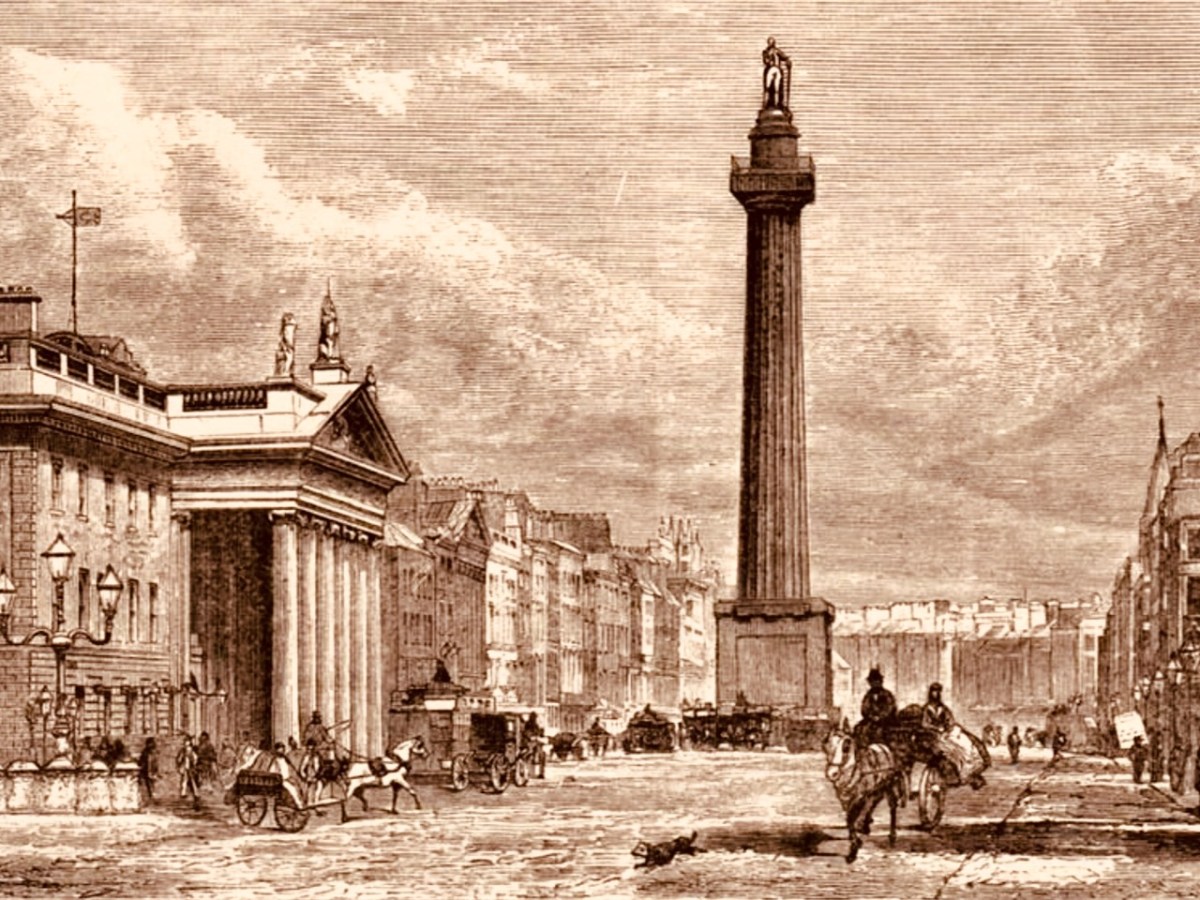In a recent post I gave some examples of public art which can be seen on the railway station at Bray, Co Wicklow. I think this subject deserves a more comprehensive airing, so here we go! Just to recap, murals were originally painted here by Jay Roche and John Carter, who won a competition in 1987. Over the years the paintings deteriorated, and were replaced by the same team – assisted by Anthony Kelly and Eileen Maguire – with a very fine set of tiled murals. I’m recording the rest of these in this post, as I am so impressed by the overall work.
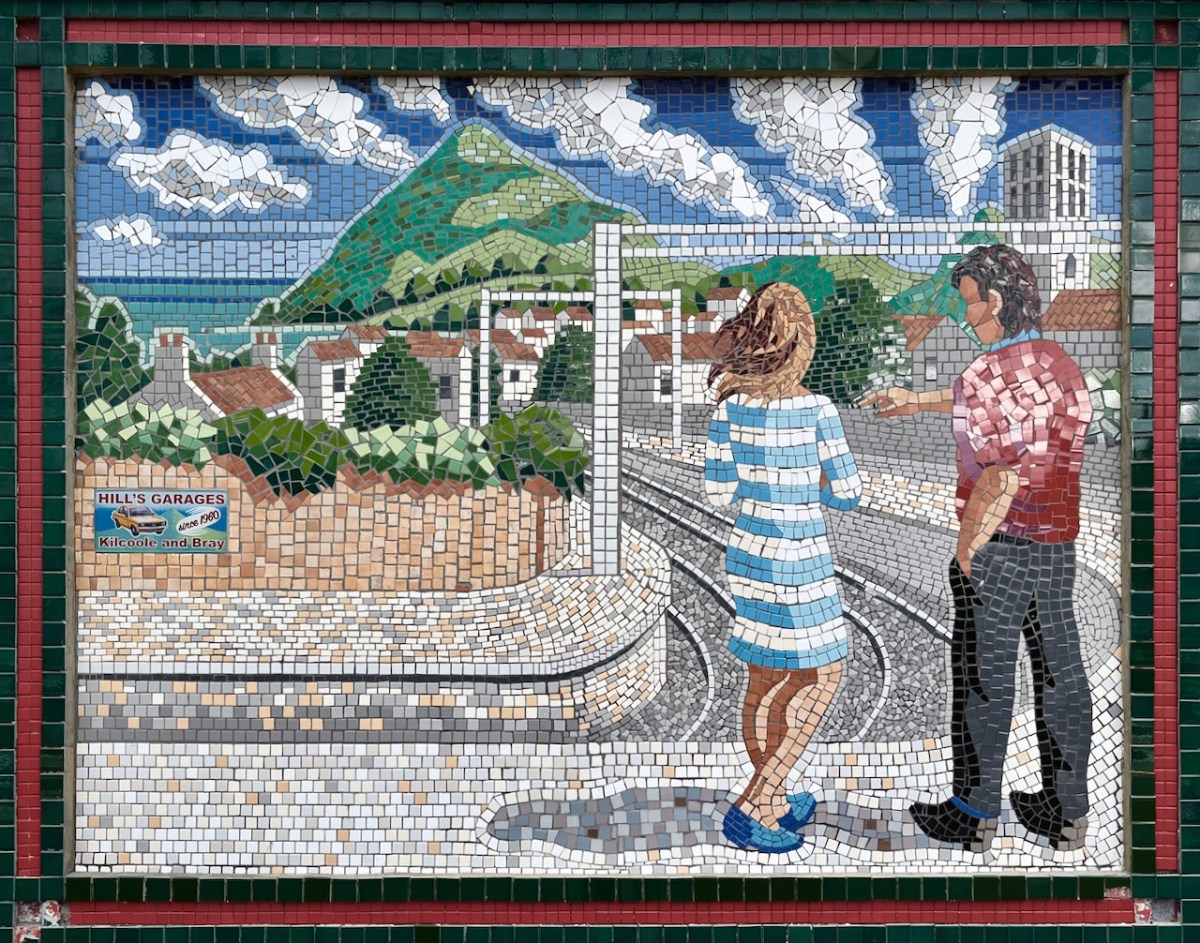

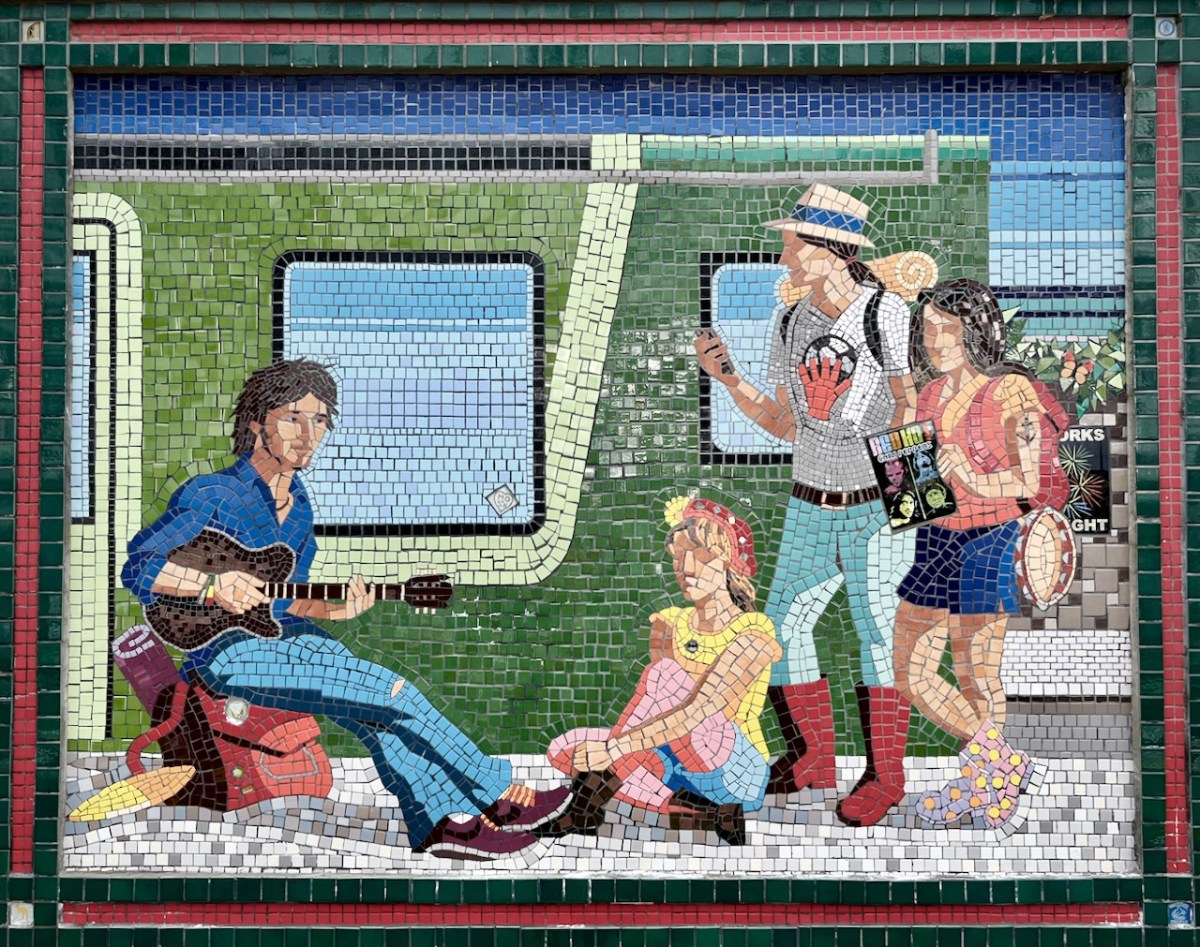
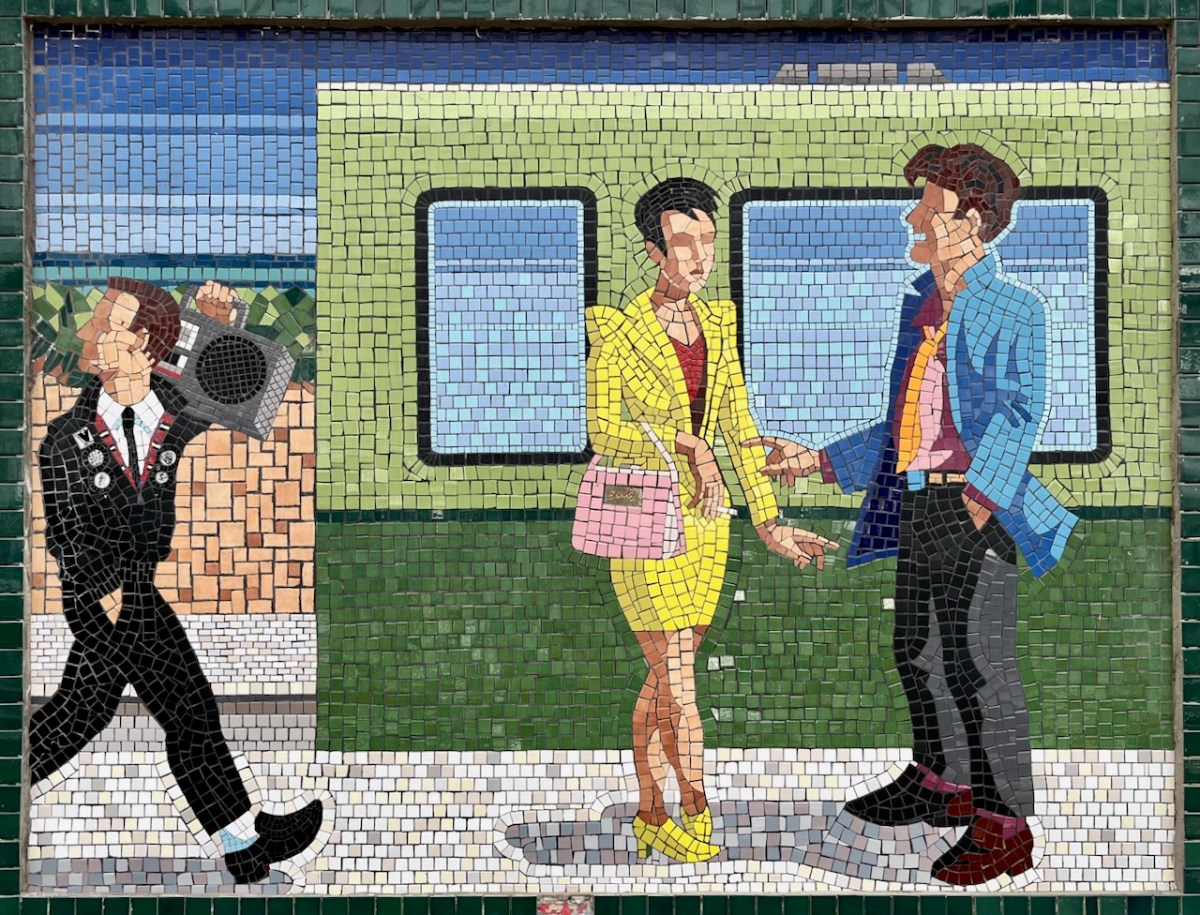
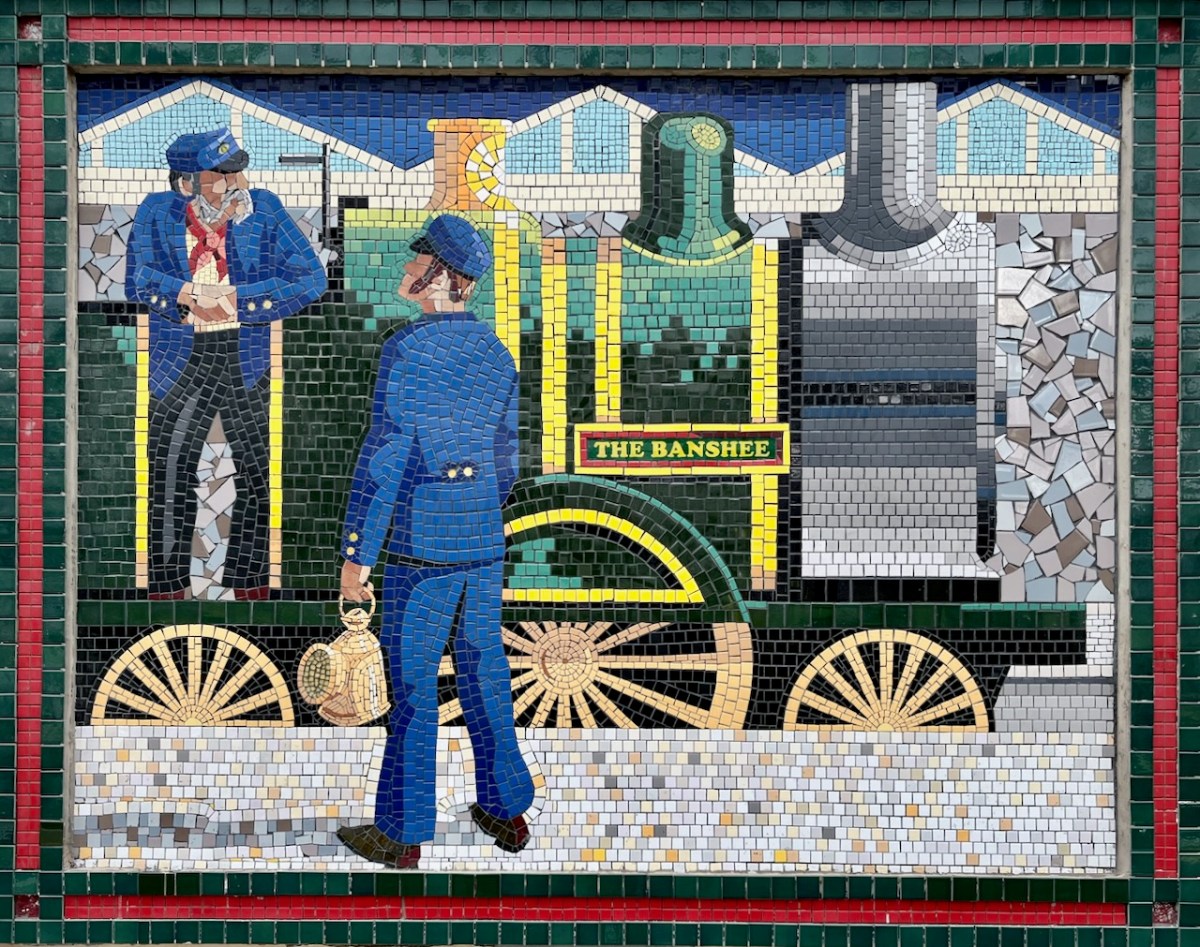
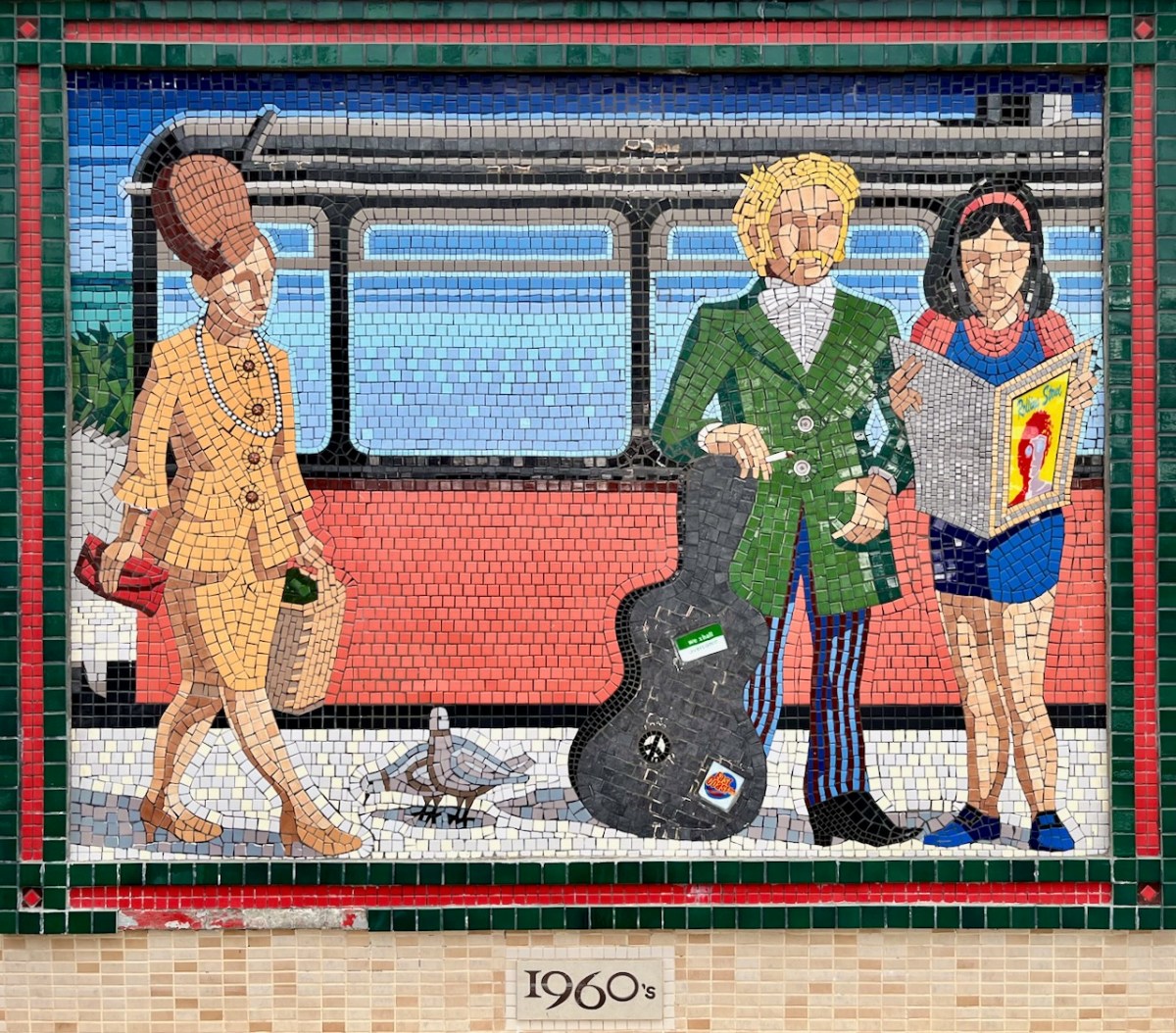
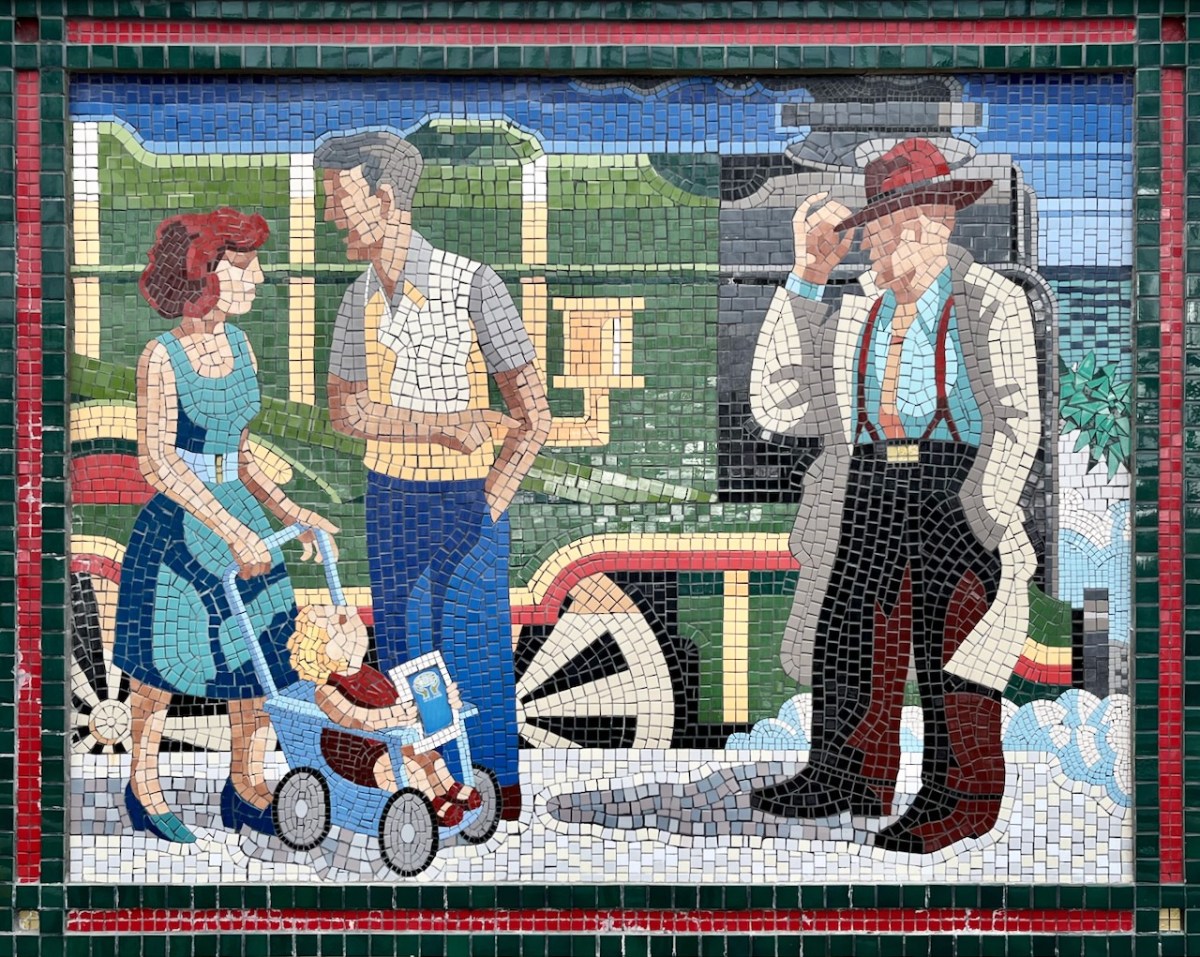
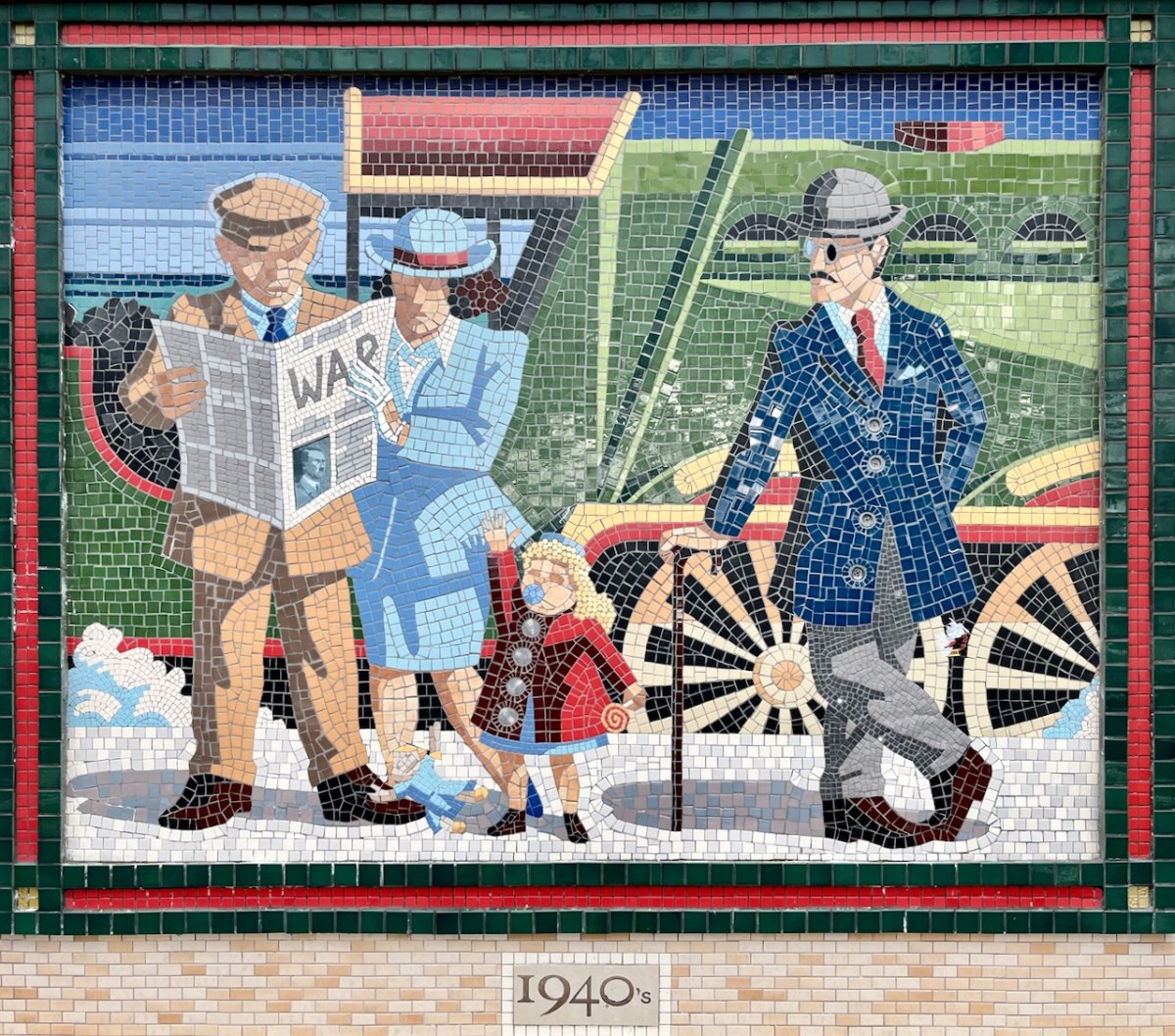
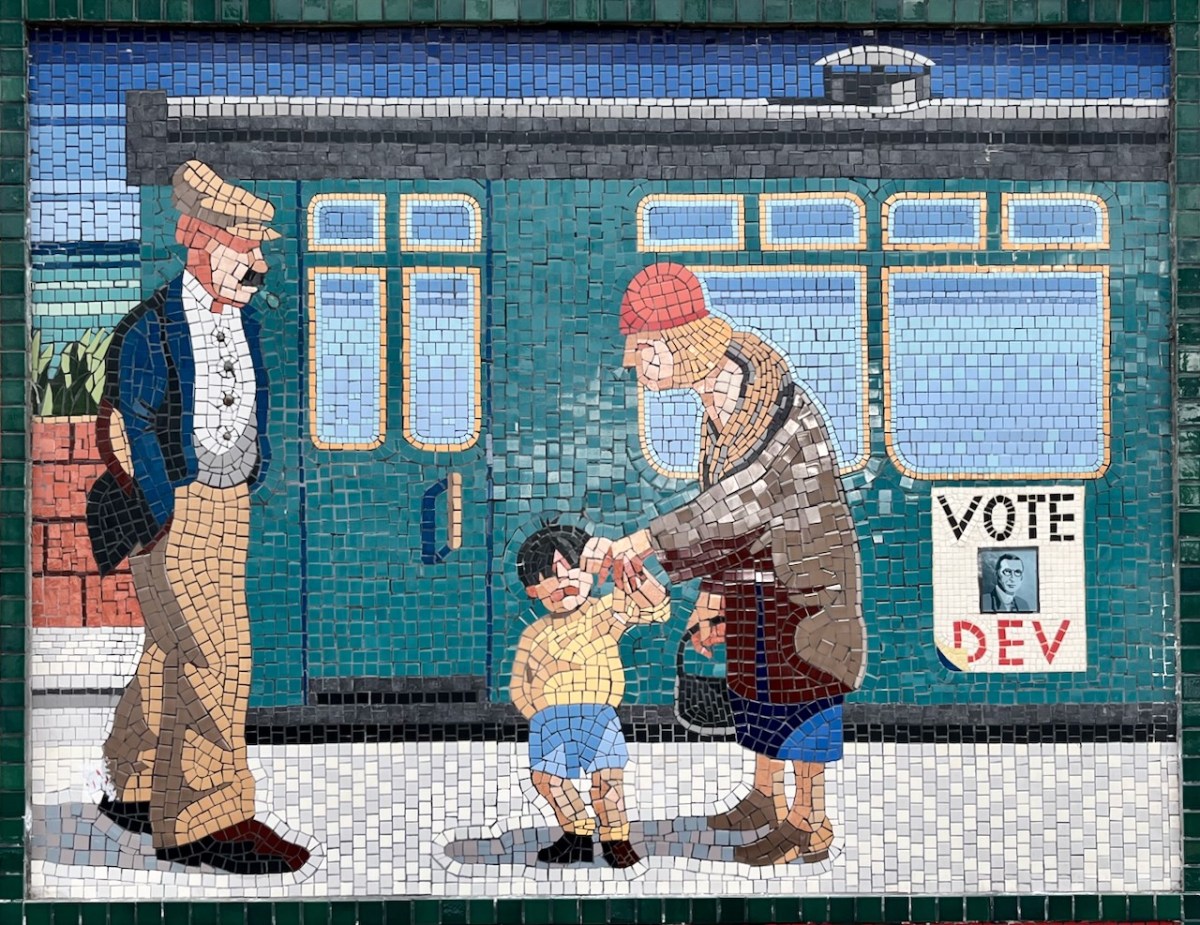
Each panel represents a decade in the line’s history. You’ll have to decide for yourselves which decade is which . . .
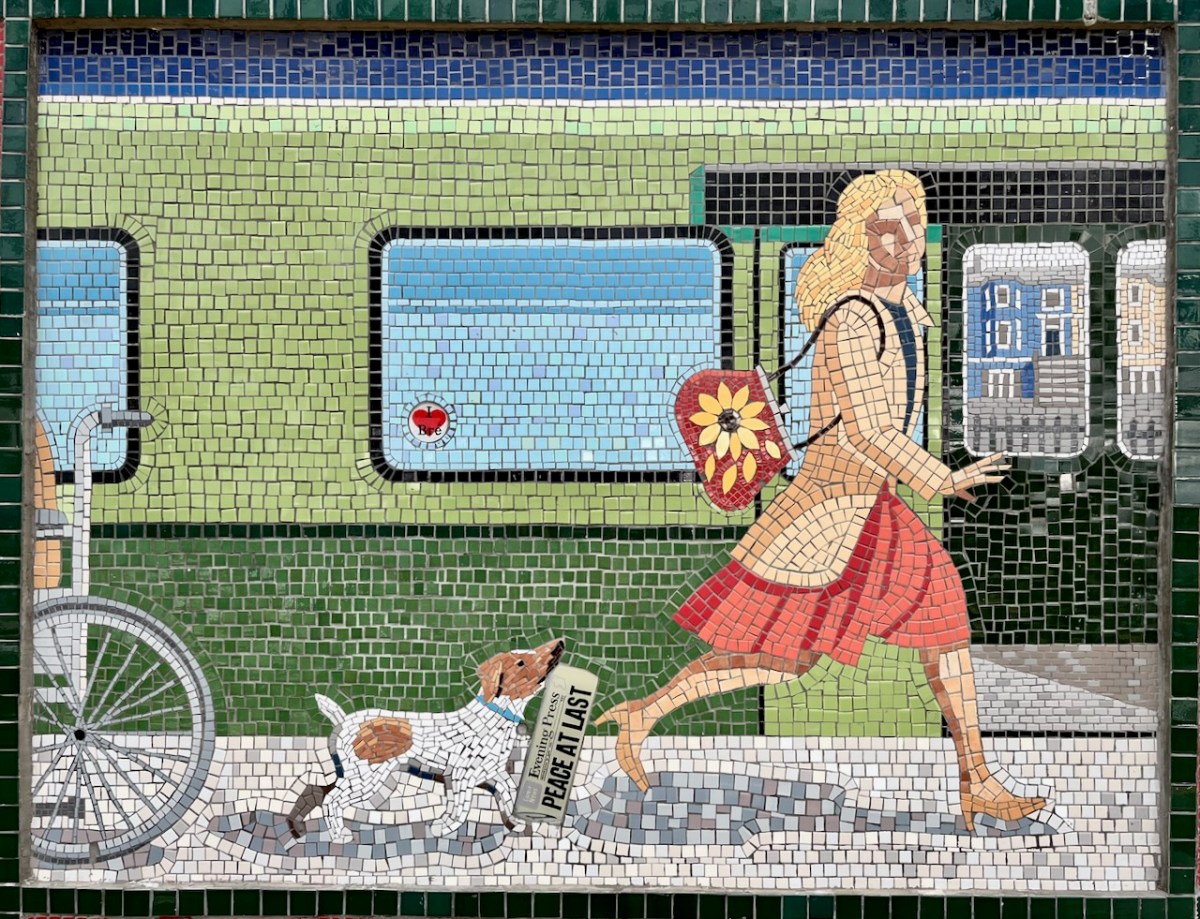


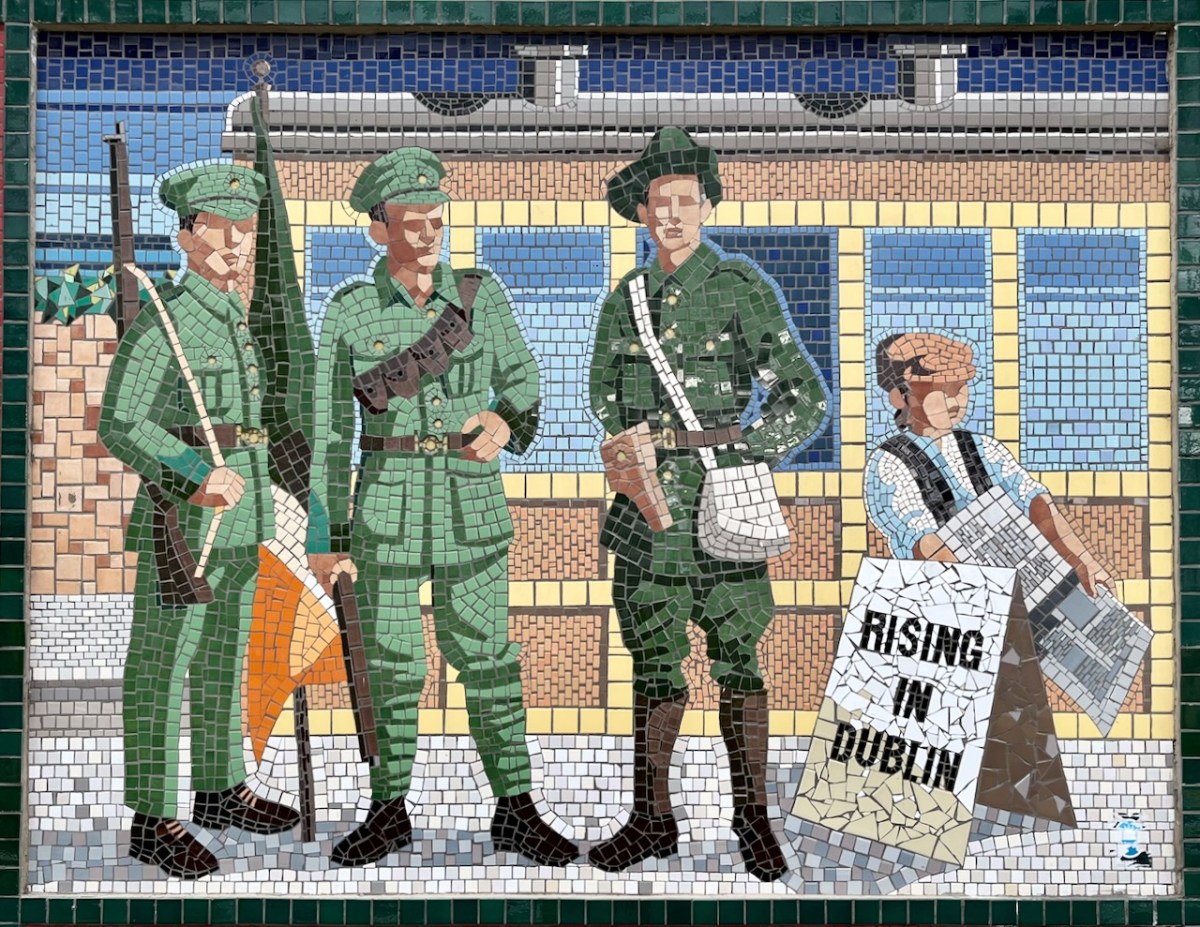
If only that newspaper headline was really true!


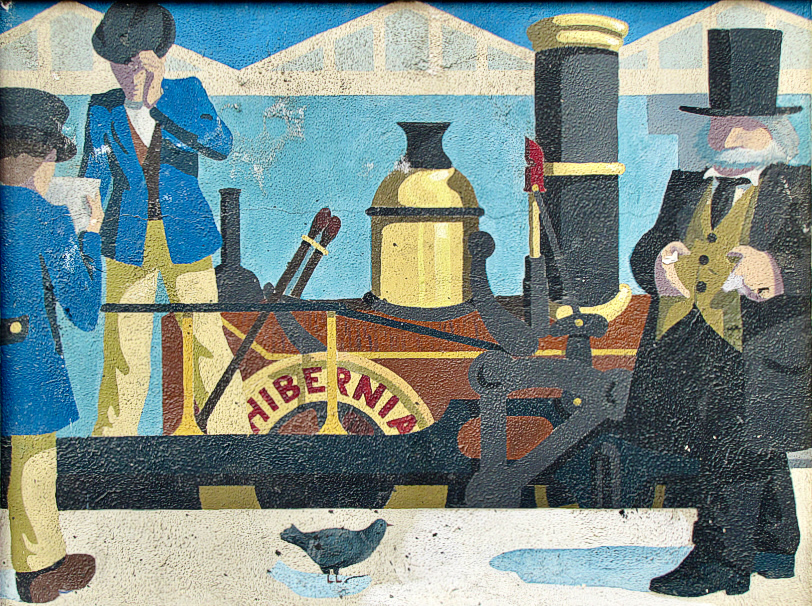
From Wiki Commons 2007: A Panel for Every Decade since 1850s in Bray Railway Station. These are the painted murals.
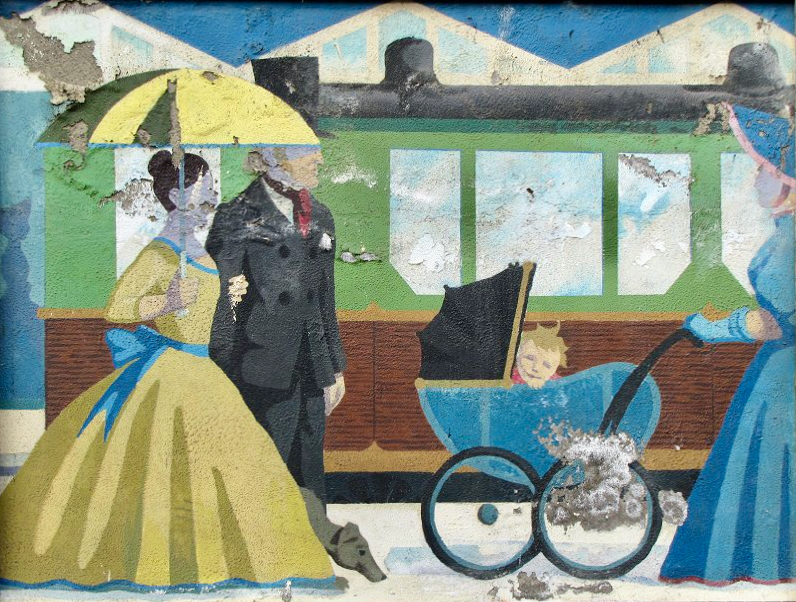


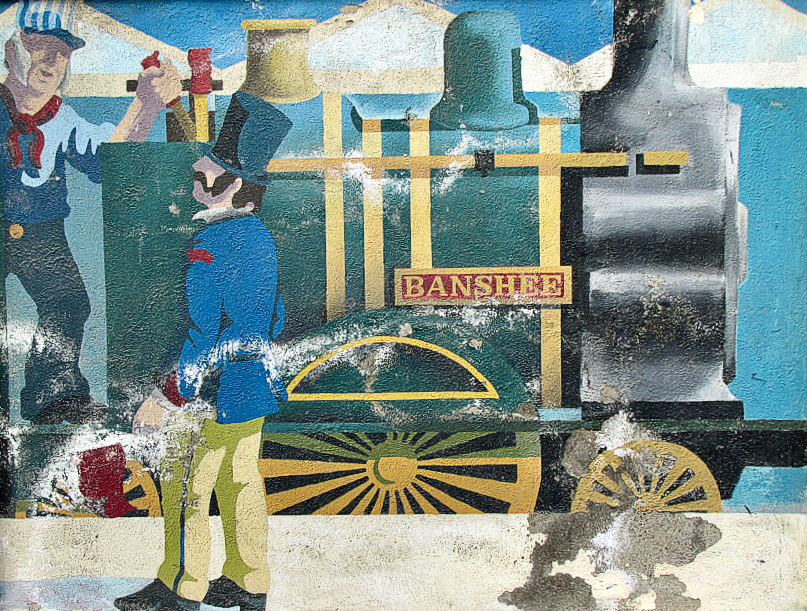
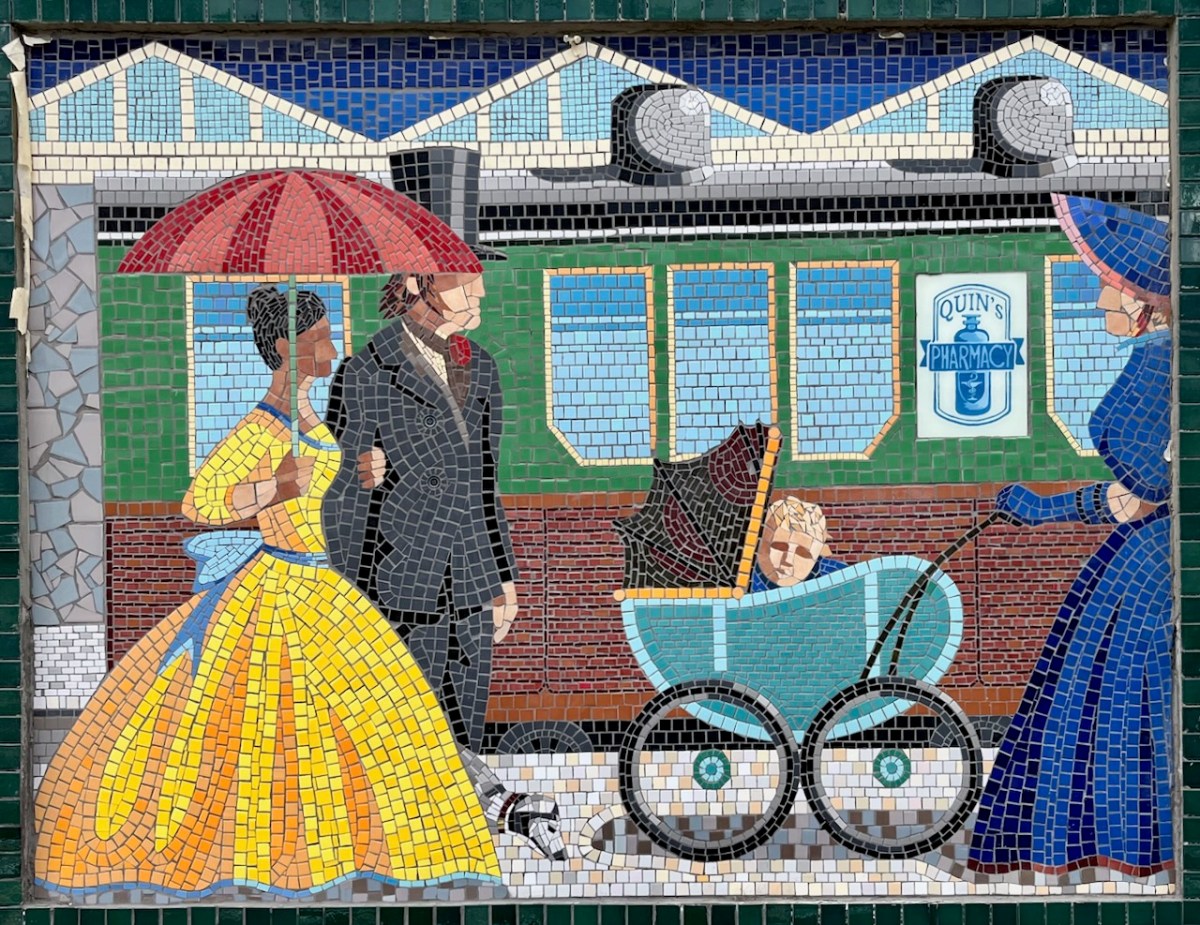
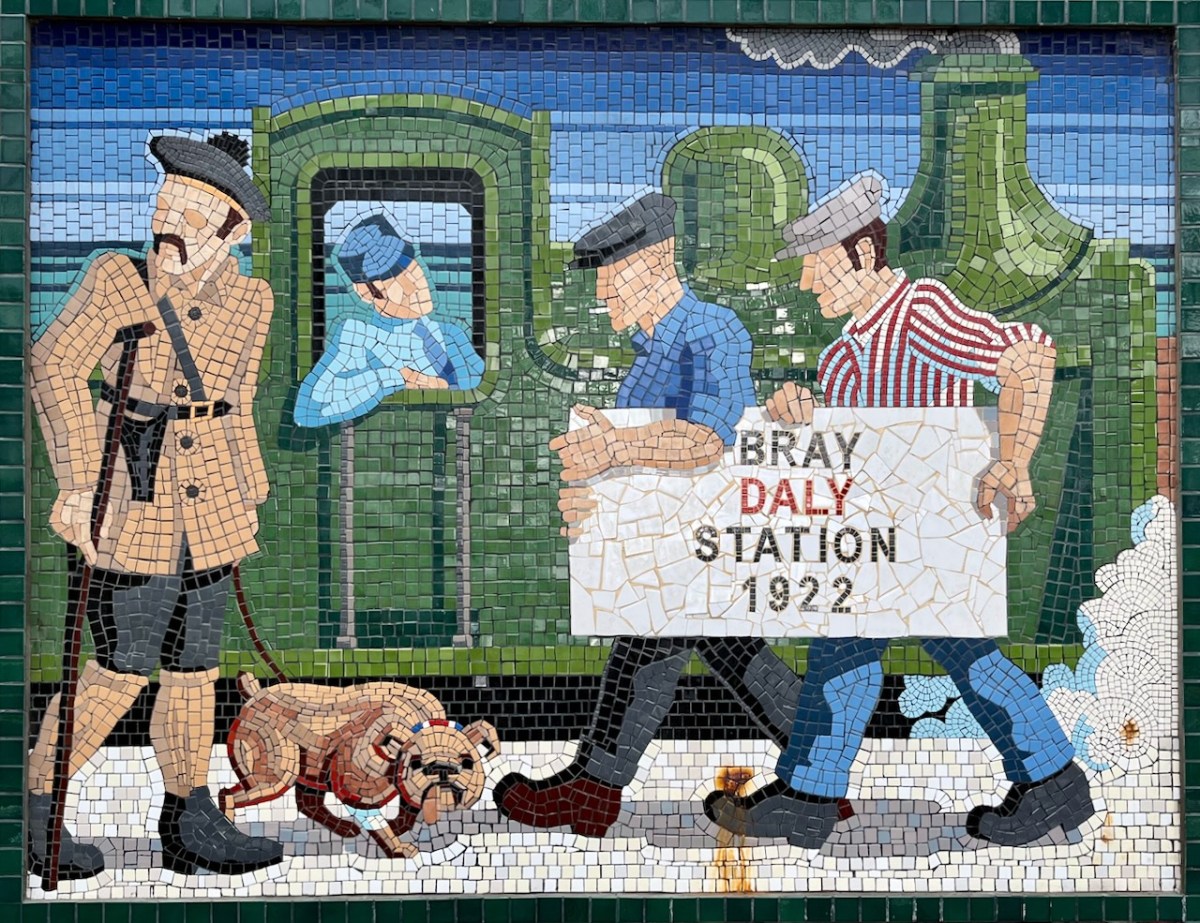
(Above) some of the painted murals in a fairly advanced state of decay: probably early 2000s. The tiled murals are loosely based on the subjects of the originals, but the artists have respected the variations that the change of medium calls out for:

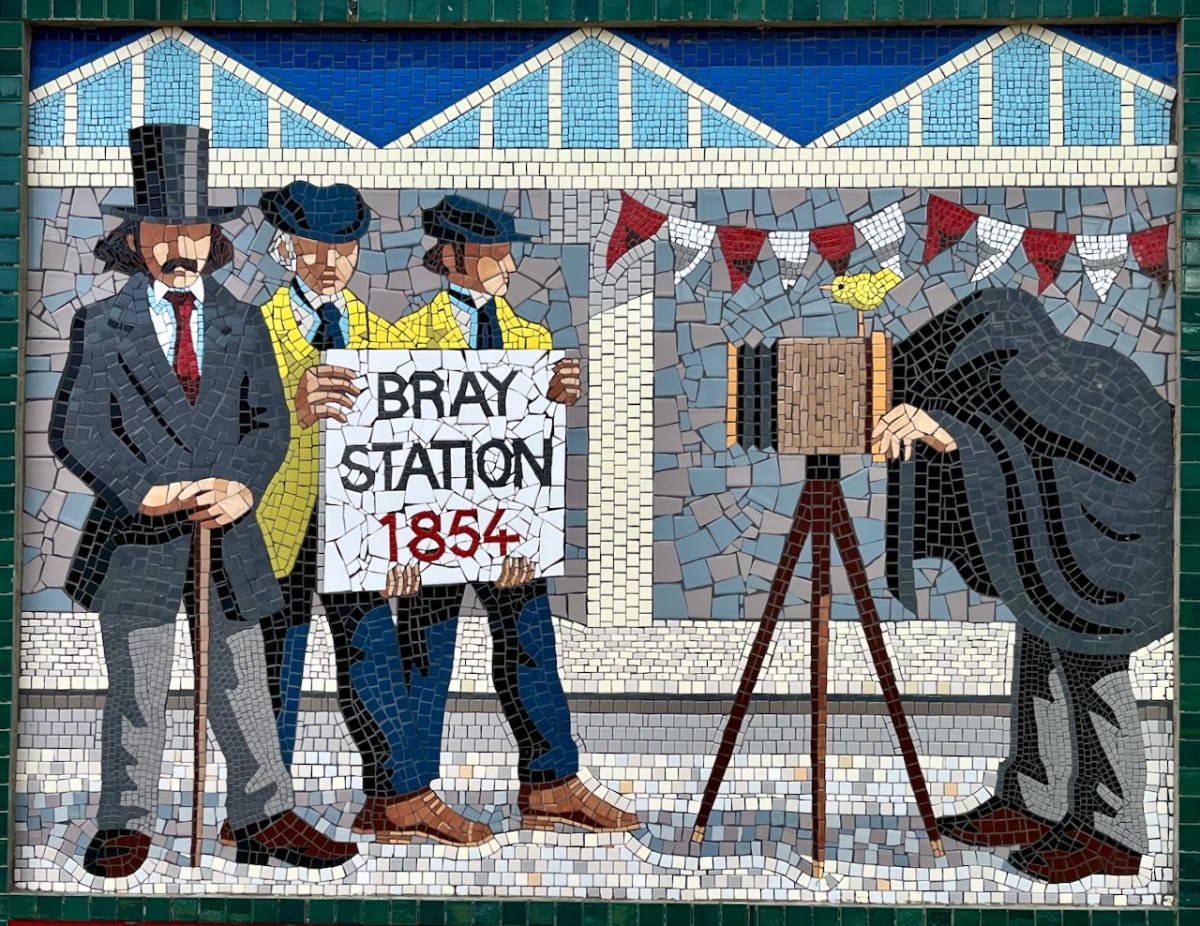
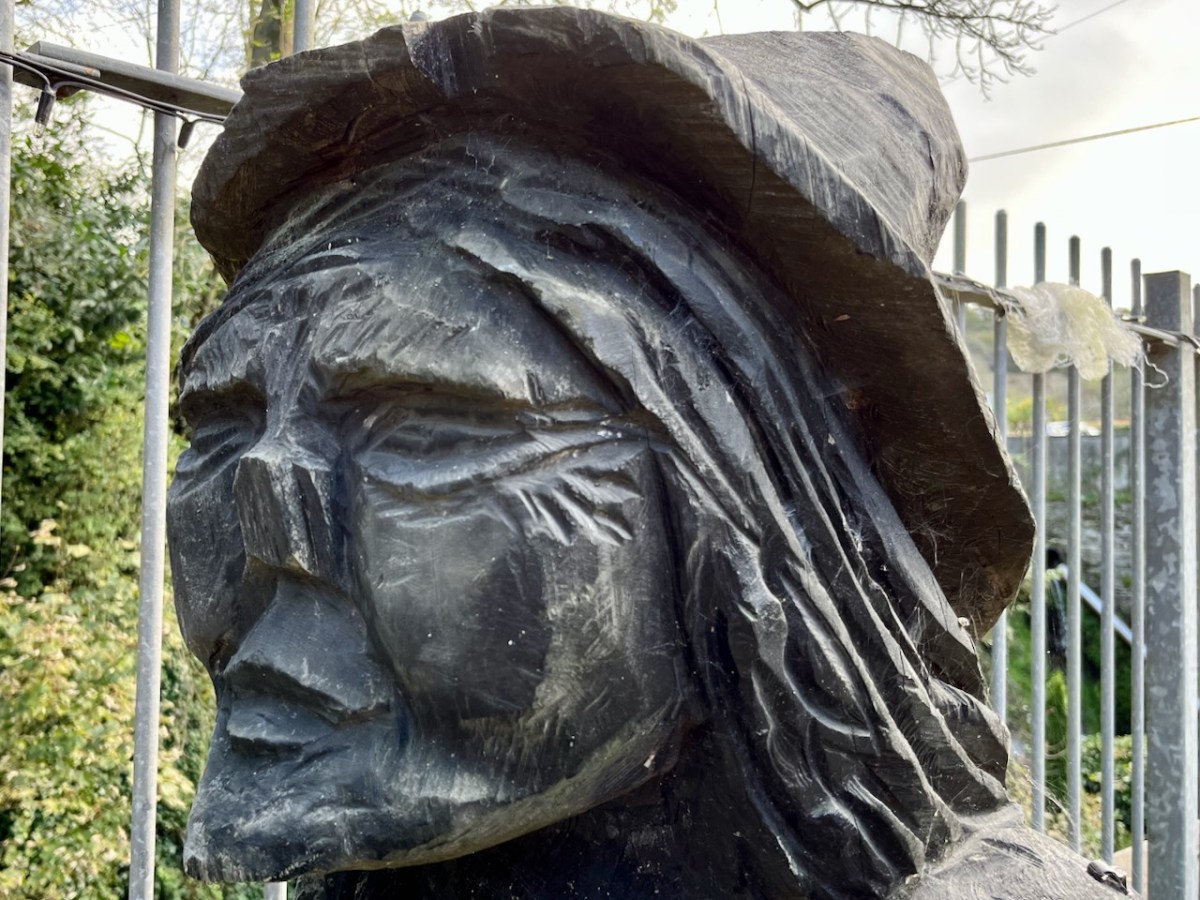
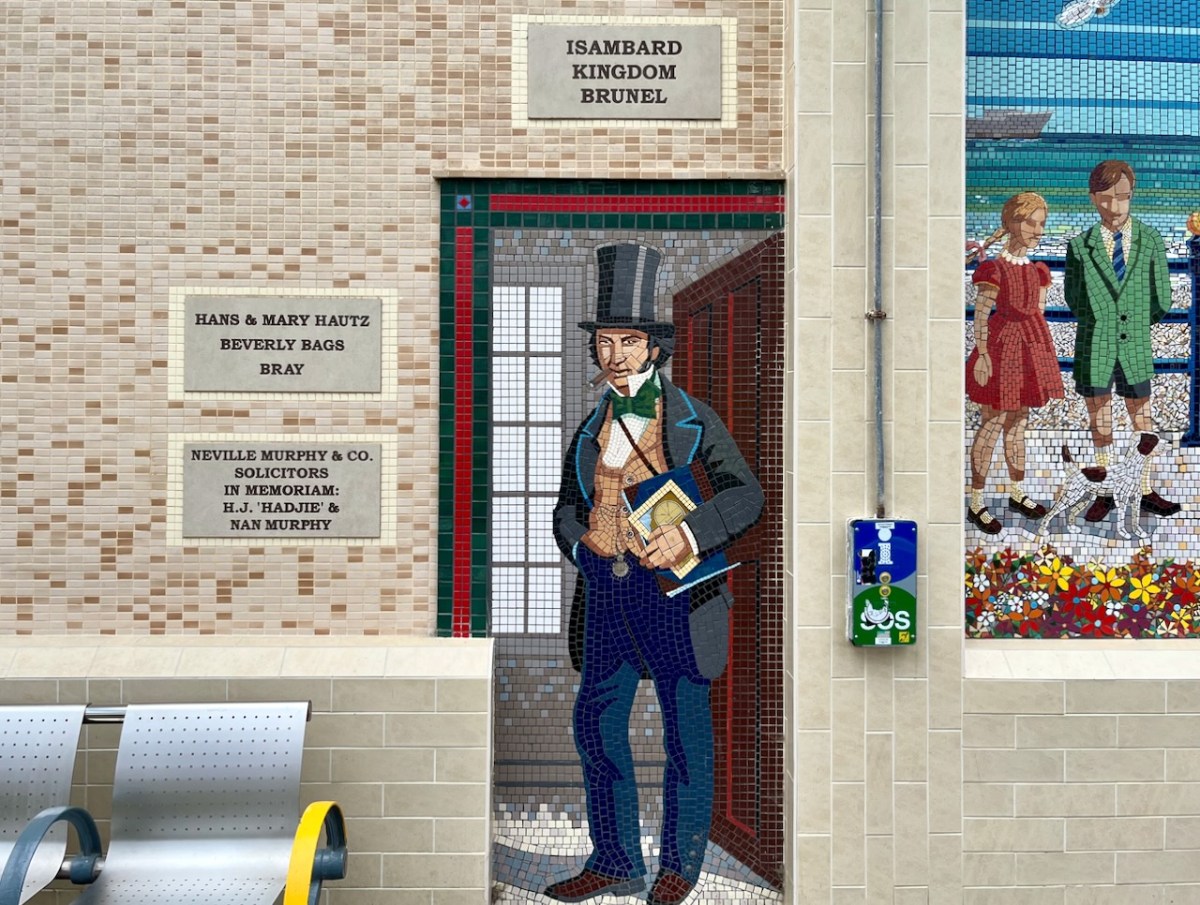
I mentioned – in Taking Notes – that Brunel was responsible for the line that runs through Bray. Here he is, standing on Bray Station:
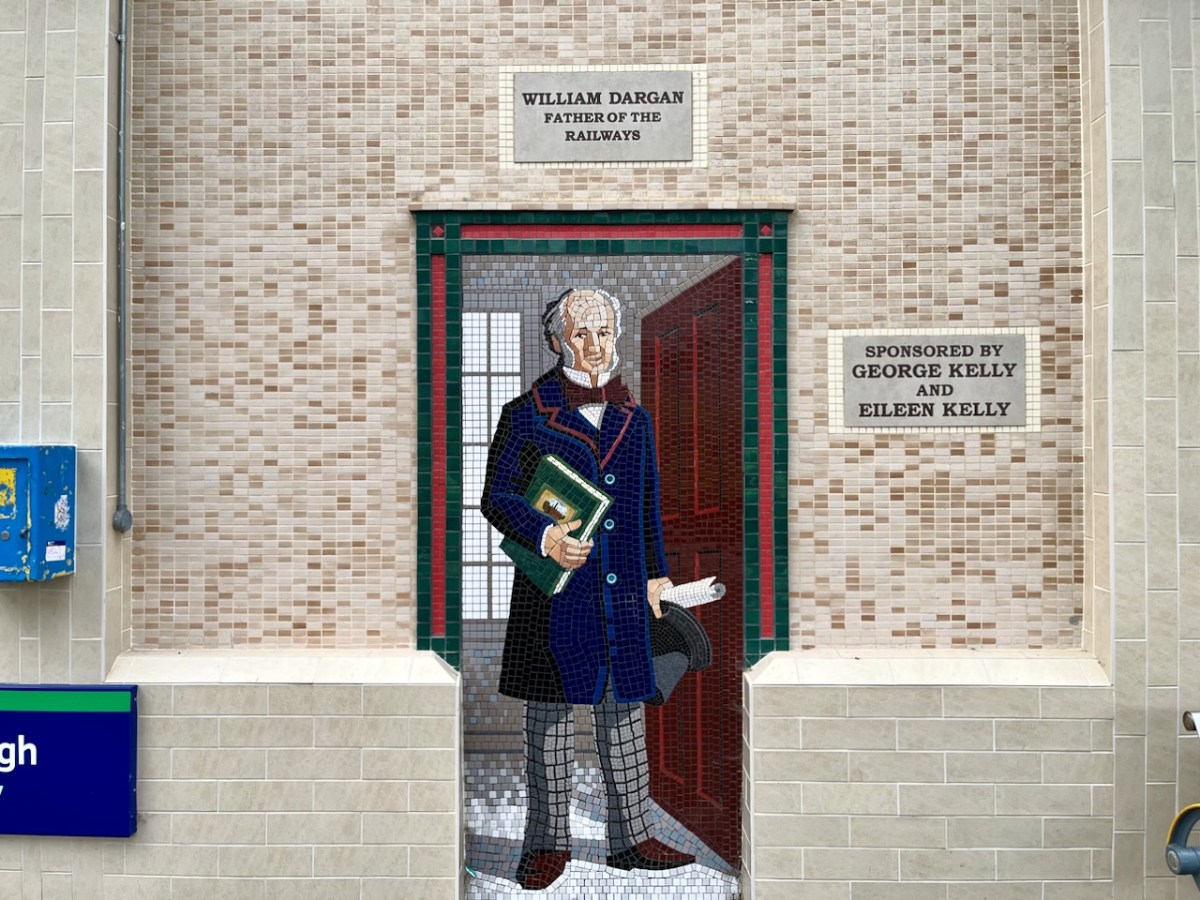


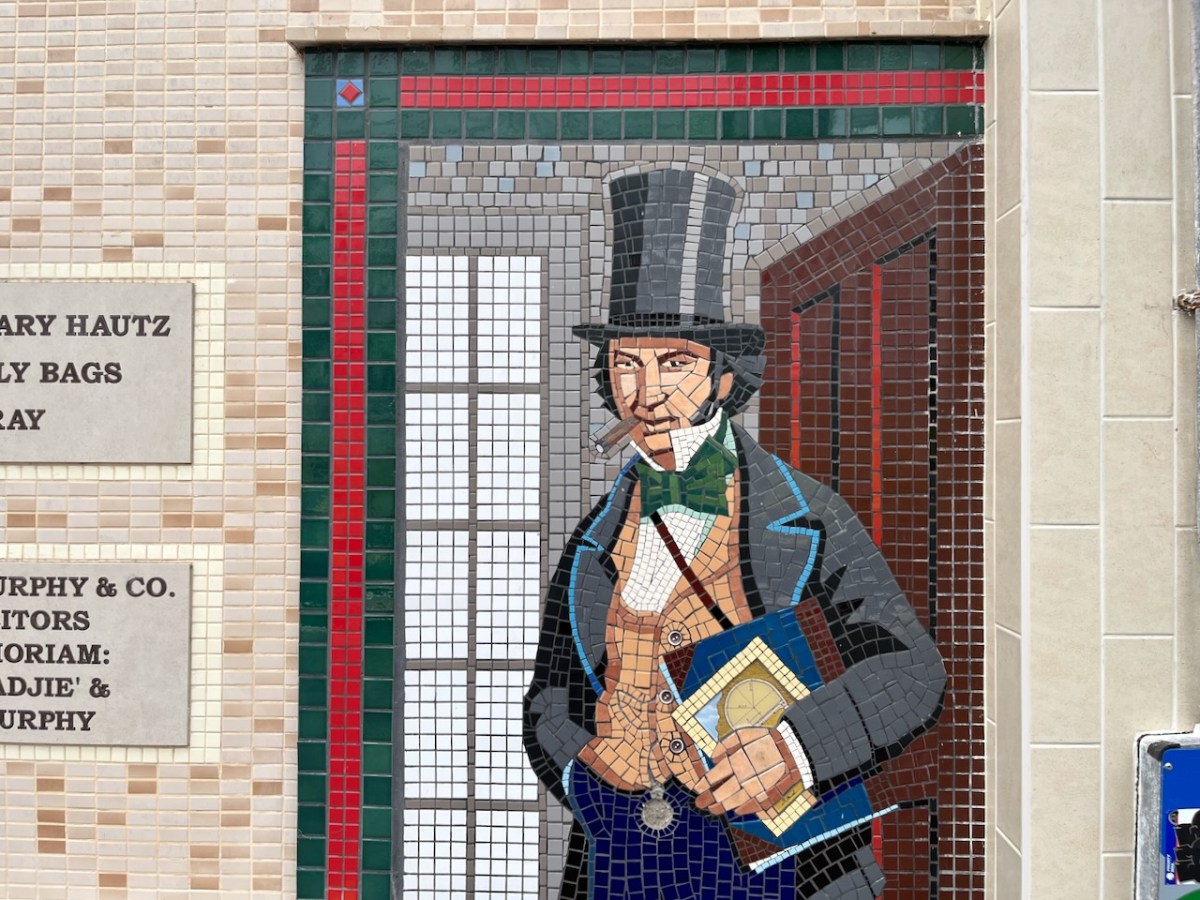
And here (above) – also one of the tiled murals on Bray Station – is a portrait of William Dargan. As you can see – considered ‘Father of the Irish Railways’ – Dargan lived from 1799 to 1867. He engineered over 1300 km of railways in Ireland. Working firstly in the UK he was an assistant to Thomas Telford, and oversaw the construction of roads and canals in the Midlands. He returned to Ireland in the 1820s and took an interest in promoting railways here. The first public commuter railway system in Ireland was designed and built by Dargan: it opened in 1834 and ran between Dublin and Kingstown, now Dún Laoghaire. The line as built was ‘standard gauge’ (ie 1,453mm between rails). This was converted to the ‘Irish standard’ of 1,600mm in 1857. The line extended south to Bray in 1854, and to Greystones the following year.


Isambard Kingdom Brunel, an engineer of Britain’s Great Western Railway, informed the Dublin and Kingstown Railway board that he was planning to build a line into South Wales and start a new sea route from Fishguard to Rosslare. He suggested a joint venture for a line from Wexford to Dublin. A coastal route from Bray (rather than inland) was chosen specifically because it would be scenically attractive for travellers. This led to engineering difficulties including tunnels and retaining structures which are still evolving to this day.


Brunel’s vision of a line going from the capital to Wexford and linking with a service of Irish Sea ferries has been fully realised, and is taken for granted. Let’s hope that this line is maintained and continues on far into the future.
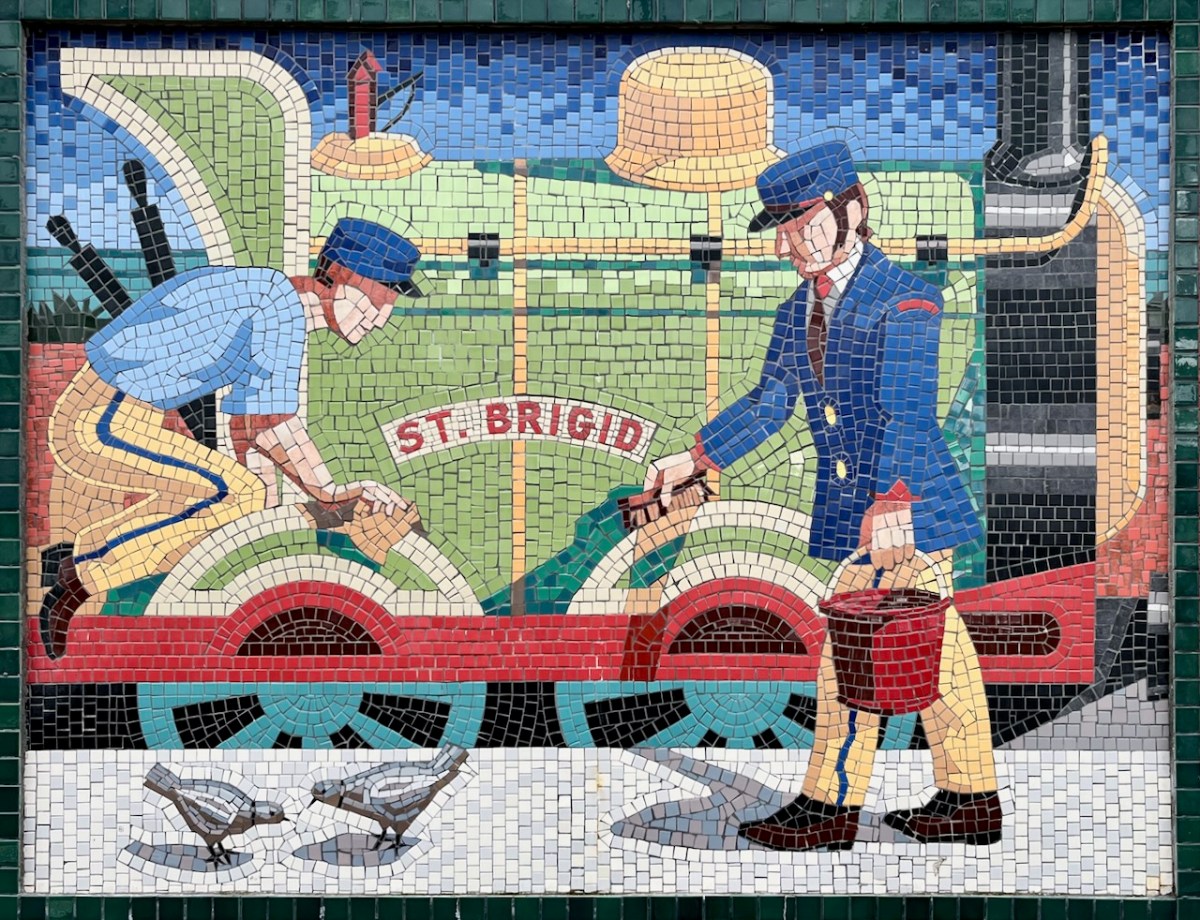
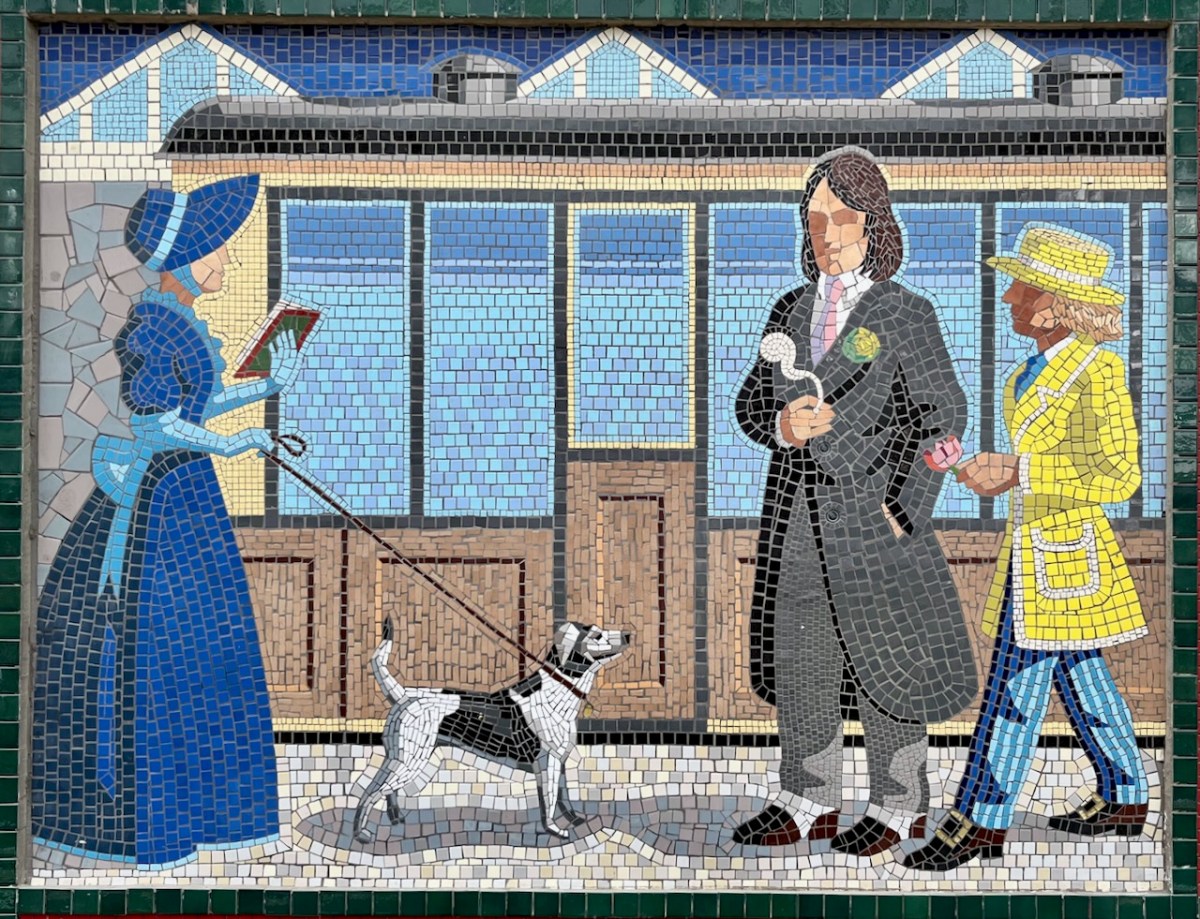


I hope you have noticed how the design of the rolling stock has been changing as we go back through the decades. The representation on these murals is accurate, as far as I can see.
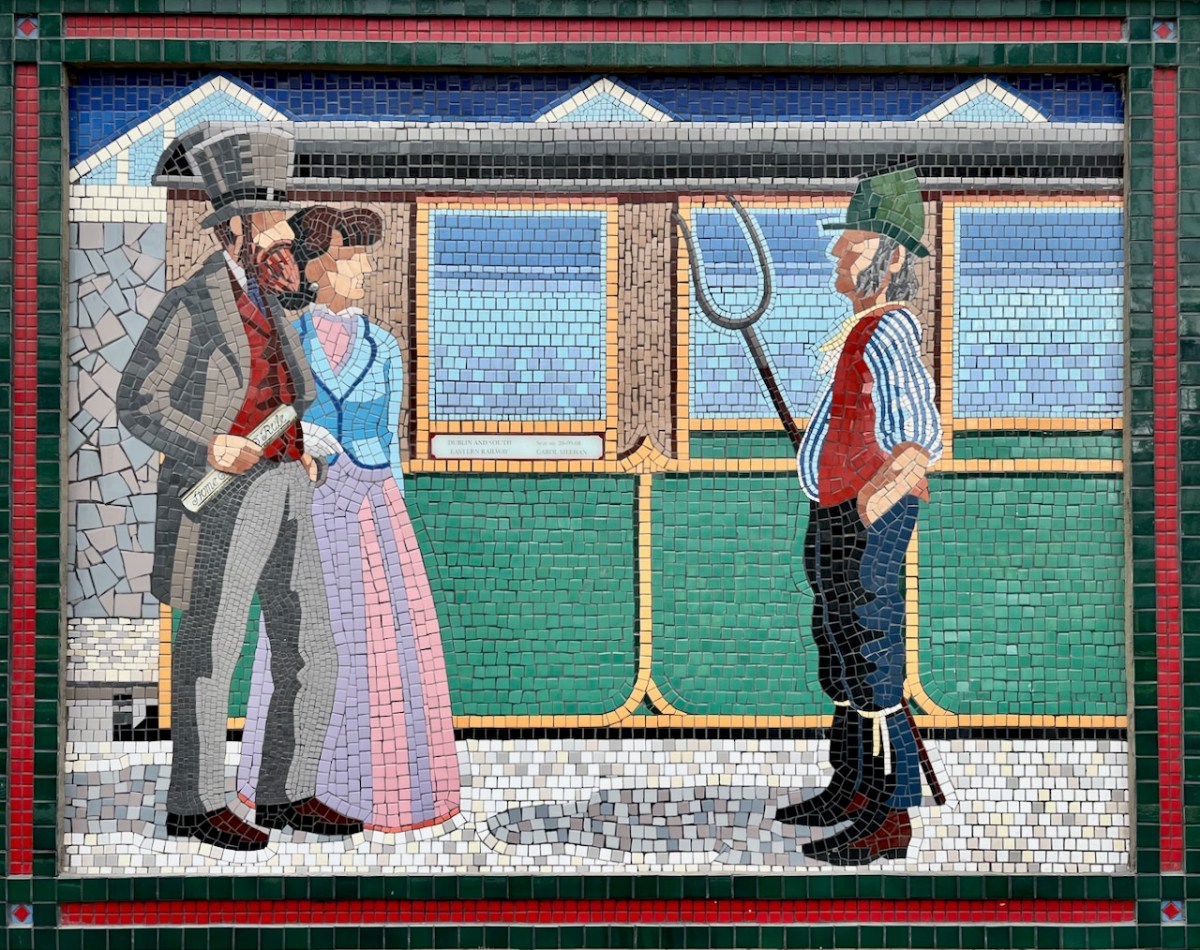
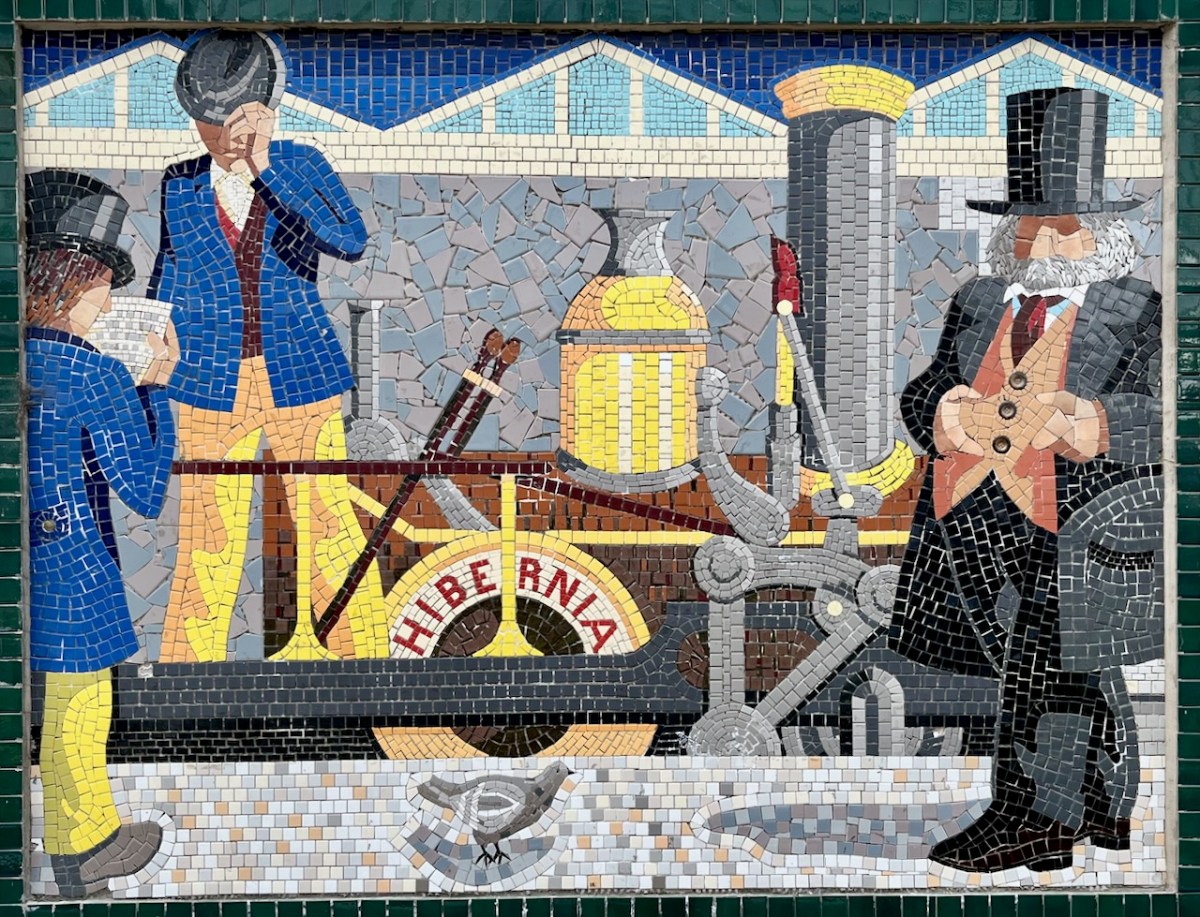


I was sorry to miss the sight of restored steam locomotives and carriages coming through Bray and Greystones on Sunday 24 September this year. Here’s a previous Steam Express visit to Wicklow in 2022 (courtesy Irish Independent):
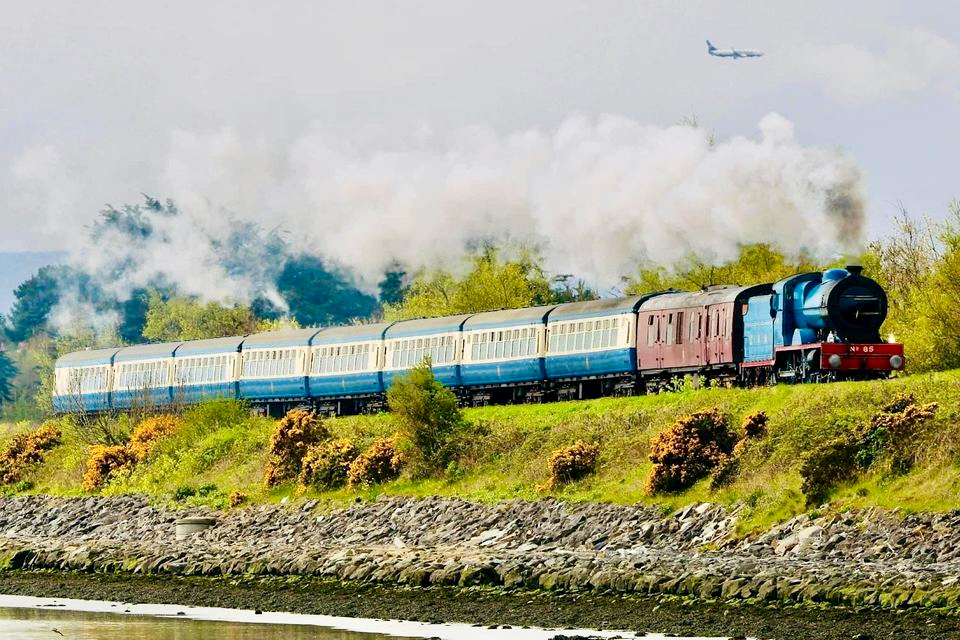

Here in the West we did have some very singular railway lines – look at these posts: The Great Southern Railway: Headford Junction to Kenmare; Aspects of Baltimore; The Flying Snail and Tracking the Trains. Sadly, it’s no longer possible to travel by train in our region: all lines west of Cork City closed on 31 March 1961. Before that you could get to Skibbereen, Ballydehob, and Schull, Bantry and Baltimore and even, on a little branch line, to Timoleague and Courtmacsherry. Don’t we miss those opportunities?