In the previous posts we looked at Catholicism in Ireland in the first half of the 19th century, and the position of the Protestant churches, especially the Church of Ireland. This period was marked by a shift to a more militant and evangelical philosophy in that Church: a determination, in fact, to make one final push to convince Catholics that their earthly and heavenly salvation lay in abandoning the pernicious faith of their forefathers and converting to the biblical-based beliefs of Protestantism. Once Protestant, they would reform their wicked habits of drinking and fighting (as in Skelligs Night in the South Mall above, by James Beale, courtesy of the Crawford Gallery) and would naturally see the errors of nationalistic agitation.
Faction Fighting, one of the evils that both Catholic and Protestants clergy railed against. The illustration, by W H Brooke, is from Traits and Stories of the Irish Peasantry by William Carleton
Irene Whelan, in her essay The Stigma of Souperism in The Great Irish Famine (The RTE Thomas Davis Lecture Series, edited by Cathal Póirtéir) writes about
the vast institutional and ideological machinery that lay behind the drive to make Ireland a Protestant country. This included not only a massive system of private philanthropy. . . but, more importantly, a fully developed political doctrine rooted in the belief that the source of Ireland’s social and political problems was the Catholic religion, and that the country would never be prosperous and developed until Catholicism and all its influences were eradicated.
From John Barrow’s A Tour Round Ireland, 1835
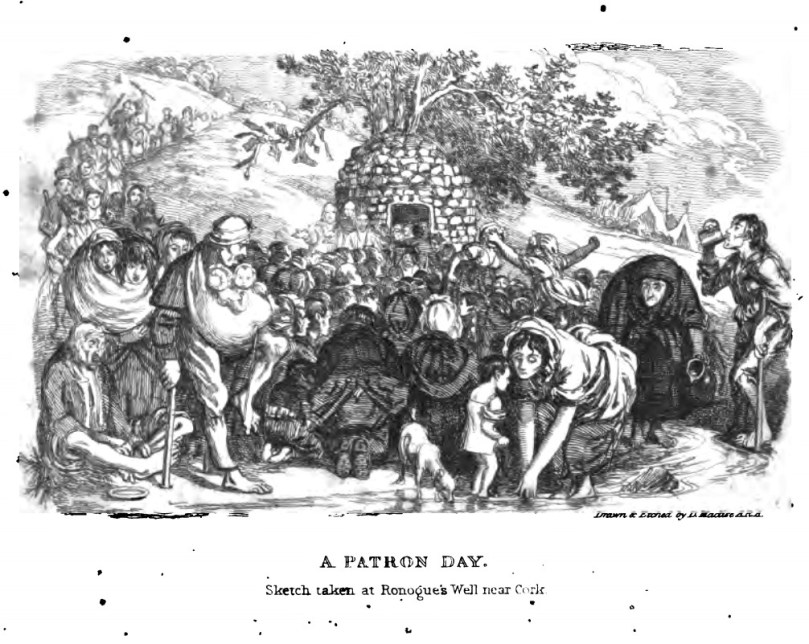
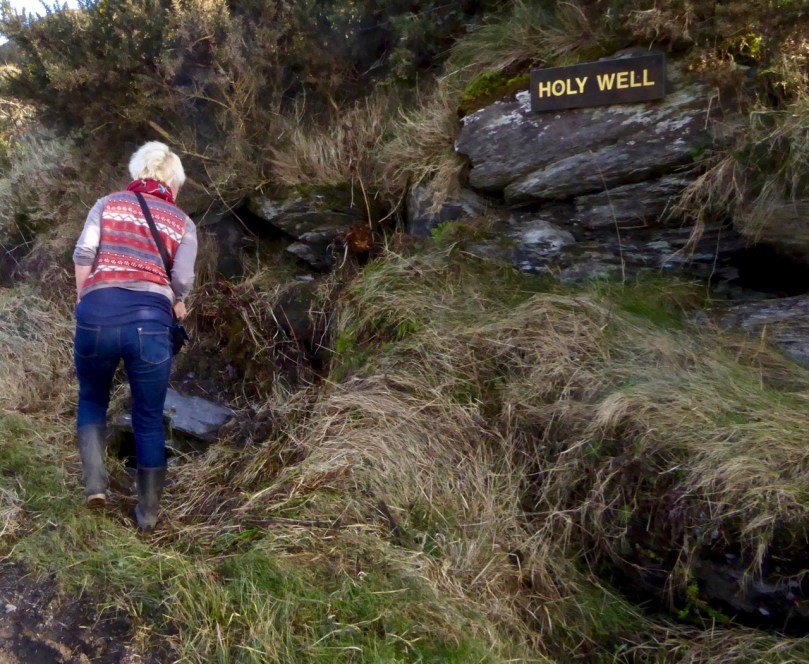
It is ironic that, in fact, major reform efforts were underway within the Catholic Church at the same time, to depress the more exuberant of the old traditions of patterns at holy wells and seasonal celebrations, or to convert them into Marian feast days (Lughnasa, for example, was conflated with the Assumption of the Virgin Mary on August 15). For an excellent description of the goings-on at Patterns, see this post from Holy Wells of Cork. The great scholar John O’Donovan wrote in 1837 the priests, I am sorry to see and say, [are] inclining very much to Protestant notions, and putting an end to all. . . venerable old customs. William Wilde (father of Oscar and a noted antiquarian and folklorist) bemoaned, The tone of society is becoming more and more “Protestant” every year. . . The priests. . . have condemned all the holy wells and resorts of pilgrimage. (Both quotes from K Theodore Hoppen’s Ireland Since 1800: Conflict and Conformity.)
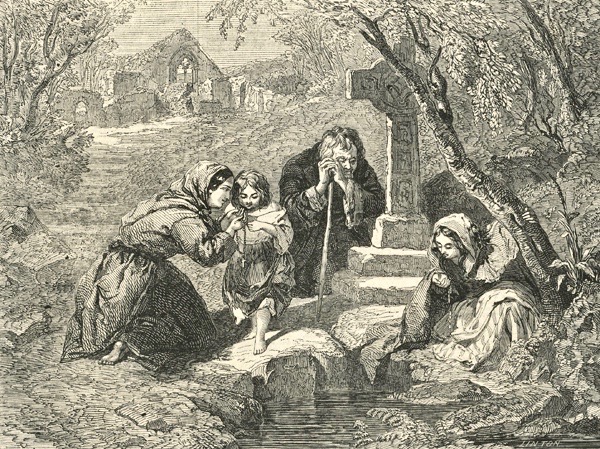
The Holy Well, an engraving of a painting by Frederick Goodall
The recognised authority on the evangelical surge of this period is Desmond Bowen. In his book The Protestant Crusade in Ireland, 1800-70, (published in 1978 but not yet superseded in its detailed examination of the religious environment of this period) he lays out the main factors in the hardening of the sectarian divide and the deepening divisions between what were essentially two separate cultures, looking to the separate education systems and the activities of firebrand preachers supported by both British organisations and committed local landlords. Of British evangelicals he writes:
Although their first desire was the purely religious one of freeing Catholics from the bondage of their sin by bringing them the blessings of biblical Christianity, they soon found it advantageous to combine their religious crusading with English ‘cultural imperialism.’ How could the Irish peasantry read the bible unless they attended schools? And how could they attend Evangelical schools and not be culturally influence by the alien but superior way of life they found there? . . .Proselytising . . . sought to bring them the twofold blessing of a reformed faith and British civilisation.
Education, as we saw in Part 2, became a field of contention with the establishment of the National School System in 1839, vigorously opposed by the Church of Ireland. The Protestant Church Education Society was founded with the object of providing an alternative education system but it struggled financially and was unable to provide enough funding to become a viable alternative to the National Schools.
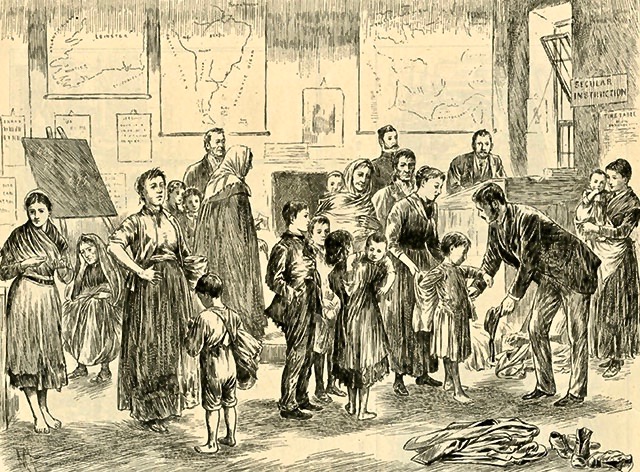
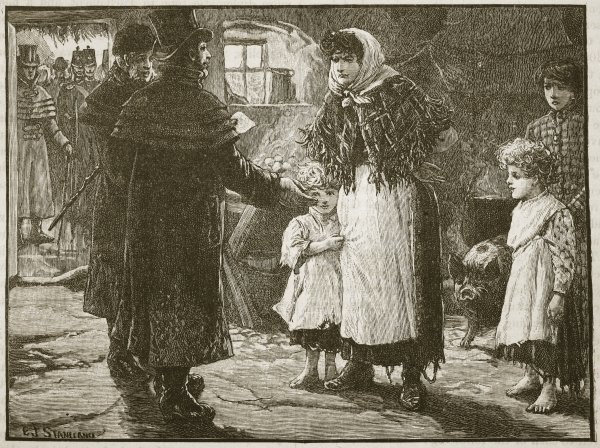
Poor children receiving clothing at a school in the West of Ireland
Up to 1839, schools on the Mizen were mostly miserable affairs with few resources and badly paid teachers. The Kildare Place Society was originally founded to provide non-denominational education to the poor, but after the establishment of the National School System, it affiliated with the Church of Ireland. This Society provided support to several schools on the Mizen Peninsula, including one in Ballydehob, another in Gortnagrough, and another in Rock Island. Other schools were maintained by the local Church of Ireland (e.g. parish schools at Gubbeen and Corravoley) and some received grants and aid from the Hibernian Society – an organisation specifically devoted to offering education with a proselytising ethos.
Now a private residence, part of this house in Durrus was the original school funded by the Association for Discountenancing Vice
Yet another Protestant education society was the charmingly-named Association for Discountenancing Vice and Promoting the Knowledge and Practice of the Christian Religion, while another, The Irish Society, had a similar mission, to provide bibles to schools and to promote Protestant religious education.
A sermon by our old friend, William Magee (see Part 3)
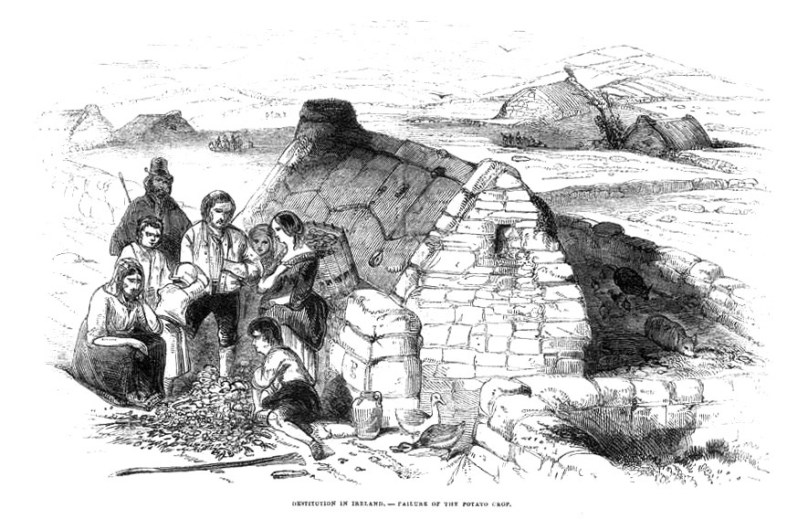
All of these societies, to a greater or lesser extent, supported schools on the Mizen, most of them educating both Protestants and Catholics and stipulating that the curriculum would include biblical instruction. For those students who did not have access to a National School, these schools provided rudimentary instruction, but were frequently accused of offering that education contingent on conversion. During the famine, the provision of food supplies to children when attending schools became a particularly contentious activity – although it does strike one as a no-win situation – damned if you do and damned if you don’t.
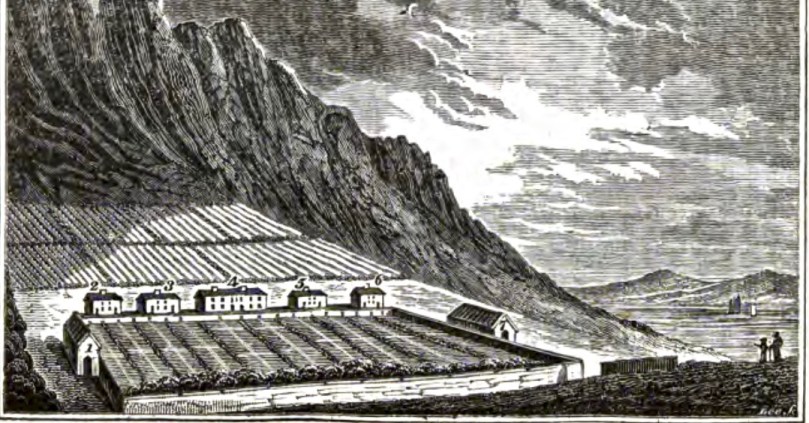
The Achill Colony. What do you think they served in the Temperance Bar?
The new spirit of fervent evangelism imbued many of the Protestant clergymen in West Cork Parishes. Protestant ‘colonies’ had been established in Achill in Mayo by the Rev Edmund Nangle and in Dingle by the Rev Charles Gayer. Highly controversial, these settlements provided food, education and employment to Church of Ireland converts and were lauded as model villages by the more enthusiastic of the Protestant missionaries. The Catholic hierarchy, on the other hand, railed against them, accusing them of buying souls with the promise of financial security. There is a wonderful first-hand, and far from favourable, account of the Achill Island colony in Vol 3 of Ireland: Its Scenery, Character, etc (pages 394 to 401) by the Halls. They describe a harsh and unforgiving Nangle (below) and a struggling colony that is despised by its neighbours.
West Cork was also a centre for Protestant missionary activities, who saw in its poverty and remoteness an ideal recruiting ground. The activities of the Irish-speaking Rev Edmund Spring on Hare Island and Cape Clear came under particular scrutiny due to the large number of conversions he claimed and his association with the Irish Islands and Coast Society, for whom he ran his parish as a ‘missionary station.’ He moved on to Cape Clear from Hare, in turn winning many converts but always under the accusation of offering ‘support’ to those who became his parishioners.
The Halls, Samuel Carter and Anna Maria, produced a superbly illustrated account of their tour of Ireland in three volumes. It’s an indispensable resource
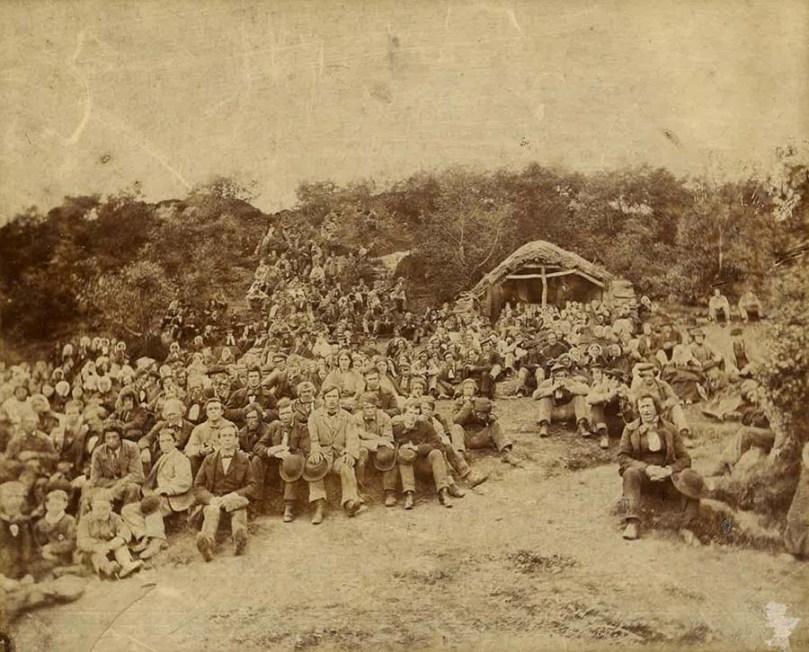
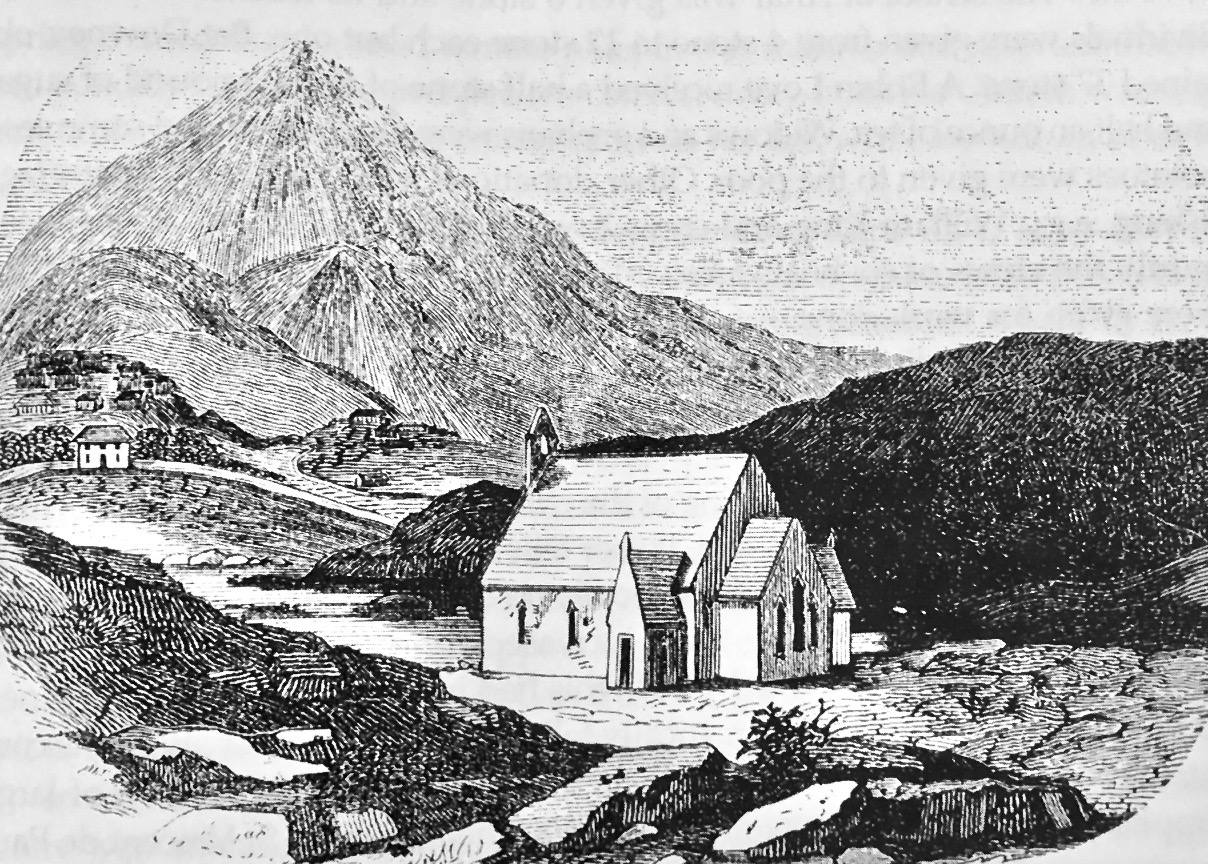
On the Mizen, in Kilmoe Parish, the arrival of the Rev Thomas O’Grady signalled the advent of the spirit of evangelism and of many conversions. Patrick Hickey’s research indicates that there were five Protestant families in Toormore when O’Grady arrived, but by 1849, with O’Grady’s friend and successor, the Rev William Fisher, now as Rector, that number had risen to eighty.

Crookhaven on the eve of the Famine
How were these conversions won? By the example, dedication, hard work and self-sacrifice of these men, or by the souperism of the Rev Fisher? In the next post I will look at the conditions that led to the latter accusation: famine in Toormore and the building of Teampaill na mBocht.
The Achill Colony, a woodcut from John Barrow’s Tour of Ireland
This link will take you to the complete series, Part 1 to Part 7