What do we need for Christmas? More books! Where will we put them? We’ll figure that out later. (You know who you are.) Or are you stuck for ideas on what to get other people? Or someone has asked you for a hint on what to buy for you?
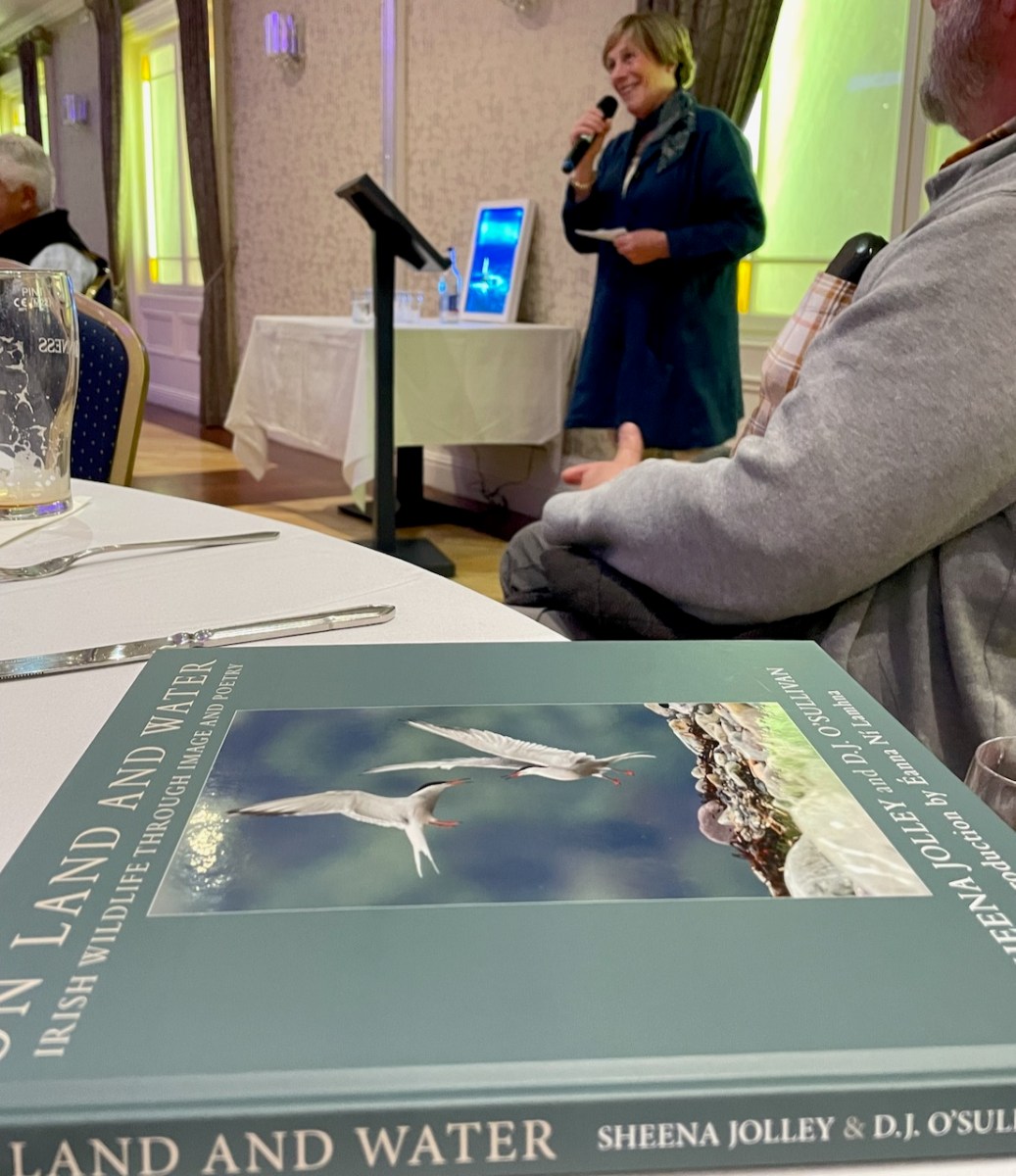

So here are my recommendations for your wish list this Christmas, and I am doing you a favour because I’m keeping it to four. I have a personal interest in all of them – but I am of course completely unbiased. The first is On Land and Water, a truly beautiful production from Menma Books (available through their website or in bookstores) that combine the poetry of lighthouse keeper DJ O’Sullivan, and the exquisite wildlife images of renowned photographer Sheena Jolley.

I cannot overstate what a lovely production this is. DJ O’Sullivan spent his life in close communion with the birds and sea-creatures of Ireland’s remotest places. He writes with the insight of one who has honed his observations skills through long hours and days.

Sheena is one of Ireland’s top wildlife photographers. At the launch in Skull we were all transfixed by her relation of what that takes – being dropped off on an uninhabited island with your equipment and food, and making the boatman promise he will remember to come back for you in a couple of days. Then getting up before dawn and being ready for that golden light when the animals stir.
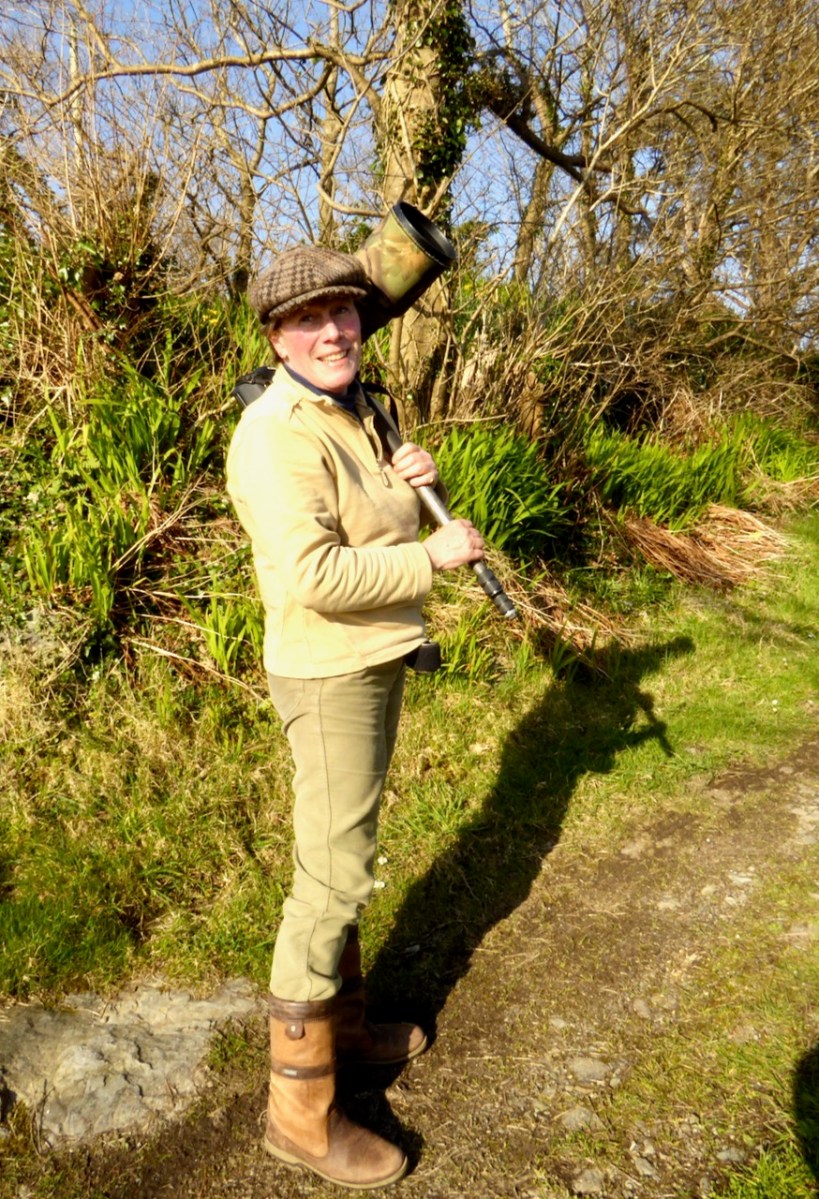

This is Sheena out to photograph some choughs
Besides the photographs, Sheena provides text that describes the creatures, their habitats and habits. This is the kind of book you will dip into over and over. And the same is true of my next choice – Cork by the artist Brian Lalor and the poet Eiléan Ní Chuilleanáin.

I have written about this book before – four years ago, in a two-part post titled Cork, Part 1: Brian Lalor and Cork, Part 2: Eiléan Ní Chuilleanáin. At that time, I was writing about a treasured gift given to me by my parents in the 70s – the amazing news is that 50 years later the book has been re-issued! It was launched (re-launched!), in a revised edition, in Waterstones in Cork at the end of October. Both Brian and Eiléan were there!

Take a look at the two posts above for a real flavour of what this book is all about. If you have ever lived in Cork, or even if you’ve visited, this is the book for you.

Wild Looking But Fine, by Ciara O’Dowd is my next recommendation. You might remember my post about Ciara and the chocolate box of letters between my mother, Lilian Robert Finlay, and other people associated with the Abbey Theatre. Eight years, and one child, later, Ciara’s book is finished and my brother and I attended the launch in Dublin. Ciara’s account of how difficult it was for women in 1930s Ireland to forge a professional and autonomous life is riveting. In her review of the book in Books Ireland, Jane Brennan asks, Why don’t we know more about their lives and achievements? Why, for example, is Ria Mooney not more widely remembered as the renaissance woman she was? Why had I never before heard of Aideen O’Connor (but am well acquainted with the name and reputation of her husband Arthur Shields)?
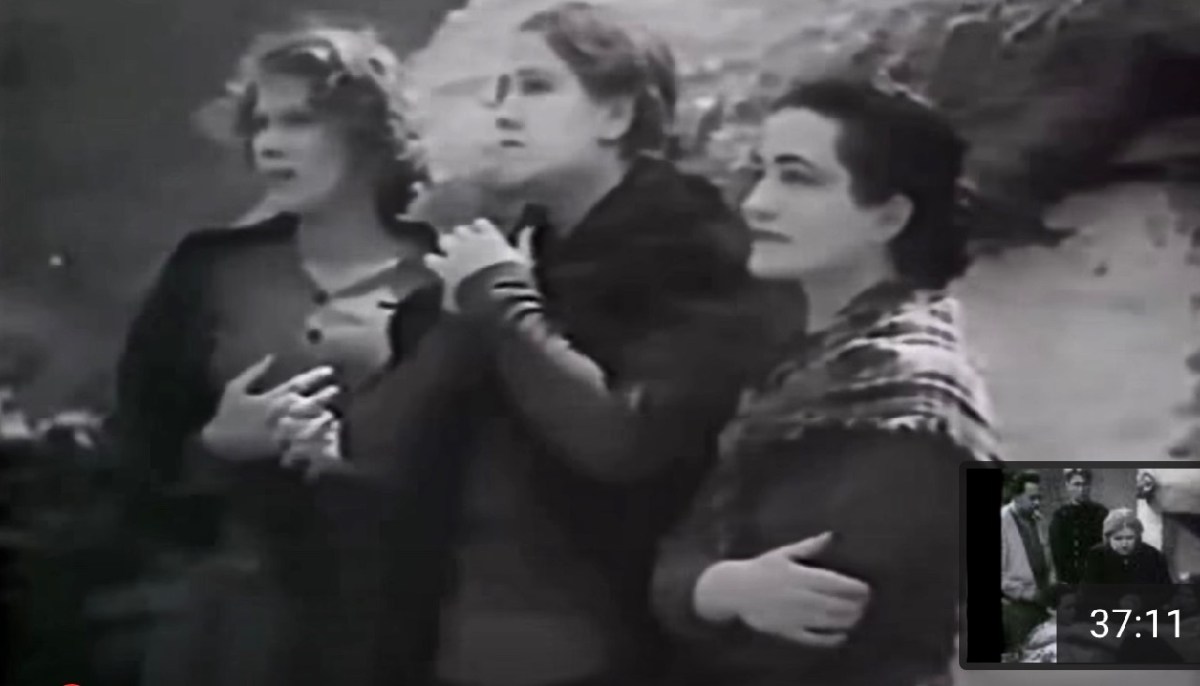

Shelagh Richards, Sarah Allgood and Ria Mooney in a 1937 film of Riders To The Sea by J M Synge
My final choice is a finalist in the An Post Book Awards. It’s 1588, The Spanish Armada and the 24 Ships Lost on Ireland’s Shores, by Michael Barry, published by Andalus Press.

The thing is, the story of the Spanish Armada was taught to us through an English lens. Prepare to have everything you thought you knew questioned and turned on its head. That’s because Michael has done his research in Spanish and Irish sources and, as is his wont, (see this post from eight years ago about his books) the book is profusely illustrated with lots of images sourced from unusual archives as well as his own fine photography.

The books are all available from their publishers or in all fine bookshops. You can think me in the New Year, once your loved ones have taken the hint and bought you one or all of the above.