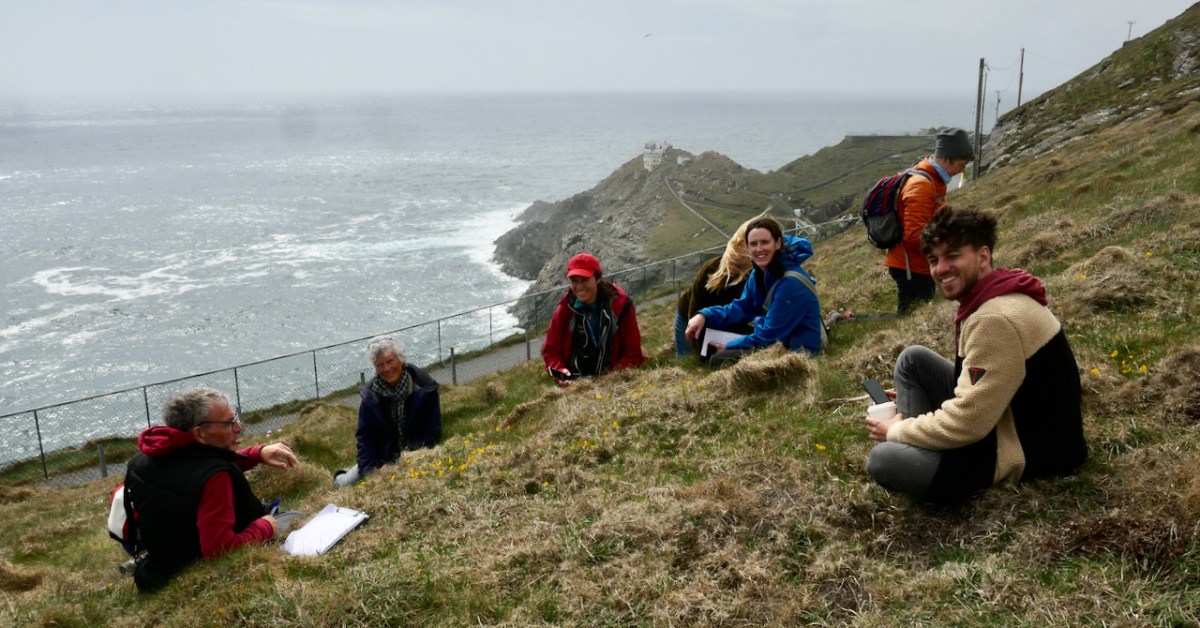
For a wildflower enthusiast there is nothing better than a day spent with like-minded folk looking for interesting plants under the leadership of a true expert.

At this time of year the buttercups all over the dunes are actually Bulbous Buttercups – if you look under the flower head you will see that the sepals turn down away from the petals
I had the immense privilege of being included in a Rare Plant Monitoring Workshop on Friday the 13th – which also happened to be the day that Biodiversity Week kicked off in Ireland. As you probably all know by now, Nature is in crisis all across the world, and although we may be surrounded by lush hills and boreens in West Cork, there are ominous signs that all is not well with our natural world here as elsewhere. Fewer than ten percent of our native species in Ireland have been assessed for their conservations status – but of those that have been, one fifth (yes – one-fifth!) are at risk of extinction.
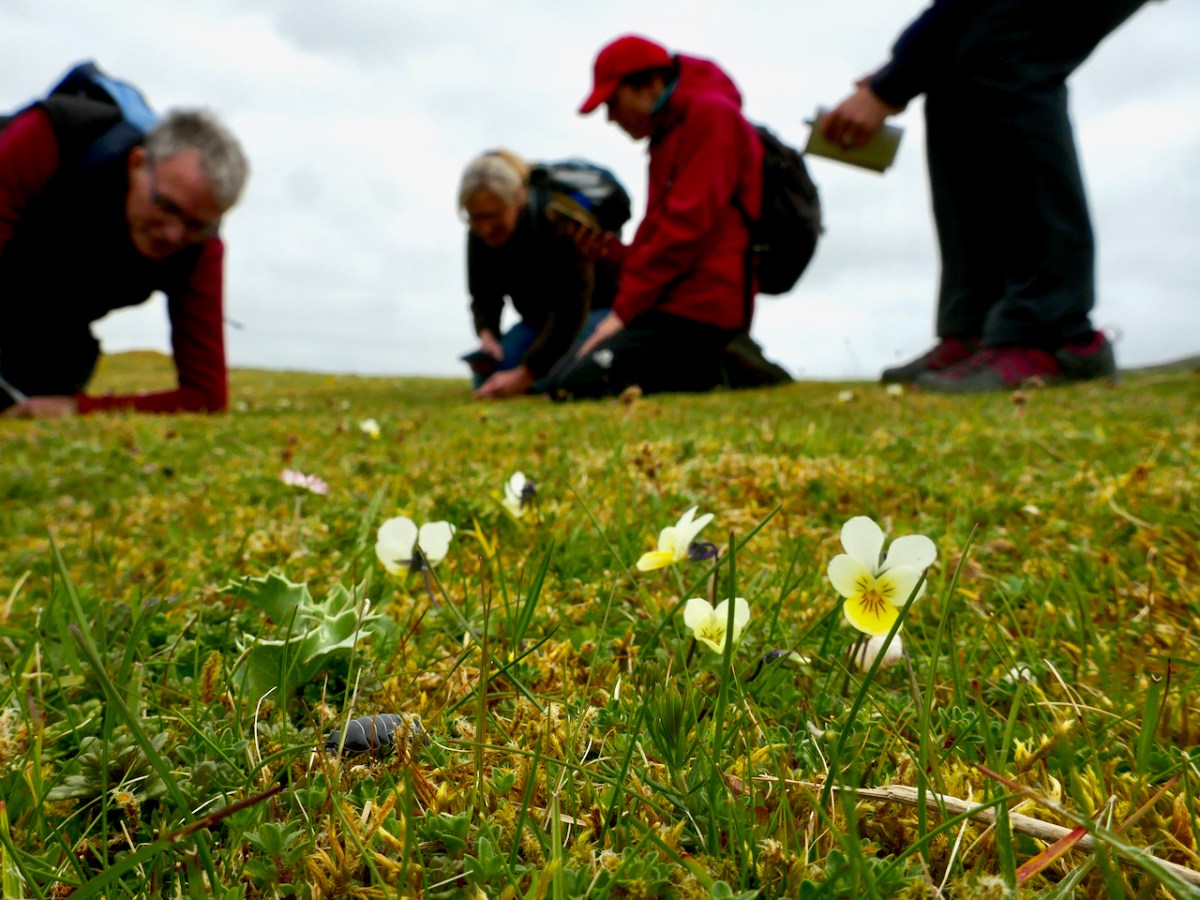

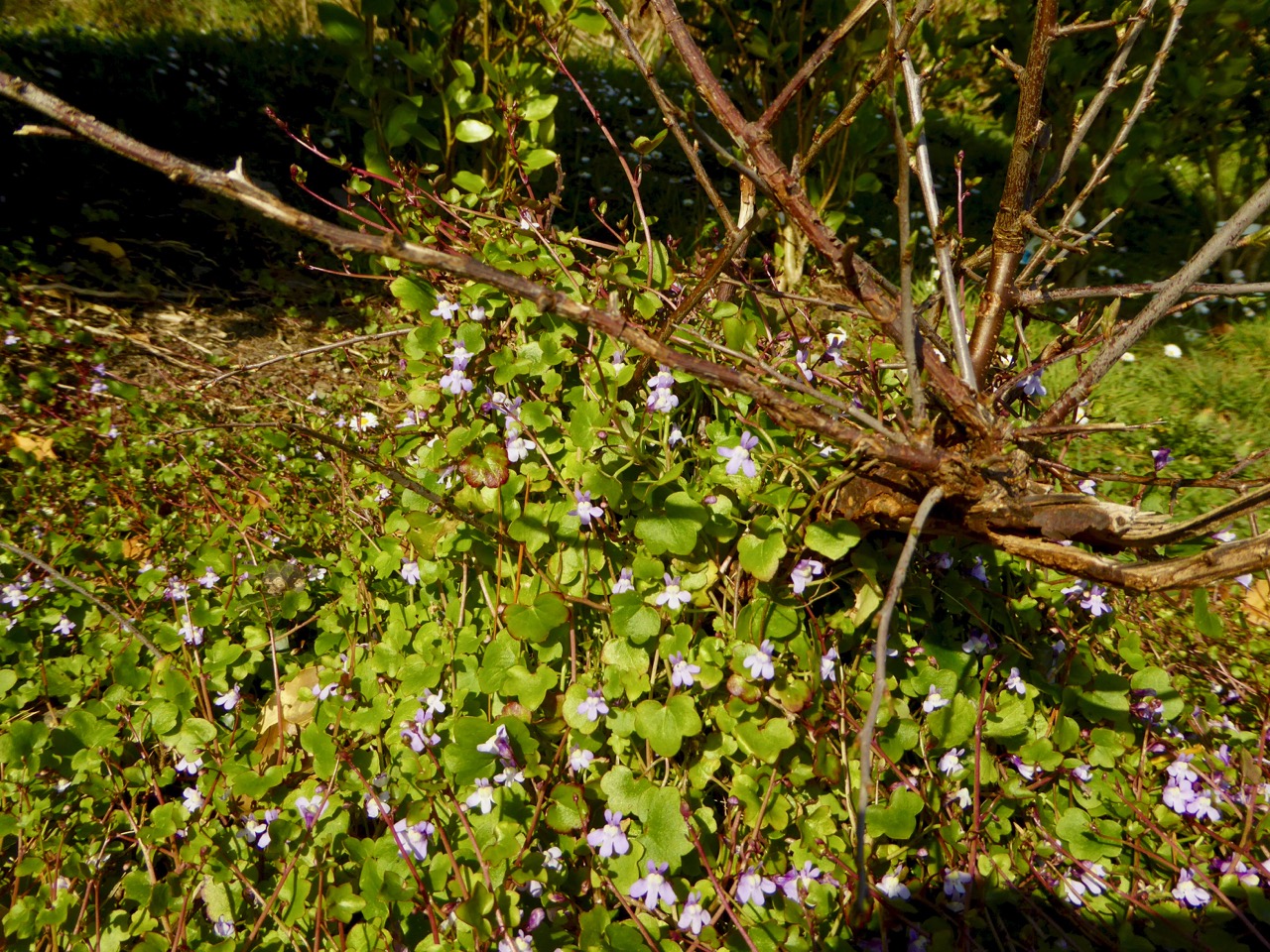
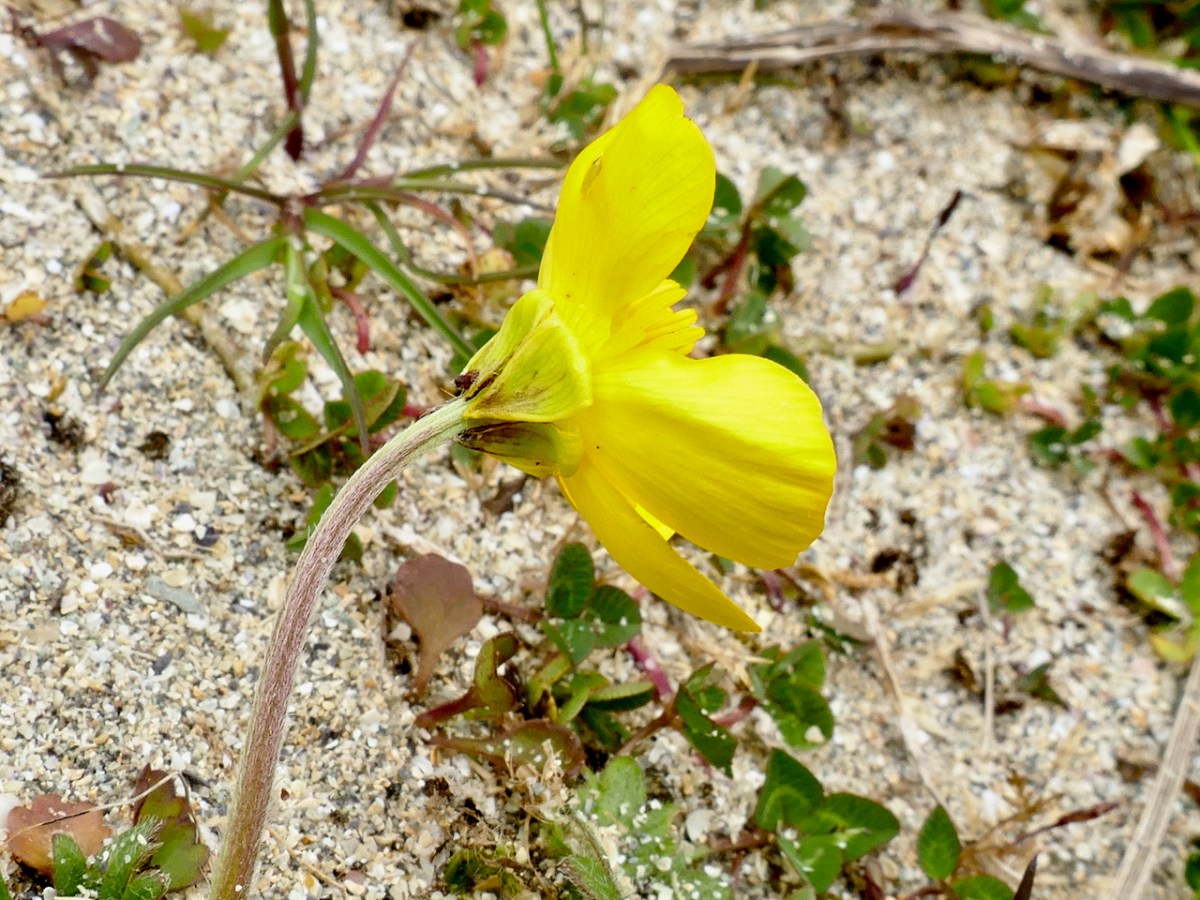
Sand Pansy – gorgeous little violas found on the dunes
That’s why counting plants is important – each one is part of the complex web of biodiversity that contribute to the health of our environment and the loss of even one can have knock-on effects on a whole cascade of others. I already monitor two rare plants for the National Biodiversity Data Centre (NBDC), Vervaine and Calamint, so I have an insight into the kinds of threats rare plants can face, from mowing to herbicides to change of land use – all of those have happened to the small populations I monitor.
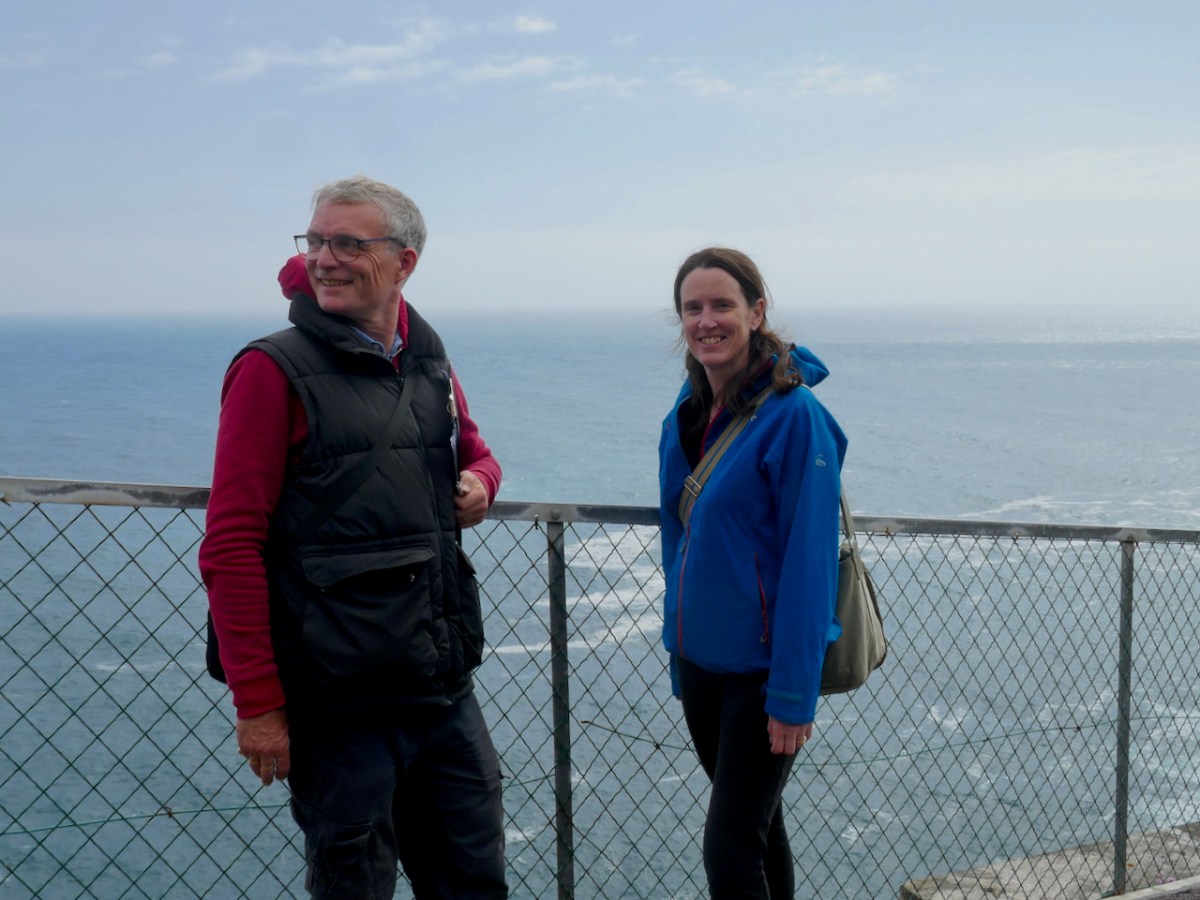

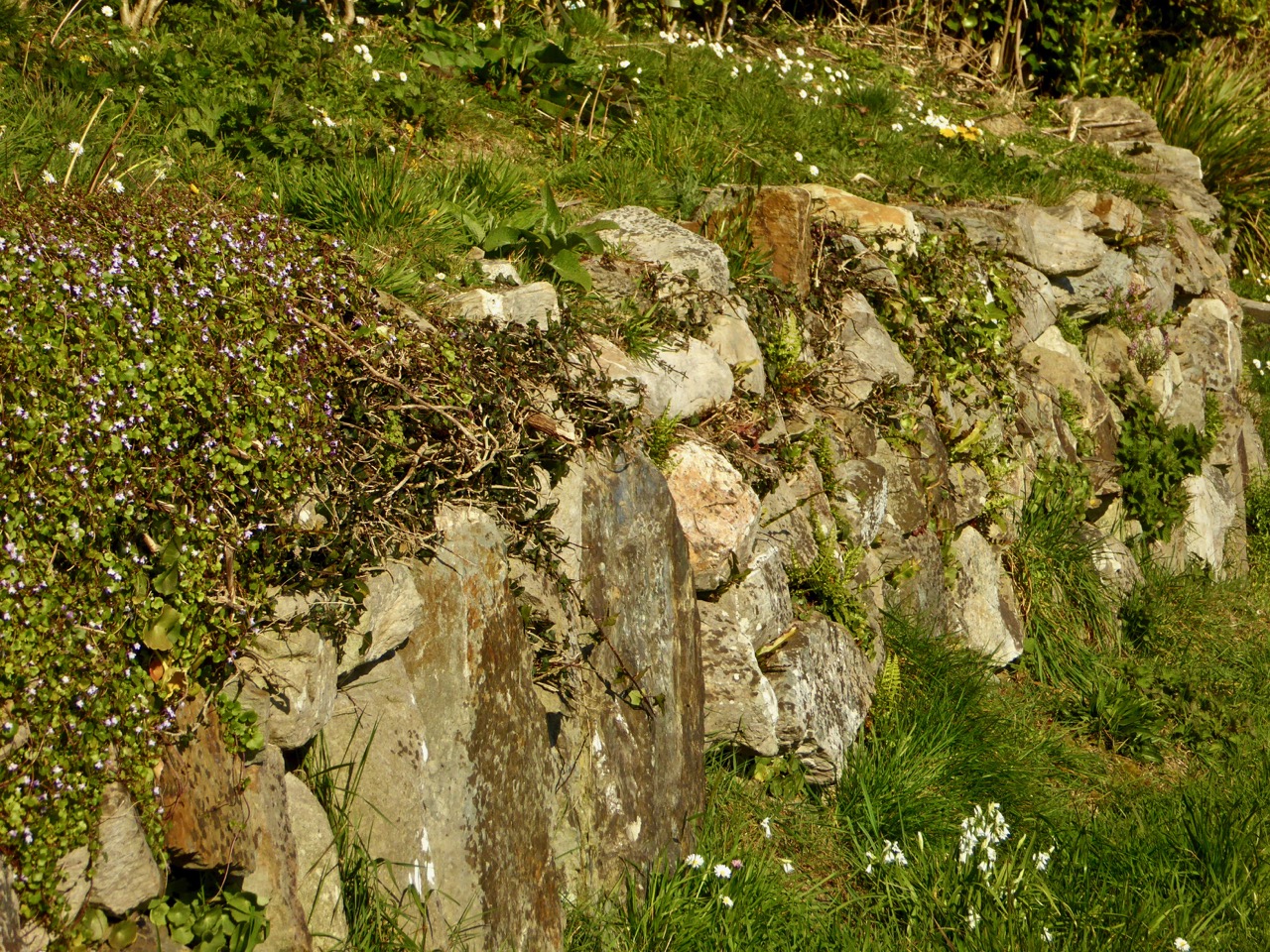
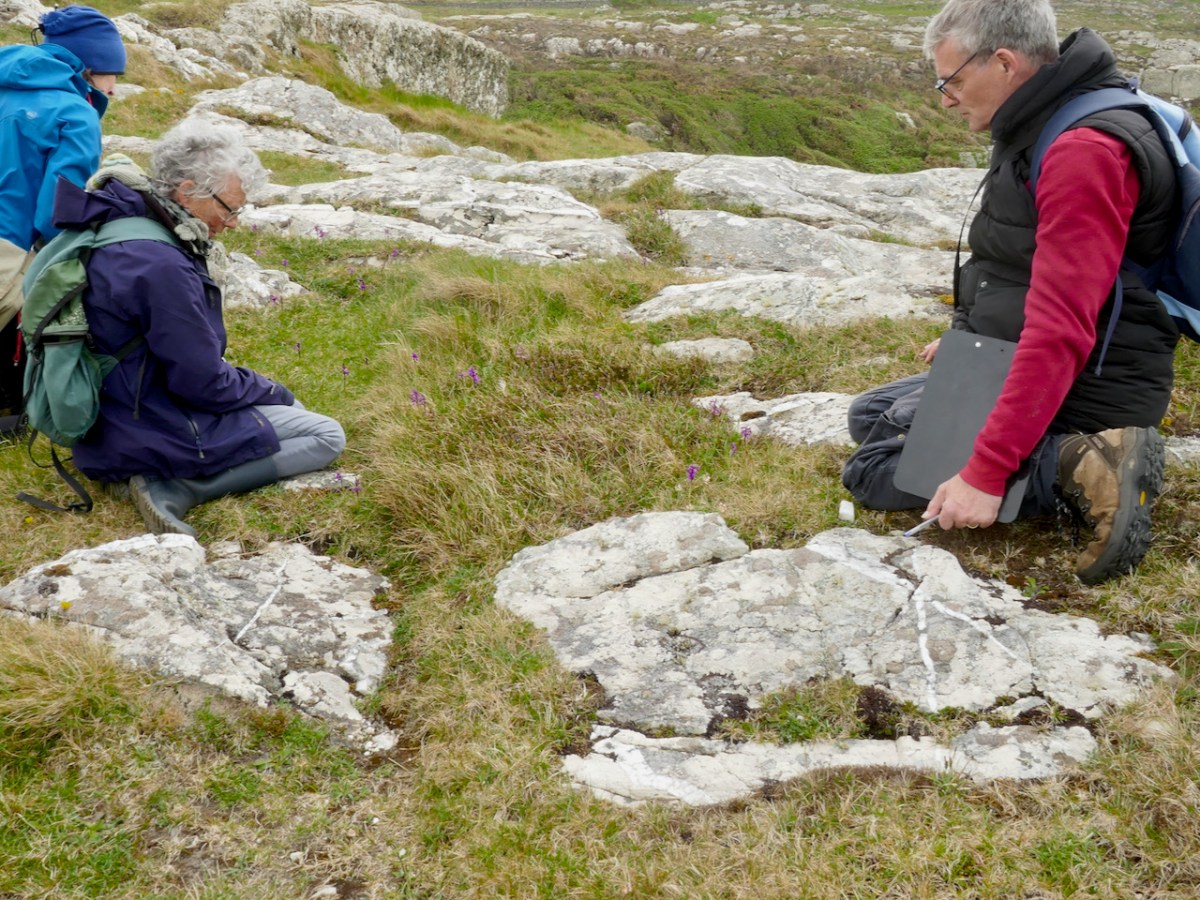
The location for this workshop was Barley Cove and Mizen Head. Having rendezvoused with Botanist Paul Green and NBDC Scientist Úna FitzPatrick (above, at Mizen Head) we set out across the dunes. I had met Paul before and so I knew that he is unfailingly generous about sharing his immense knowledge. Throughout the day we stopped frequently to exclaim over a plant that one or another of us spotted (like the Bulbous Buttercup) on the dunes or the rocks, and Paul always took the time to stop and educate us about each one.
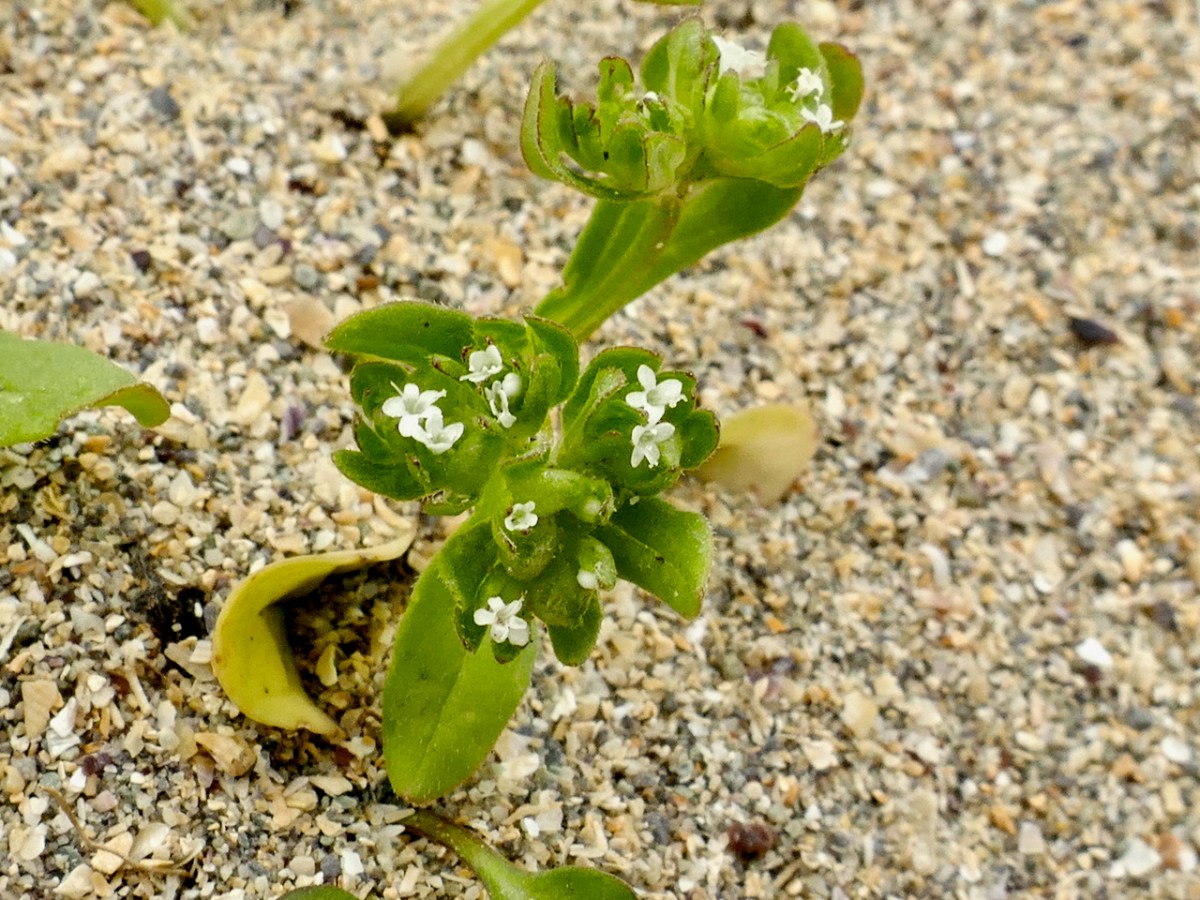

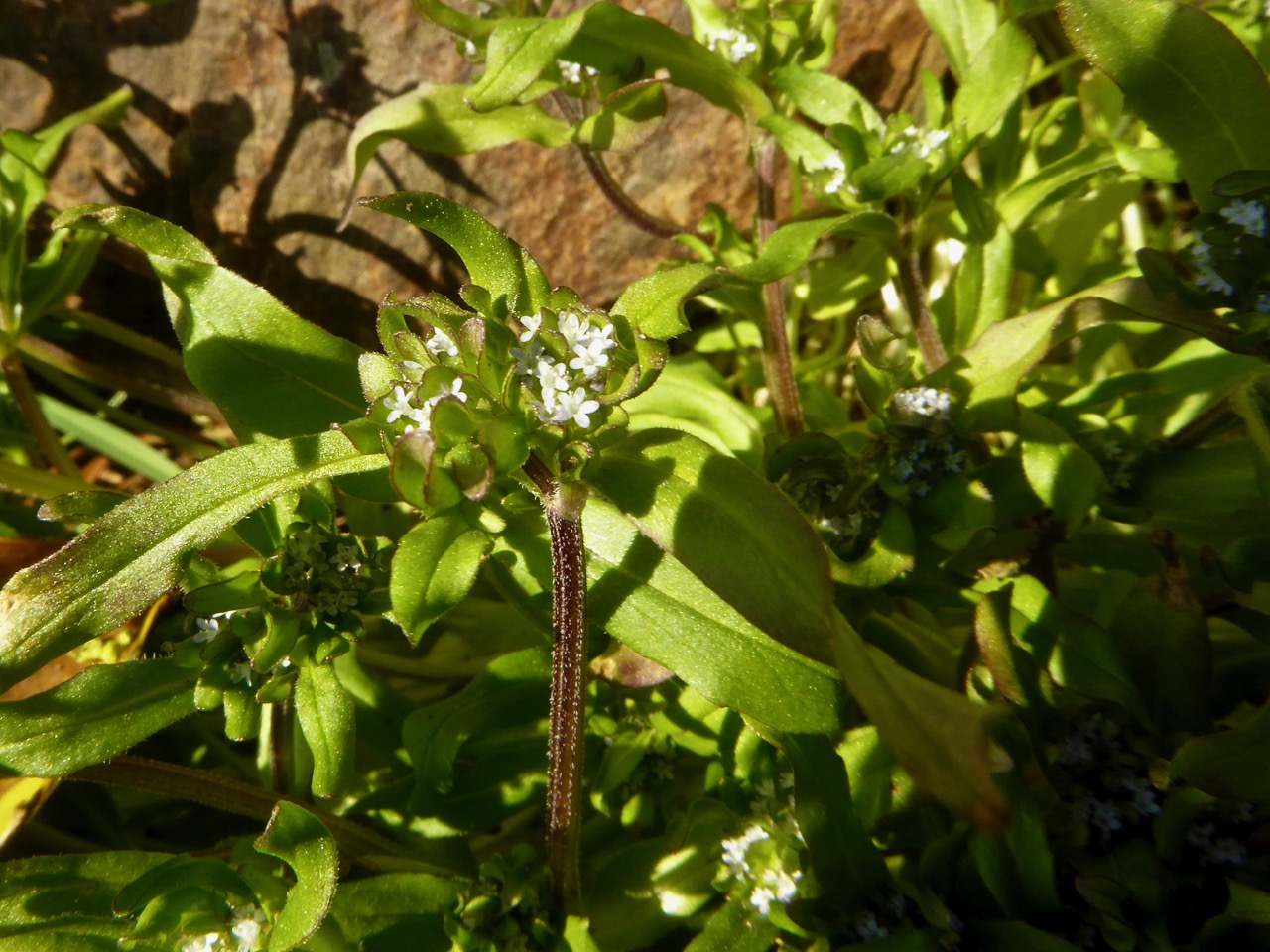
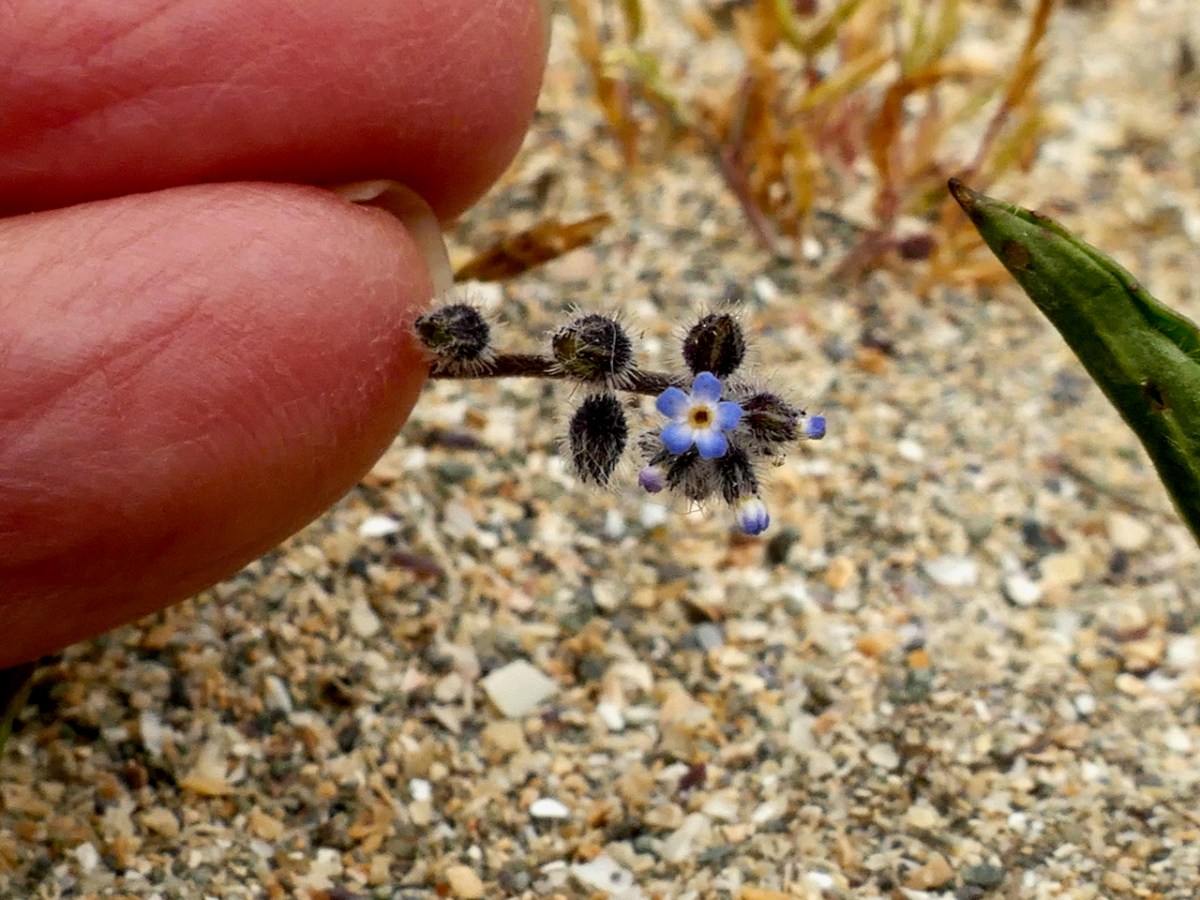
Thus, along the way, I was introduced to several plants that were entirely new to me. Despite the fact that I have been to Barley Cove on numerous occasions, many of them spent lying in the grass on the dunes (see this post and the wildflower slideshow within it, for example), I had never seen Common Cornsalad (above) nor Early Forget-me-not (below) before Friday.

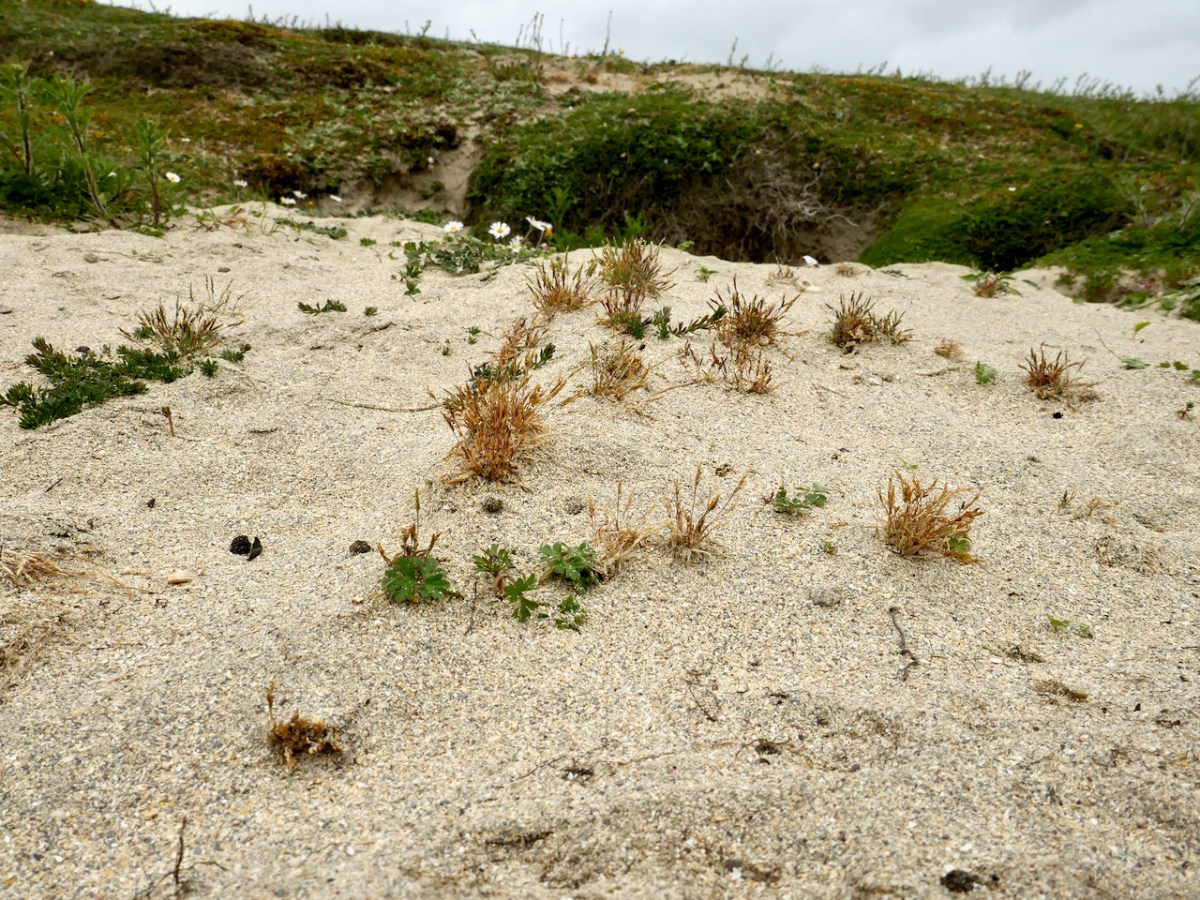
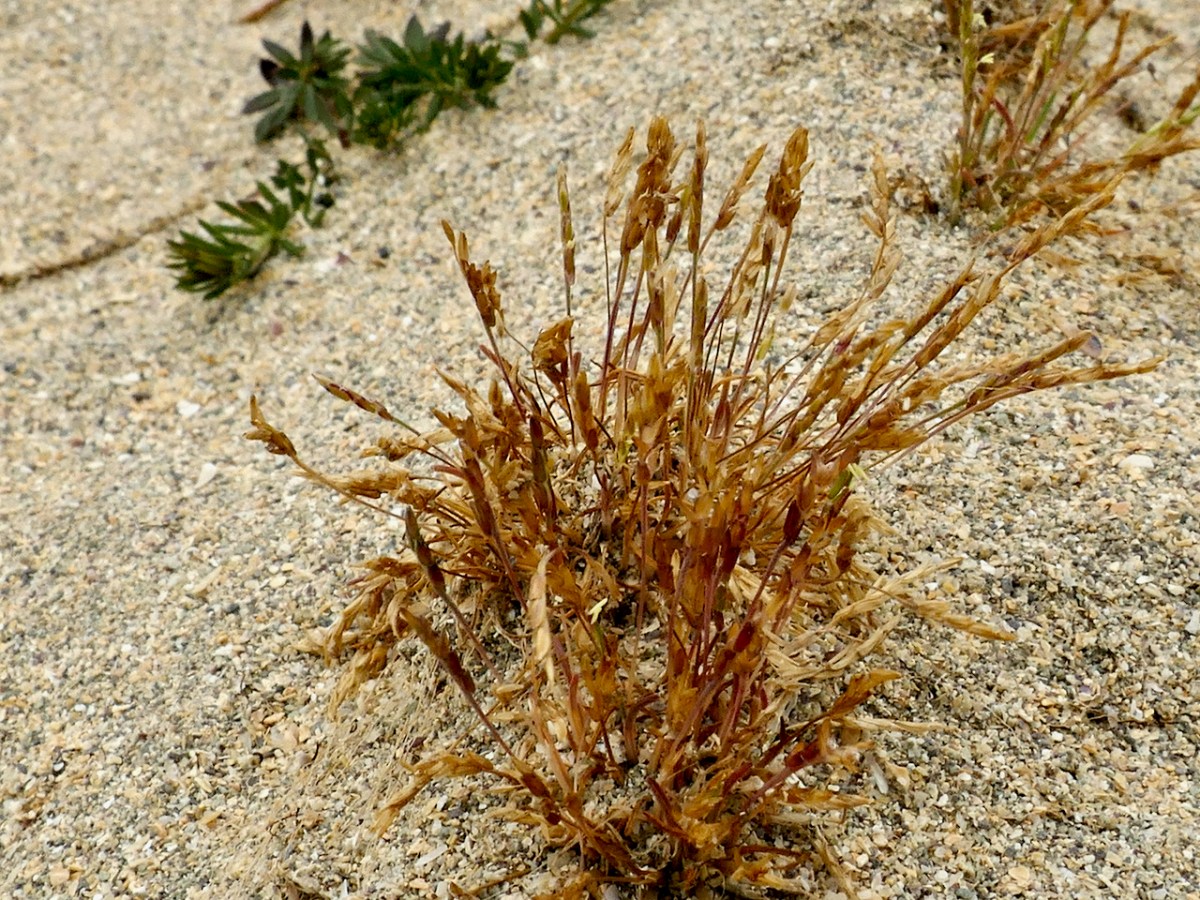
As our first rare plant, we were in search of Early Sand-grass, the kind of undistinguished little plant that you would walk over unthinkingly, but which is so rare that it only occurs here and in the Bull Island Nature Reserve in Dublin. That’s the distribution map below, courtesy of the BSBI.

Paul found it and we collectively traced its extent across the dunes. This is an area with much rabbit activity and Paul speculated that the bare patches of sand created by the busy bunnies was what had encourage or allowed the Sand-grass to colonise this area. It’s a complex issue – those Barley Cove Bunnies can be destructive to the dunes in some ways, but here we have an instance where their presence has been beneficial – one of those complex interactions that are so hard to predict.


Our next target was an orchid – the Green-winged Orchid. But, on the way, we found another Orchid – the Irish Marsh Orchid (below). It was beautiful and bold and instantly visible in the short grass on the dunes.
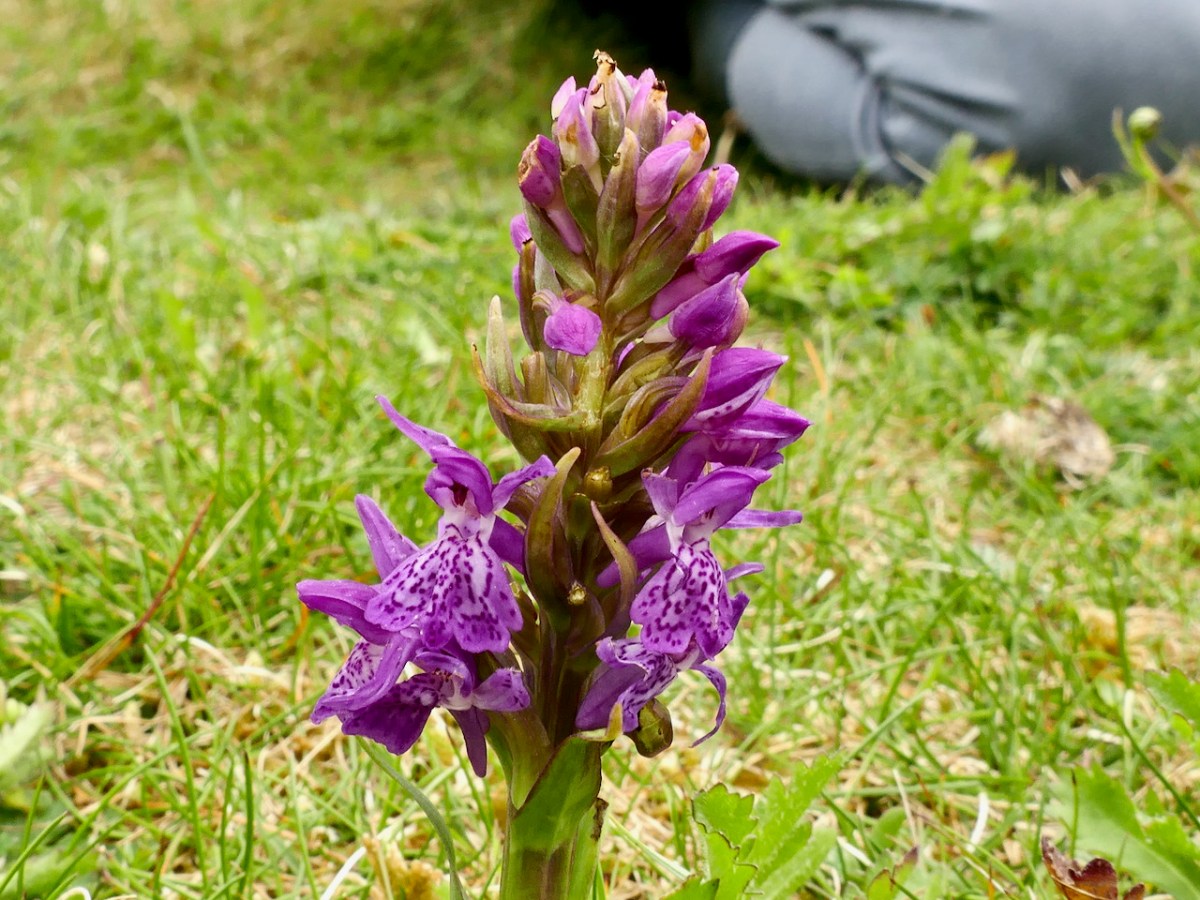


In contrast, we almost tripped over the Green-winged Orchid, which upon first glance looked spindly and unremarkable. This is one you have to get close to – can you see them in the grass, below?

Here’s what Zoe Devlin has to say about this flower:
Surely the most exquisite wild orchid in Ireland. . . Green-winged Orchid is a small, erect plant which grows to about 30cm tall in grassland and meadows where grazing occurs. It bears flowers, well separated, in short spikes and these flowers appear in several colours – from snow-white through pink and magenta to deep purple. The three sepals are purple-veined with strong, green lines and these sepals form a hood over a broad, downward folded lower lip which is three-lobed and heavily spotted at its white centre. There is also a stout, slightly-curved spur. These incredible flowers bloom from mid-April to mid-June. The leaves are shiny green, unspotted with the upper leaves sheathing the stem and the lower leaves forming a rosette.
Zoe Devlin, Wildflowers of Ireland

Can you see all that in these photos? I’m not sure you can, which is one of the things that makes wildflower identification interesting – especially with a family like the orchids where there are quite a few that look similar until you really examine them.
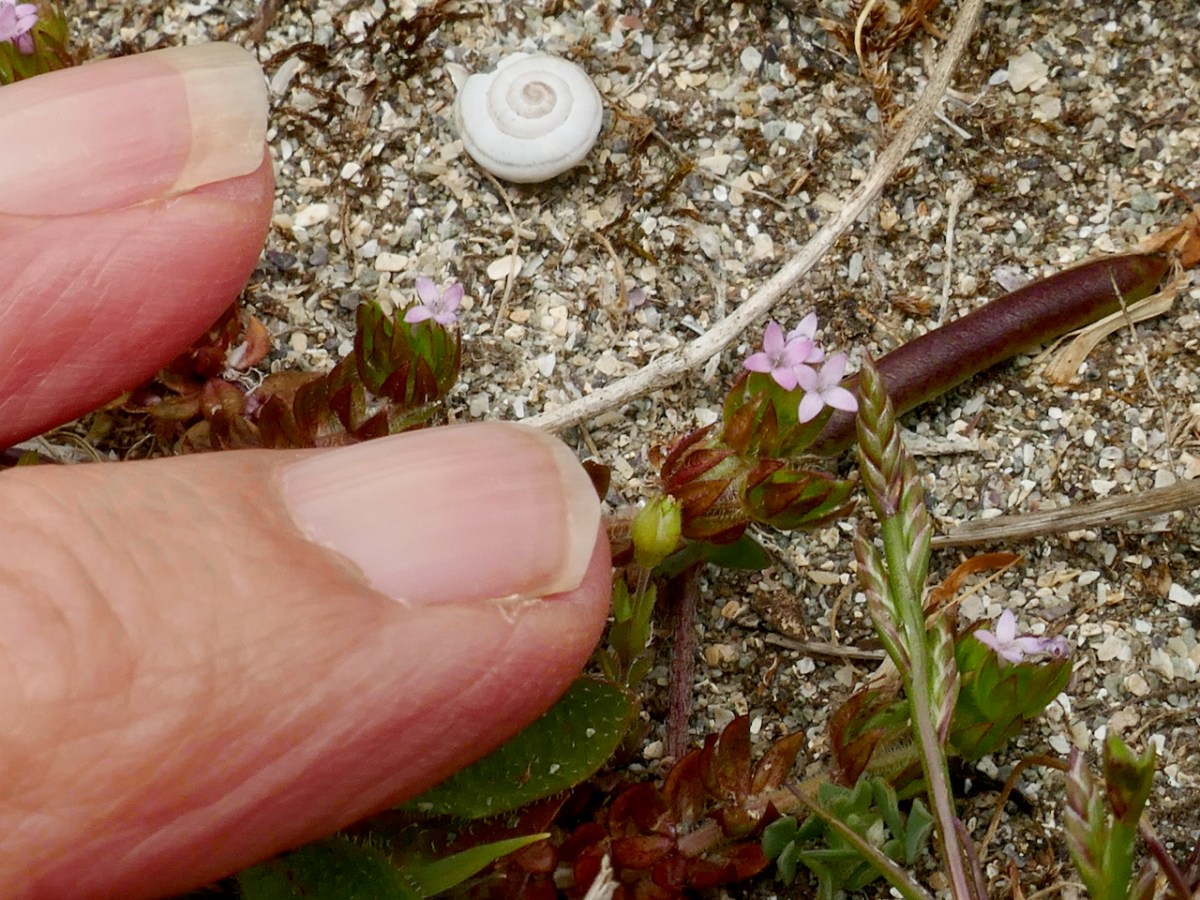

There were more plants on the dunes – I was amazed to find Field Madder (above), which I always assumed was a plant of arable ground. One of the things we had to get used to was how tiny many of the plants on the dunes were compared to those that grow in less challenging environments – like miniature versions of themselves.
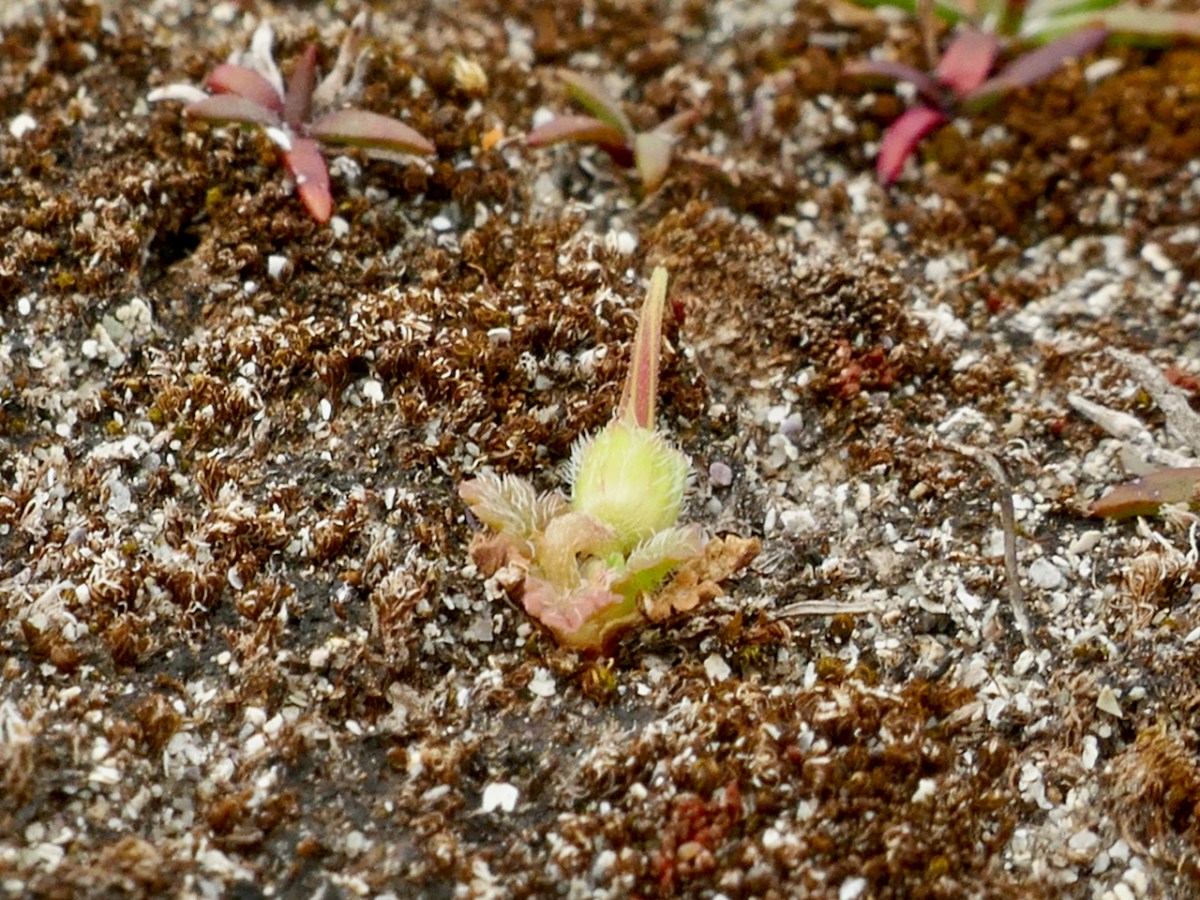

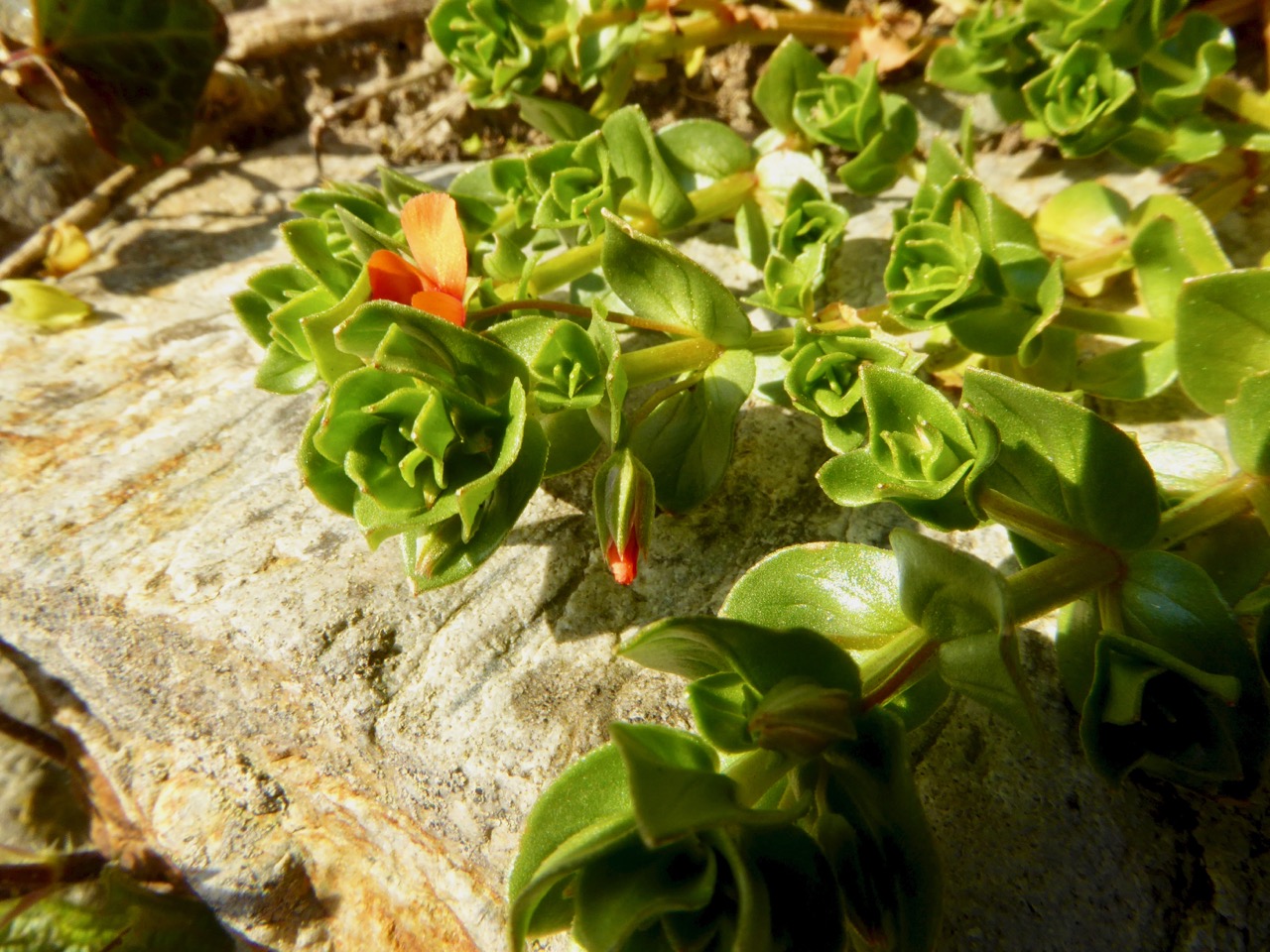
Then there was one of our target species, the Sea Stork’s-bill (above) – really, a flower that only its mother could love, but very rare in Ireland and therefore one of the plants that enable us to chart the conservation of its habitat.

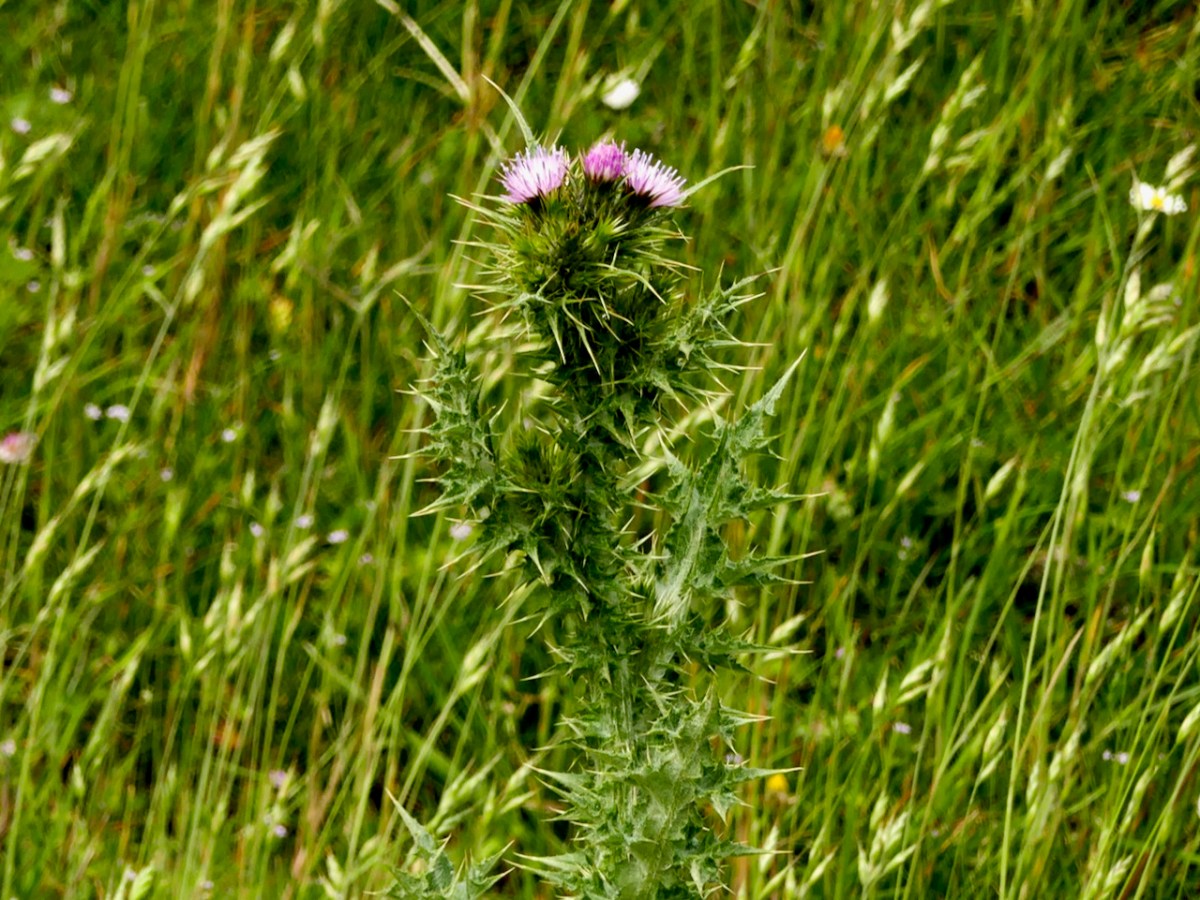
We drove from Barley Cove around to the Holiday Park but were unable to do a count of the Slender Thistle. The land was being grazed by sheep and every access was blocked (above). So we contented ourselves with noting that currently it appears to be abundant, if very localised. I managed a distant shot of this fine head (below) showing the pink flowers but also how spiny it is.

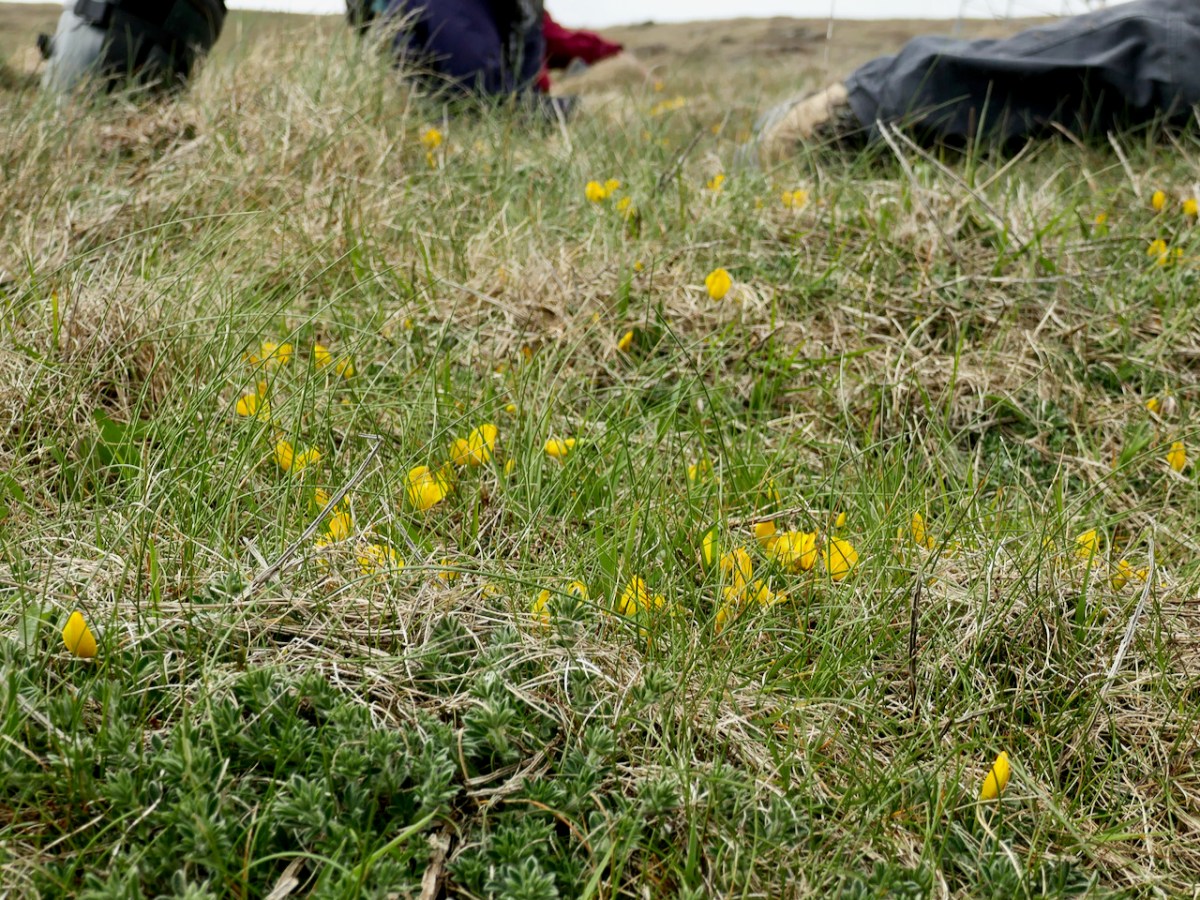
Our final stop was Mizen Head, one of the very few places in Ireland (see map below and the Broom below that) where you can find Prostrate Broom (try saying that fast). This was another exercise in a different kind of counting, since the plant is on sea cliffs and behind fences at the Visitor Centre, so it has to be identified at a distance and the count is an educated estimate. Add in the fact that there are two other yellow flowers gaily blooming around it (Kidney Vetch and Bird’s-foot Trefoil) and you get an idea of the challenge involved.
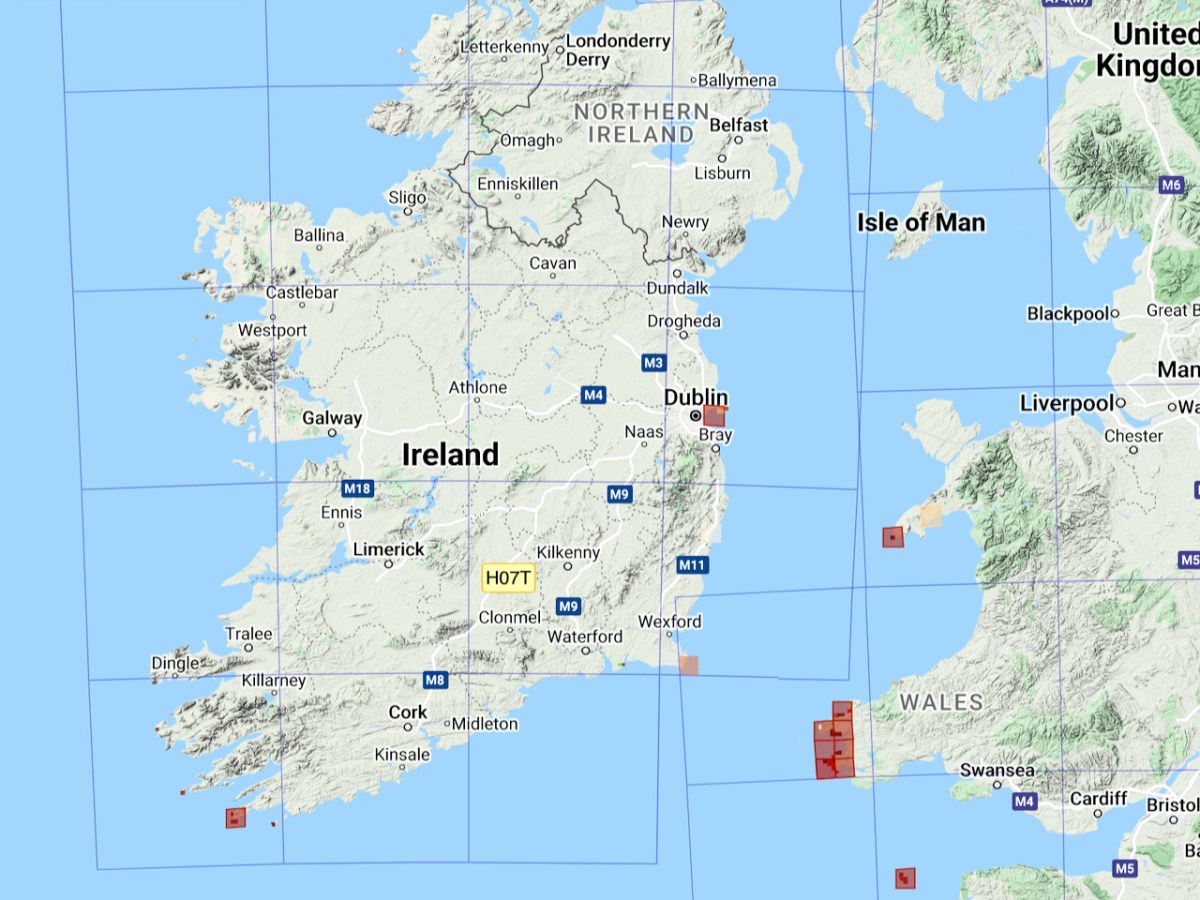
I have taken on the task of the Early Sea-Grass count. It may bloom as early as February or March, so I’ve made a calendar note to head out to the Dunes next year at that time. Another one of the participants, Damaris, and I will work together on our counts – it’s always more fun if you have a companion and probably more accurate too.

Thank you, Úna and Paul, for such a profoundly educational experience, that also managed to be great fun.














































