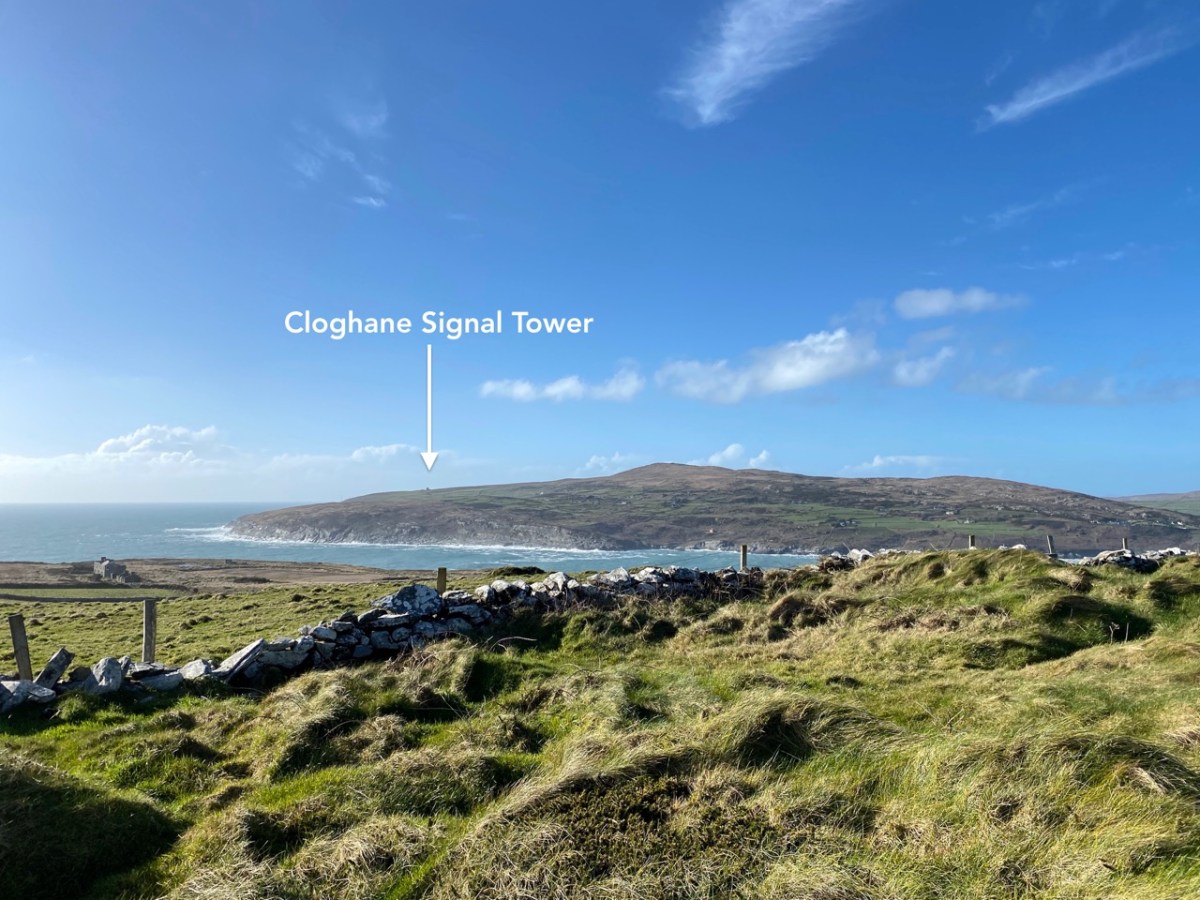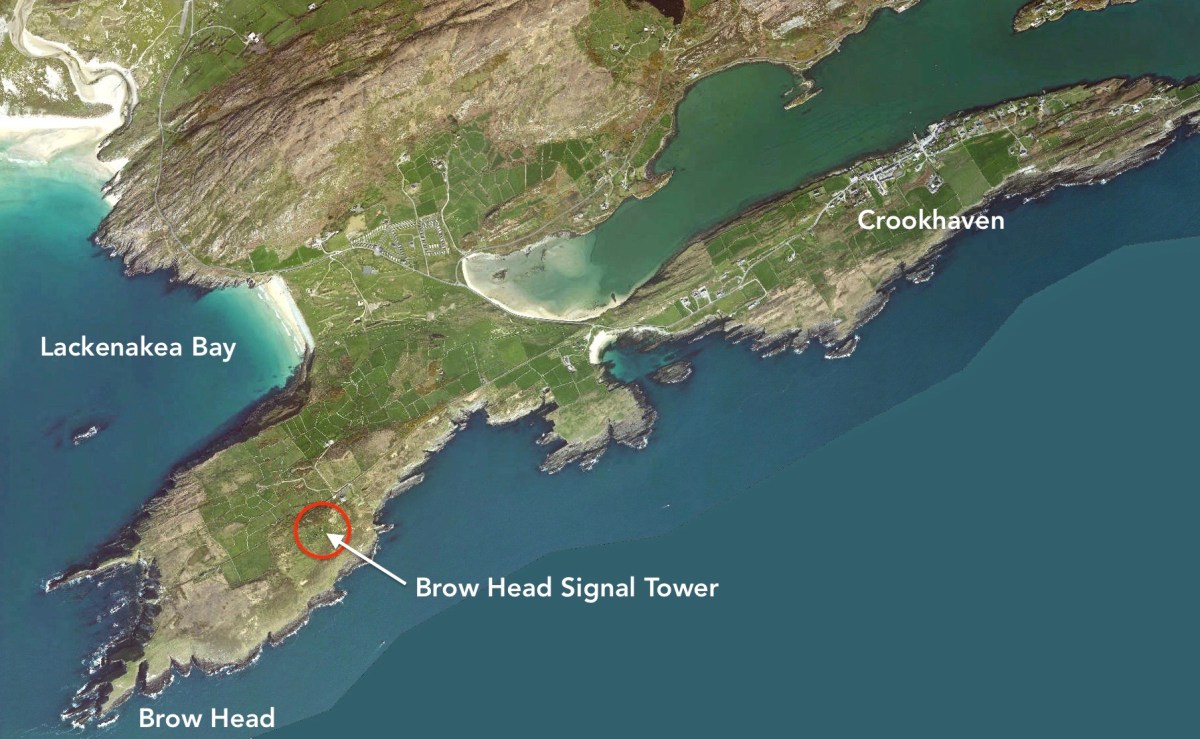
Our readers with good memories may remember a long-running series I penned five years ago, about the canals of Ireland. I revisited that series recently – for a Trasna na Tíre talk* – and realised that I had left it incomplete back in 2017! What better time to finish off the journey than now – when we can only travel outside our lockdown limits through virtual technology?

In 2016 Finola and I explored part of the Irish canal system, following in the footsteps of Tom and Angela Rolt who had voyaged the same way exactly 70 years before, in 1946. They were pioneers in their day, as boating for ‘pleasure’ on the canals was rare. In their book Green & Silver they also managed to capture, in words and photographs, the essence of a decaying transport system in Ireland immediately following WWII, and our travels tried to give an impression of the considerable transformation of inland waterways in Ireland since their time. We traversed, on road and on foot, their voyage around the Shannon Navigation, and the Grand and Royal Canals.
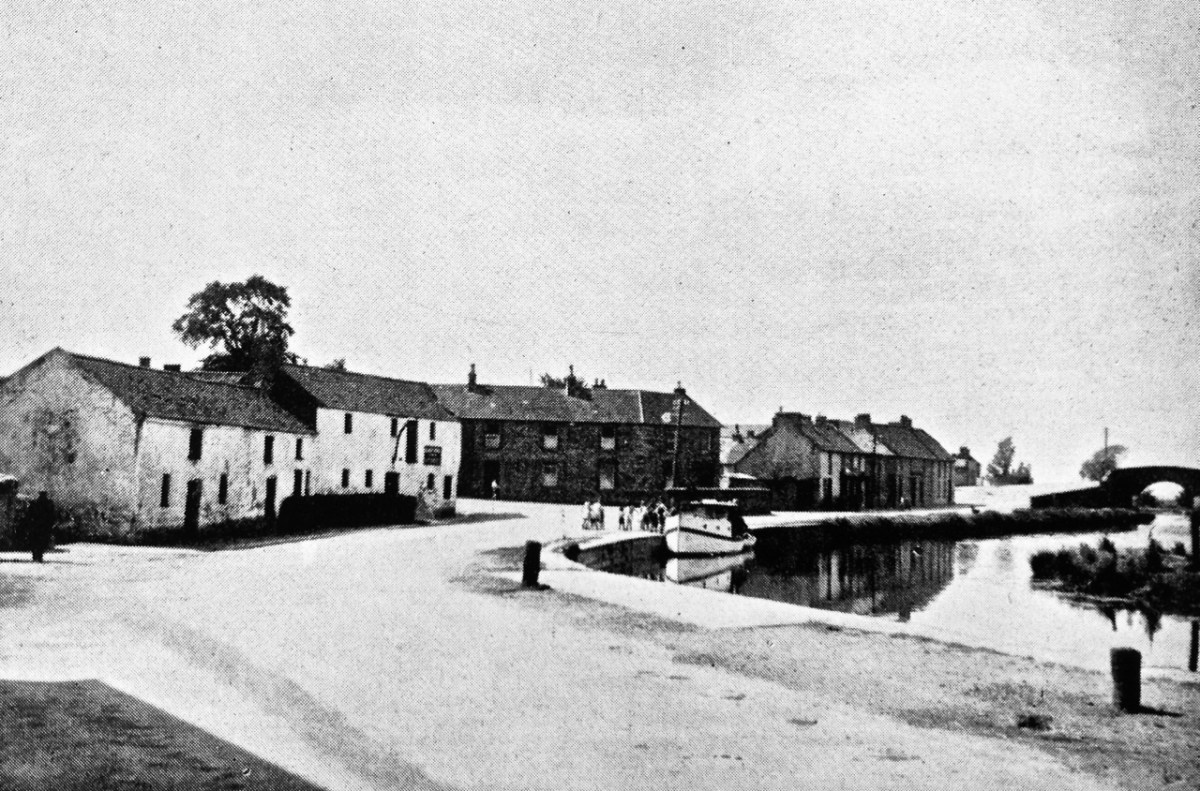


The upper photograph was taken by Angela Rolt in 1946: it shows the Rolt’s boat moored up in sleepy Robertstown (Grand Canal), receiving the attentions of a crowd of small children who had never seen a pleasure cruiser before. Below that is the photo of Robertstown we took in 2016, seventy years later. Our own travels in that year, however, omitted the Rolt’s journey through Dublin, when they had to pass across the Liffey and Dublin Port to get from the Grand Canal to the Royal Canal. The header is an extract from a 19th century map of the docks area in Dublin.
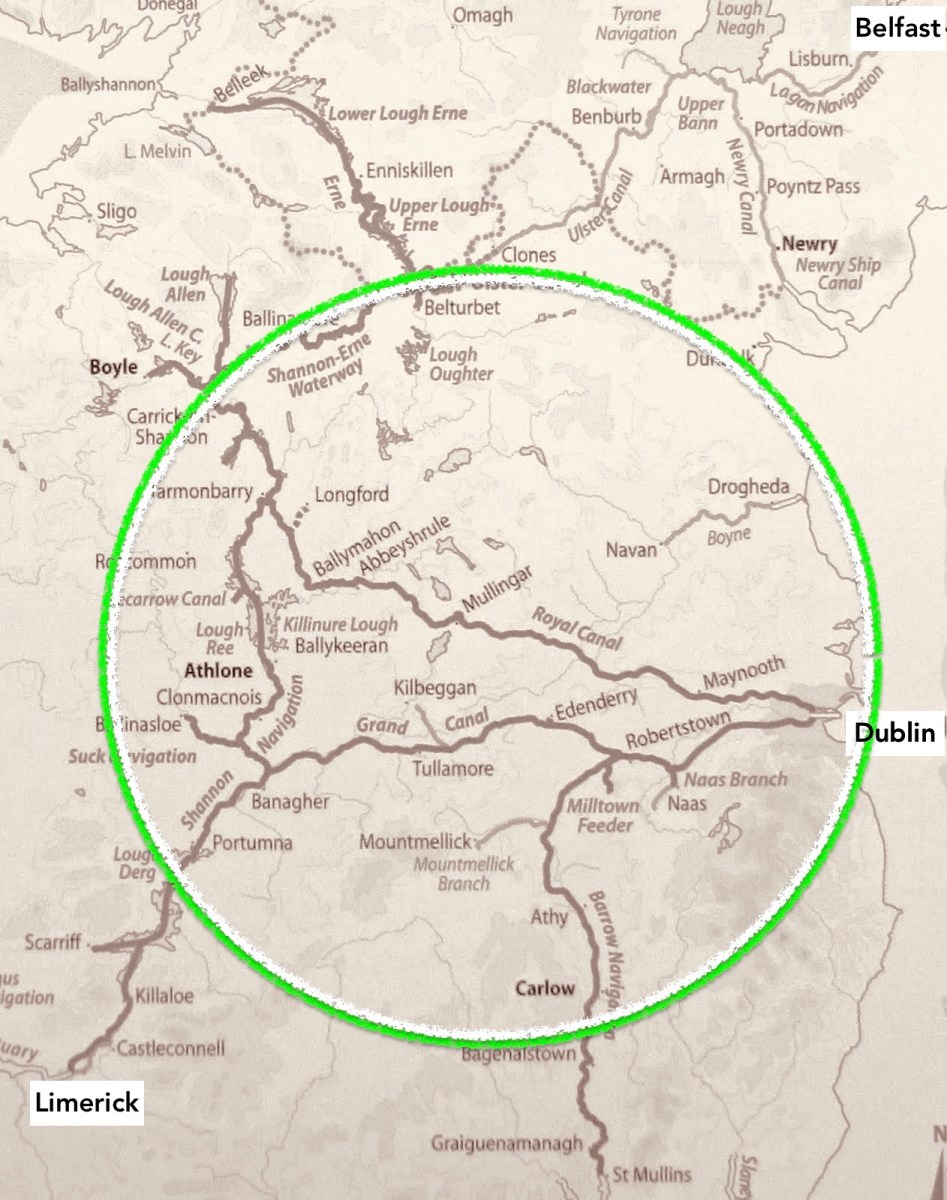
That’s the ‘Green & Silver’ route, above, which the Rolts travelled in 1946. Starting from Athlone they went anti-clockwise around the triangle formed by the Shannon Navigation, Grand Canal; and Royal Canal. This involved crossing the Liffey in Dublin
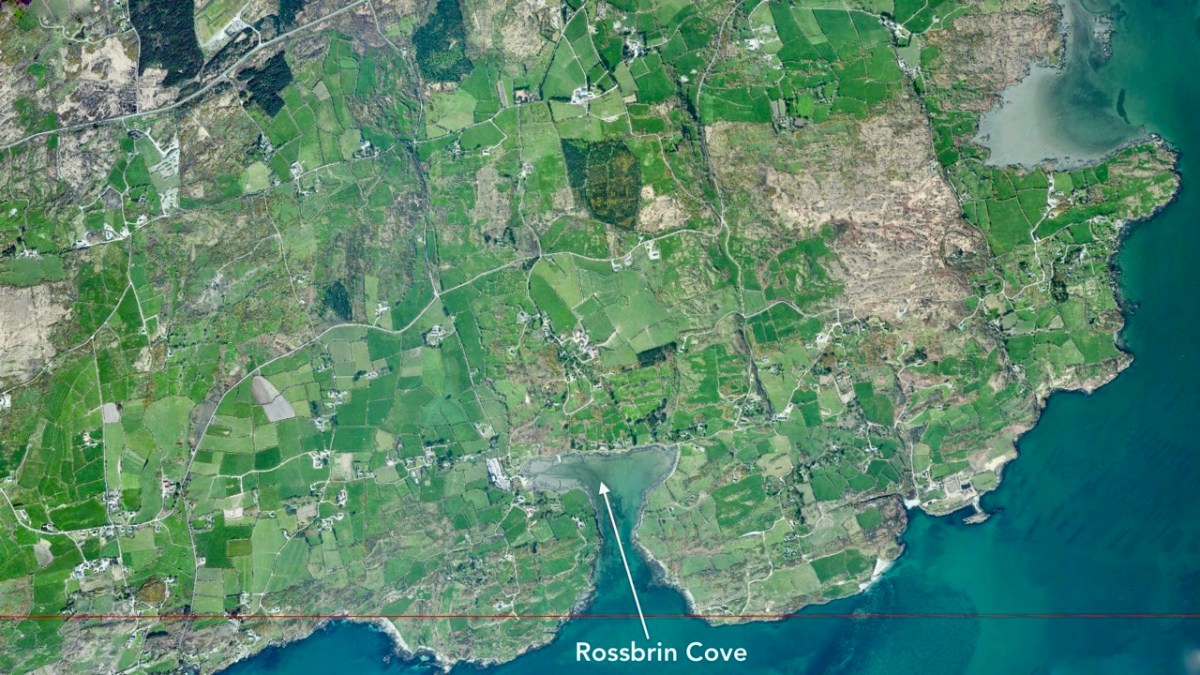
We have visited Dublin many times in recent years, and I managed to take photographs to complement those of the Rolts, in order to finally complete the ‘Green & Silver’ series today. First, however, let’s try to get an idea of the scale of Dublin Port by comparing aerial views, like by like, of that district and our own Rossbrin Cove in West Cork. The scale and area of each of these two photographs is exactly the same (1600 hectares): the demography (population and land use) couldn’t be more different.


. . . After tea we journeyed on through Landestown and Digby Bridge Locks to the Leinster aqueduct over the River Liffey. It was an attractive pound, the canal skirting a ridge of high ground on our right with a view over the valley to the left until it turned to cross the river. As there was little traffic about, we stopped for a few moments on the aqueduct, an impressive structure of four arches, to look down at the swift flowing peat-stained waters which we next should see, and enter, in the heart of Dublin . . .
Green & Silver by L T C Rolt, Chapter 6
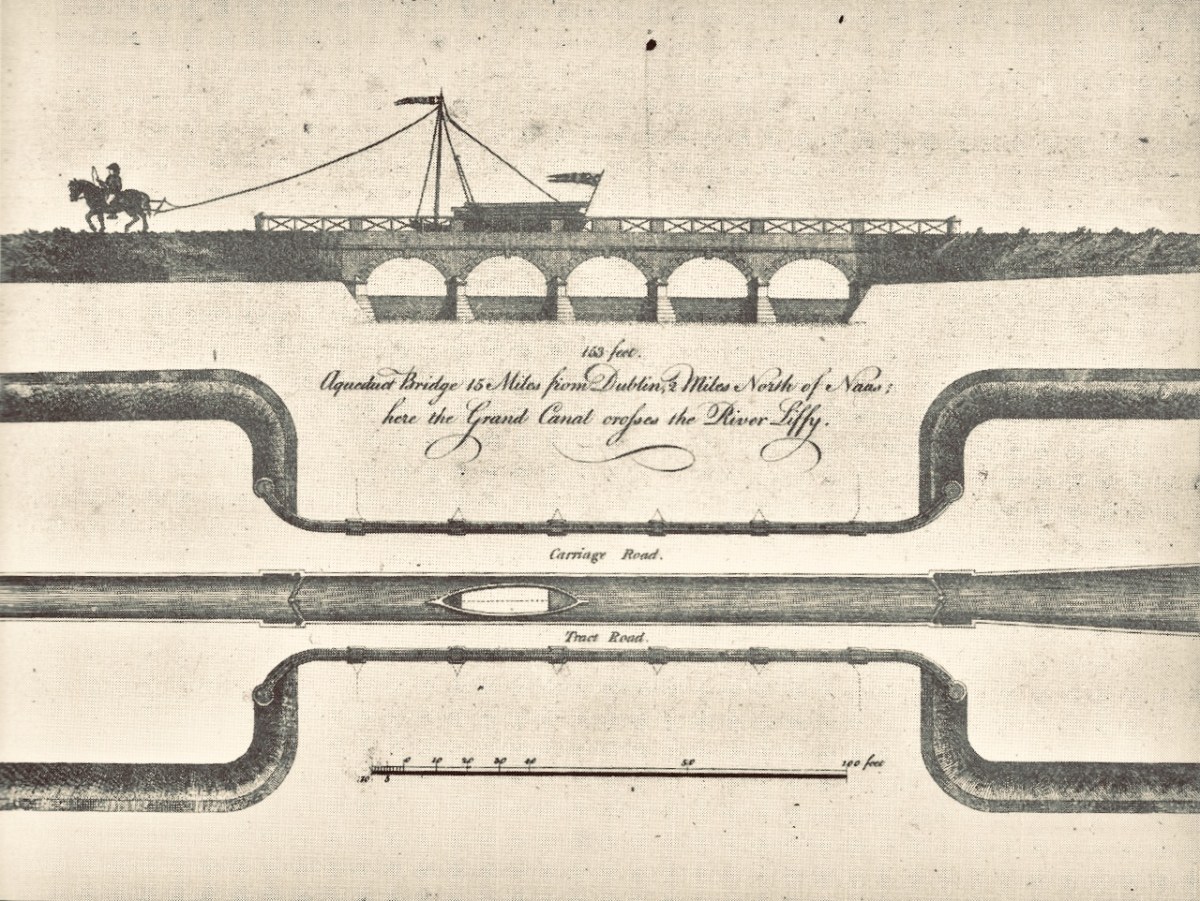

Top – early print of the Leinster Aqueduct, Grand Canal; lower – the Rolts pause to admire the structure as they cross the Liffey on the aqueduct
. . . The day before we were due to leave our moorings at Grand Canal Dock I thought it as well to reconnoitre the entrance from the Liffey into the Royal Canal at Spencer Dock, North Wall. The channel into the tidal lock was barred by an enormous rolling lift bridge over which an endless procession of cars and lorries was rattling and thundering. To my eyes it appeared as though this formidable barrier was seldom or never moved. In any case it seemed optimistic to suppose that this ponderous mechanism would be operated, and the traffic along North Wall suspended, merely to allow the passage of our small craft. Looking up at the dock I saw yet another obstacle; a drawbridge this time operated by two steel beams high overhead which looked at this distance, with their long rods linking beams to bridge, like a pair of slender, long-beaked birds. This carried Sherriff Street, another busy thoroughfare, across the dock . . .
GREEN & SILVER BY L T C ROLT, CHAPTER 8
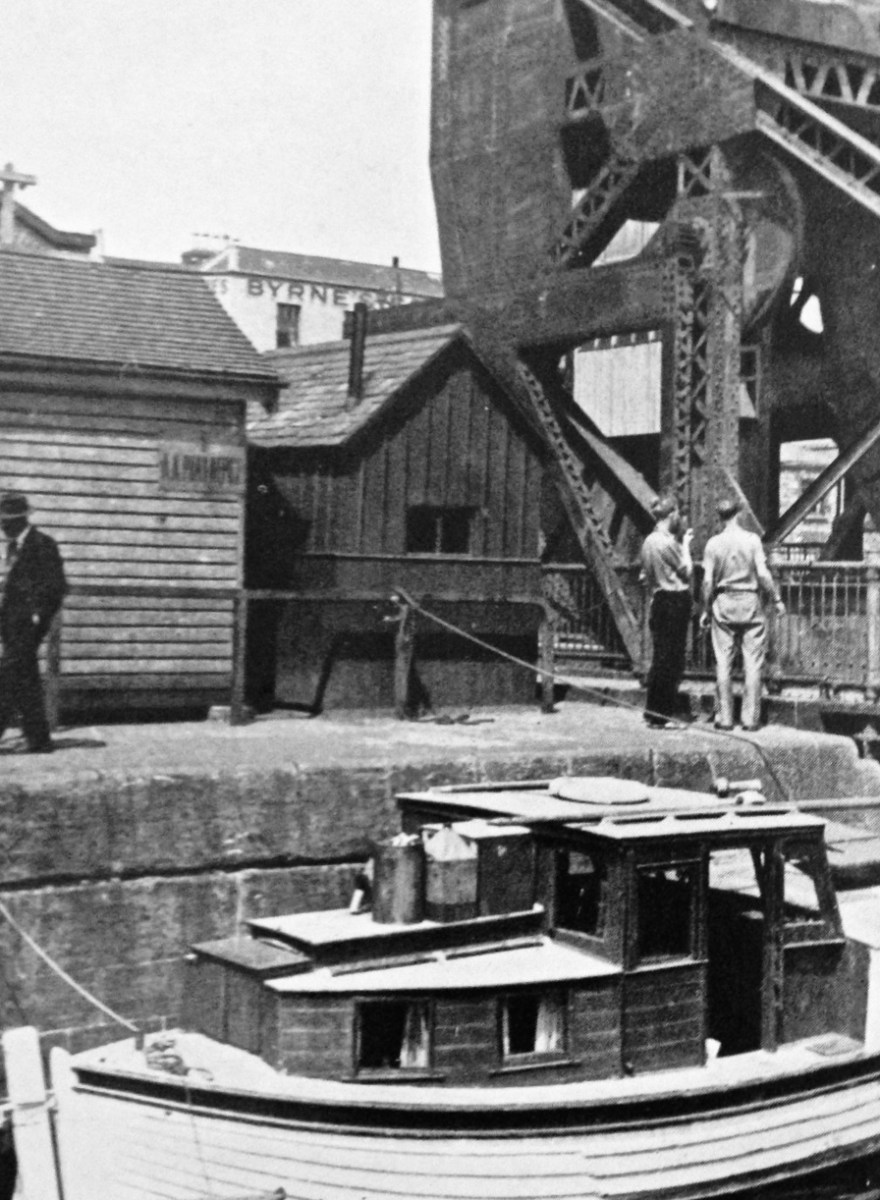
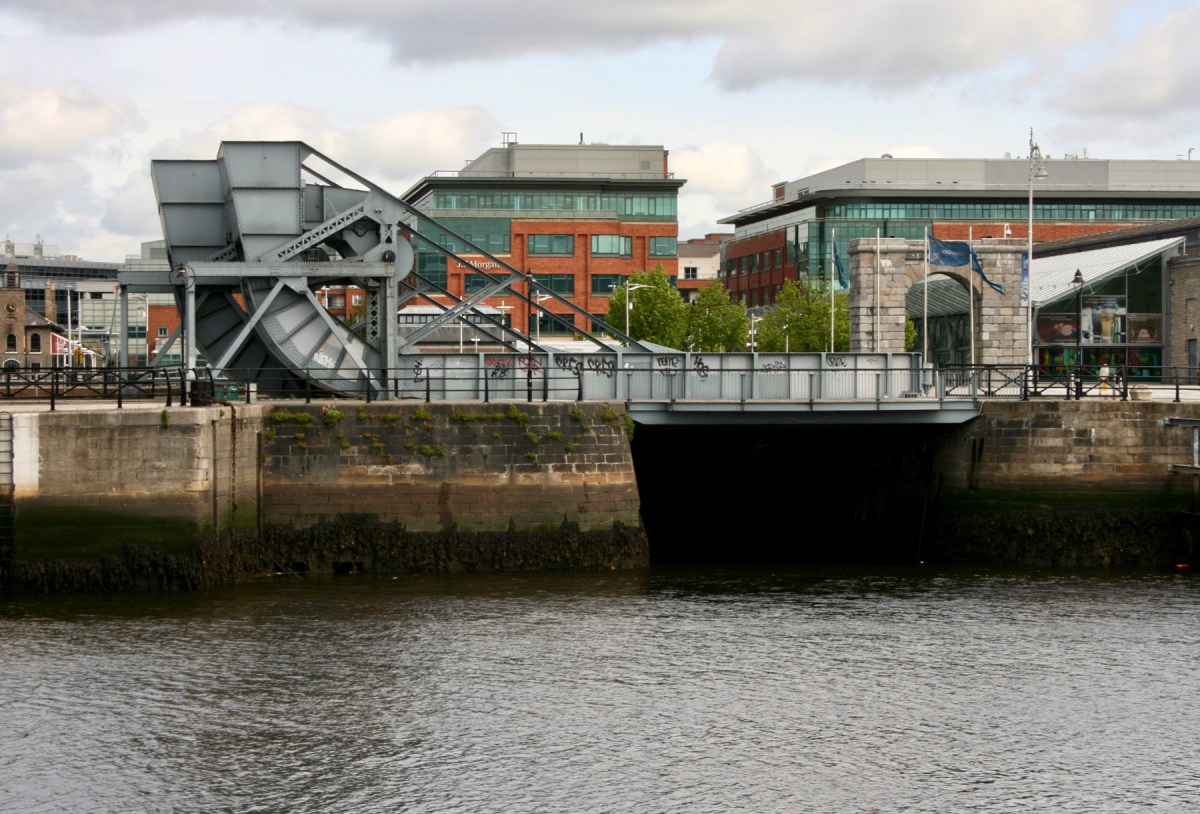


Top – Tom Rolt surveying the Scherzer style ‘rolling lift bridge’ located at the entrance to Spencer Dock, Royal Canal, in 1946. It was erected by the firm of Spencer & Co of Melksham, Wiltshire, in 1912. The bridge was worked by an electric motor – now removed. Lower – the bridge in the present day
. . . It looked as if our passage bade fair to dislocate the traffic of Dublin. I thereupon visited the engineers department of Corus Iompair Eireann at Westland Row Station where I tactfully suggested that if I came up to North Wall at low tide we might just be able to get under the bridge there, but I was received with helpful courtesy and matters were quickly arranged. Of course the bridge would be lifted, that was no trouble at all. And when did I wish to come up the river. To-morrow? High tide was at noon; if I would undertake to be at the bridge at that time it would be opened at once. Arrangements were made on the spot by telephone . . .
GREEN & SILVER BY L T C ROLT, CHAPTER 8
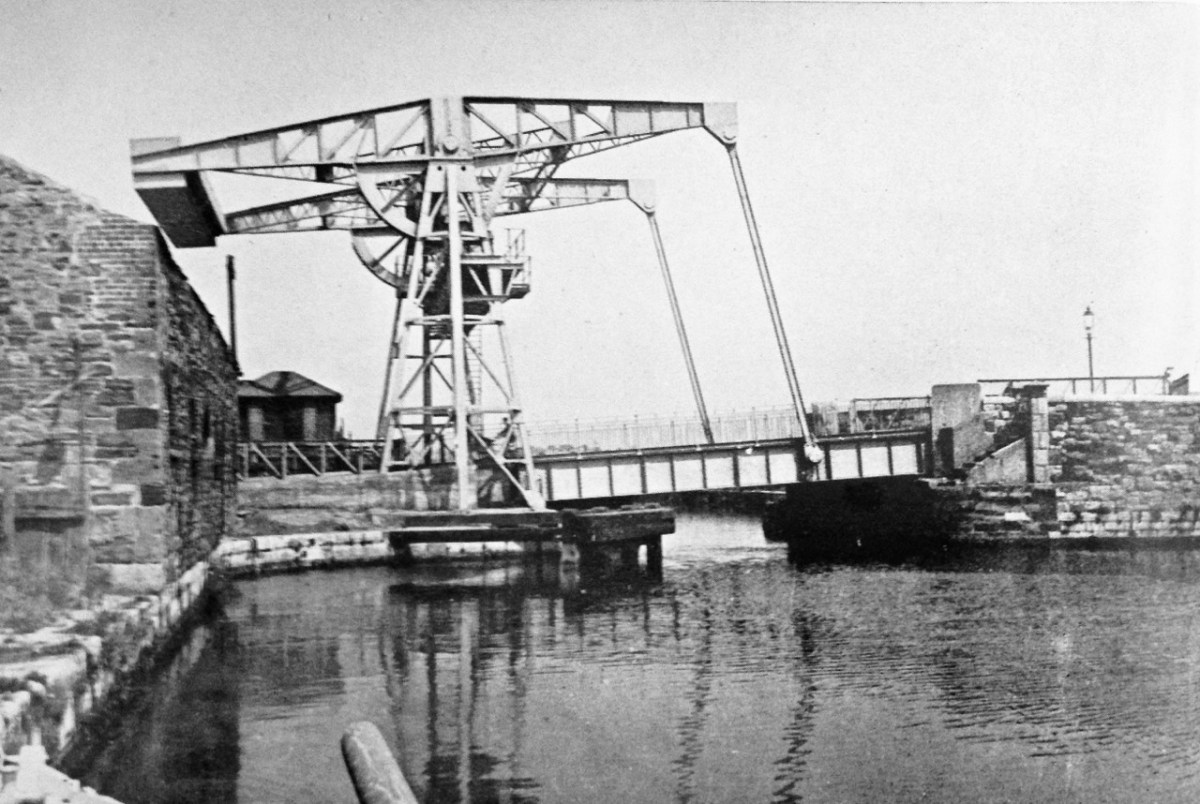
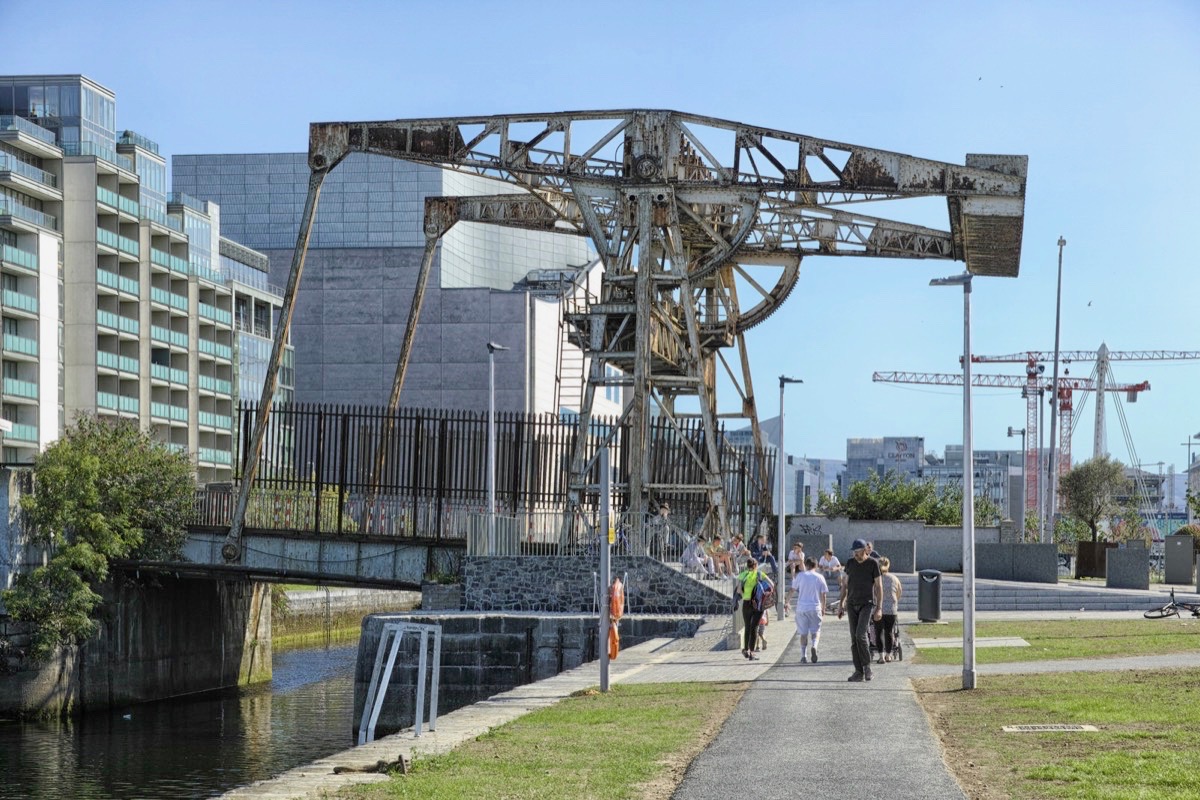



Upper – Angela Rolt’s photograph of the Sherriff Street lift bridge at Spencer Dock, Royal Canal, in 1946; centre – the lift bridge today (courtesy William Murphy aka Infomatique). Lower – the overhead beam lift bridge mechanism is a principle often found on canal navigations: here is a more vernacular example on the Barrow Navigation (from Ireland of the Welcomes, 1971)
. . . Next morning we crossed the waters of the outer basin and entered the tidal lock. Actually there are three locks of different sizes here, side by side, and we entered the smallest of them which was on our port side. The lower gates opened, we paid a final farewell to the Grand Canal, and were soon dancing over the little waves of the Liffey mouth. It was our one brief taste of salt water. Having made sure that no steamers were on the move to or from the quays, we headed straight across the channel and came up the river close to the North Wall side. We swung straight in and got our lines onto the quay wall precisely at the time appointed. Everything went like clockwork. The bridgeman clambered up into his overhead cabin, men appeared from nowhere armed with red flag to stop the traffic and in a few moments, with a rumble of machinery, the bridge opened remarkable swiftly. We passed through into the tidal lock, and the bridge as quickly closed behind us. While the lock was filling, I paid my dues, two pounds for the ninety-two miles and forty-seven locks to Richmond Harbour. This done, the Sherriff Street Bridge drew up with similar despatch and we sailed through to begin our journey on the Royal Canal. Probably very few of the thousands who pass over the North Wall Bridge or board the steamer for Liverpool or Glasgow at the nearby quay suspect that this is the gateway of a forgotten water road which leads through the heart of Ireland . . .
GREEN & SILVER BY L T C ROLT, CHAPTER 8
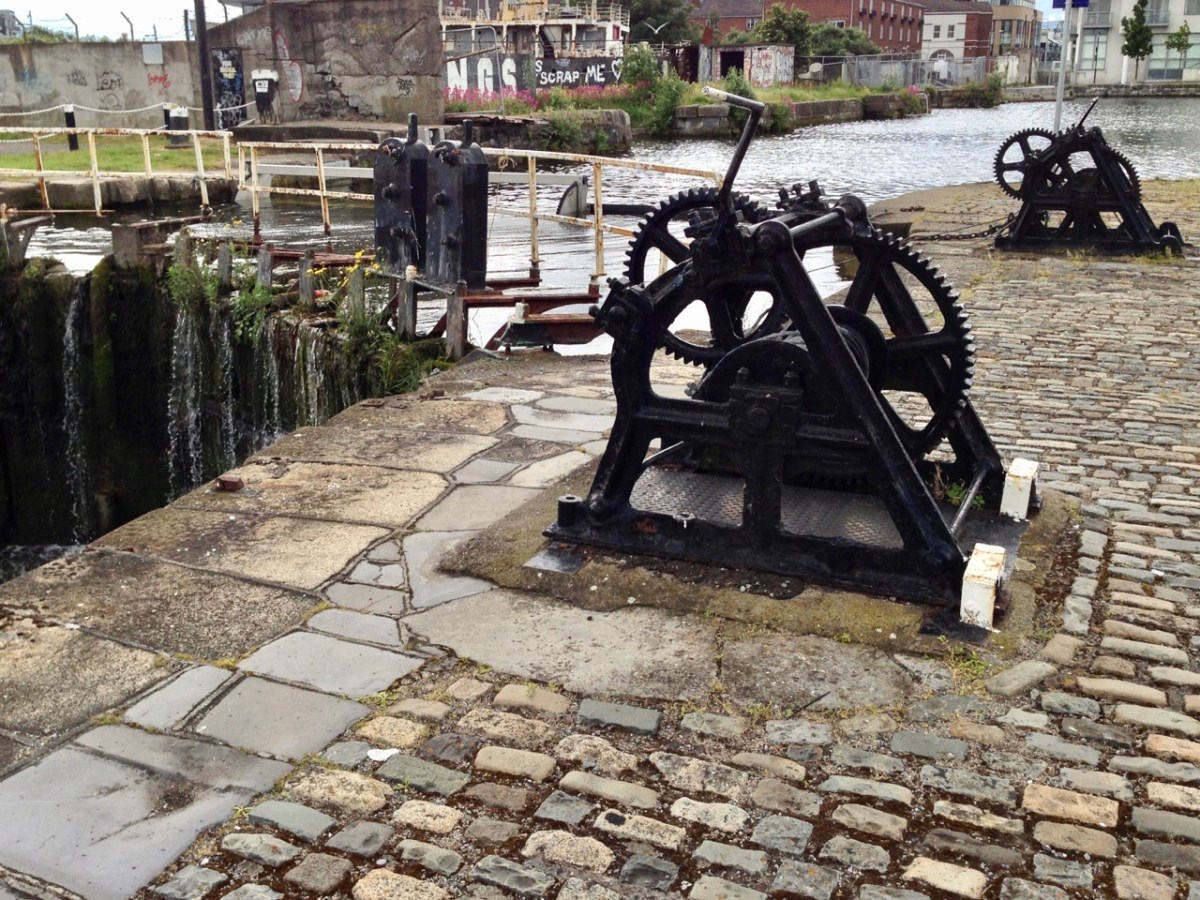


Grand Canal Dock, Dublin – photographs which we took in 2014 (above). The decline which was apparent then continues to this day. Currently there is a plan to sell much of the land for redevelopment. It goes without saying that navigable water will need to be retained to allow access from the Grand Canal itself to the Liffey. Below – another context for the Port of Dublin in the 1950s!
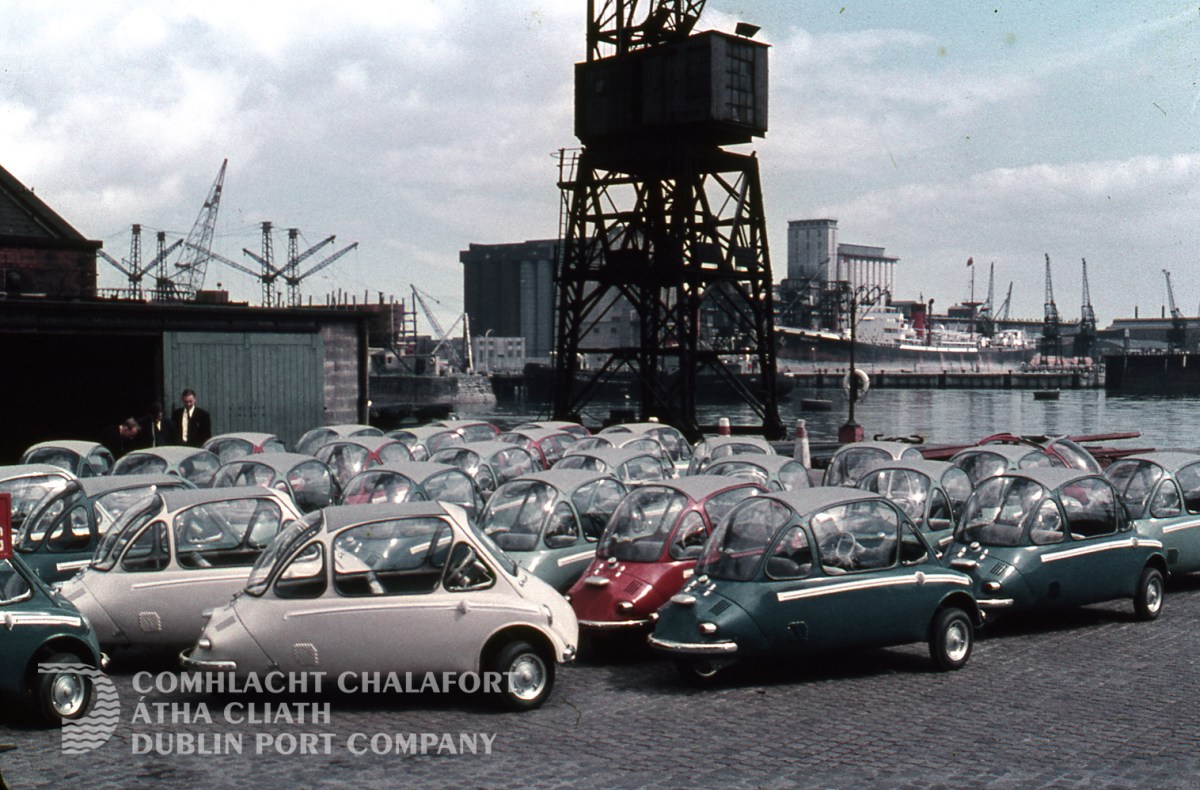

The Heinkel Kabine ‘bubble car’ was designed by the same company which produced German long-range heavy bombers during the Second World War: this famous micro-car was manufactured for a short time between 1956 and 1958 under licence in Dundalk’s Great Northern Railway Ireland (GNRI) works. More than 6,000 were manufactured here.
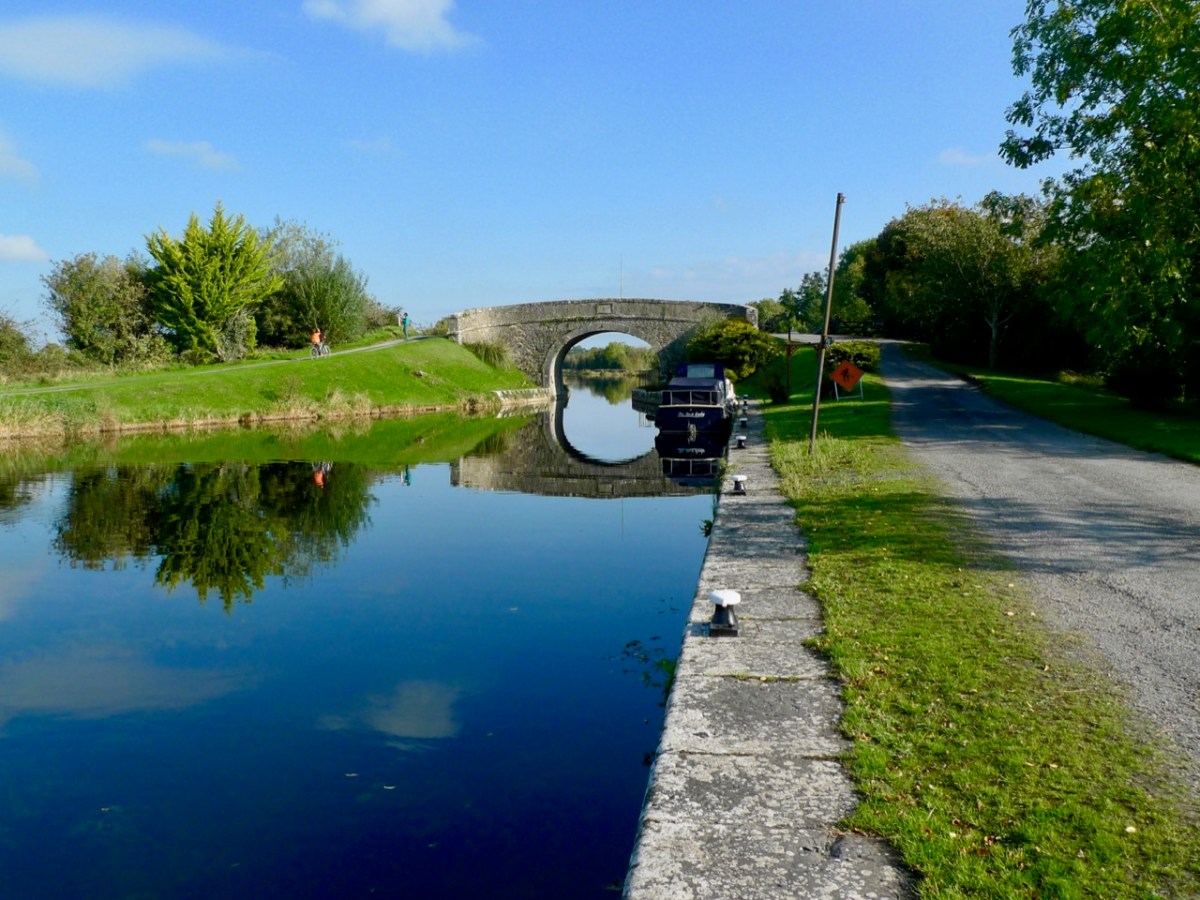


The beauty of the rural Royal Canal: Chaigneau Bridge, Ballybranigan, Co Longford in 2016
The previous series of Roaringwater Journal posts on Irish waterways can be found (in reverse order) here.
*Robert’s Trasna na Tíre talk can be reached on this link.