
If you read nothing else right now, please read Ireland’s Changing Flora: A Summary of the Results of Plant Atlas 2020. All the quotes and charts in this post are from that report, while the photographs are my own. The report is written in English and as Gaeilge.
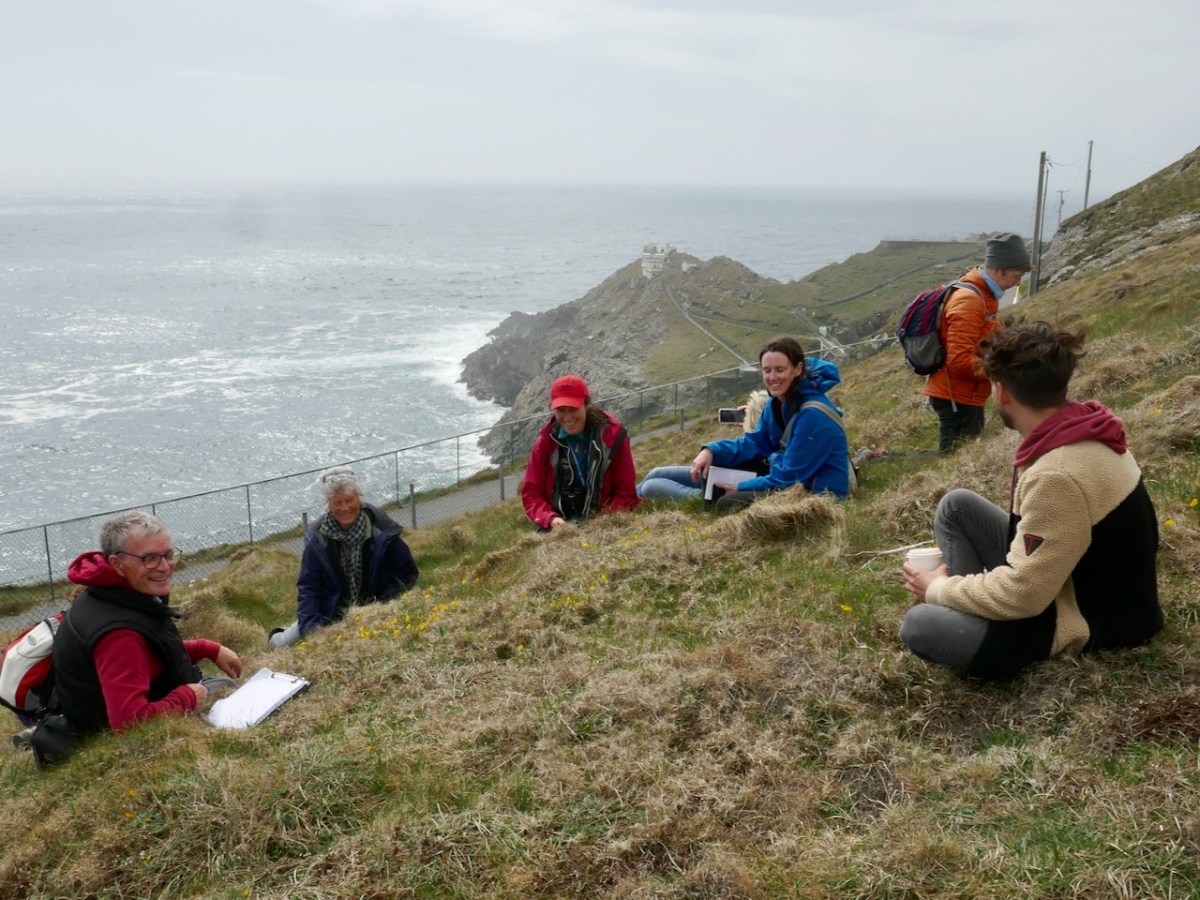
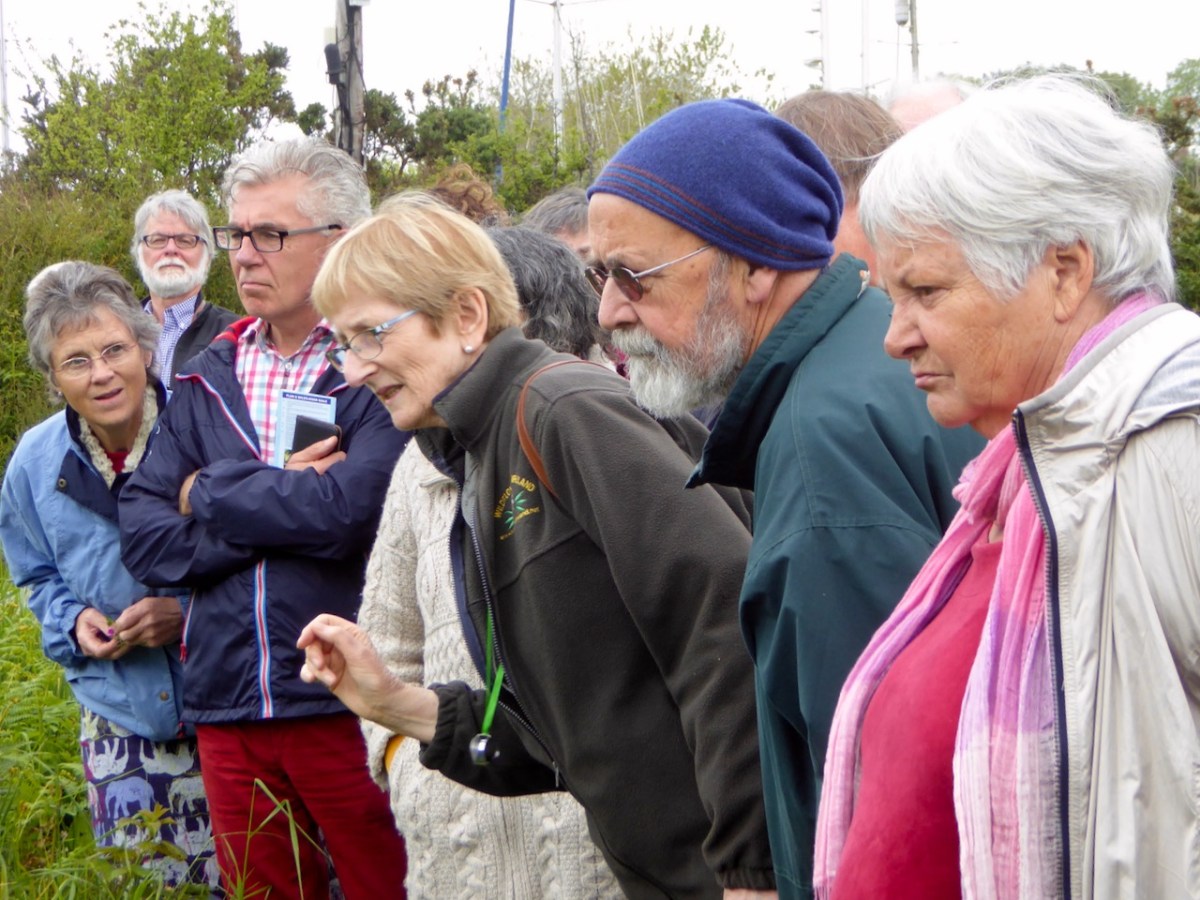
A publication of the Botanical Society of Britain and Ireland, and written in an accessible style, this vital report, a summary of a much longer book, charts what has been recorded of the changes in plant diversity in the last 20 years, based on the hard work of hundreds of recorders in the field. I’ve had the privilege to participate in a Rare Plant Monitoring Workshop (below, on Mizen Head) and every year I monitor three rare plants for the National Biodiversity Data Centre.

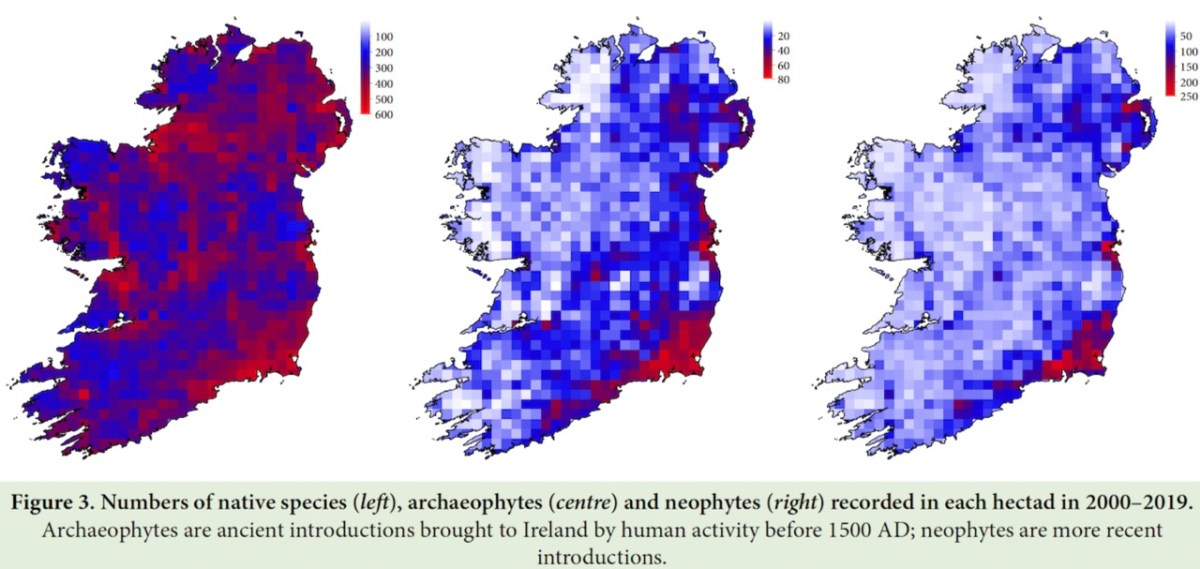
The results are, as you might expect, not happy. Here is a bar chart, for example, showing how Native Plants, Archaeophytes and Neophytes are trending.
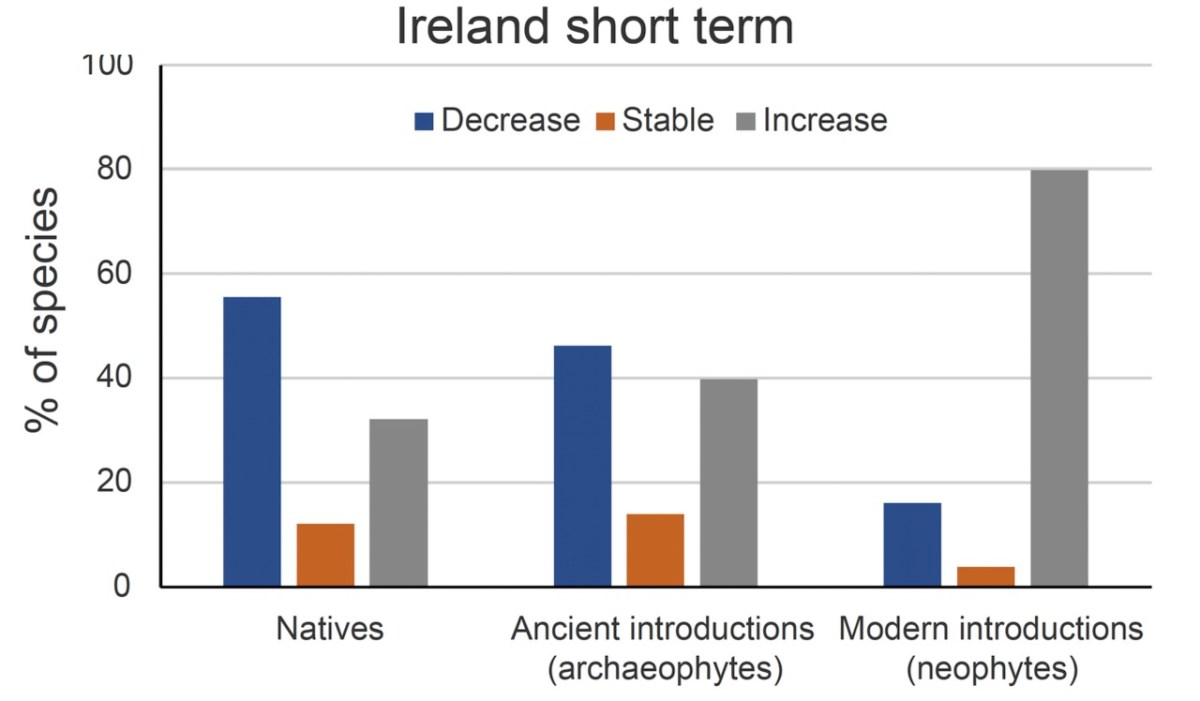
The chart shows that more than half of all natives have decreased, whereas the overwhelming majority of neophytes have increased. These figures are based on short term trends, i.e. since 1987.
Why does this matter?
The decline in awareness of plants has occurred when plants need our attention the most. Globally we know that 40% of plant species are threatened with extinction. Many insects and other forms of life depend on specific plants, so the extinction of plants leads in turn to the extinction of many other things. In the Ireland Red List, 18% of plant species are in one of the threat categories and a further 9% are on a waiting list because of insufficient data. Time is not on our side.
The report looks at examples of plants which have increased or decreased and our own experience in West Cork will readily confirm its findings. Sitka Spruce, of course is one of those that have increased enormously, but here are four other examples from my own files.
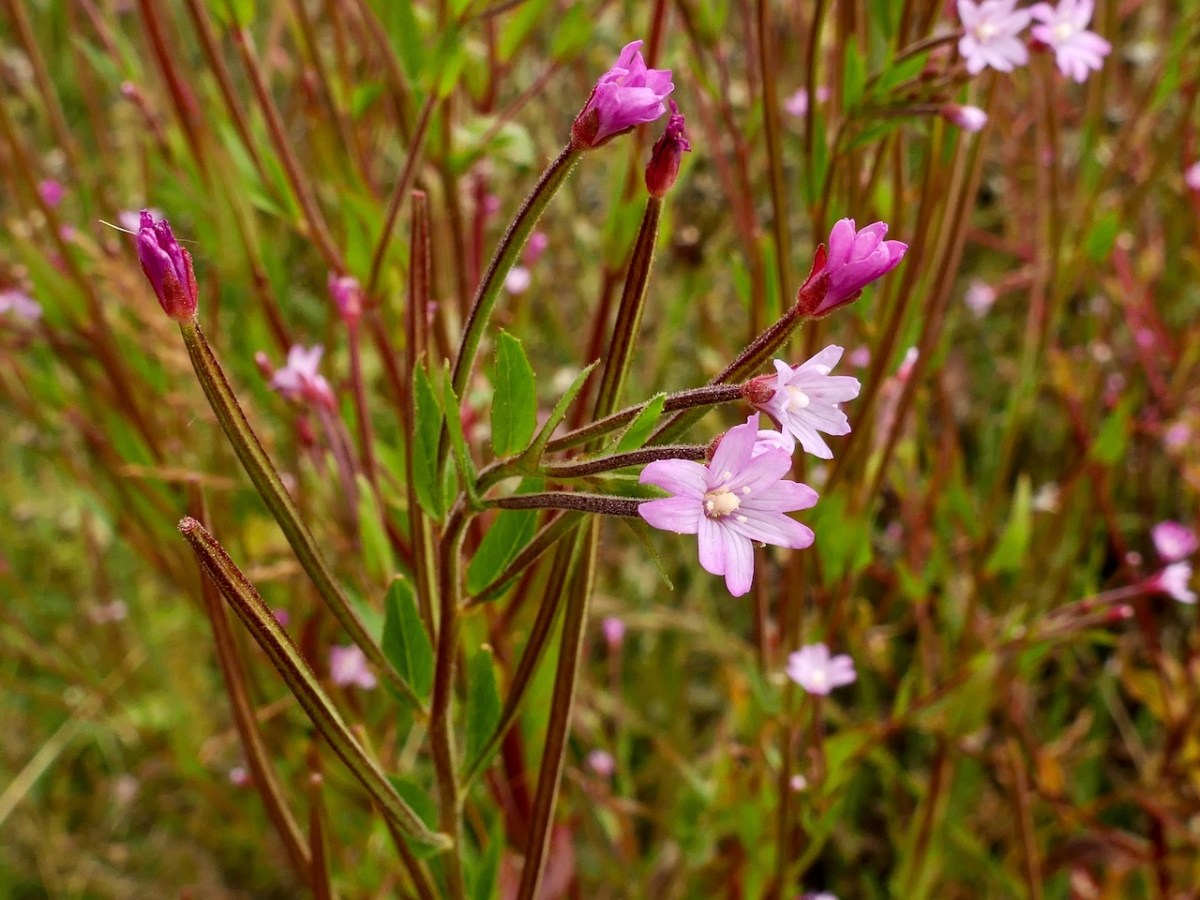

American Willowherb, first recorded in 1958 and now everywhere, including my own garden.
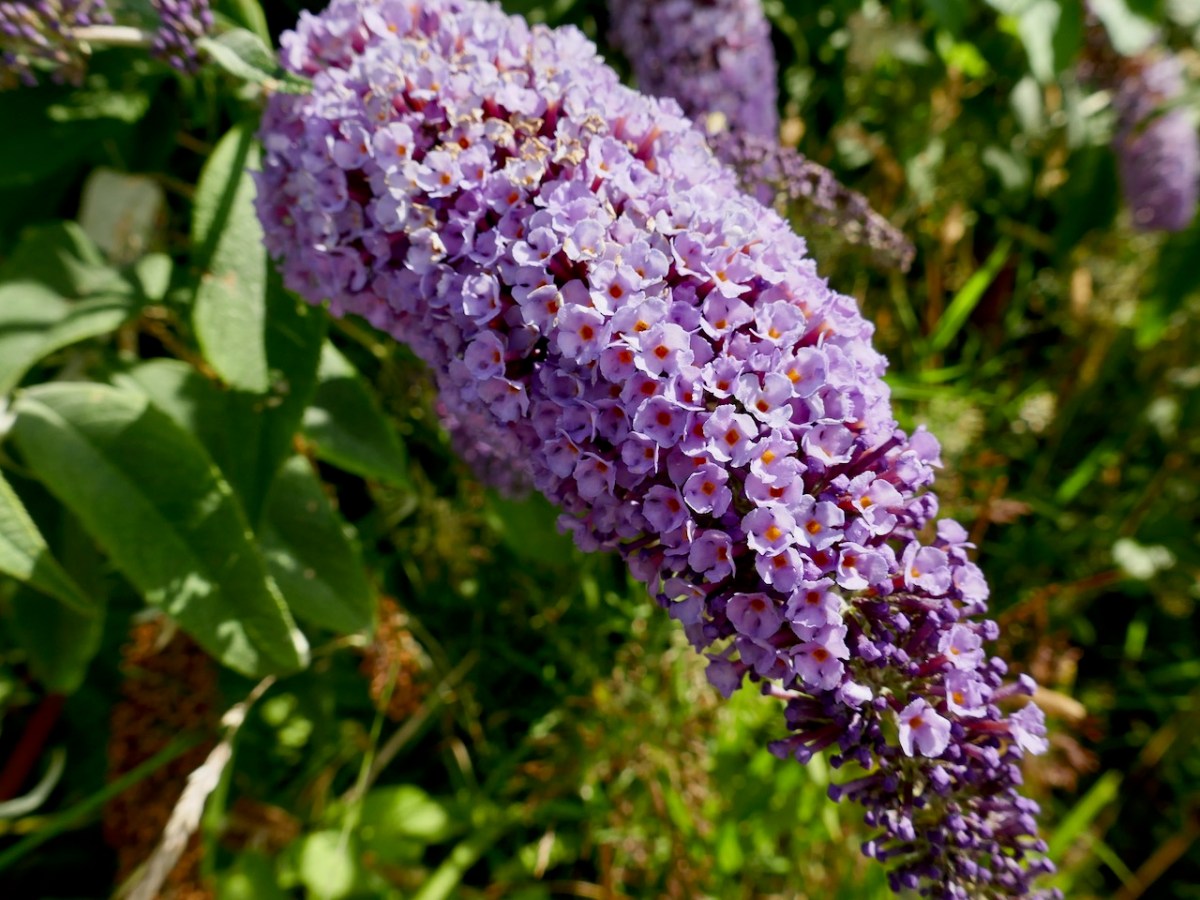

Butterfly Bush has spread rapidly since the 1960s. Butterfly Bush may seem benign but like many other introduced species there is a dark side. First of all, as Tony O’Mahony points out in his Wildflowers of Cork City and County, it’s quite invasive and can take over and crowd out native species. The roots can do significant structural damage to the very walls it depends on for survival. More serious is the charge that, while it provides nectar for butterflies it is not a butterfly host plant – that is, one that butterflies can use to deposit their larva, which will then feed on the leaves. According to a spokesperson concerned about the destruction of chalk grasslands at Folkestone Warren in Kent: If left uncontrolled, then buddleia and other shrubs would have engulfed the chalk grassland. Clouds of butterflies used to be seen there, but now only common species can be spotted and even these are in decline, with the rarest ones disappearing altogether. Buddleia was eliminating butterfly habitat by killing off everything else, and while the shrub provided food for adults and larger insects, other plants were needed for butterflies in their larval stages.

Himalayan Balsam, a beautiful but highly invasive species that can colonise waterways, choking out our native flowers.
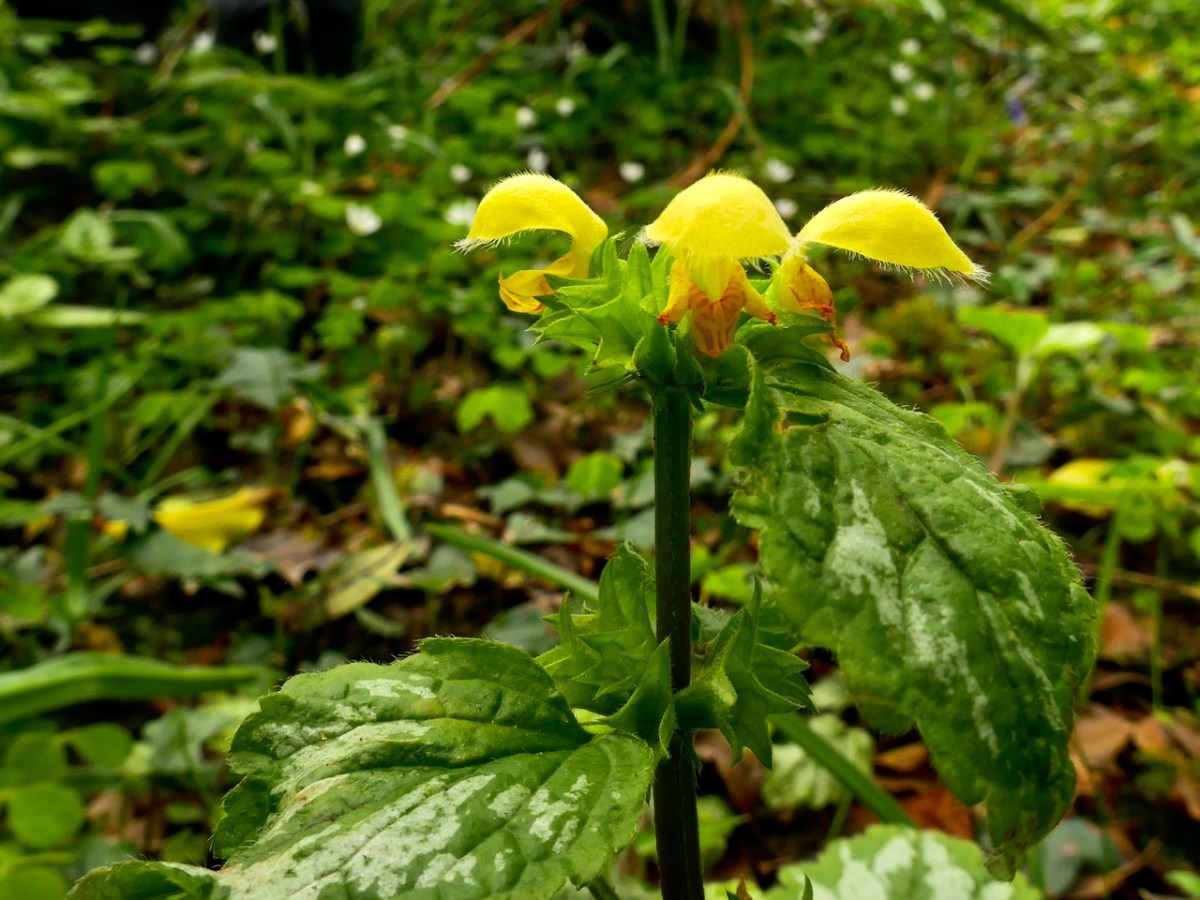

Variegated Yellow Archangel – only here since the 70s, it can carpet woods in the spring, crowding out our native woodland species.
Examples are also given of plants that have decreased, and indeed most of these I have never seen, such as Agrimony, Corn Mint, Field Gentian, Heath Cudweed and Mugwort. Two that I have been fortunate to observe and photograph before they get even rarer are Corn Marigold and Marsh Lousewort.

Corn Marigold – just as it is supposed to grow, on the edges of arable fields. It is hanging on in West Cork here and there and it’s always a treat to see it.
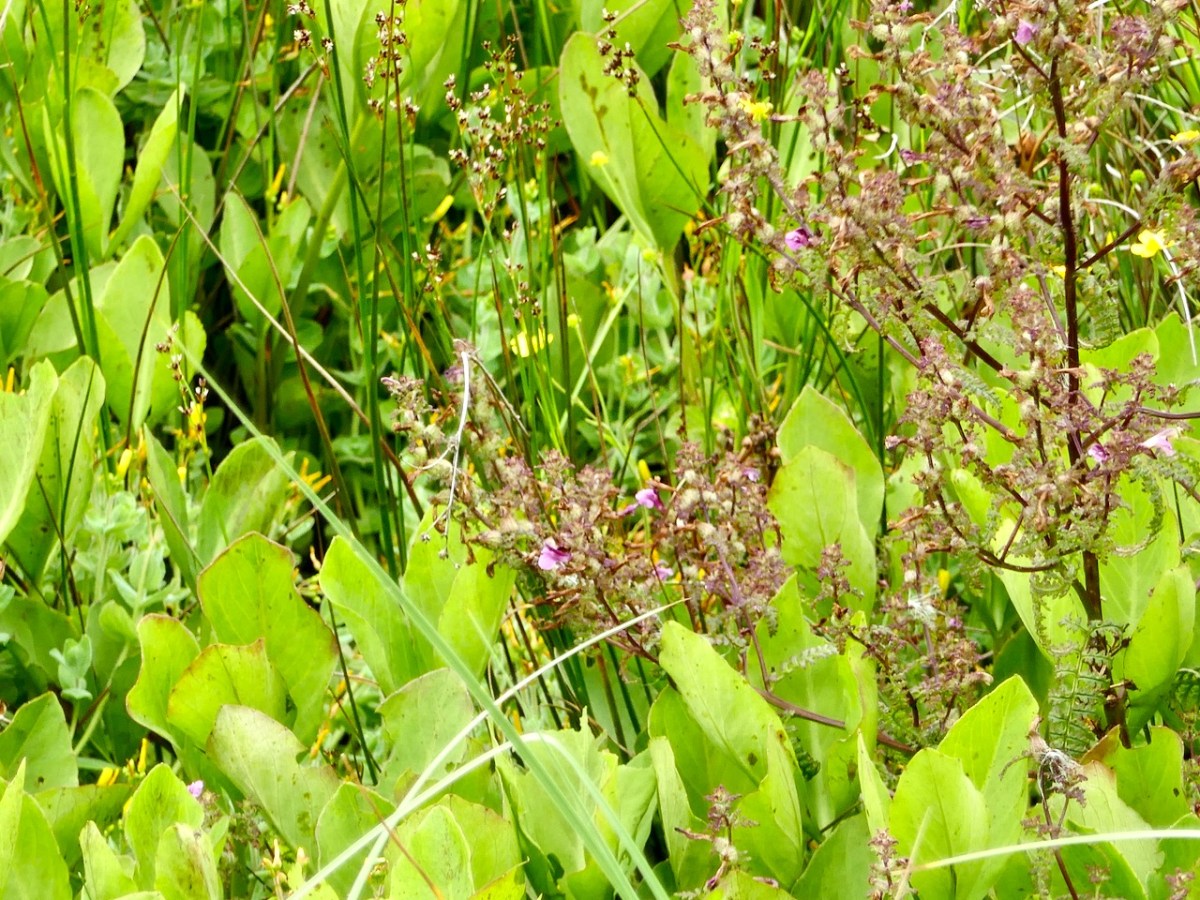

Marsh Lousewort – I have only found this once, in the Derreennatra Bog I wrote about in my post “The Wildest and Richest Gardens” – West Cork Bog Soaks
A section of the report looks at Habitat Loss and another at Climate Change and its effects on our wild flora. Reading about the loss of species-rich native Grasslands is particularly sobering.
It may seem ironic that grassland should be threatened in Ireland, but it is the loss of certain types of grassland – those on less fertile soils and rich in wild species – that is the issue. These ‘semi-natural’ grasslands supported a large number of our characteristic native species, including many orchids. They were maintained by extensive grazing, or by the cutting of hay in mid to late summer. Converting these habitats rich in species into more intensively managed grassland, or in some cases abandonment to scrub, has led to the loss of many species that could not compete in the altered environment. The underlying reason for the decline of many grassland plants lies in their response to nutrient concentrations, such as soil nitrogen levels and nitrogen deposition from the atmosphere. For the most part, native grassland species require low levels of fertility; they cannot compete successfully at higher levels. It may at first seem counterintuitive that high fertility levels could be inimical to plant diversity, but there is now a very large body of evidence pointing in this direction. We can conclude that grassland plants generally are in trouble, with the exception of those few species that thrive in highly fertile conditions.

Even in West Cork, our fields are becoming larger and hedgerows are disappearing. Wetlands, woodlands and ‘Arable land and other disturbed habitats’ are also dealt with. The report notes that while the volume of ‘weeds’ in agricultural lands has reduced, what is mostly missing are the native plants, while the variety has increased with the advent of new species. The Common Poppy, for example, might be making a comeback since it is often included in wildflower mixes. I saw the ones below in a field in Wicklow.

The report concludes with some highly charged questions.
A botanical visitor to the present day from the 1950s would see vast changes in Ireland. Changes in the landscape would stand out, with large swathes of dark conifer forest in the uplands having replaced areas of blanket bog and hill pastures. There would be larger, more uniformly deep-green fields in the lowlands, less length of hedge, more fence, and many fewer areas of marsh and bogland. Roads would be larger and straighter with verges that were mown by machine once or twice a year rather than grazed or cut spasmodically by hand. There would be fewer small potato patches, and arable crops would be less widespread and more concentrated in favourable areas.
Looking more closely, they would see that the mature conifer plantations consisted mainly of one species, Sitka Spruce, in huge numbers of even-aged stands, and had very few plants growing within them. The green fields of the lowlands would have a few plants of familiar common species like Dandelions, Docks and Chickweed along with the ubiquitous Ryegrass, but the diverse flower-rich meadows would have disappeared. Road verges would be dominated by rank growth of grasses. Pockets of wetland would be far fewer except in the West. All these changes and many more have been documented, implicitly or explicitly, by the findings of Plant Atlas 2020 and comparisons with those of its predecessors.
Our visitor might raise a flurry of questions. Have scientists been looking the other way? Why were the best habitats not protected? Who should have prevented the pollution of water bodies by nutrients? How did the idea of planting vast uniform stands of one alien conifer on deep peat take root Whose job should it have been to develop a long-term vision for Irish land-use? Were the consequences of moving towards energy-intensive farming systems foreseeable?
These are questions closer to the realm of politics than of science. Plant Atlas 2020 itself cannot answer them, but the information within it provides an enormous wealth of data about the distributions of Irish plants and how they have changed.
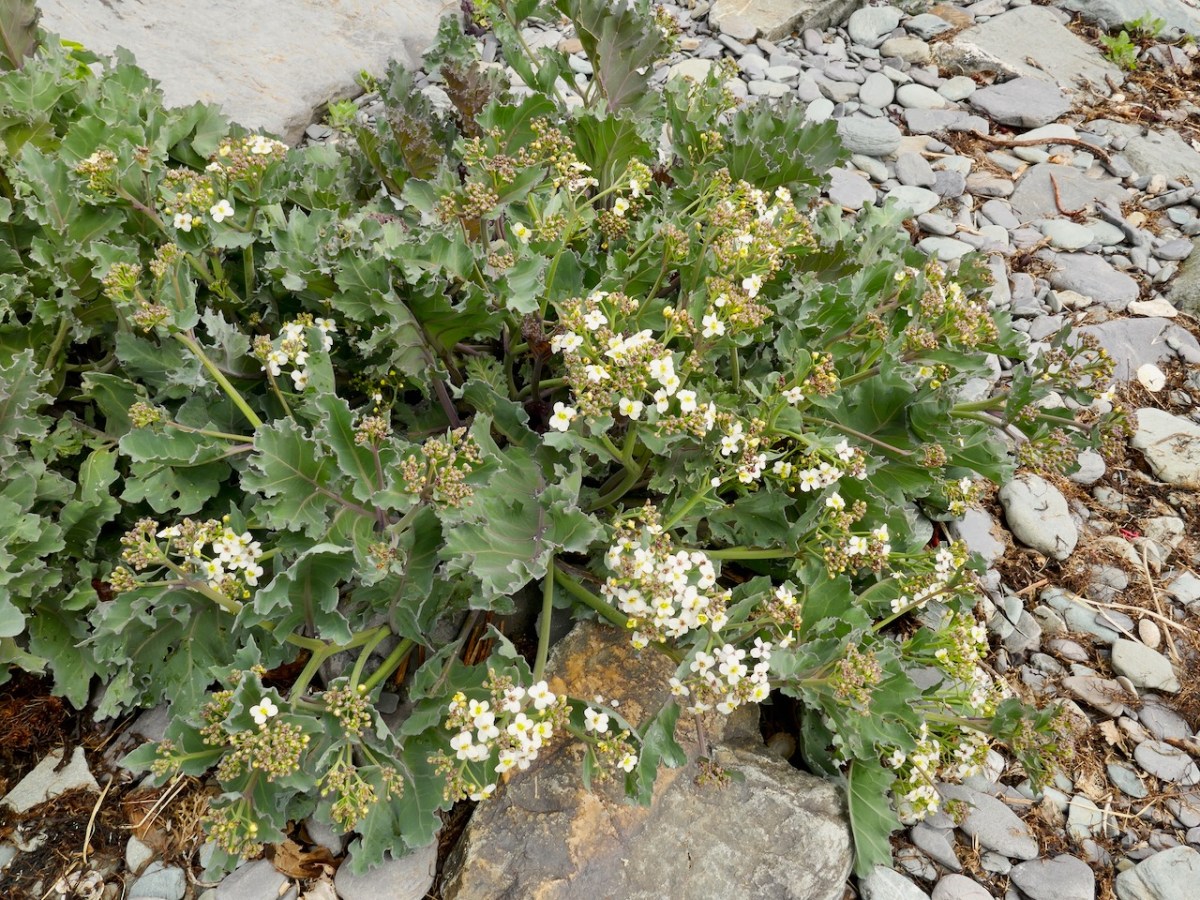

Sea Kale, above, is a rare plant that seems to be more abundant now that it was 20 years ago. As the report points out, there are a few examples like this that may relate to how records are collected rather than the absolute abundance/rarity of the plant, and the report tries to provide a model that corrects for this.
Finally, there are a set of recommendations based on protecting and restoring habitats, and the last is this one:
Repair the cultural standing of plants. As generations of people become more distant from their origins on the land, they tend to overlook the vital roles of plants. Their place in formal education has dwindled, and most people can name very few of them. By omission, plants are misunderstood, downplayed, ignored, and dismissed, even though we still need them as much as ever. Plants require more of our attention and it is in our interest to give it to them.

So what can we- you and I – do about this? Here are my own actions – they are simple and doable by anyone.
First, I have educated myself about wildflowers. Buy a copy of Zoe Devlin’s Wildflowers of Ireland and take it with you as you walk (that’s Zoe, above, with a group of us hanging on her every word). Or take your phone and use her website or one of the new plant ID APPs. People swear by their own, but I have to say I have found the Picture This app to be reliable and easy to use.
Second, I have tried to spread the good word. I do this using this blog – see the Flora and Fauna of West Cork Page for many many posts on our wildflowers – including lots of slideshows for pure enjoyment. The one above, Wandering the Boreens, is one of my favourites and shows what can be seen along a typical West Cork road in summer. I have also developed a Wildflowers Brochure for use along the the Fastnet Trails, and occasionally lead wildflower walks (below) and give talks. Perhaps most importantly, I am now using my Instagram page for short (I aim for 30 seconds or less) videos on individual wildflowers. I’ll be starting that up again soon for 2023.

Third, I have set aside part of my own One Acre as a wildflower meadow. How I have done this is all laid out in my Rewilding My One Acre Posts and it has taken very little work on my part. If you have a garden or any bit of land around your residence, do consider whether you can do this too. The Pollinators will be very grateful.

Finally, I try to mow as little as possible and I have changed my mindset about ‘weeds’ and such concepts as ‘curb appeal’ and ‘tidiness.’ True gardeners would be horrified, but the insects don’t seem to mind. A tiny rare plant, Sharp-leaved Fluellen (below), showed up on my driveway, who knows how – but if the ‘weeds’ had been eliminated, I would never have found it.

PLEASE read the report, and see what you can do to protect our precious biodiversity.

Discover more from Roaringwater Journal
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.
Finola… many thanks for that post. I was unable to attend the launch on Friday but the summary is most useful, if not immensely depressing. The recent Red Data List (2016) was bad enough but I know the situation deteriorates every day. There are so many ways that I feel things could stand some chance of improving, beginning with primary school children, but parents have to come on board too. Local authorities, policy makers… influencers…all need to step up before more is lost. There’s a handful of really committed and dedicated folk working in the field but I wonder what support they are getting…oh its getting late and I am now ranting! Again many thanks.
LikeLike
Yes, very depressing. The only thing that keeps me hopeful is seeing the successes of the All Ireland Pollinator Initiatives. And as for ranting – we could all do with ranting more! But I do have hope that the Greens, and our local TD, Holly Cairns, will make a difference. And it does seem that the National Biodiversity Data Centre is on a more solid funding footing now.
LikeLike
These volumes collect a tremendous amount of work, twenty years of work, and are valuable for that alone. The conclusions of those involved carry the authority of that research and that make this a publication of great significance. I haven’ a copy to had yet and, despite realising how signigicant a work it is, had been reluctant to order one. You might wonder why and it is for he rather peculiar reason that I have another recent publication from the same group to hand and was terribly disappointed by the quality of the physical production, especially the binding which is destined to break and tear before too long. I suppose I imagined it would be a book I would handle and read regularly and not simply stand on a shelf and feel it would not take that wear.
LikeLike
I know what you mean – publications like this need to be sturdy at least.
LikeLiked by 1 person
Very depressing reading but we can be led by you and make sure we are doing our own small things to help wherever we can. I always think about your post on the flood defences in Skibbereen, a good example of a thriving ecology annihilated.
LikeLike
Yes a good and very depressing example. And I was hopeful at the time.
LikeLike