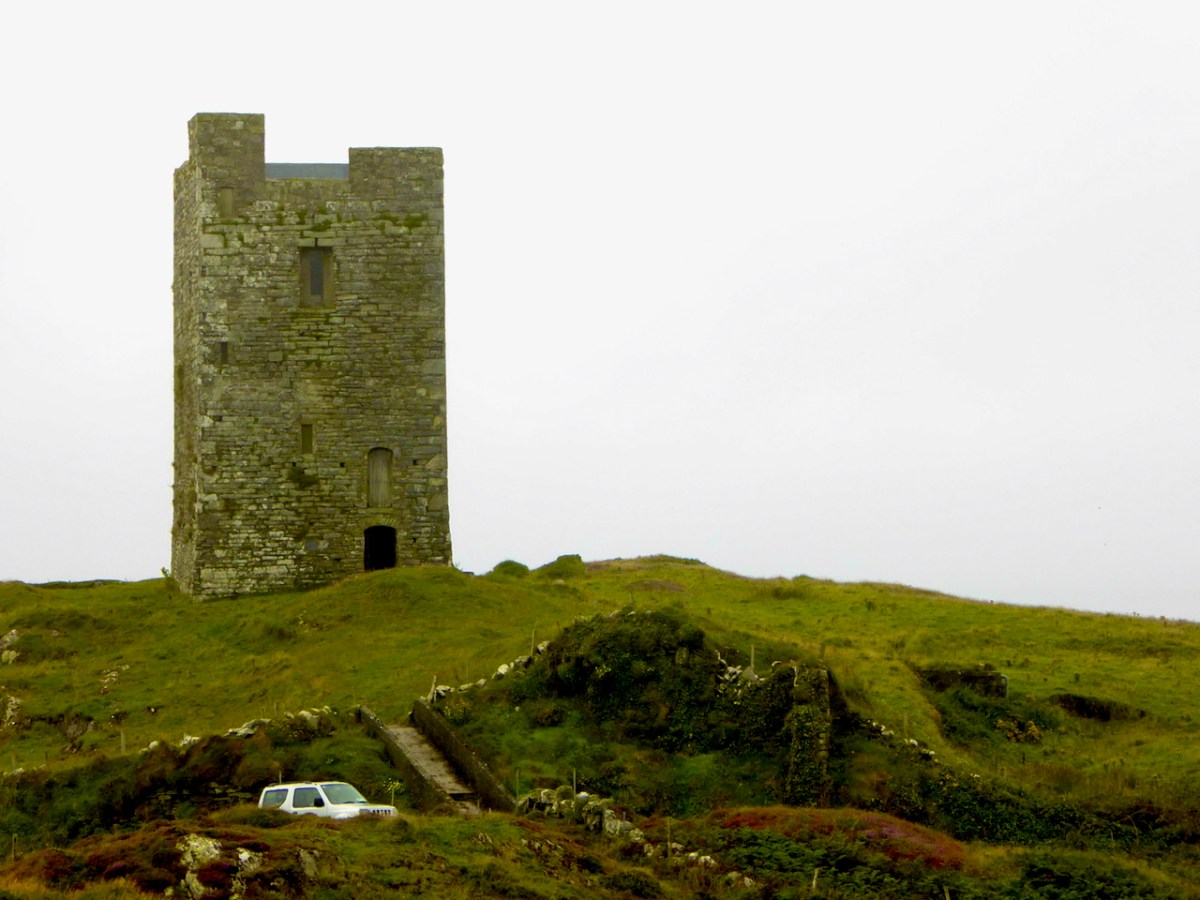
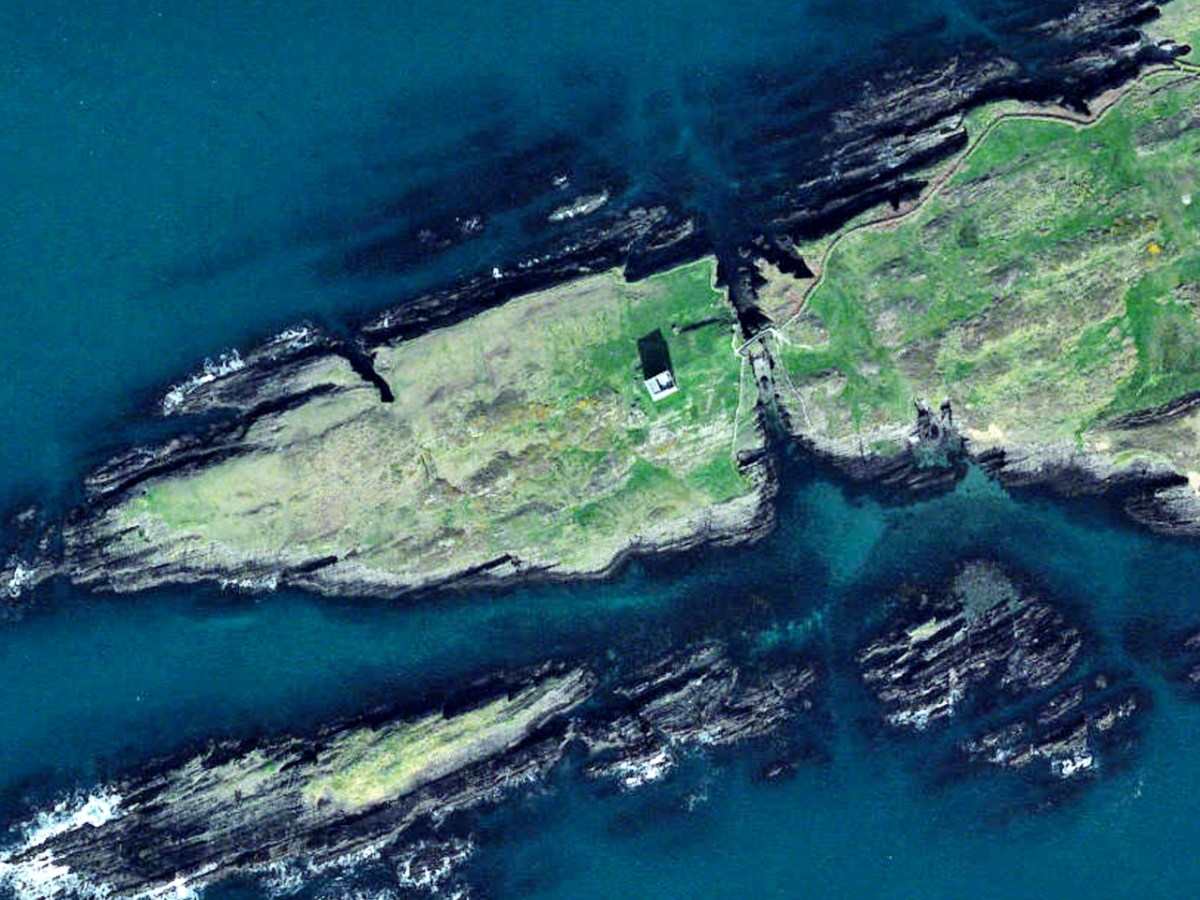
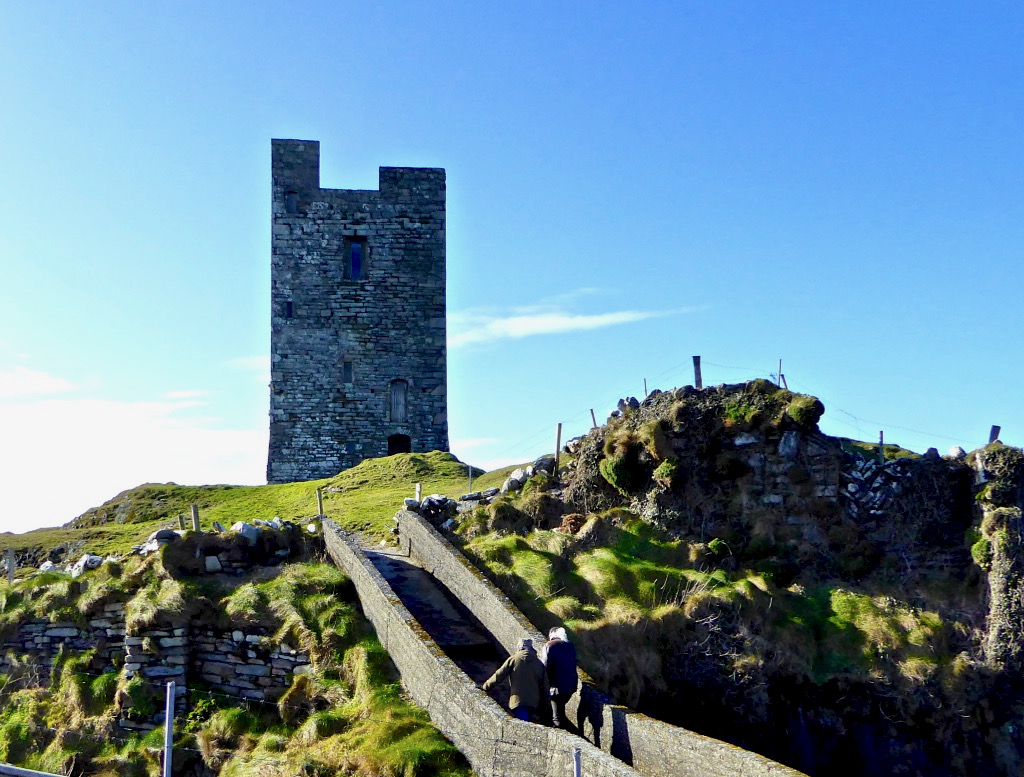
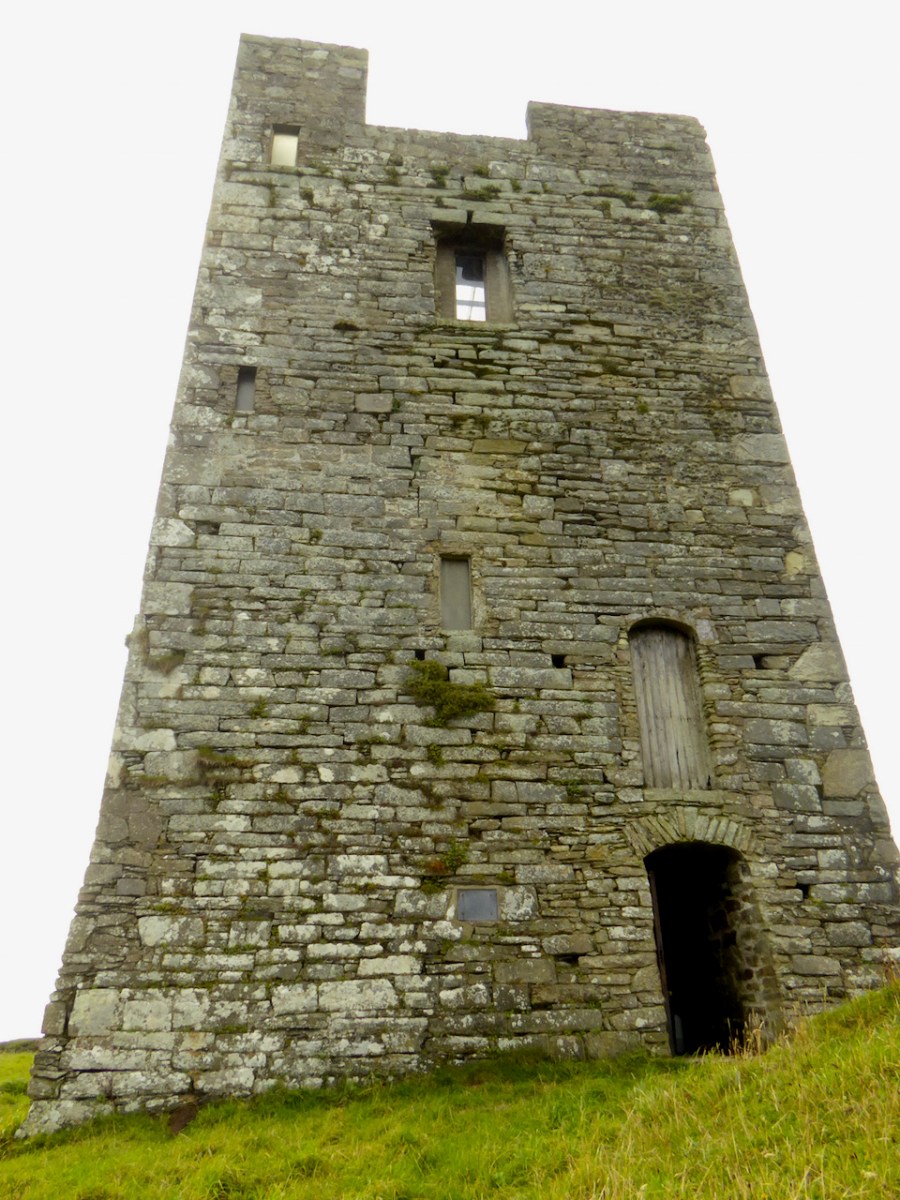
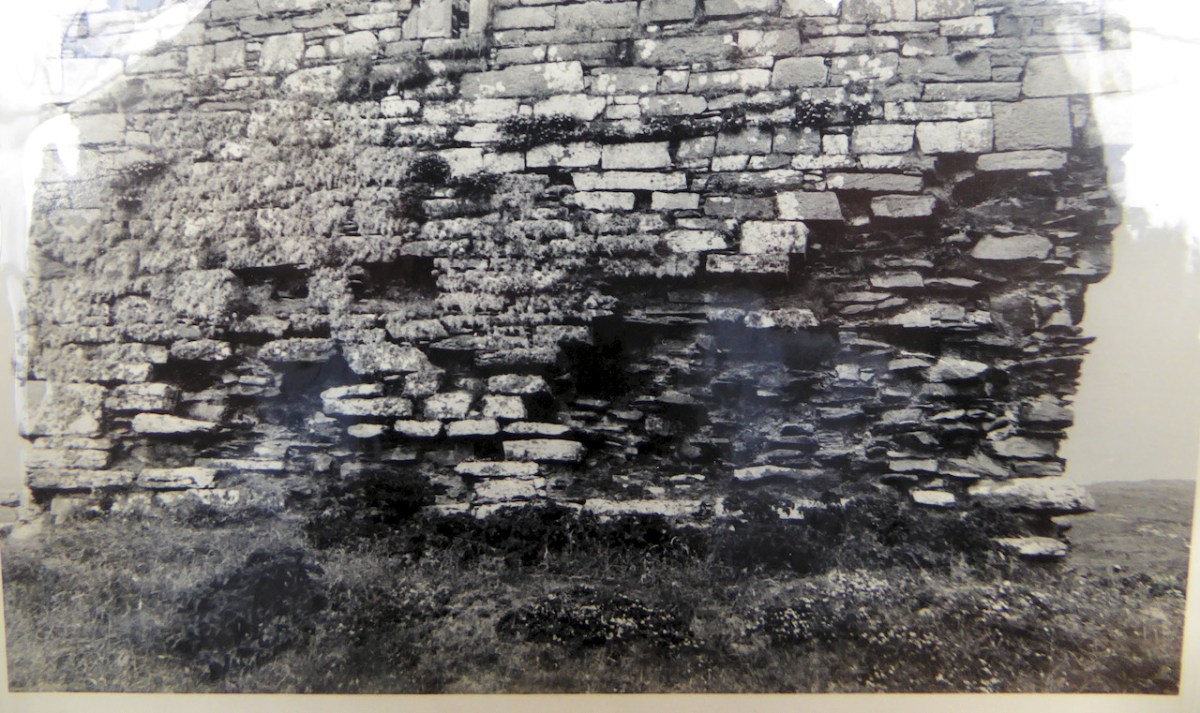
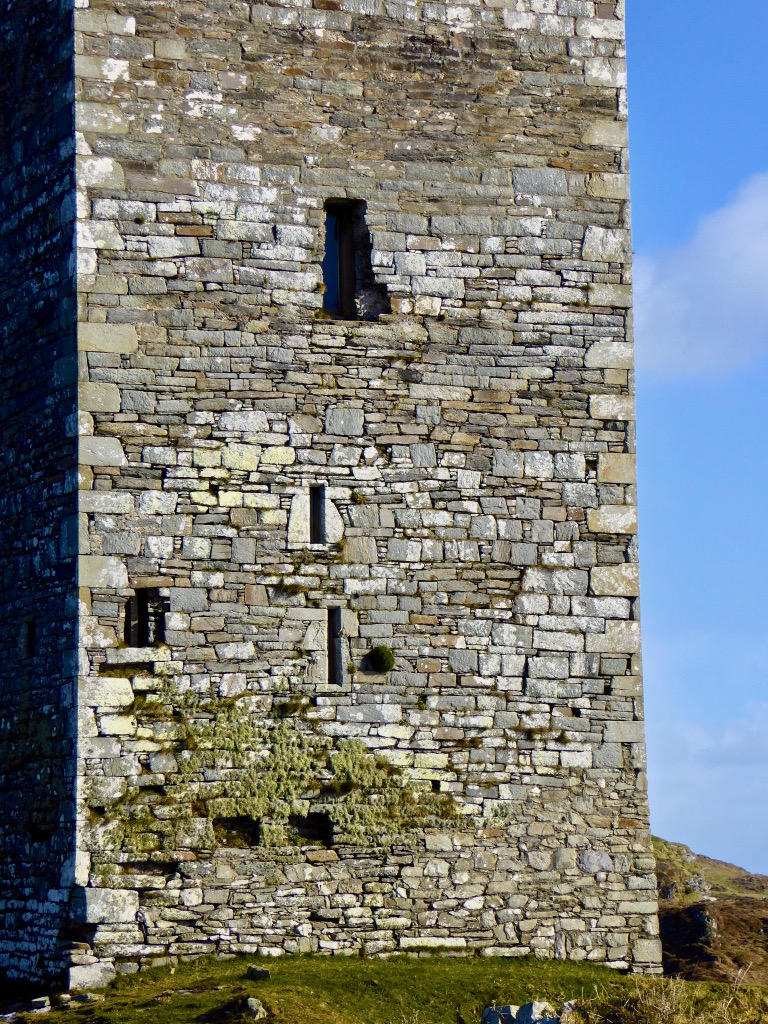
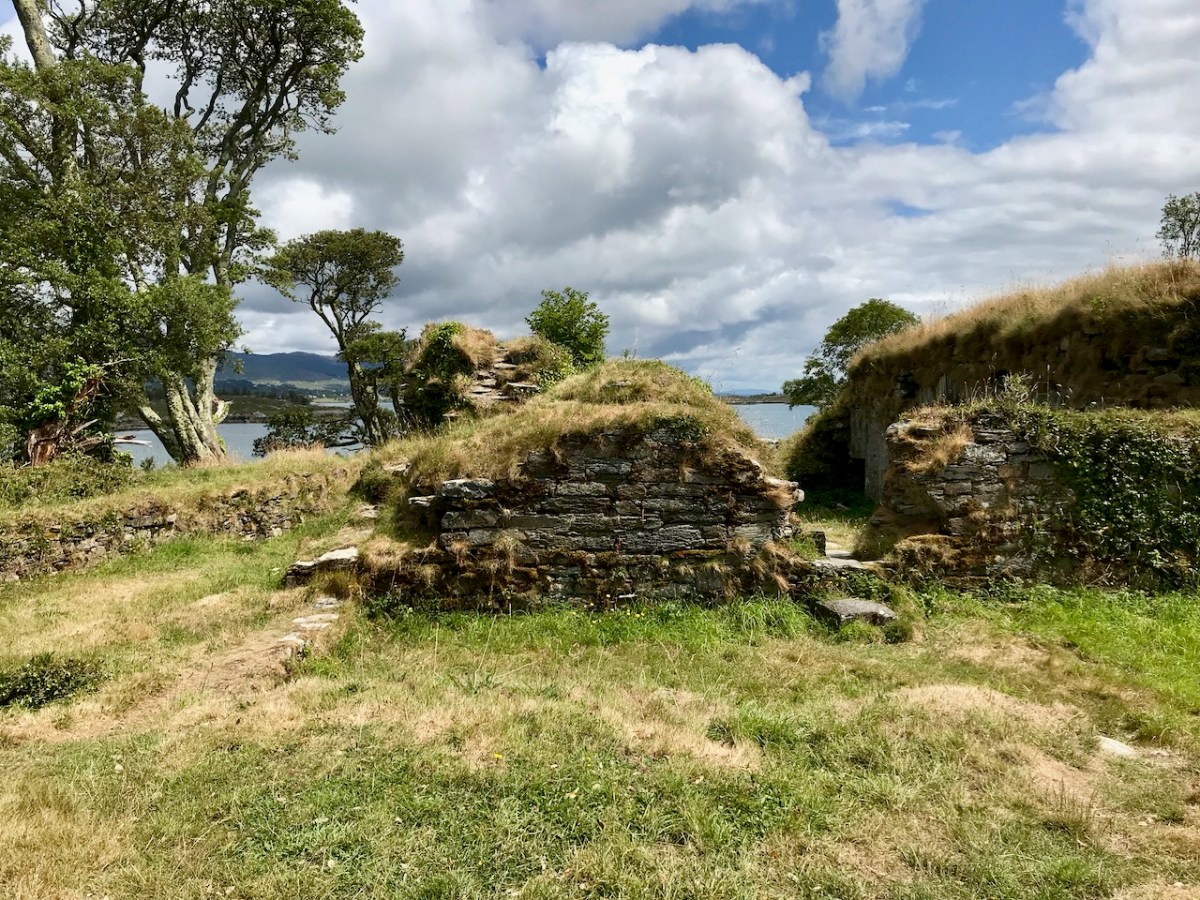
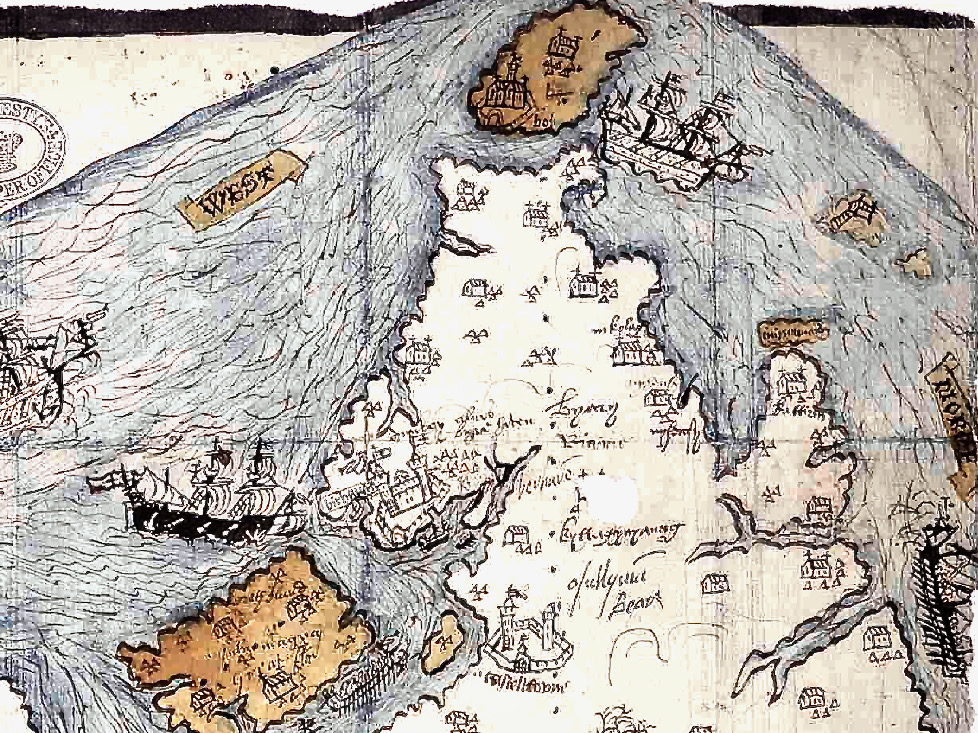
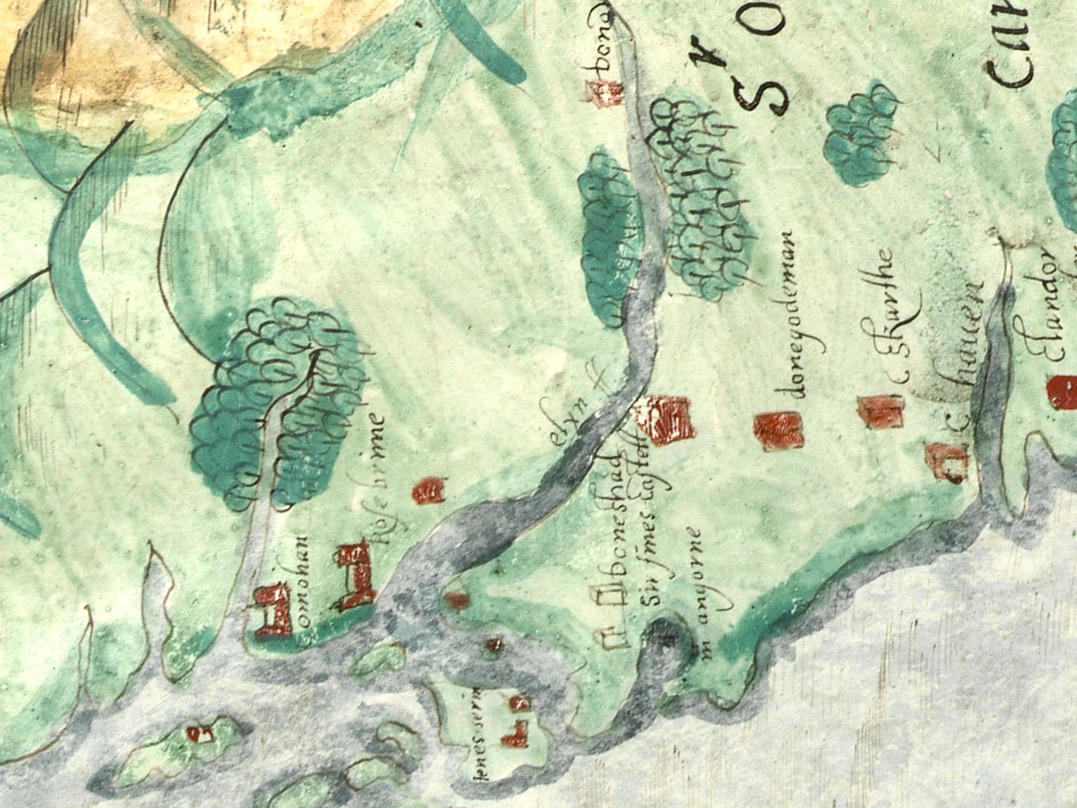
Honing in on Roaringwater Bay, below, the two most prominent castles are Ardintenant and Rossbrin, labelled C omohan and Rosebrine. Ardintenant is called the Castle of the O’Mahonys here as it was the home of the Taoiseach of the O’Mahony clan, while Rossbrin was the home of the Táiniste, or chieftain-in-waiting. Both are shown as very substantial castles, surrounded by bawn walls with additional towers.
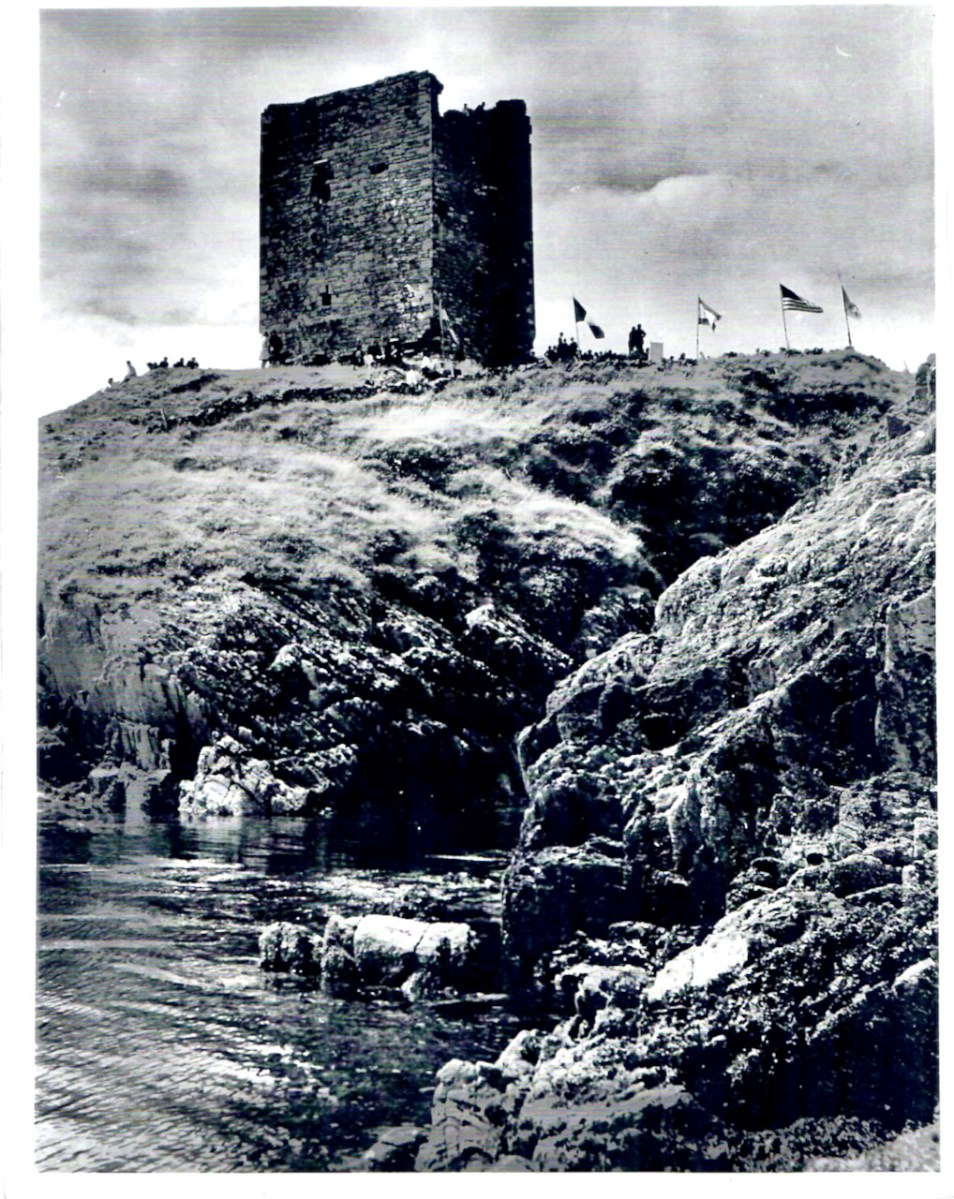
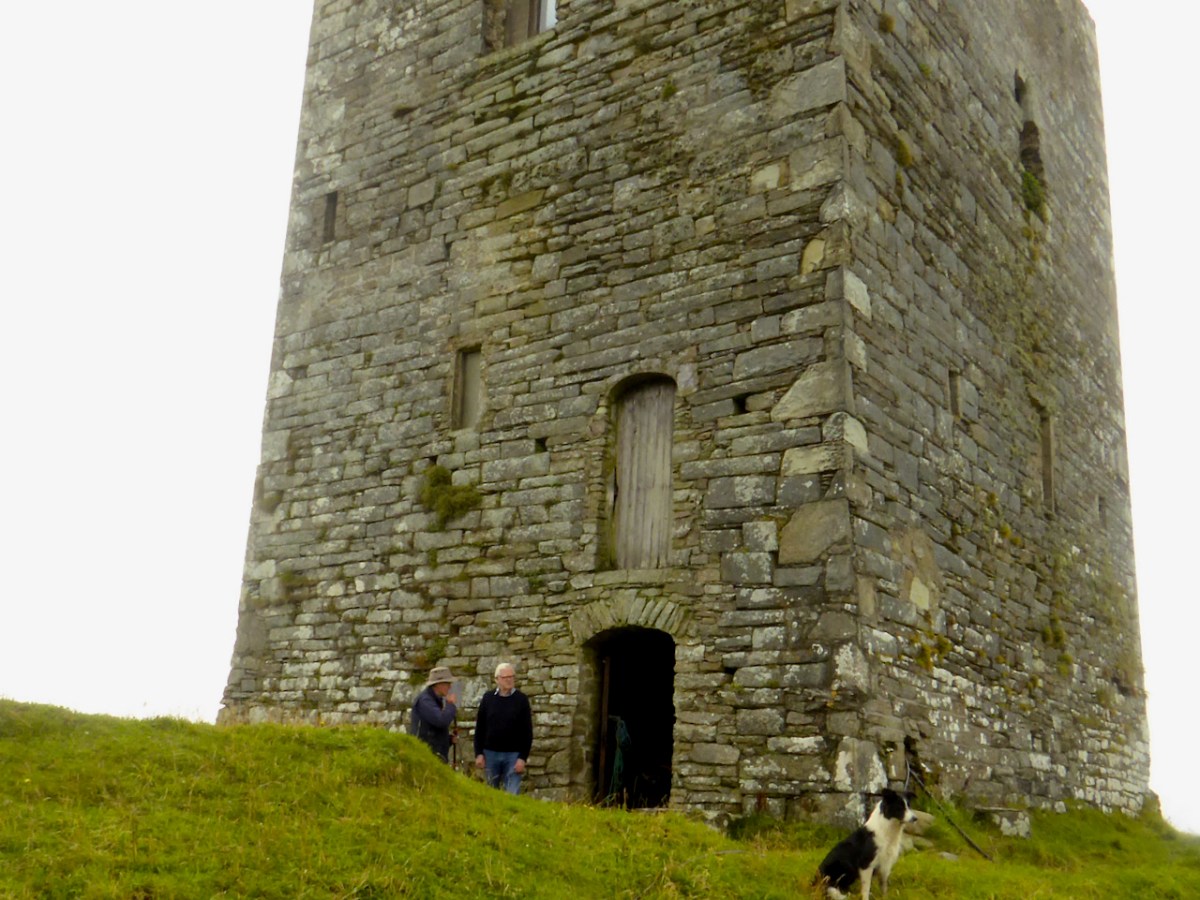
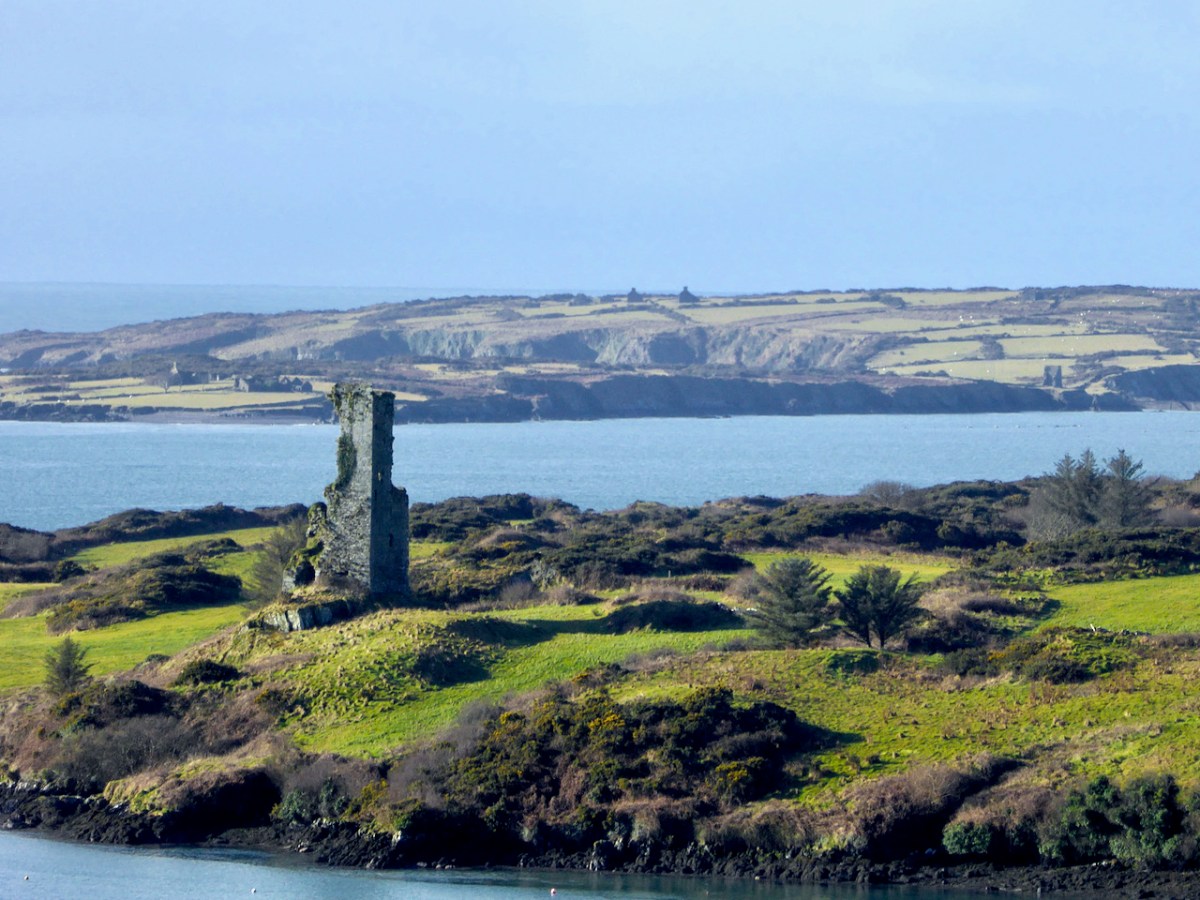
While Ardintenant still has one wall-tower, Rossbrin is a vestige of what it once must have been. This is what it looks like now, and you can see the remnants of what was once also a small castle on Castle Island behind it.

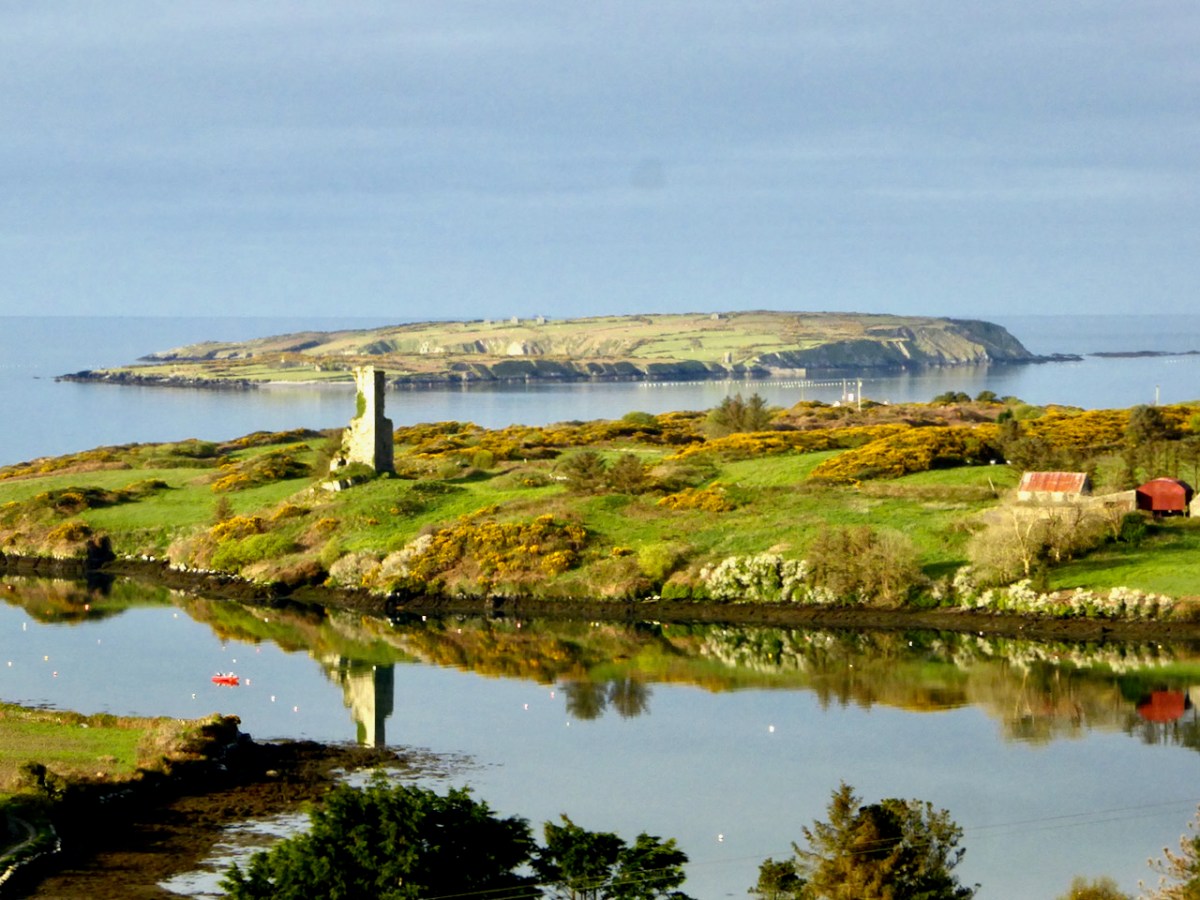
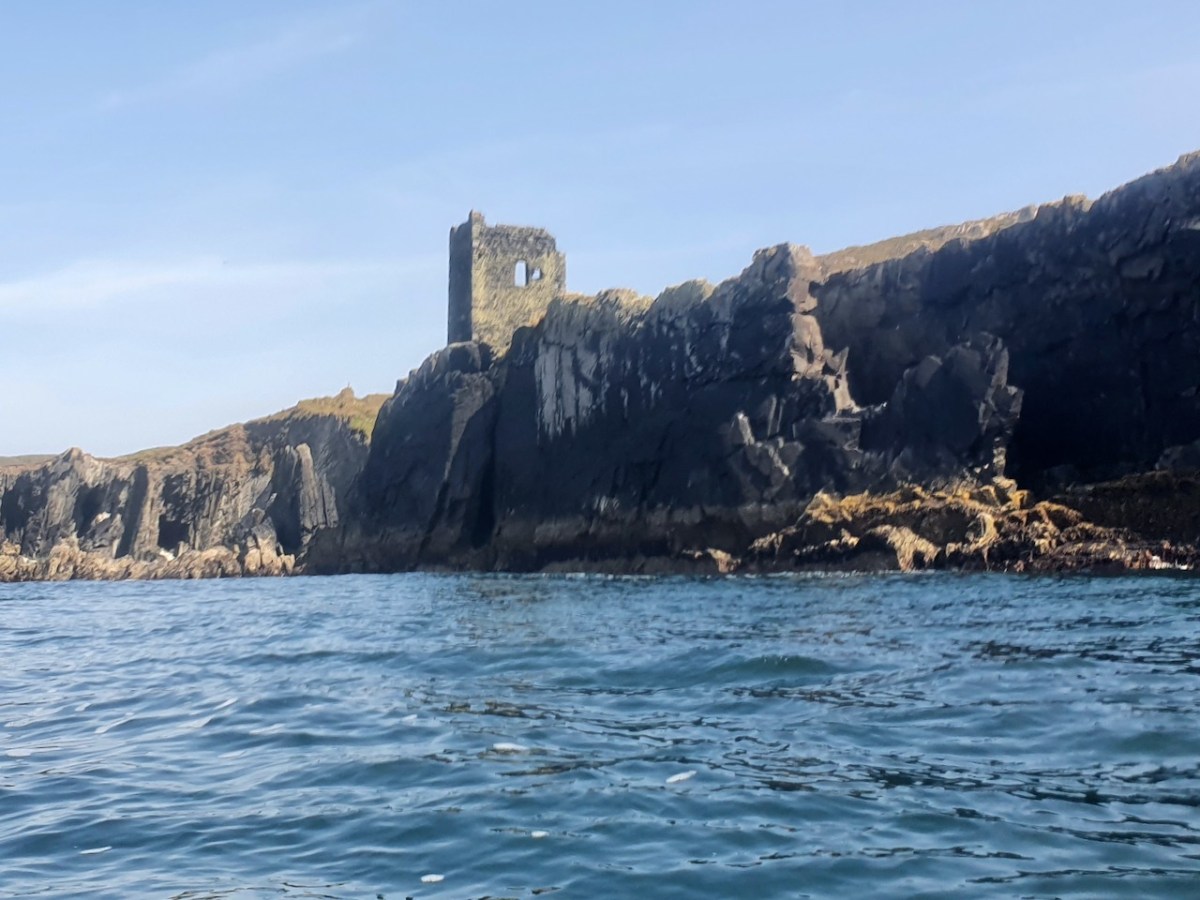
Castle Island castle and Dún an Óir Castle on Cape Clear are shown although not labelled, as is both the Castle (Dúnalong, or Castle of the Ships) and the Friary on Sherkin Island. It’s hard to imagine when you look at what remains of Dún an Óir now (below) that its name means Castle Of Gold – a testament to the wealth of the O’Driscolls who built it. Thank you so much to our reader, Tash, who sent me this wonderful photograph.

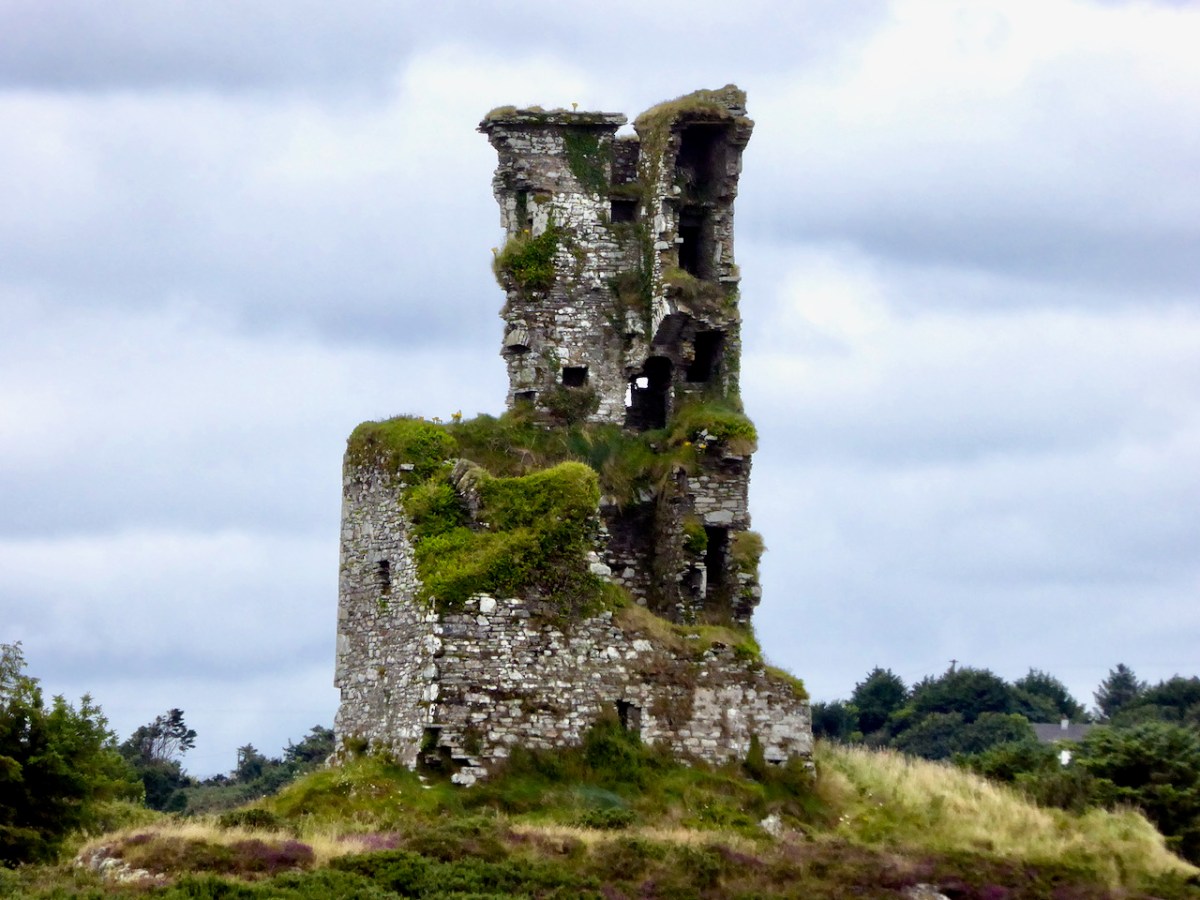
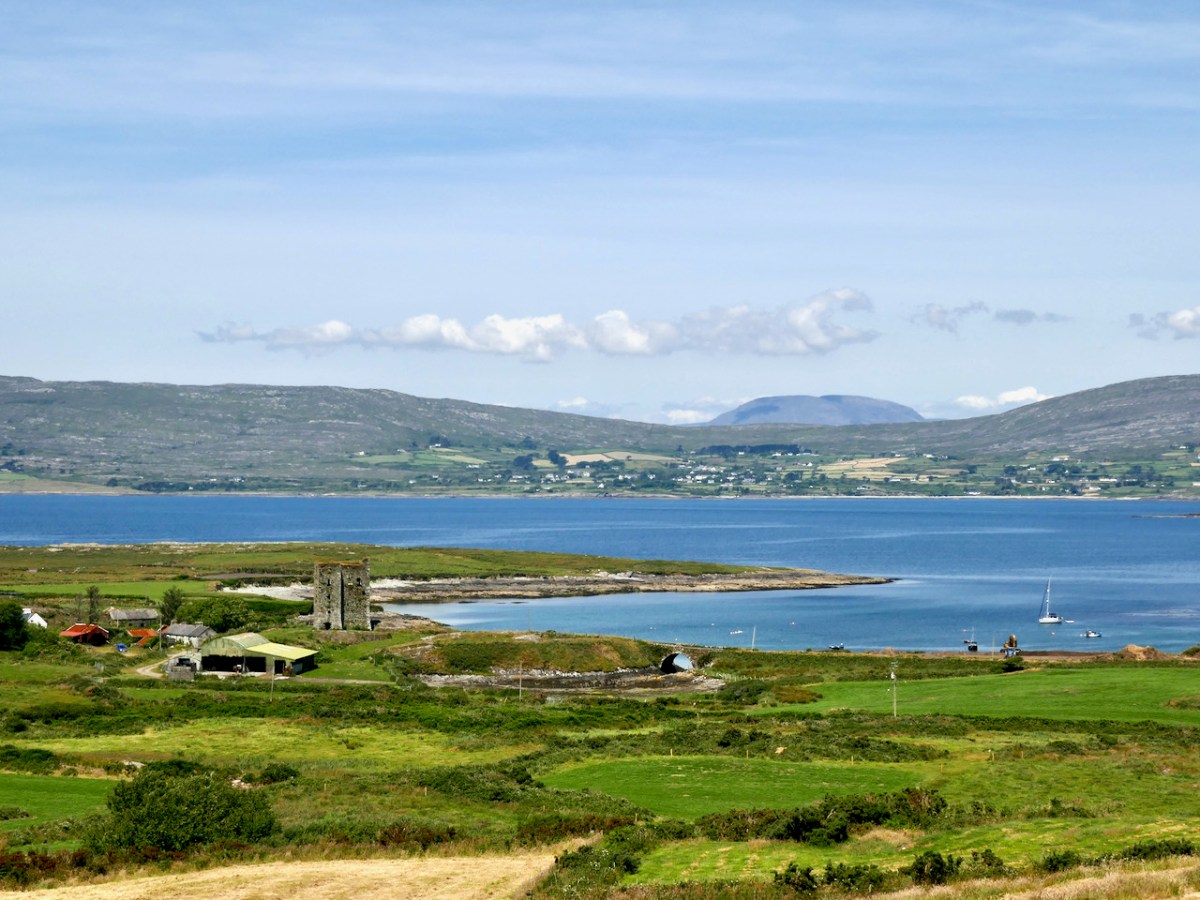
Moving West, into O’Driscoll territory (below), we see Baltimore in outline (the colorist ran out of brown ink?) – it’s called Doneshade (Dún na Séad, or Castle of the Jewels). Beside it is the brown square used to indicate tower houses and the words Sir Jmes Castlell. Following the Ilen Rover (Elyn ff) to its source we find Castle Donovan. Two more brown blobs at the entrance to the Ilen River may indicate Dún na Gall (Fort of the Foreigners) on Ringarogy Island, and Old Court Castle.
I’m going to leave it at that for now, but I hope your appetite is whetted to see more of this invaluable record of Cork 400 years ago.
For more on the Magic of Old Maps, see this page.
A Map of the County of Cork, Part 2
A Map of the County of Cork, Part 3