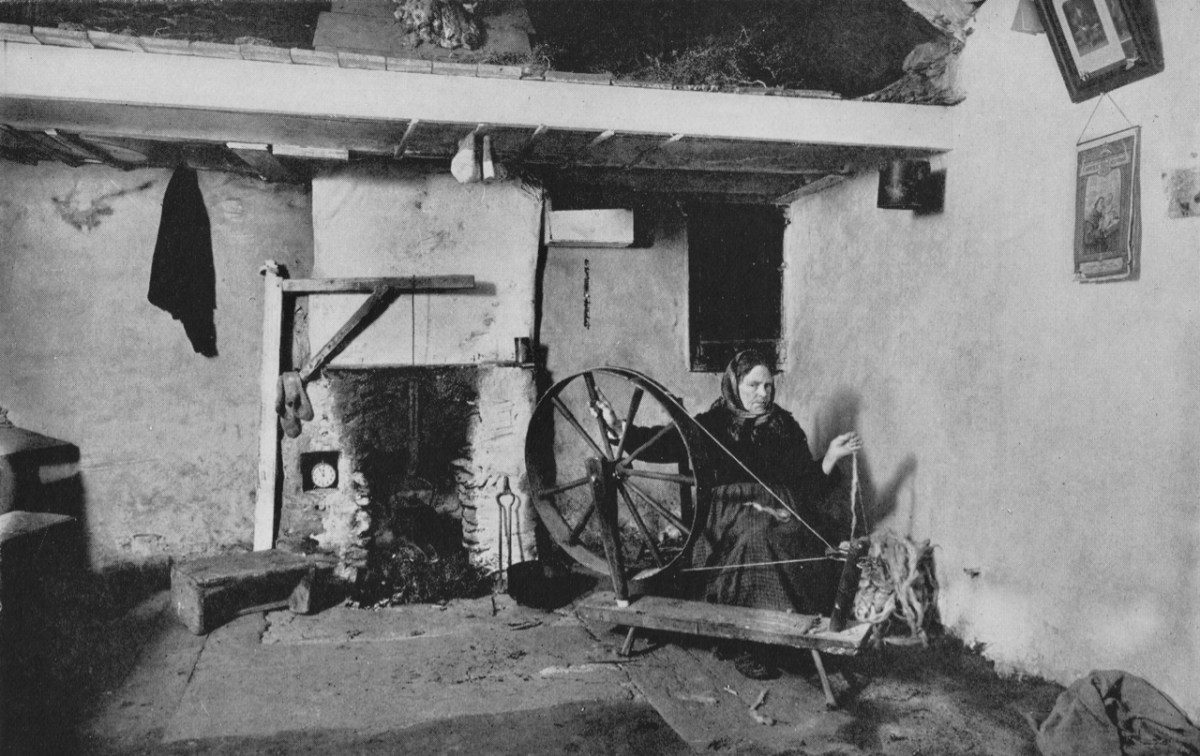
This post was originally published several years ago, but I have edited and updated it, so am giving it another airing.
Old maps are magical places to get lost in. Pouring over them, trying to identify what I know now, attempting to look at the territory with a seventeenth or eighteenth century mindset – well, several hours have gone by and I realise it’s dinner time. I’m going to share some of my favourites with you in a couple of posts. Mostly, the maps I am using are from the marvellous David Rumsey Map Collection where the maps are free to use for non-commercial use under the Creative Commons license. We are very grateful to you, David Rumsey – what a service to mankind!
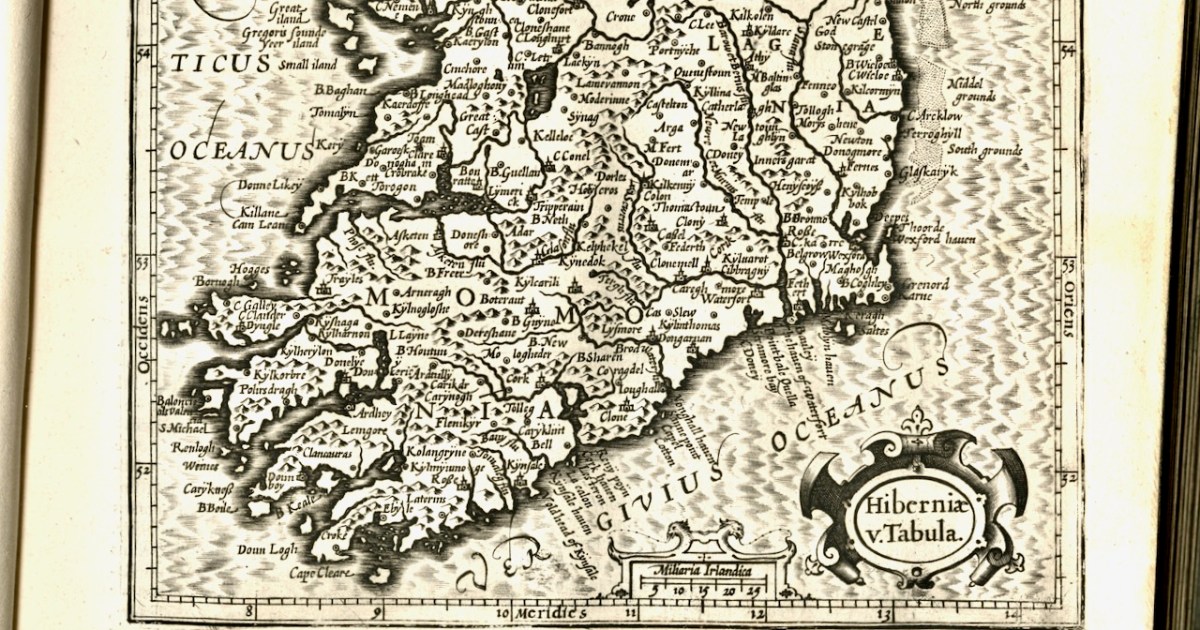
The first map here is by the famous Gerhard Mercator (1512-1594) and Iodocus Hondius (1563 to 1612) and it was published in an Atlas in 1607, after Mercator’s death. The map, therefore, predates the Atlas and was probably done in the late 1500s.

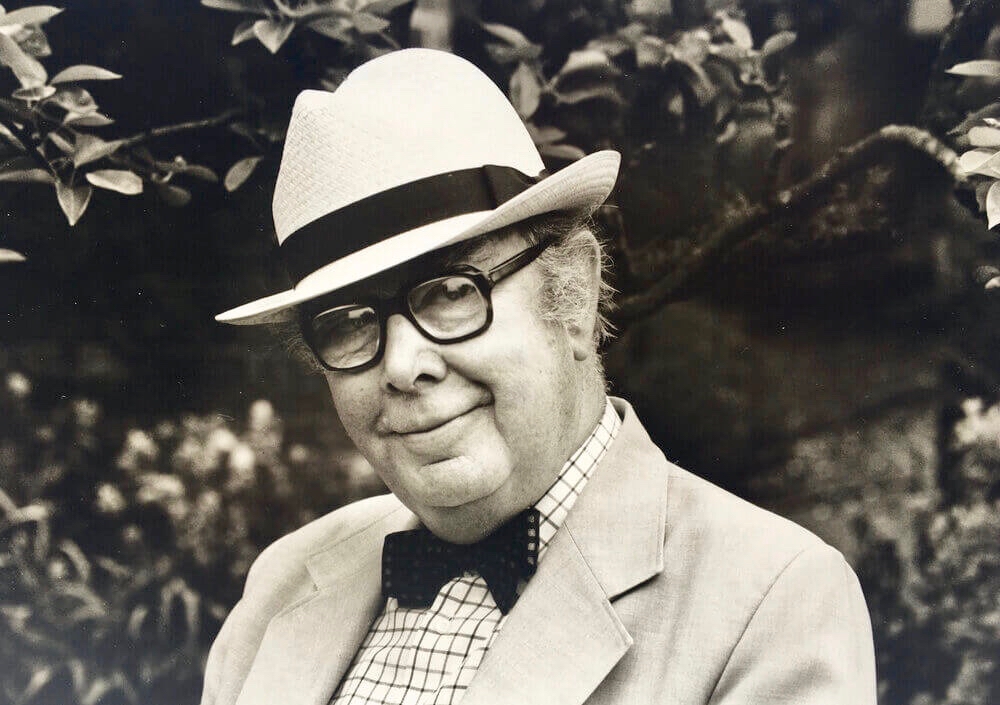
Who was Mercator? This is him, courtesy of Britannica, and his influence on mapmaking was incalculable – he really was the father of modern cartography.
In the 1500s, globe-making was a precise and difficult art. Mapmakers often etched their maps onto paper that they then painstakingly pasted onto paper mache spheres. Old maps had problems, however. Mapping a three-dimensional globe onto a two-dimensional map always involves some distortions, but early maps had serious issues for navigators. They were mostly elliptical and struggled to capture the curvature of the Earth for sailors who were plotting a course. Sailors using them were constantly twisting, curving, and recalculating to compensate for their maps’ deficiencies.
In 1569, Mercator developed a better, more accurate projection. Although the execution was difficult, the basic idea was simple: Imagine a globe with a paper cylinder wrapped around it — Mercator projected that globe onto the paper and then unwrapped it. He then expanded degrees of latitude as they approached the poles, which distorted land, but allowed the directions to be clearer.
https://www.vox.com/2015/3/5/8151303/gerardus-mercator-maps
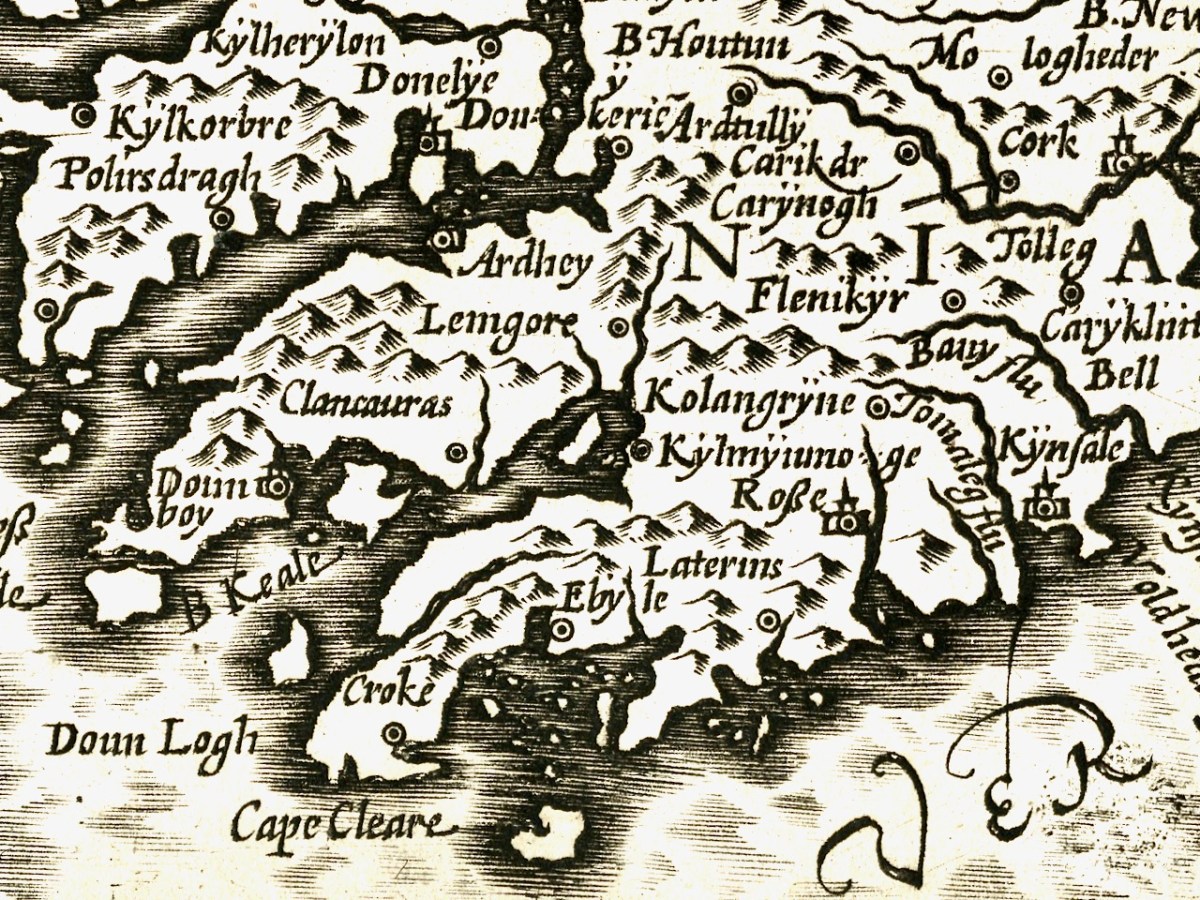
We can recognise some things in this map and not others. Croke is Crookhaven, Doun Logh is Dunlough (or Three Castle Head) and Doun boy is Dunboy Castle home of the O’Sullivan Beares. We can also see Roße – this is Rosscarbery, with the symbol of a church, and Kynsale. But after that I was stumped. However, one clever reader (thank you, Philippa Barry!), when I published this first, added Currently doing some reading on Bantry and O’Sullivan Bere, so getting familiar with placenames. In the first map Kylmyiunoge might be Kilmacomoge, Ardhey is Ardea Castle on the Kenmare River. Looks like Timeoleague is in there too.
The second map is from 1655 and it’s from Joan Blaeu’s Atlas Major. Blaeu, a Dutch cartographer, lived from 1596 to 1673 and this map is from his Atlas Maior of 1665, considered one of the greatest achievements ever in Atlas publishing. It was also the most expensive book you could buy in the 17th century – worth a year’s wages for a skilled craftsman. The first thing we notice, of course, is that this version is in colour, but you could also buy an uncoloured version for a hundred guilders less. Given printing capabilities of the time, each copy must have been hand-coloured.
There is much more detail now, and more recognisable elements. It’s a wonderful record of what the major sites were then – sites which nowadays hardly exist, or exist as ruins. Let’s take it from east to west.
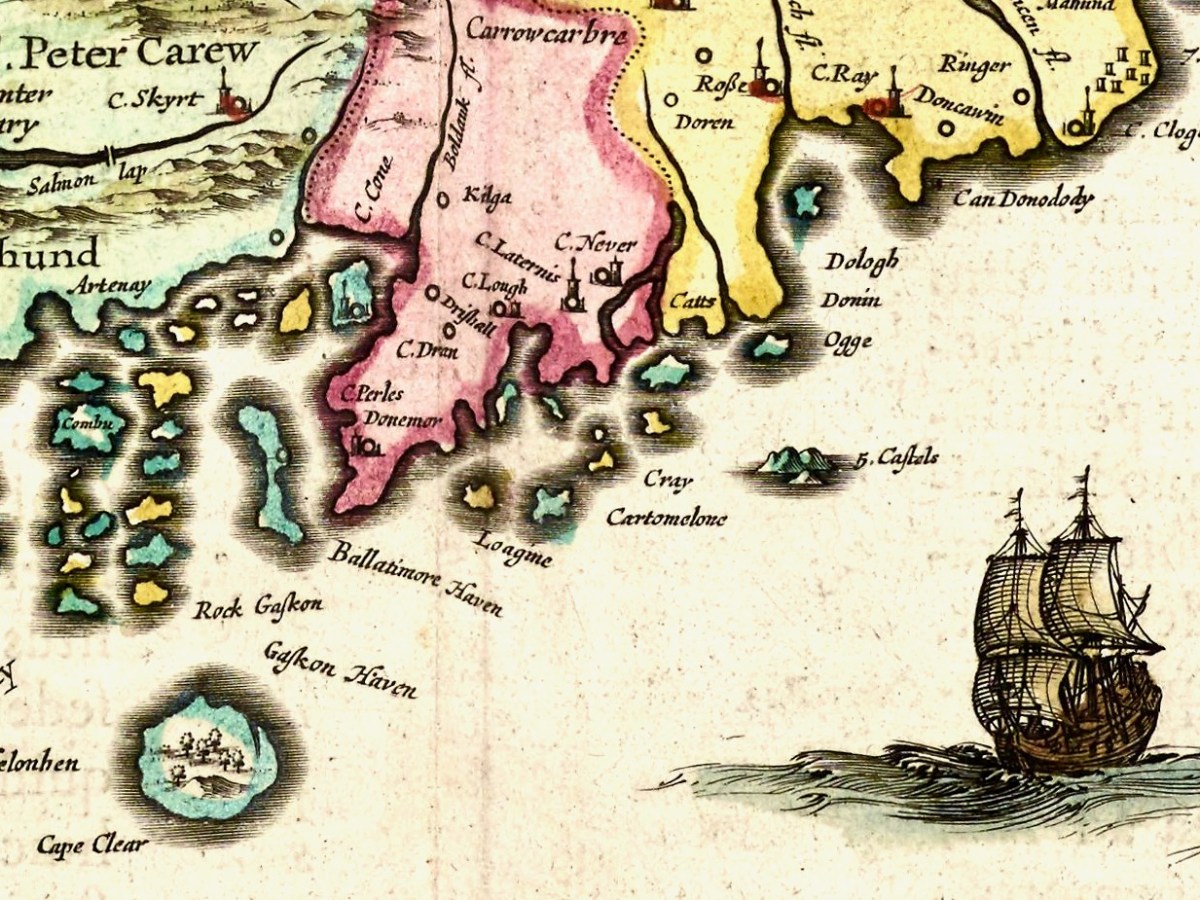
I recognise Dunowen and Dundeedy, and Ringer must mean the area now known as Ring. The letter C denoted a Castle (or Manor House) as in C Perles. or Castle of Pearls, which is Dun Na Séad (Fort of the Jewels), the O’Driscoll Castle at Baltimore. But what is C Ray? There was a tower house at Castlefreke built by Randal Oge Barry in 15th century, maybe that’s it? And, even more intriguingly, what is C Never?
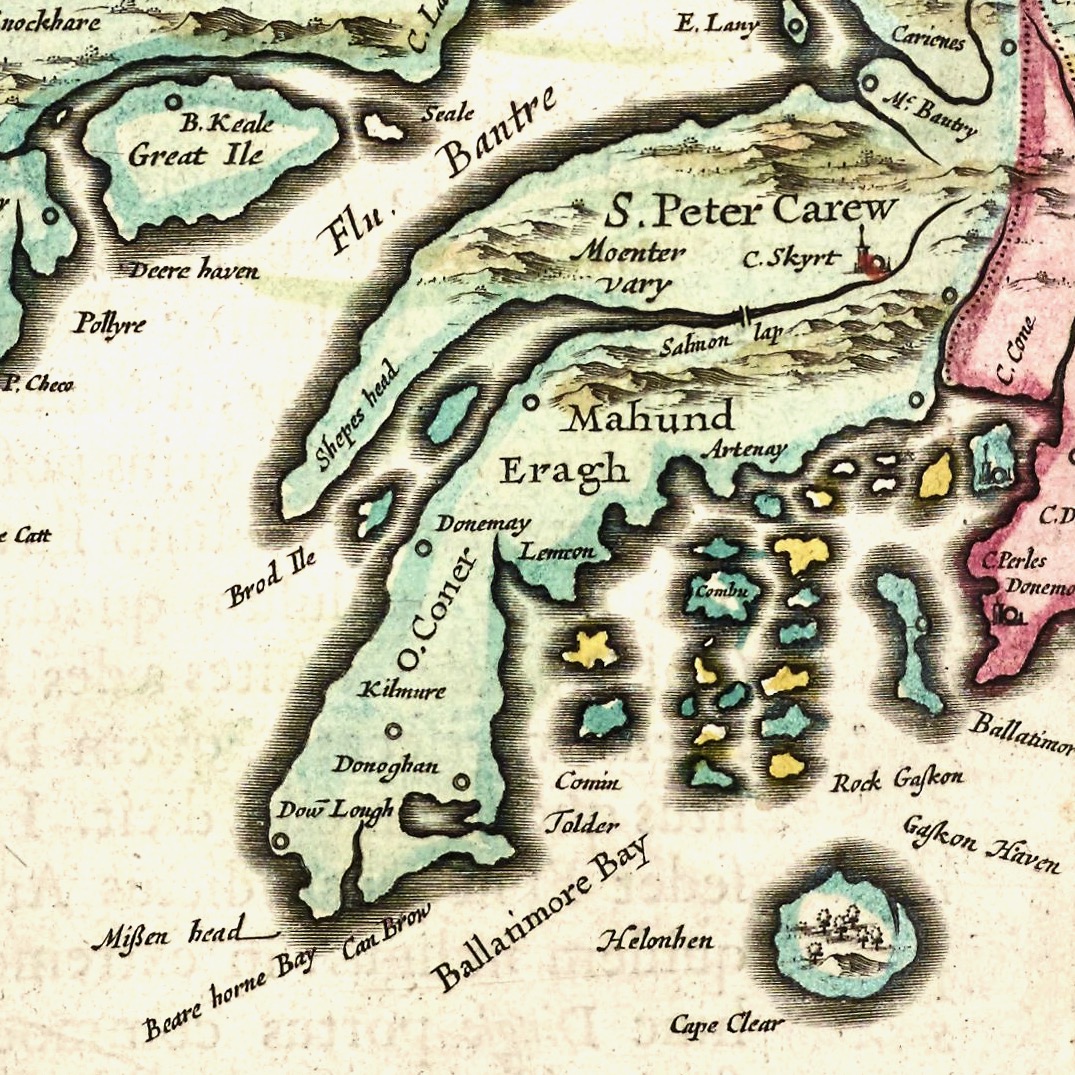
Moving on to Roaringwater Bay and its hinterland, we find Artenay, now known as Ardintenant Castle, one of the ruins of what was once a string of O’Mahony Castles. Ardintenant was the home of the Taoiseach, or clan chief, which is why it would be marked on the map. Other O’Mahony Castles are Dunmanus (Donemay), Dunlough (Dow lough) and Leamcon. Territories of the McCarthy’s, the O’Donovans, Sir Peter Carew and O’Mahonys are given, but also an O’Coner clan, about whom I have no knowledge. The Sheep’s Head is divided into Moenter vary (Muinter Bhaire) at the north end and Shepes head at the south end. Mizen Head has already acquired its name, although I suspect Eragh is a form of Ivaha, the old name for the Mizen Peninsula. Could C Skyrt be Castle Donovan – no other castle is located in this general area?
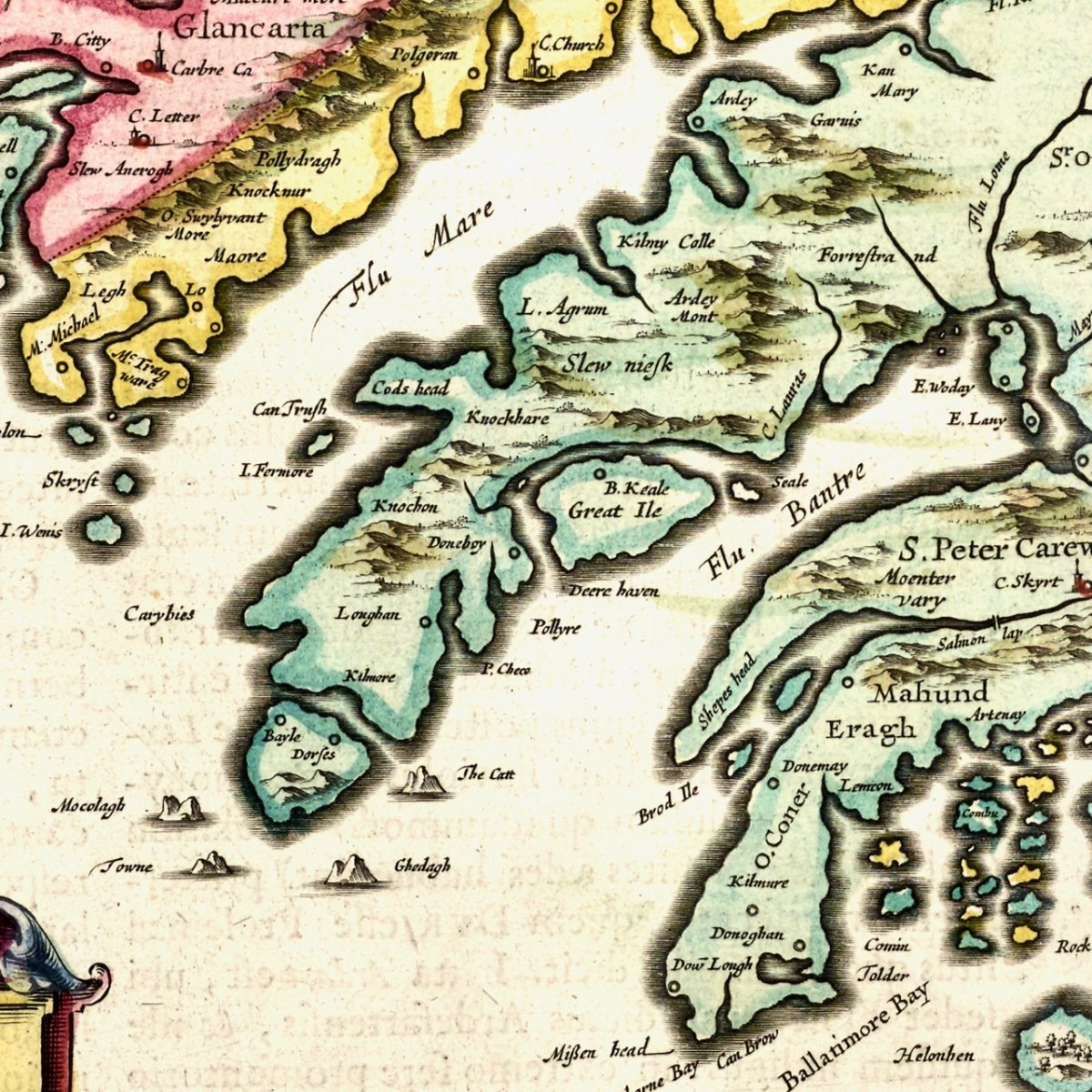
Finally, on to Beara – we immediately recognise Bear Island, or the Great Island, as it was known historically, and Dunboy Castle, as well as Dursey Island. C Lauras, may be Lauragh, although Lauragh is on the north, not the south side of Beara. I need an expert here, to find other place names that equate to modern sites. So take a browse dear readers, and let me know what you find.