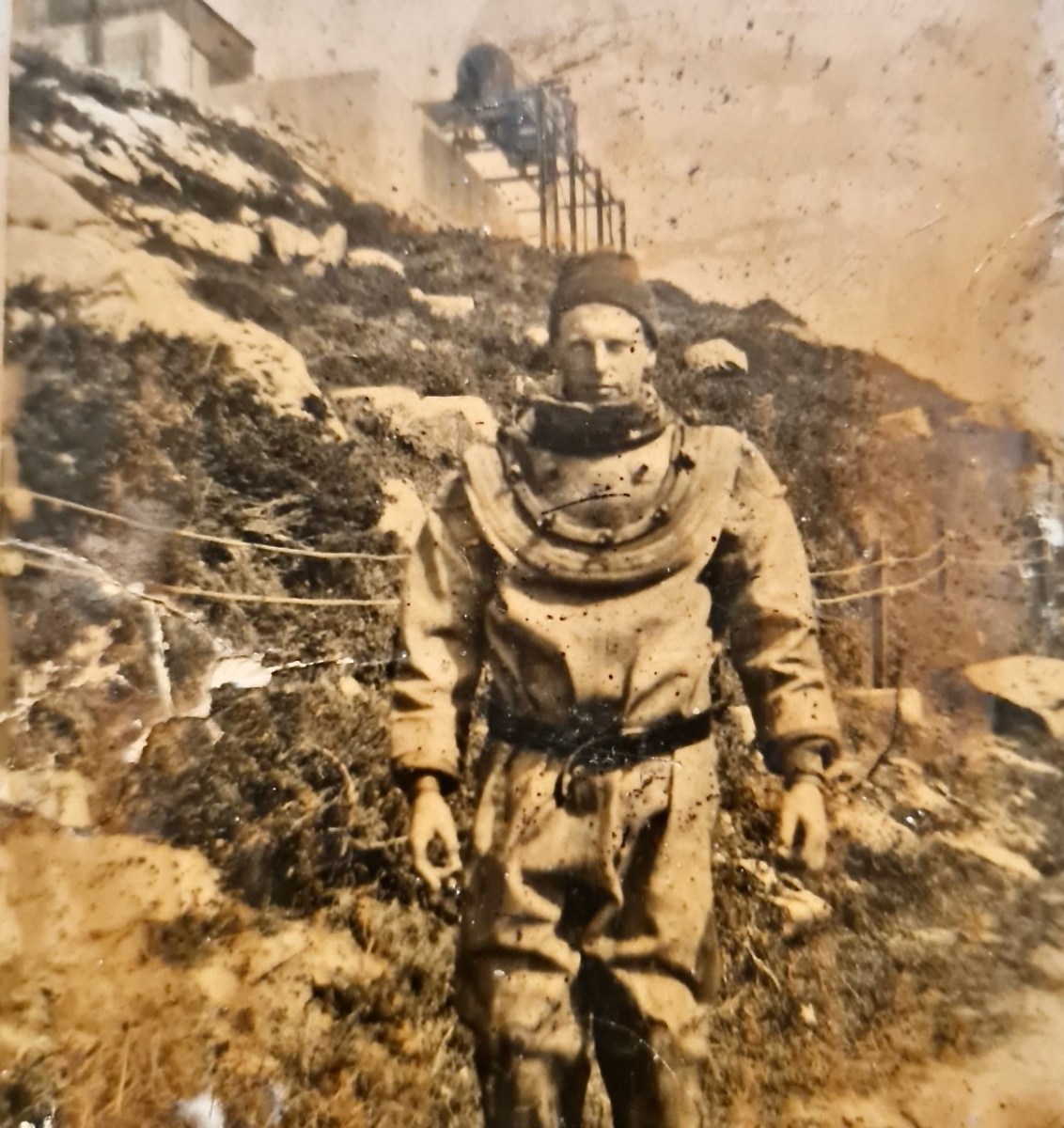
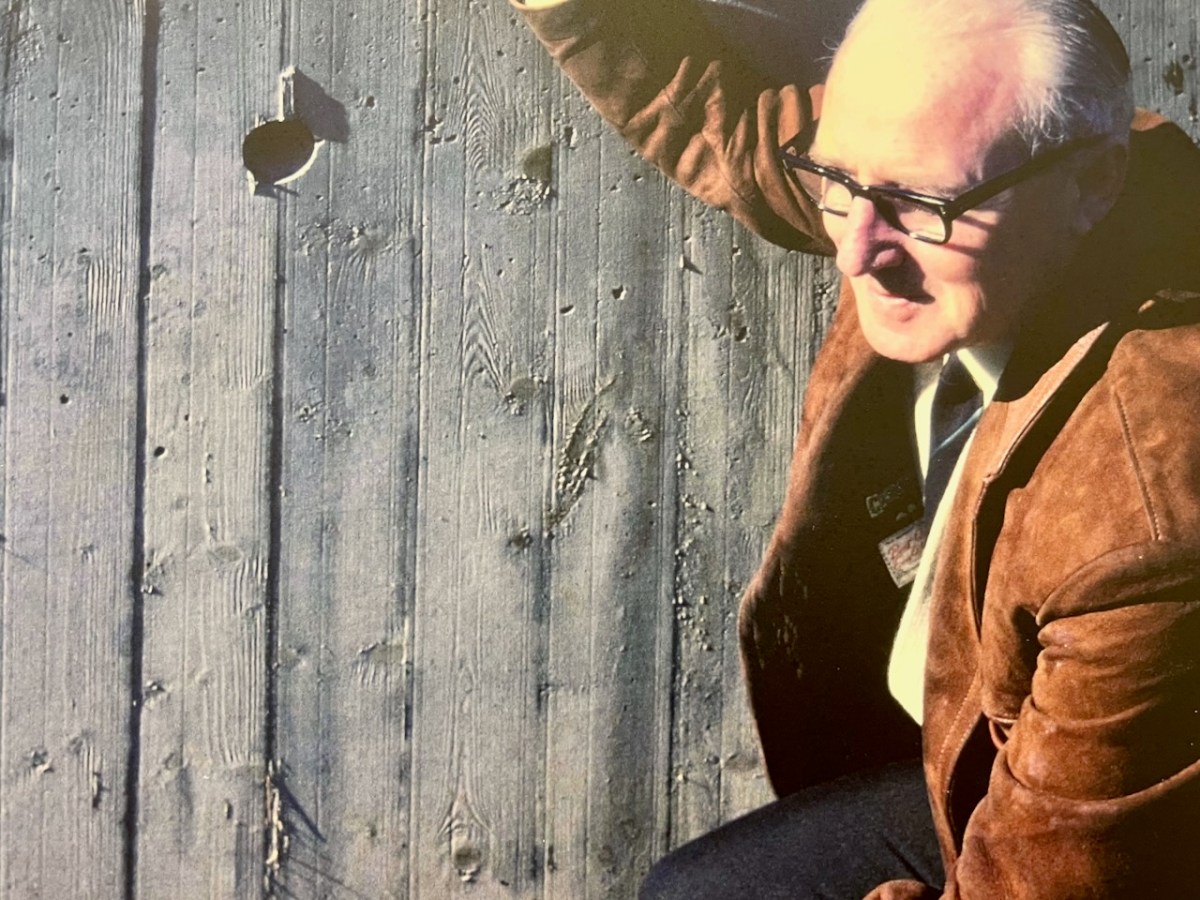
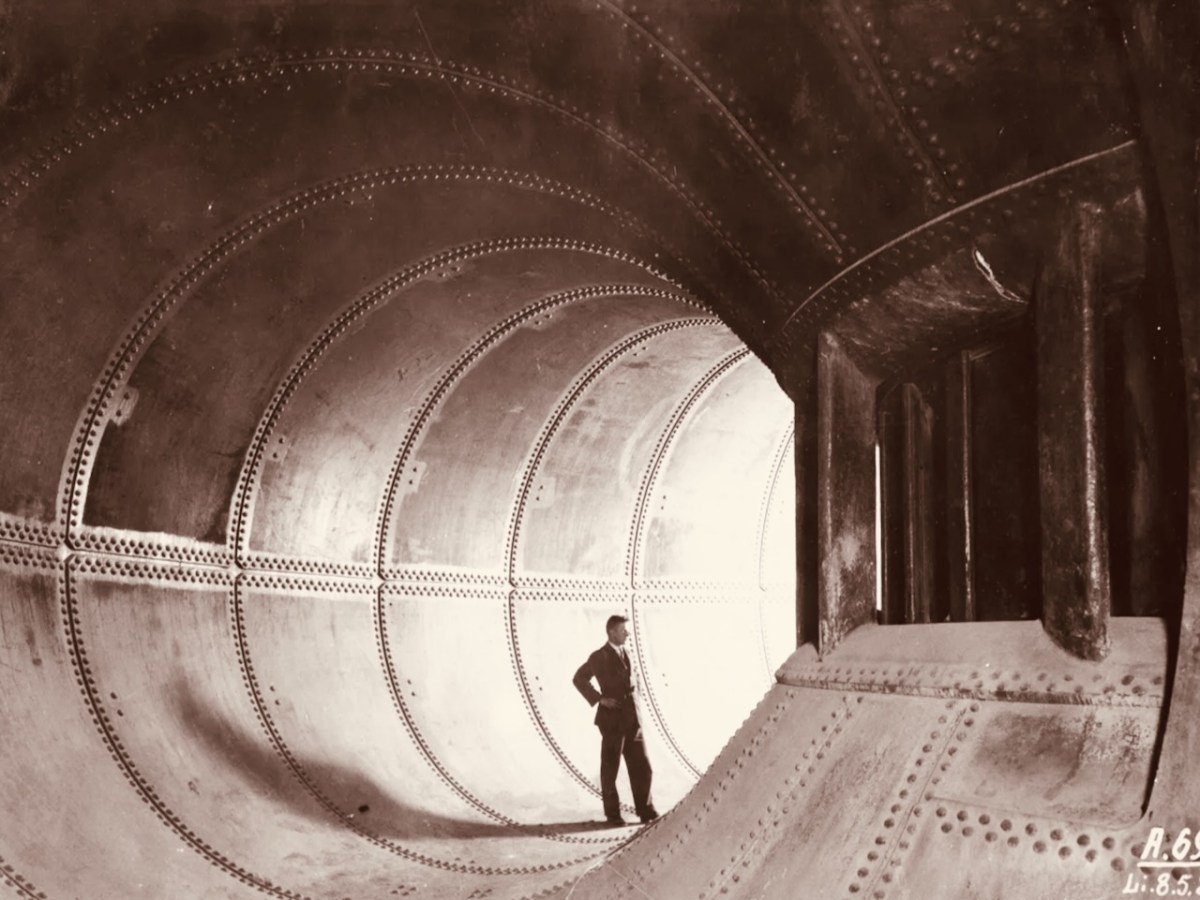
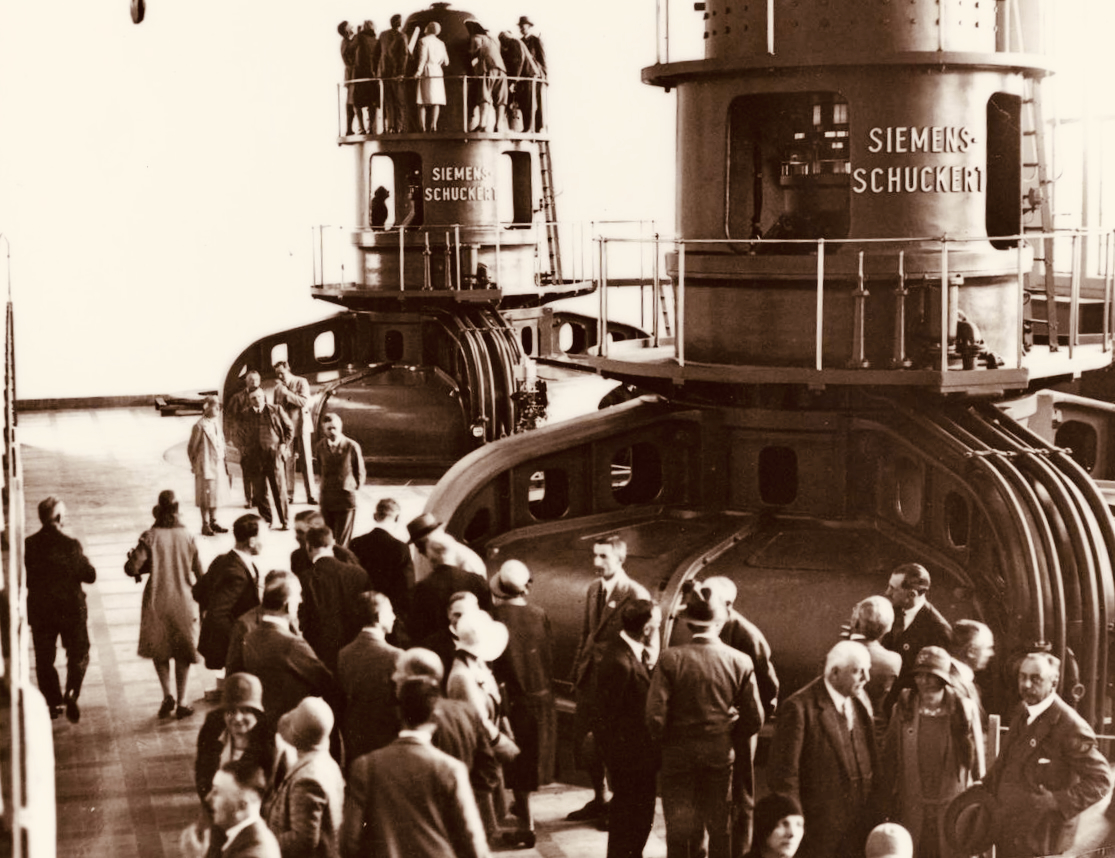
I’ve had the most marvellous emails from James Goggin – thank you James! Three of his grandparents came from Crookhaven – and the fourth, well that’s him in this spectacular photograph. Yes, he’s in a diving suit. James tells me: His name was Allen G Tyson, and he had come from Wales to work at the Crookhaven Quarry, seconded from Flintshire council in North Wales. Aggregates from the quarry were sent to North Wales amongst other places. He was a tall man and brilliant mathematician and civil engineer and lived with us in later life until his death in ’79. He designed the first dual carriageway in N.Wales and worked on the blue jubilee bridge in Queensferry (similar to and at the same time as Sydney and Newcastle bridges).
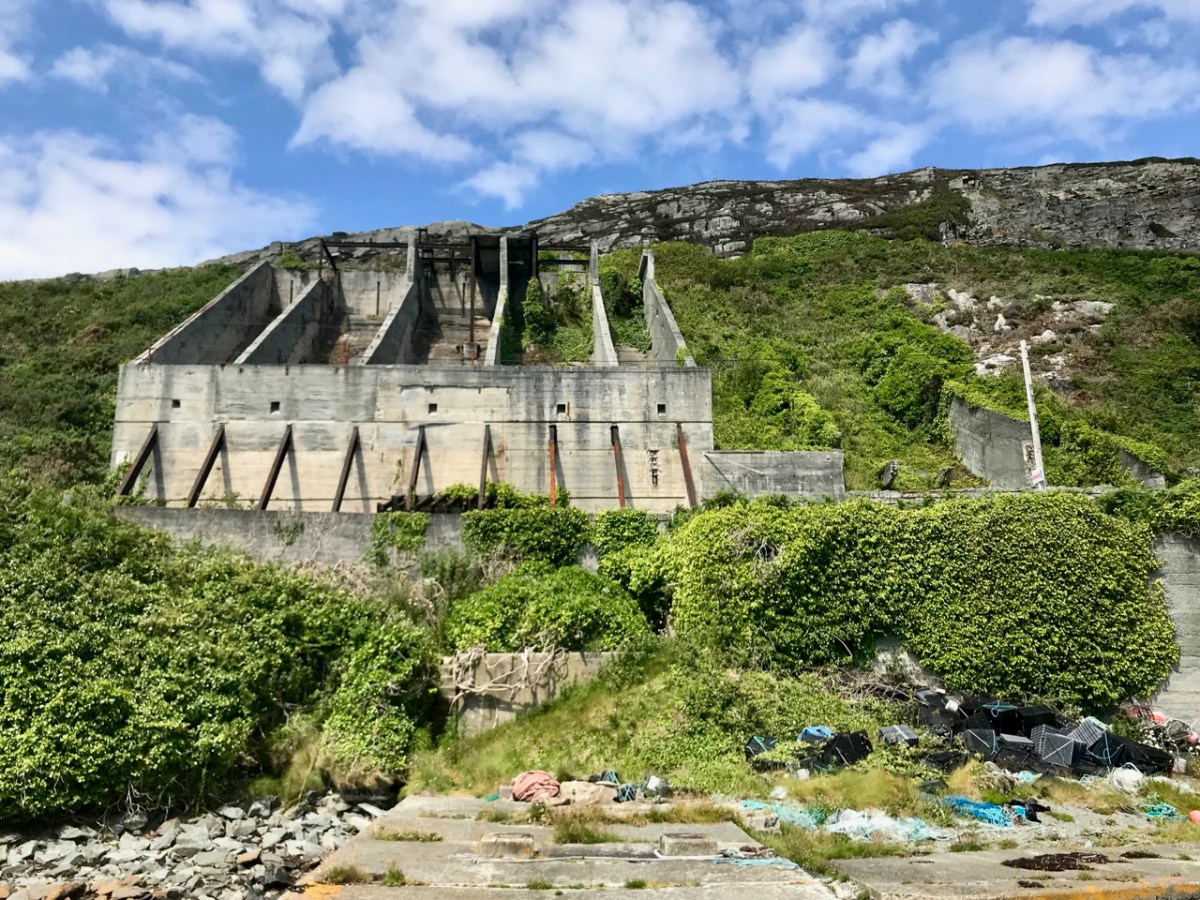

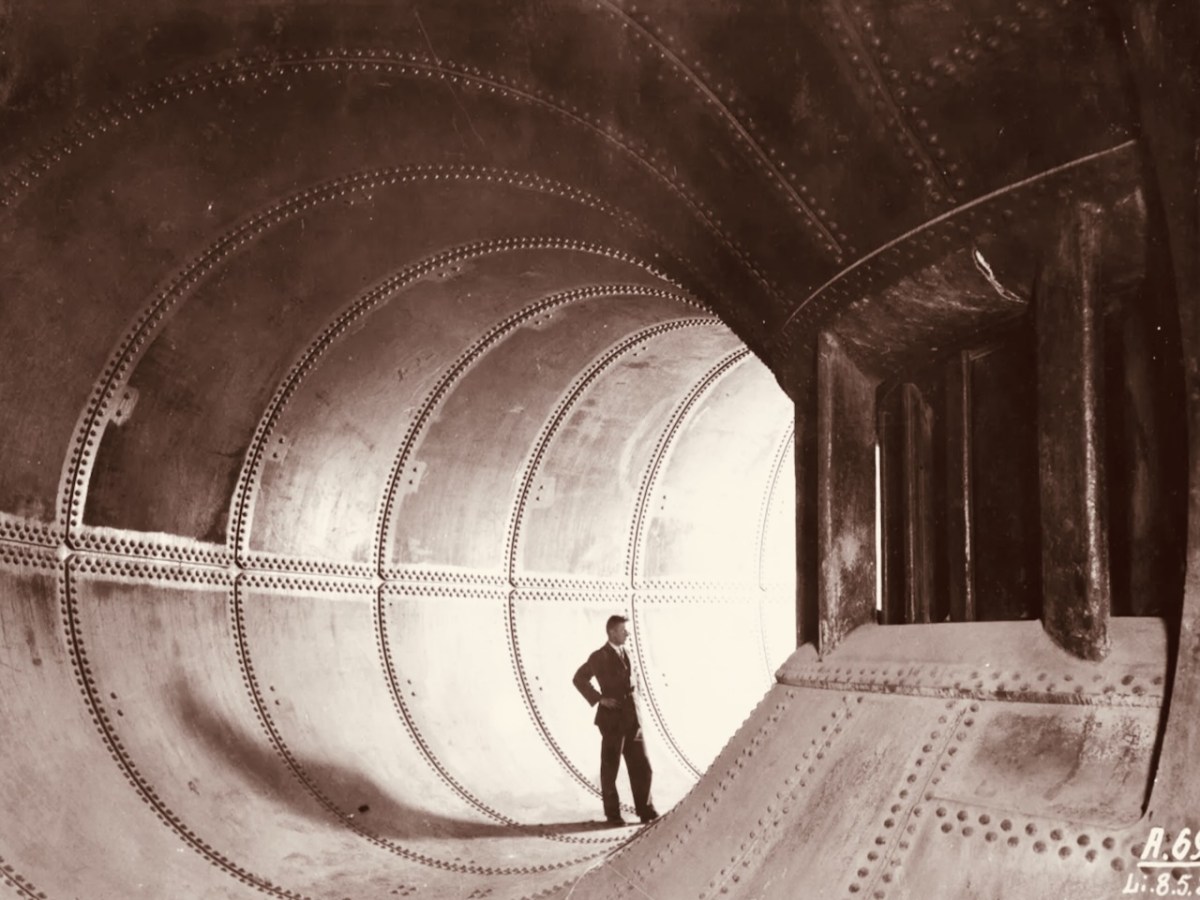
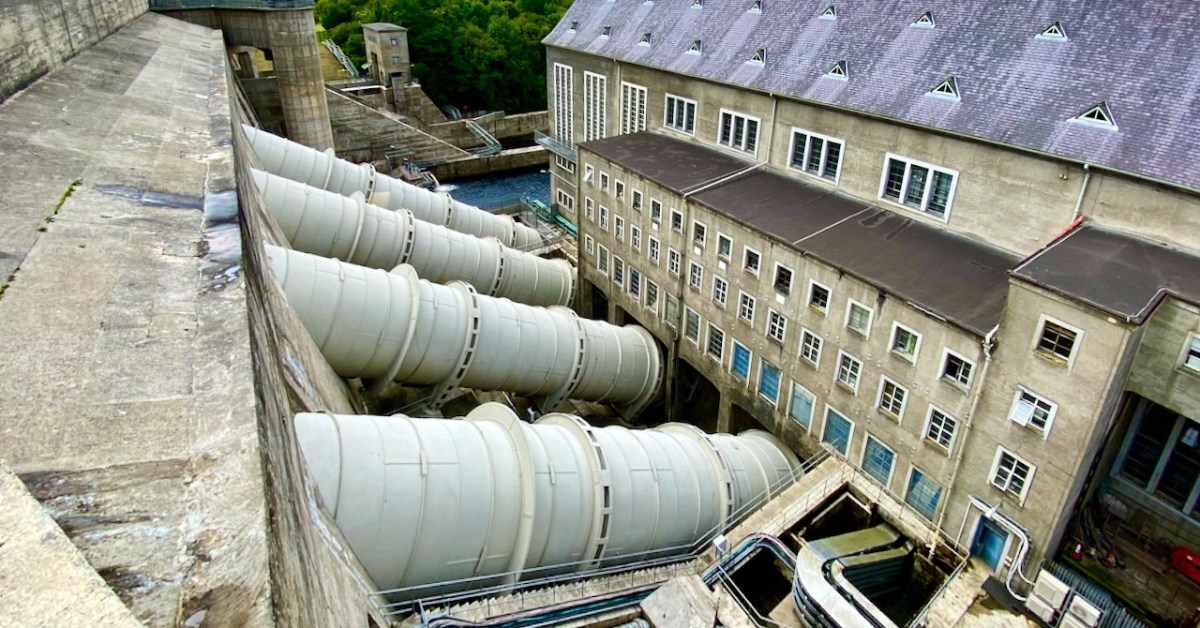
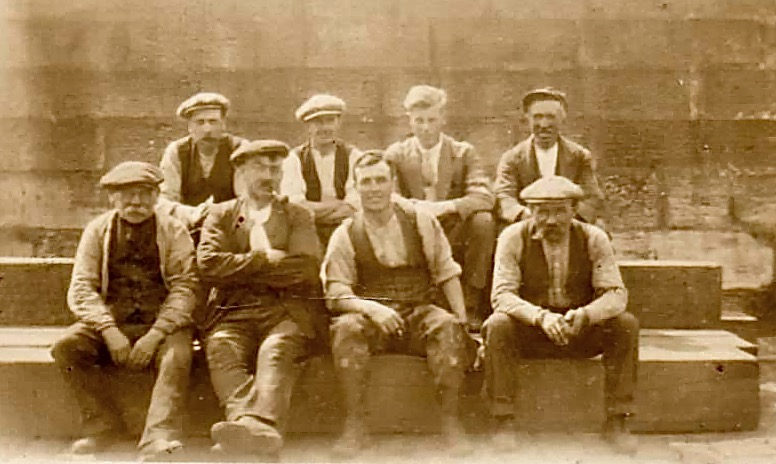
The quarry, of course, is the monumental structure, above, that Robert wrote about in his post Industrial Archaeology in Crookhaven, one of our most popular posts. It seems that anyone who has ever been to Crookhaven has wondered about that wall of concrete across the bay. James also sent me this shot of a group of men who worked at the quarry. Cloth caps and moustaches were the order of the day – except for Allen Tyson – he’s the suited and coiffed individual in the back row.

Once in Crookhaven, Allen met and married Bridget O’Driscoll. They had 5 children, including James’s mother Phyllis, who married Joe Goggin. Joe died not too long ago at the age of 91 and still has a sibling in Clonakilty, James remembers happy family holidays in his Nana’s house, the old Barracks next to the Marconi House in the village. He is full of stories and precious memories.
My father used to row coal to the Fastnet for a shilling or two. He told me of an uncle who used to shoot the sea mines ( like prickly conkers) with a .303 from Carrigeen cliffs off Rock Street. Nana would climb down to the sea for driftwood for the fire into her 70s. I remember the sacred heart picture and light, and the lights would flicker as I believe there was a generator in the village for power. A large old transistor radio in the kitchen with all the valves visible. Cold cupboard (a safe) under the stairs. Soda bread (and marmalade daily made in the range.
James told me several other stories about his father, whom he admired and loved. But he also sent me another gem! A link to a movie, I Thank a Fool, made partly in Crookhaven, and released in 1962. You can watch it here – the Crookhaven parts start around the 1:09 mark and it is a complete nostalgia fest for those of us who love this part of the world. Here are some screen captures.
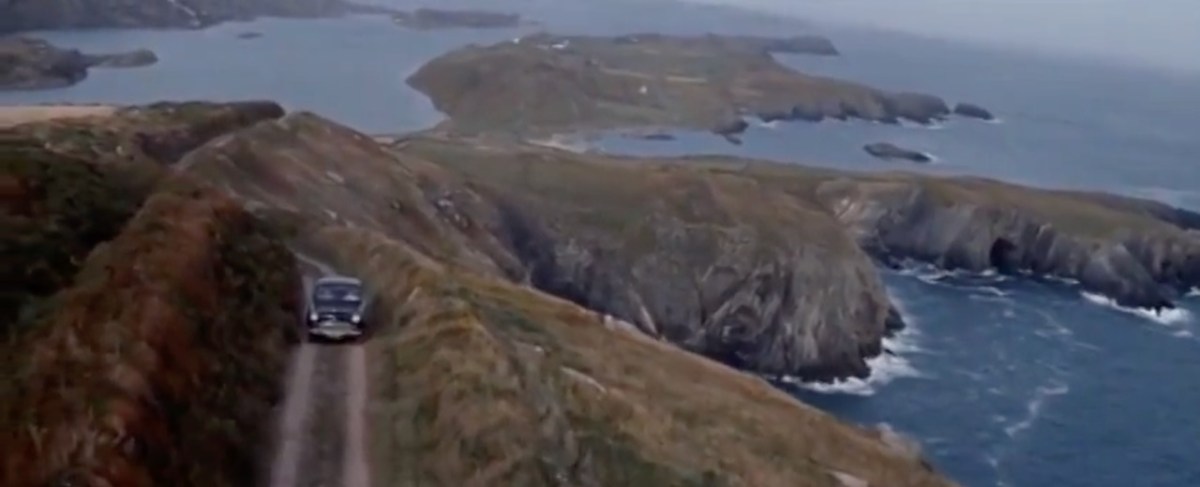

The village is still totally recognisable.
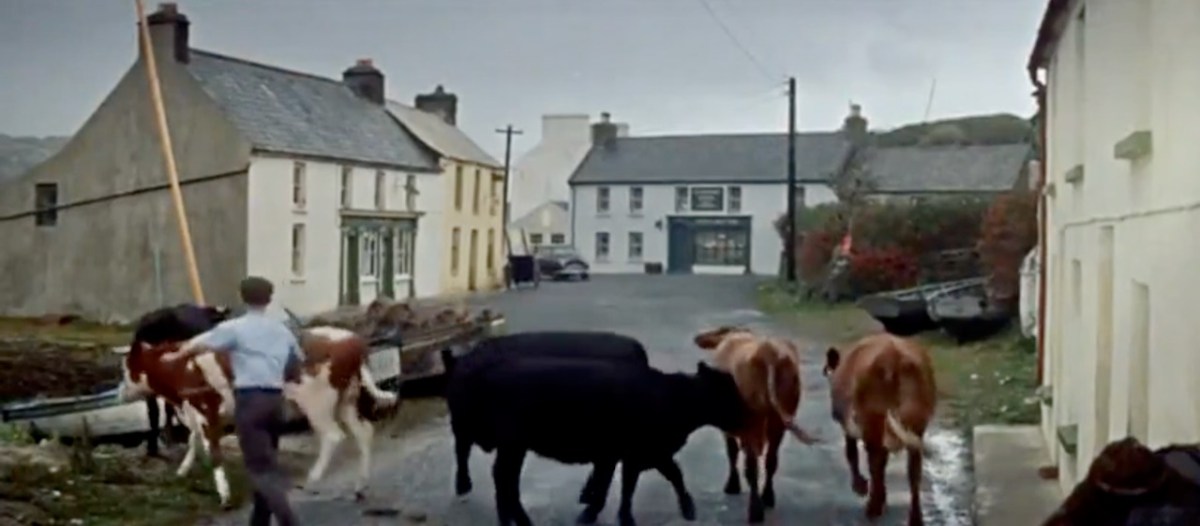

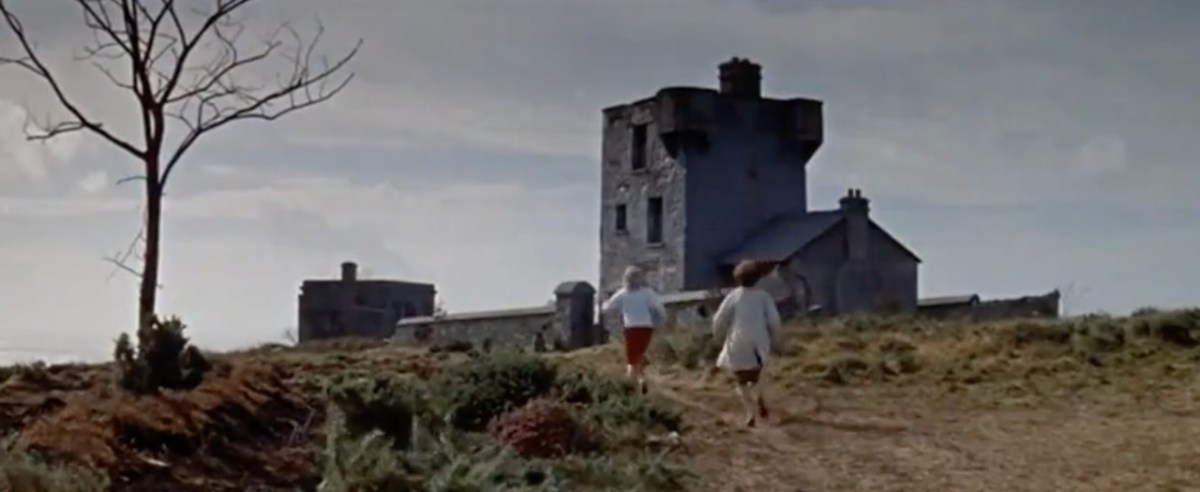
The 1804 Brow Head Signal Station is used as a ‘house’ where some of the action takes place. You can see Marconi’s Wireless Telegraph station in the background. For more on these structures go here for Marconi and here for the Signal Station.

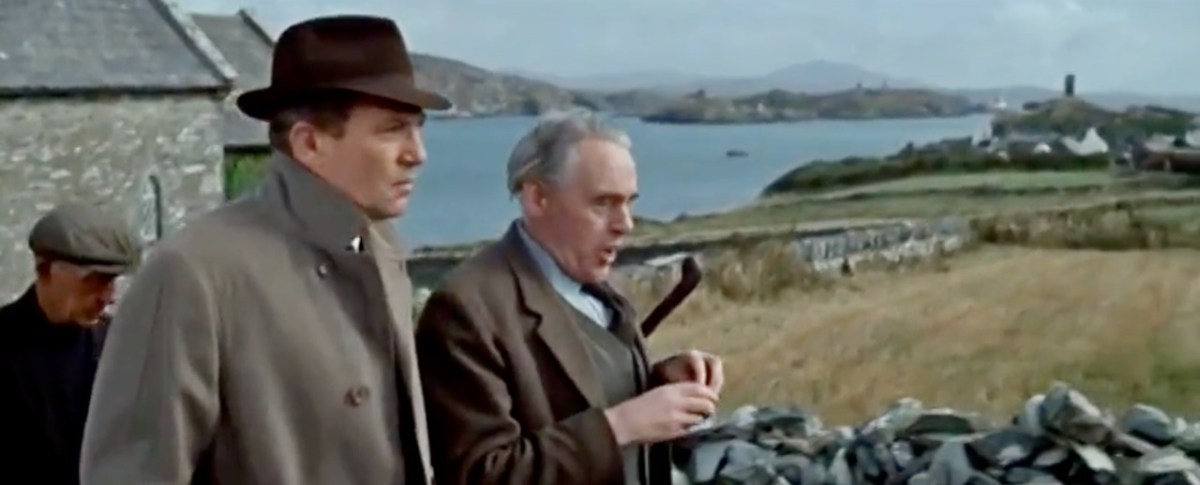
There is also a funeral at St Brendan’s Church. The procession gives us a marvellous opportunity to see back to Crookhaven and the mining magazine that was once clearly visible behind the town, but which is no longer a mark on the landscape. I’ve used that as my feature image at the top of the post, but here’s another take. That’s Peter Finch as the leading man.

I love it when this kind of serendipity happens – thanks again, James. I know that anyone who loves Crookhaven, as we do, will really like this walk through past times.