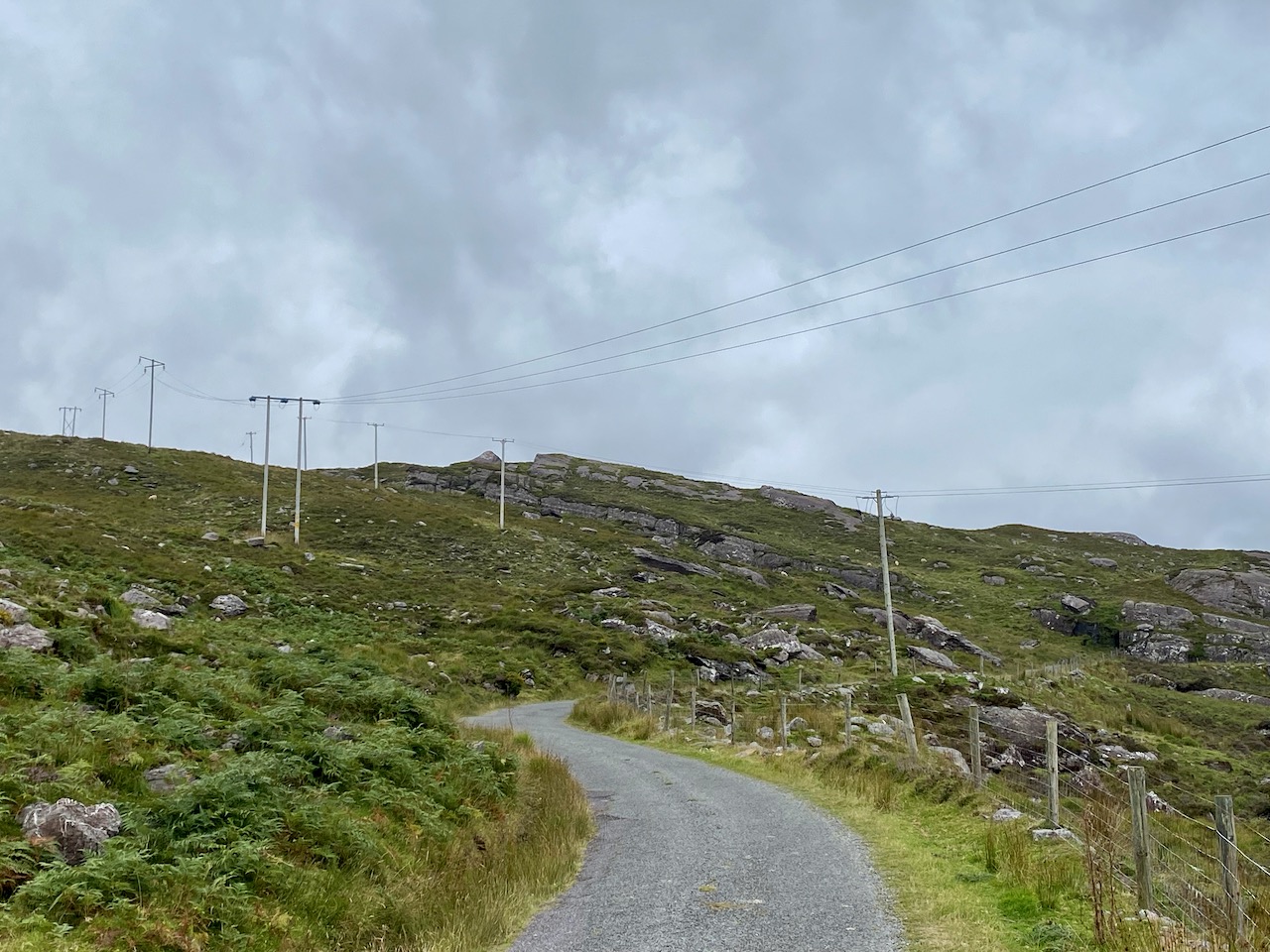
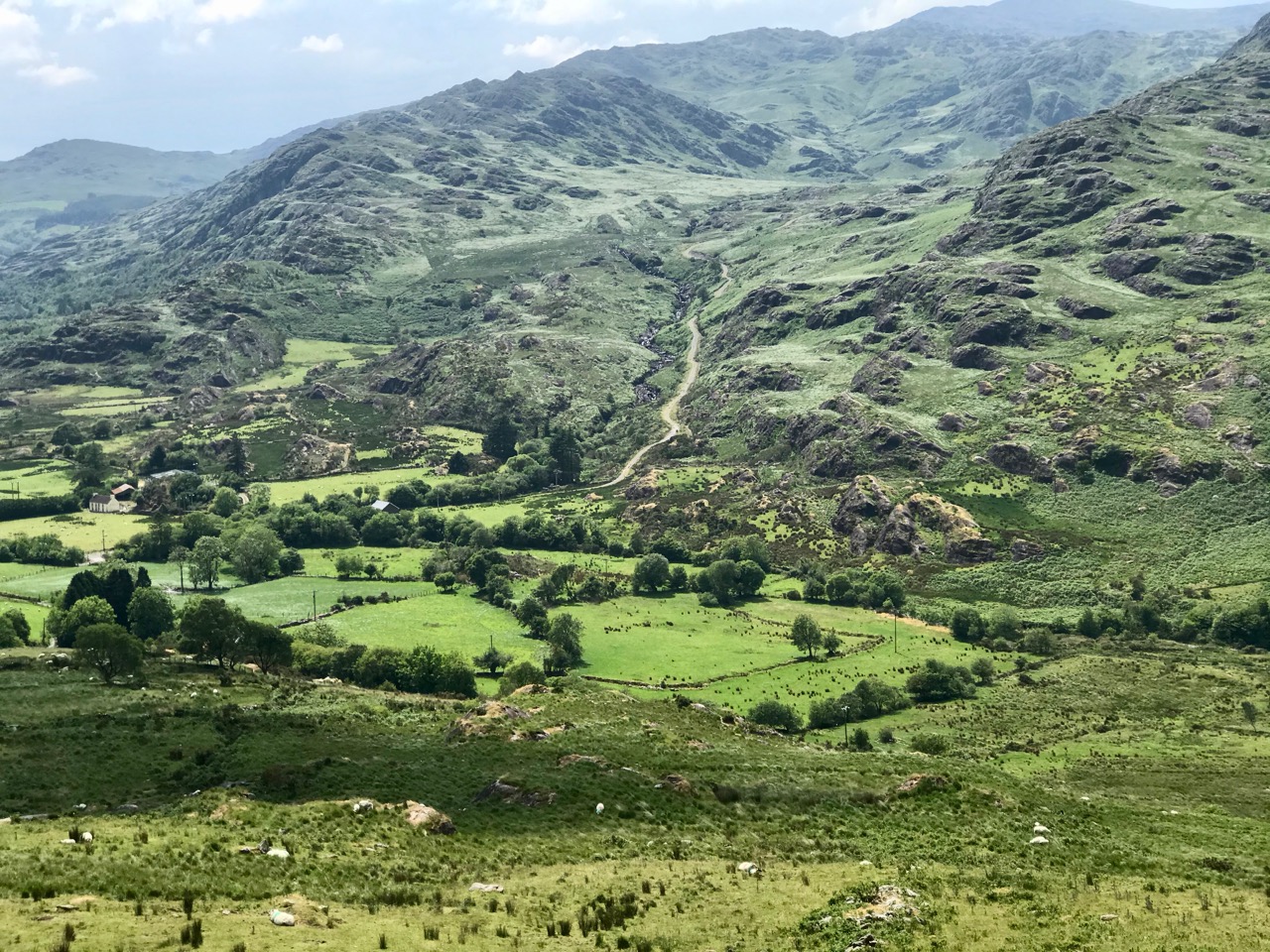
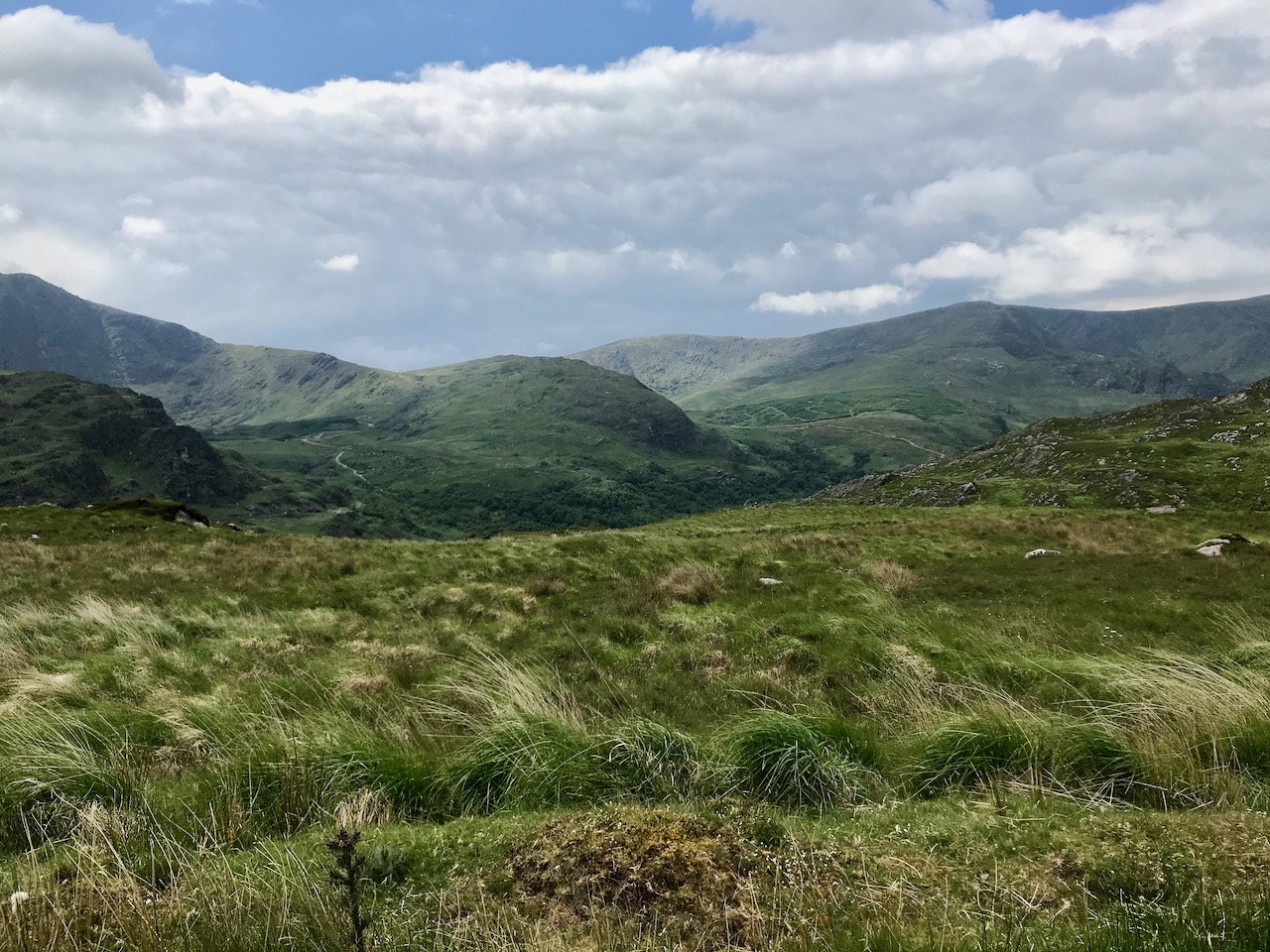
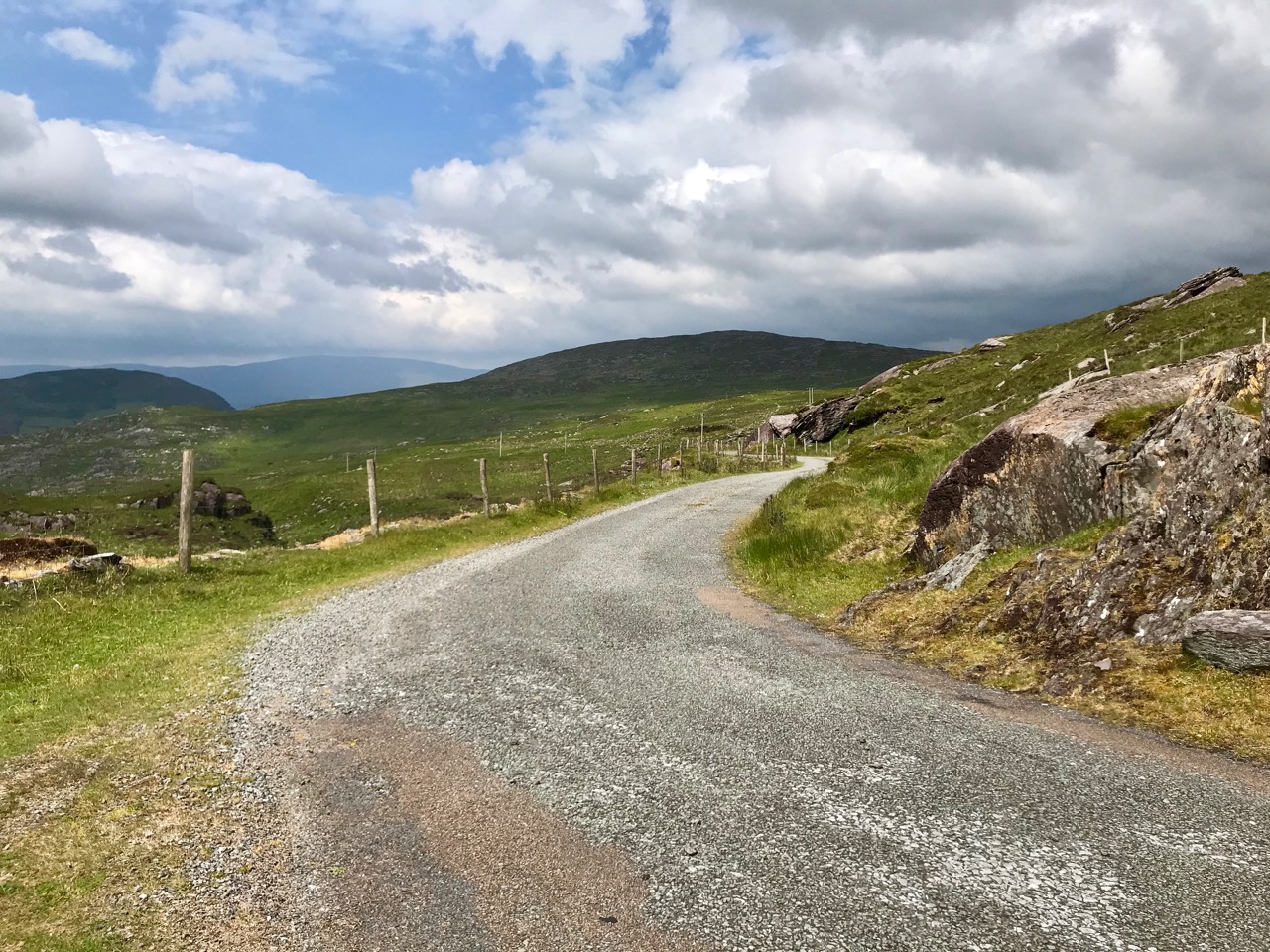
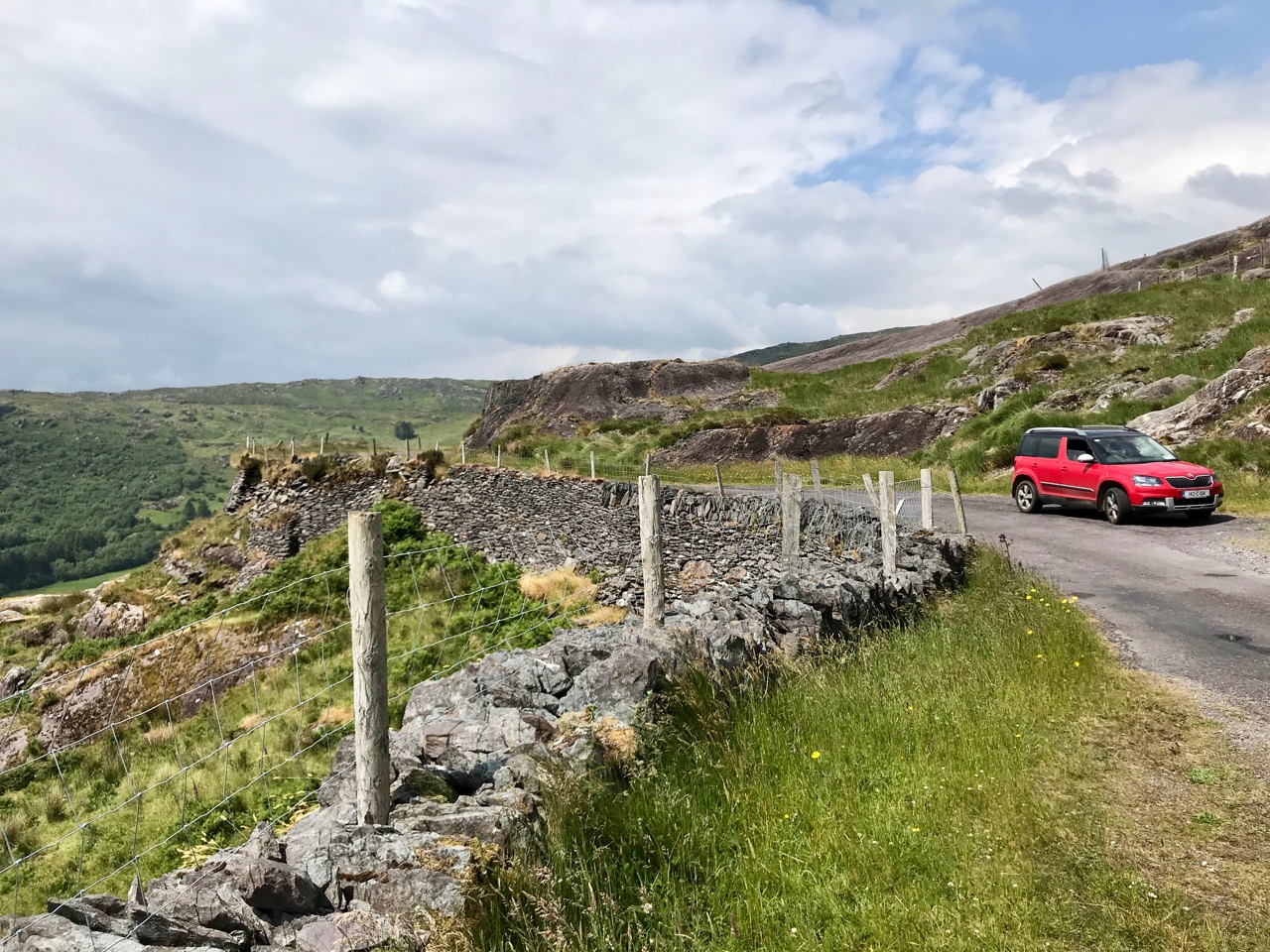
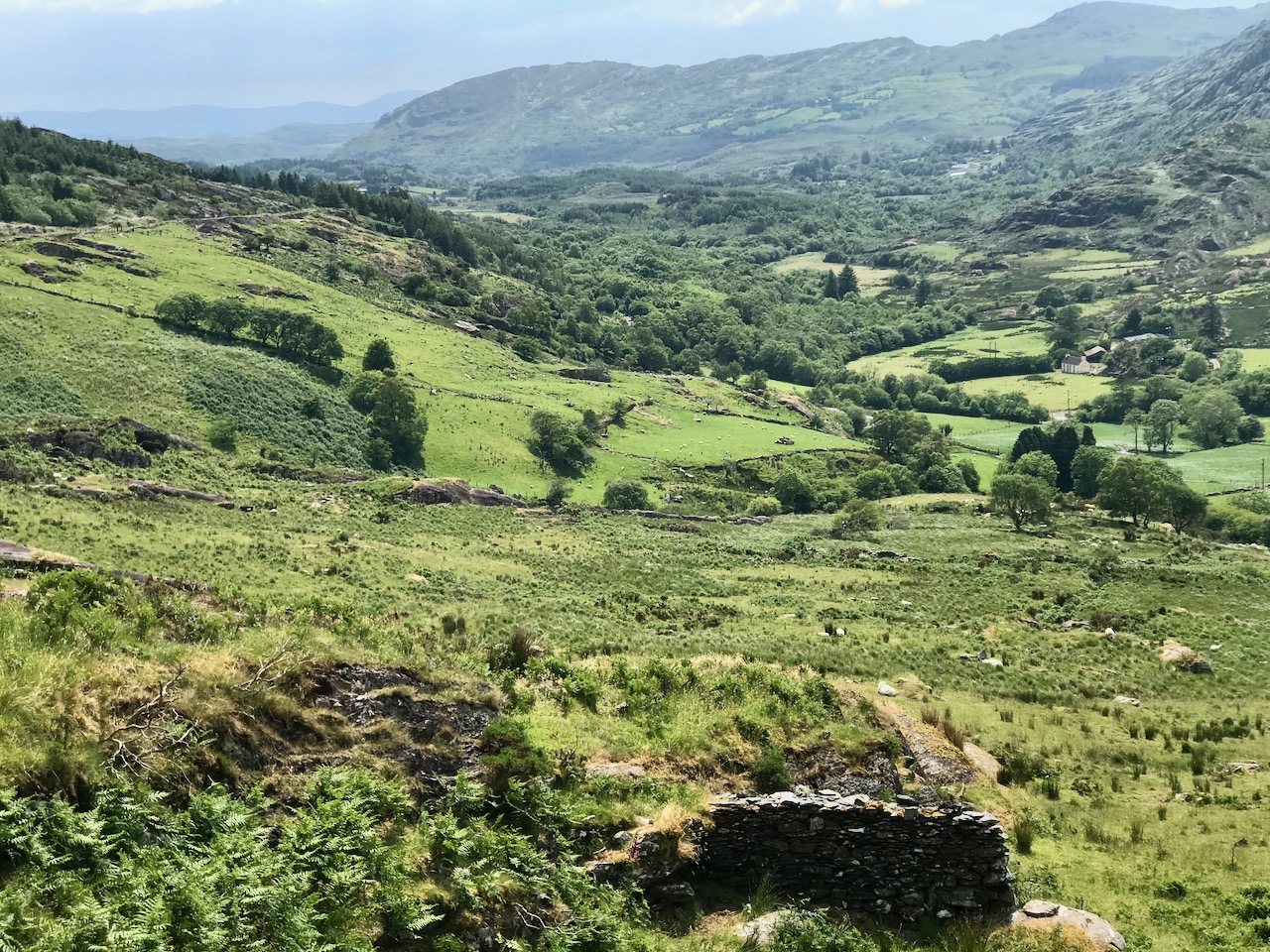
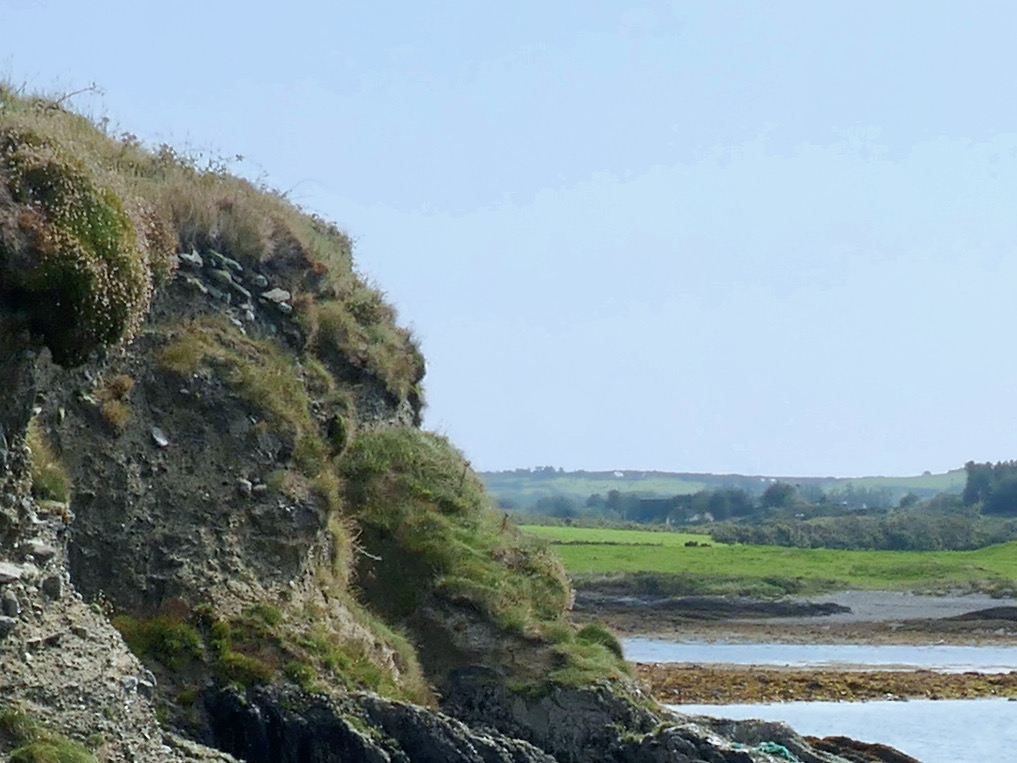
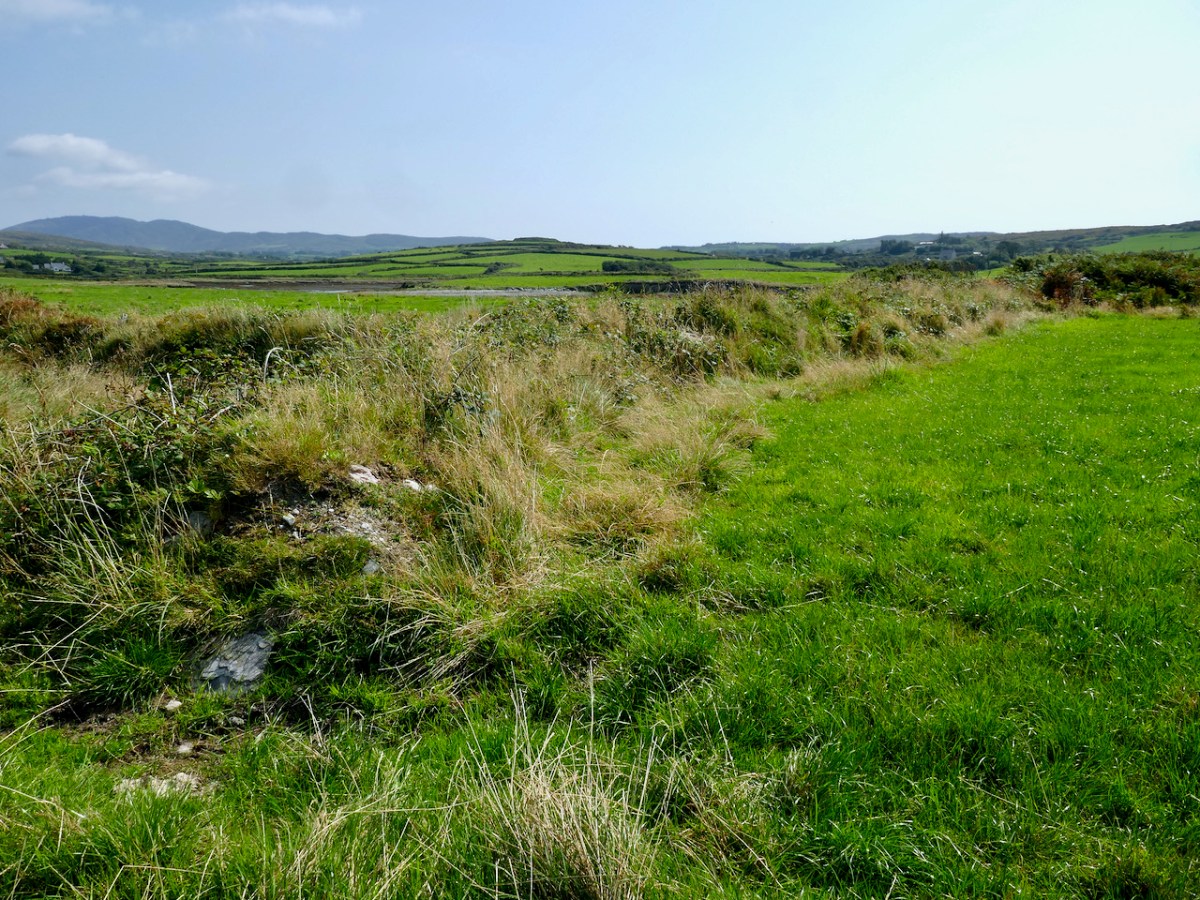
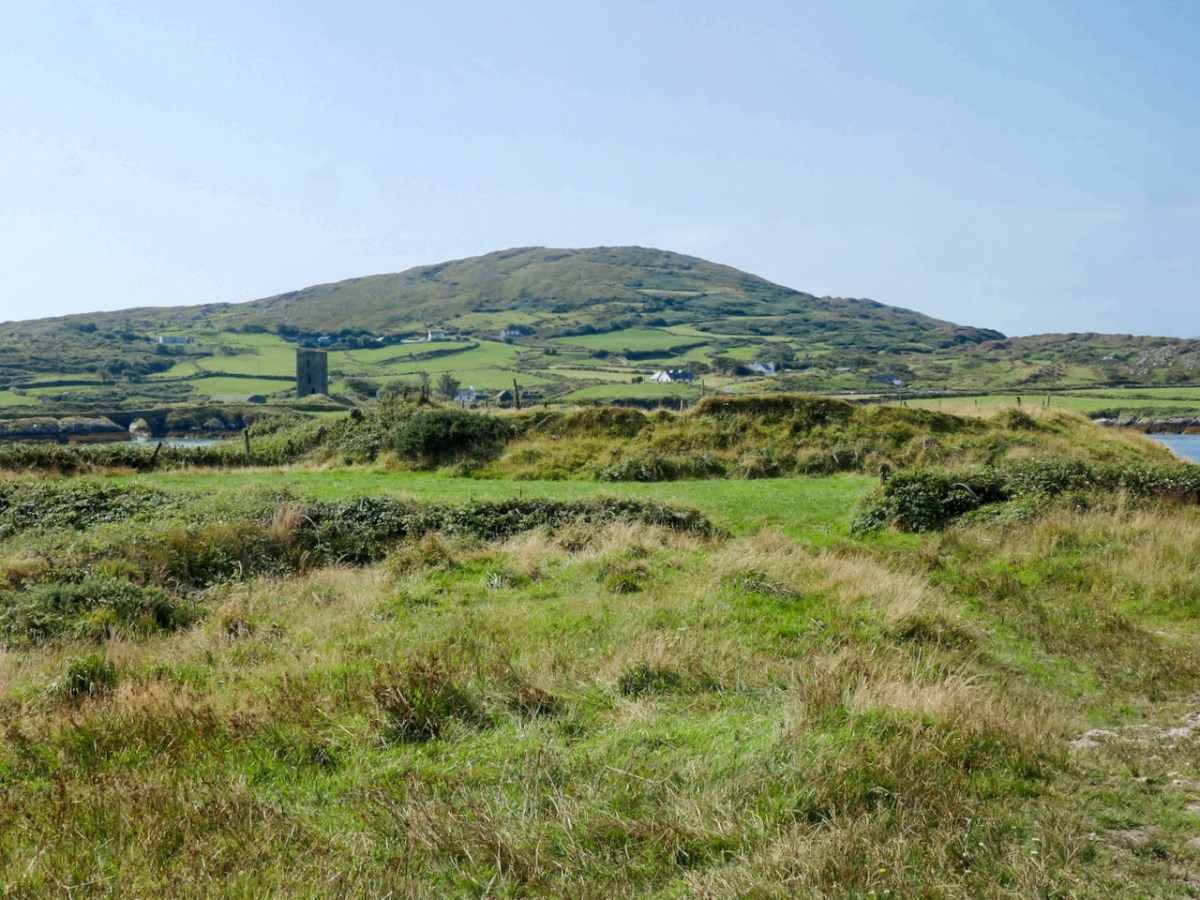
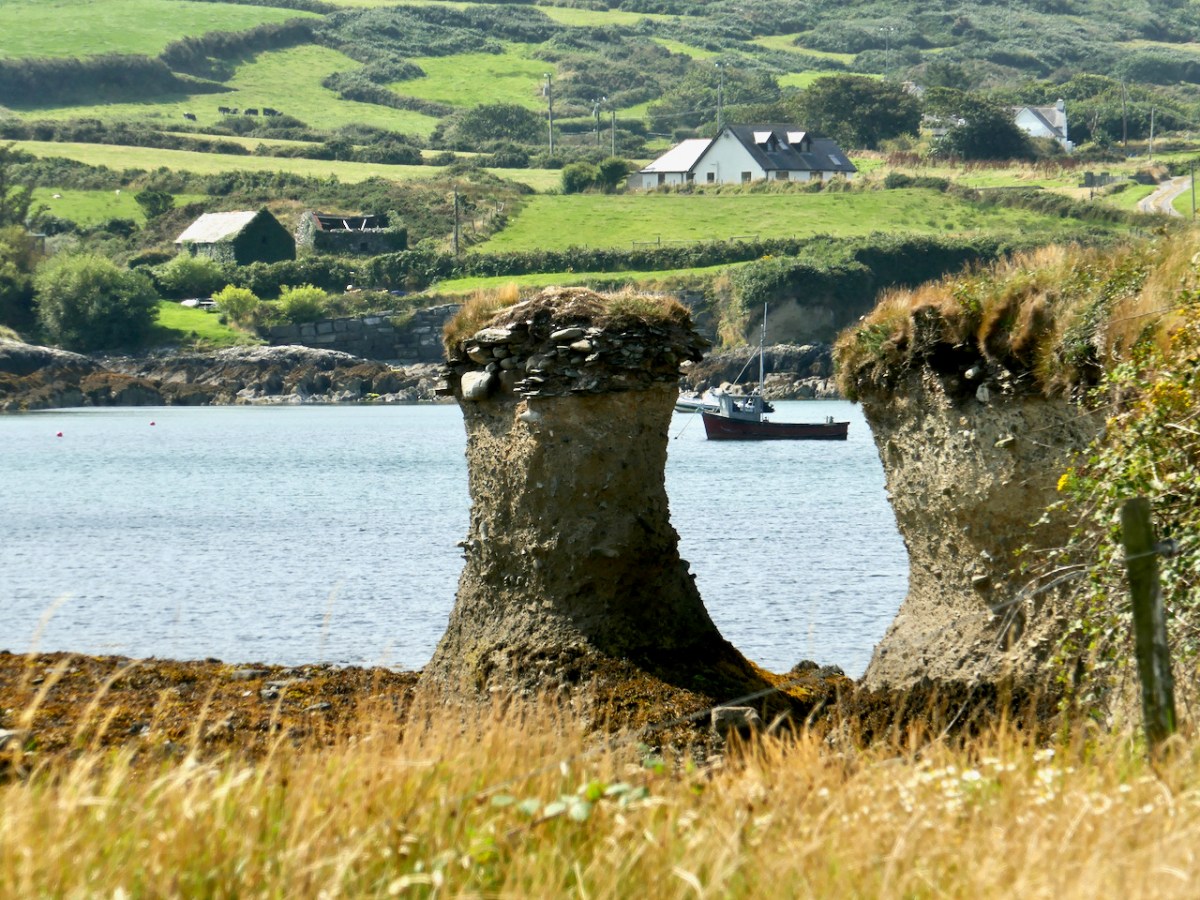
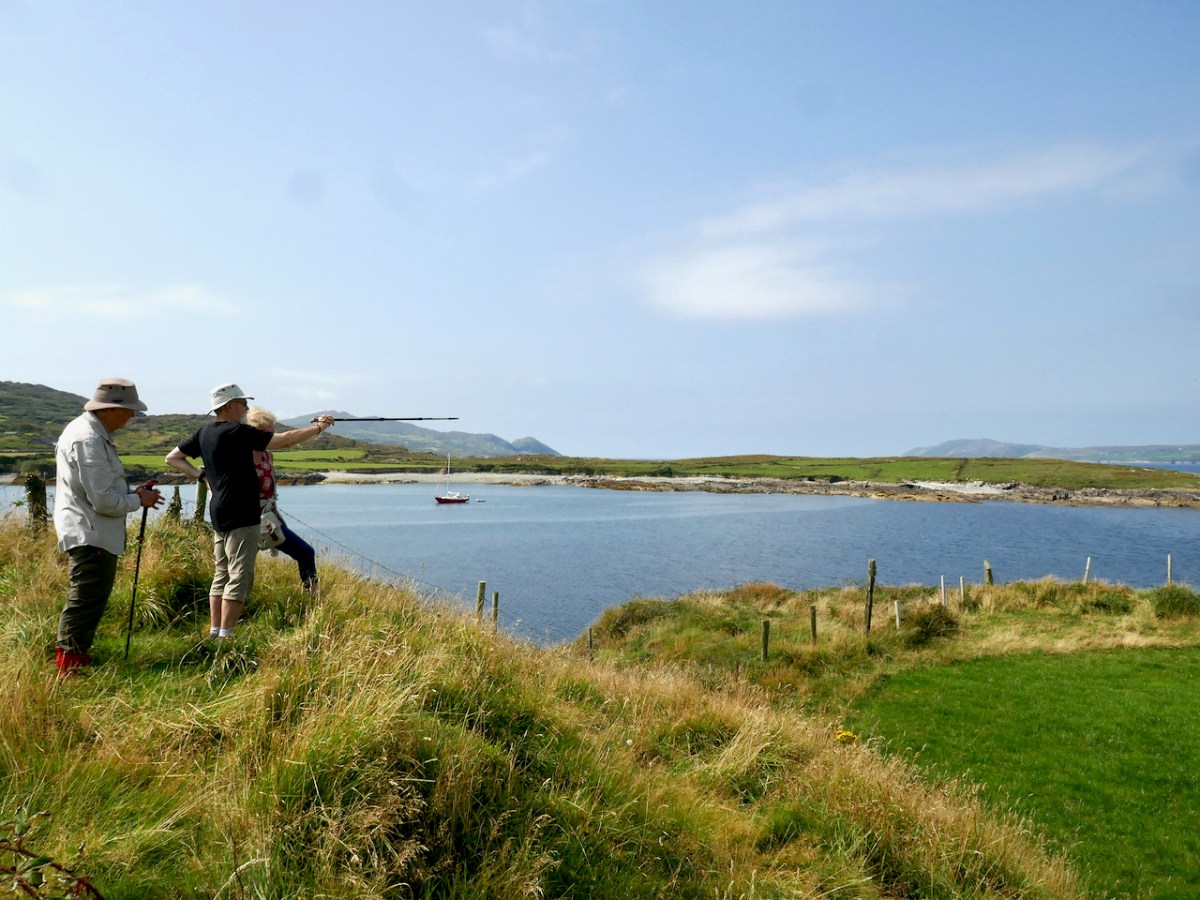
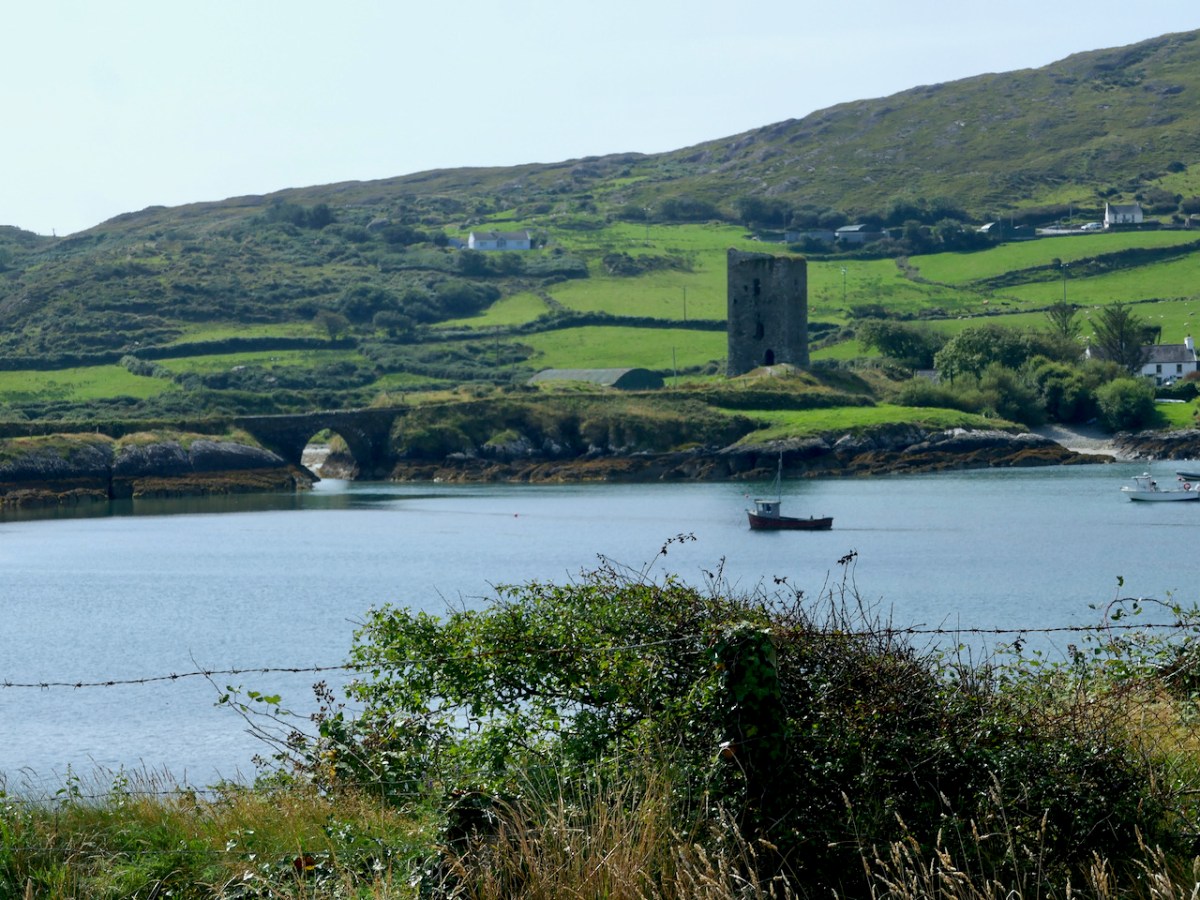
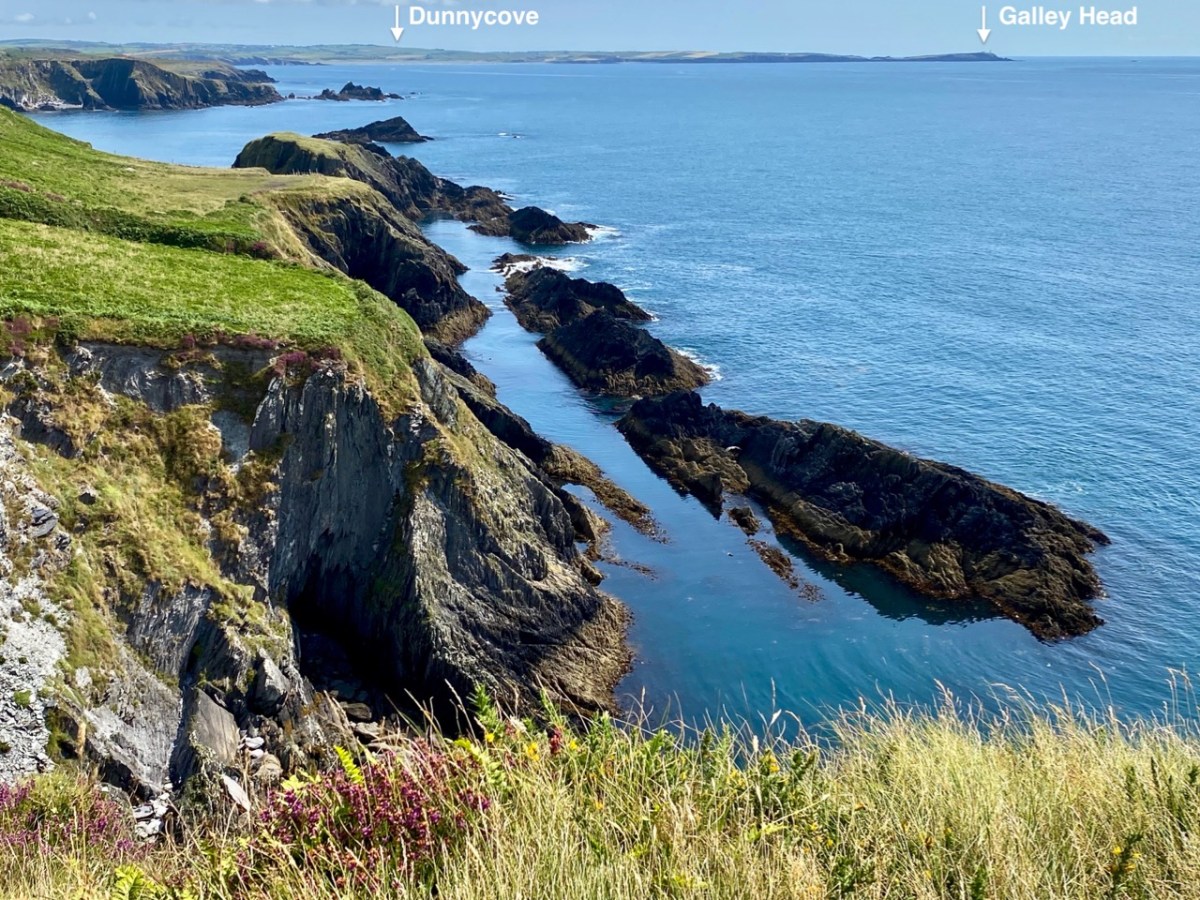
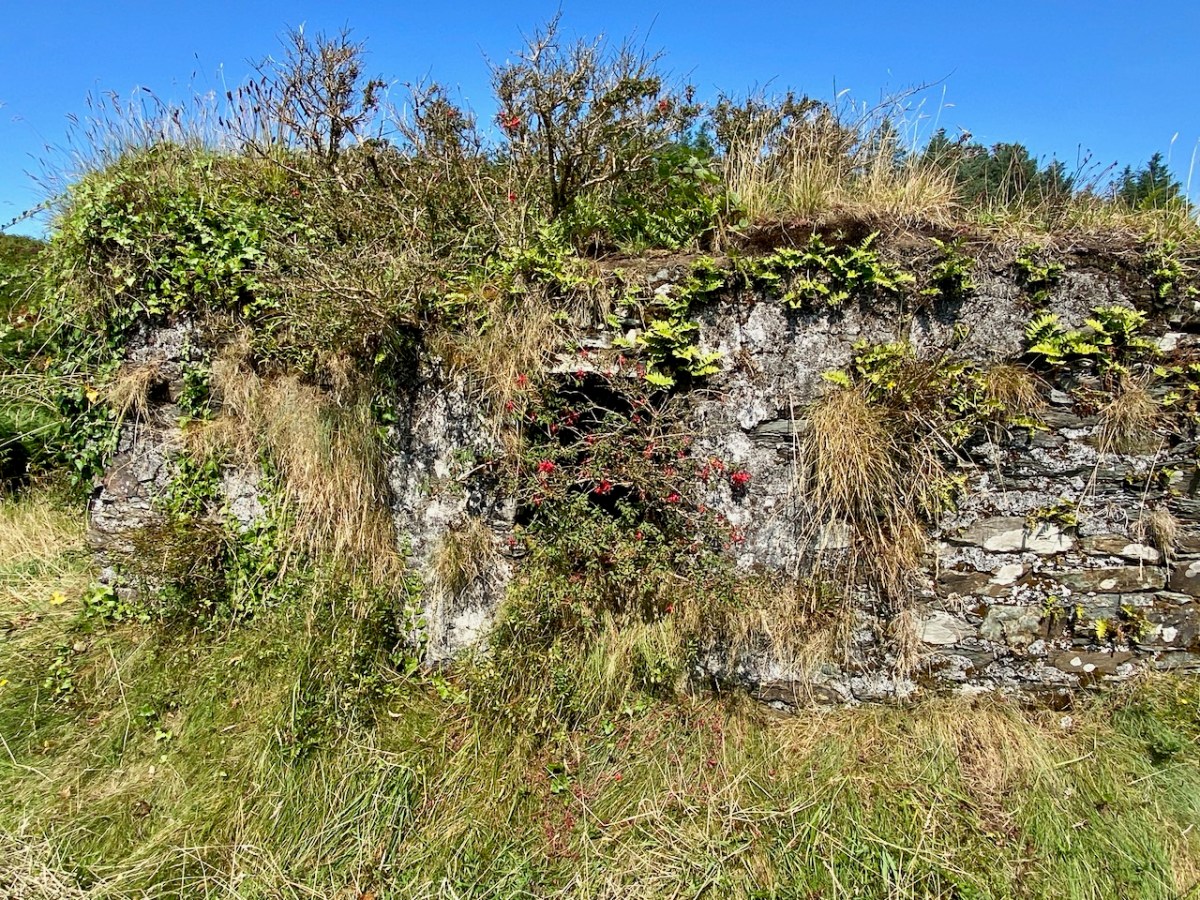
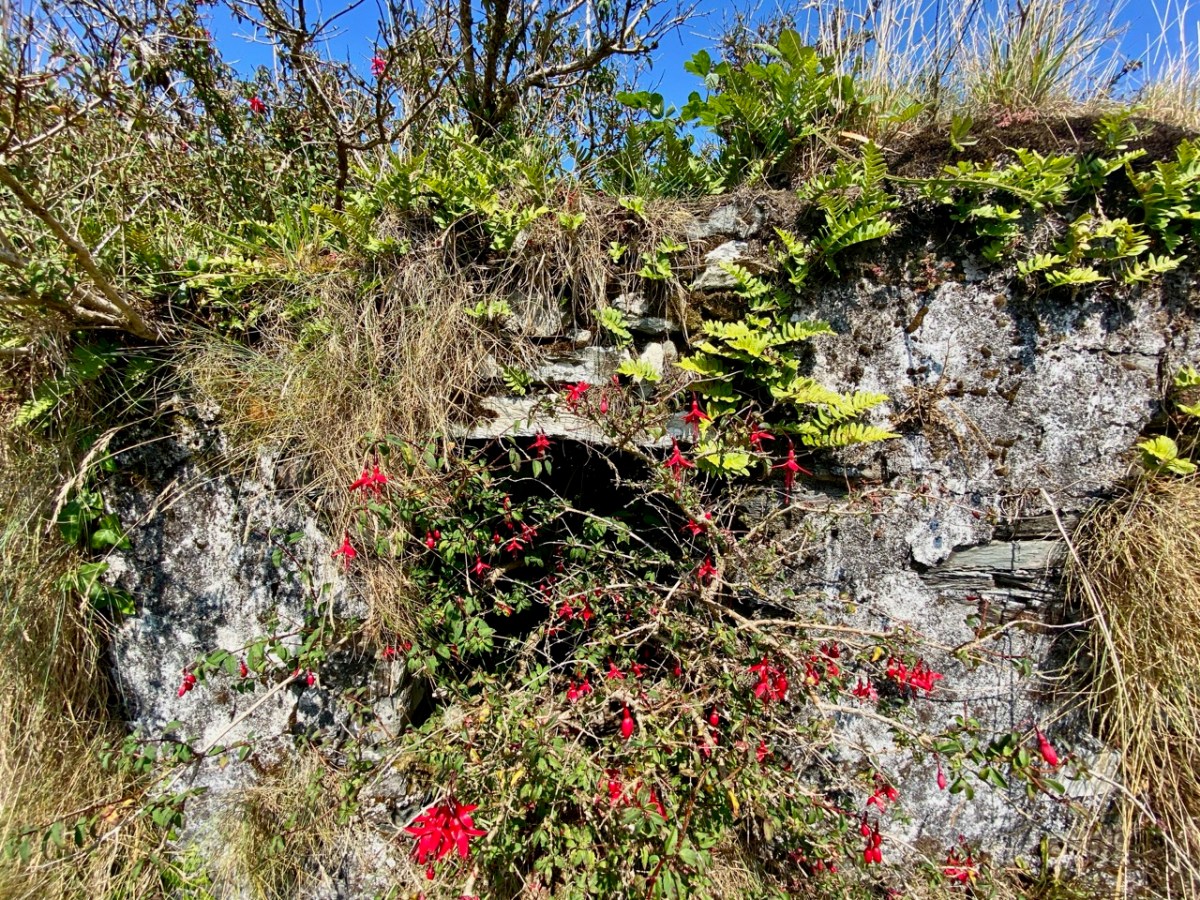
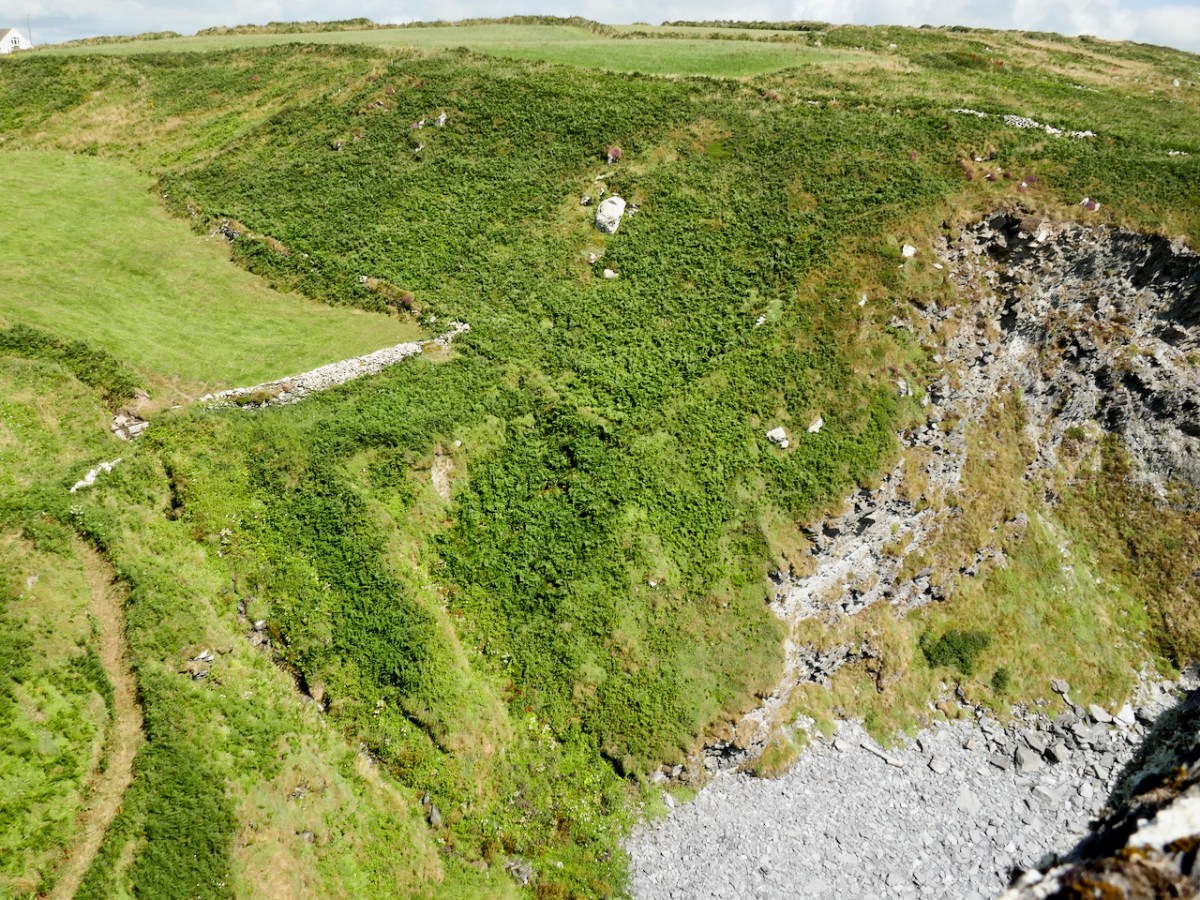
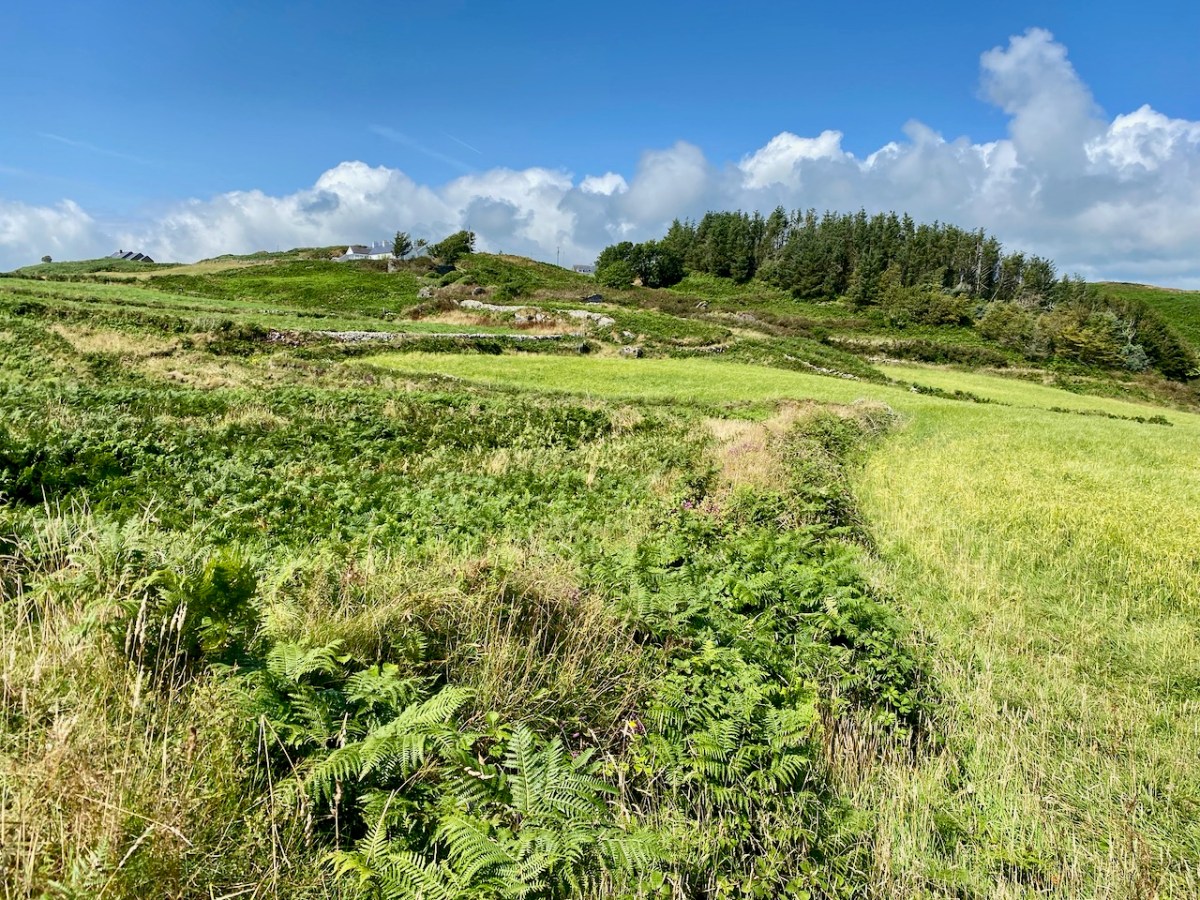
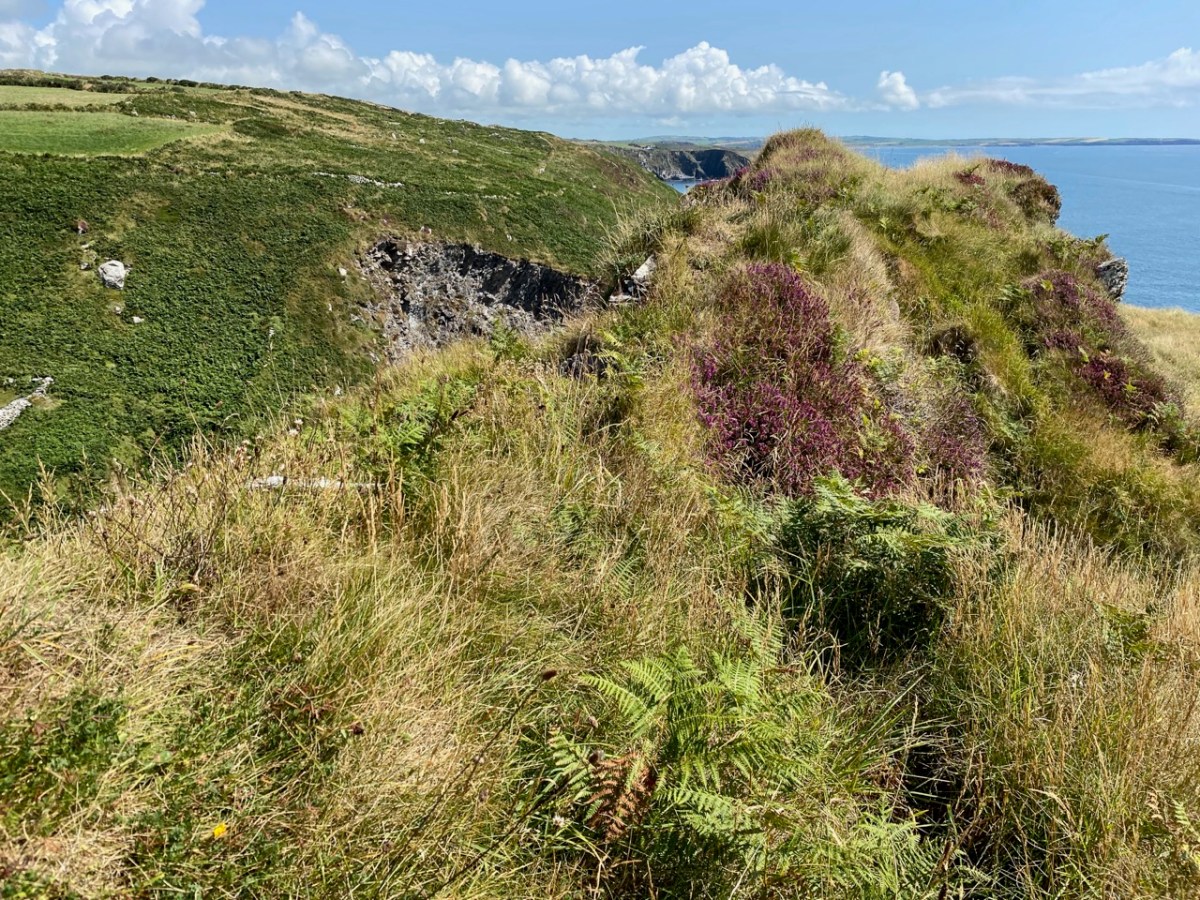
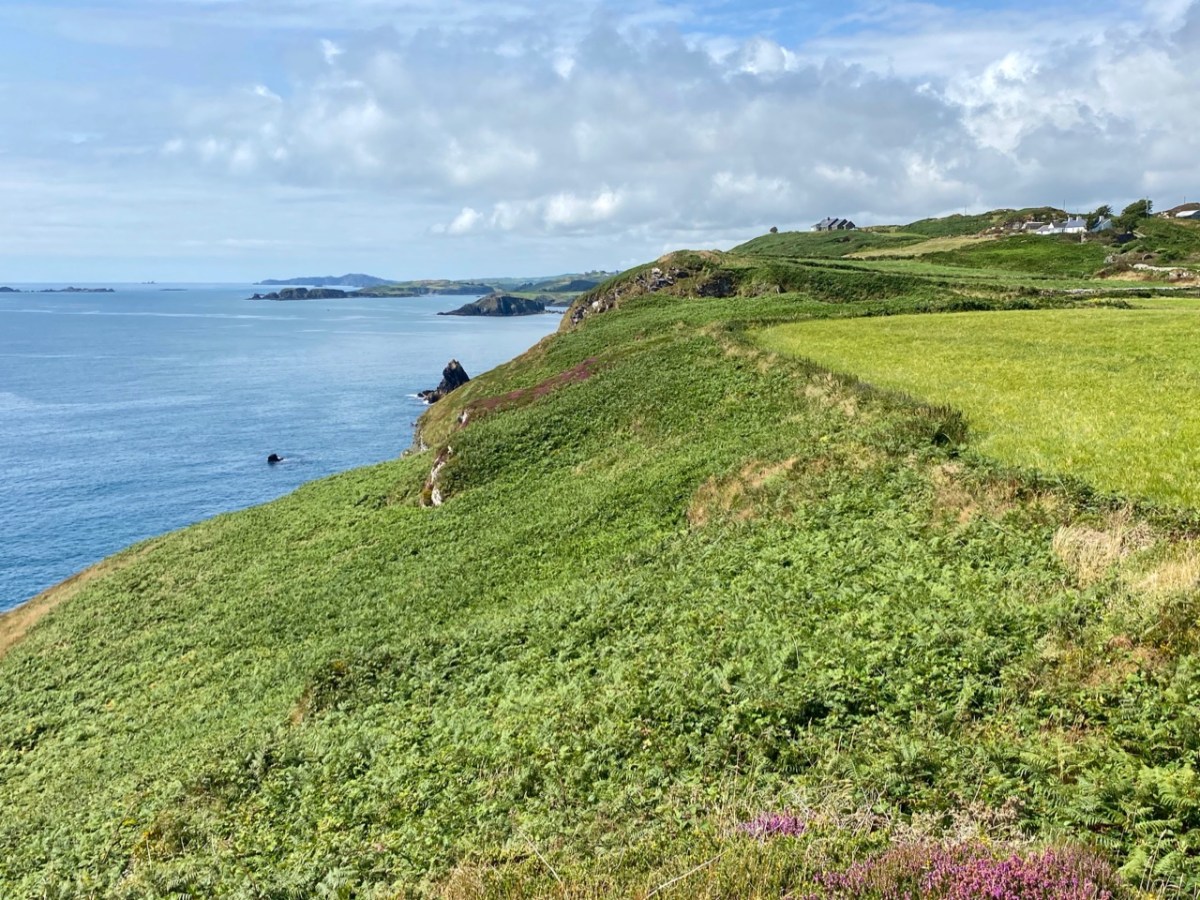
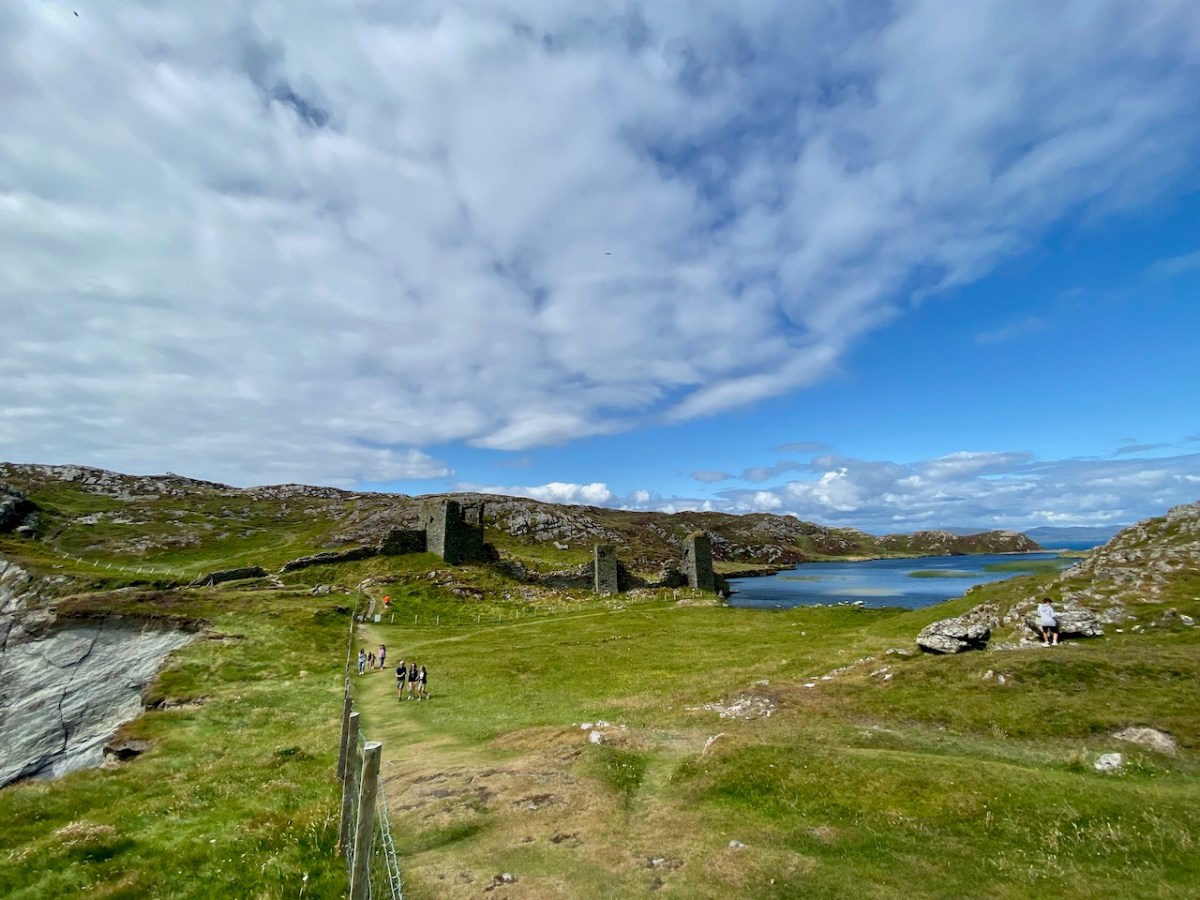
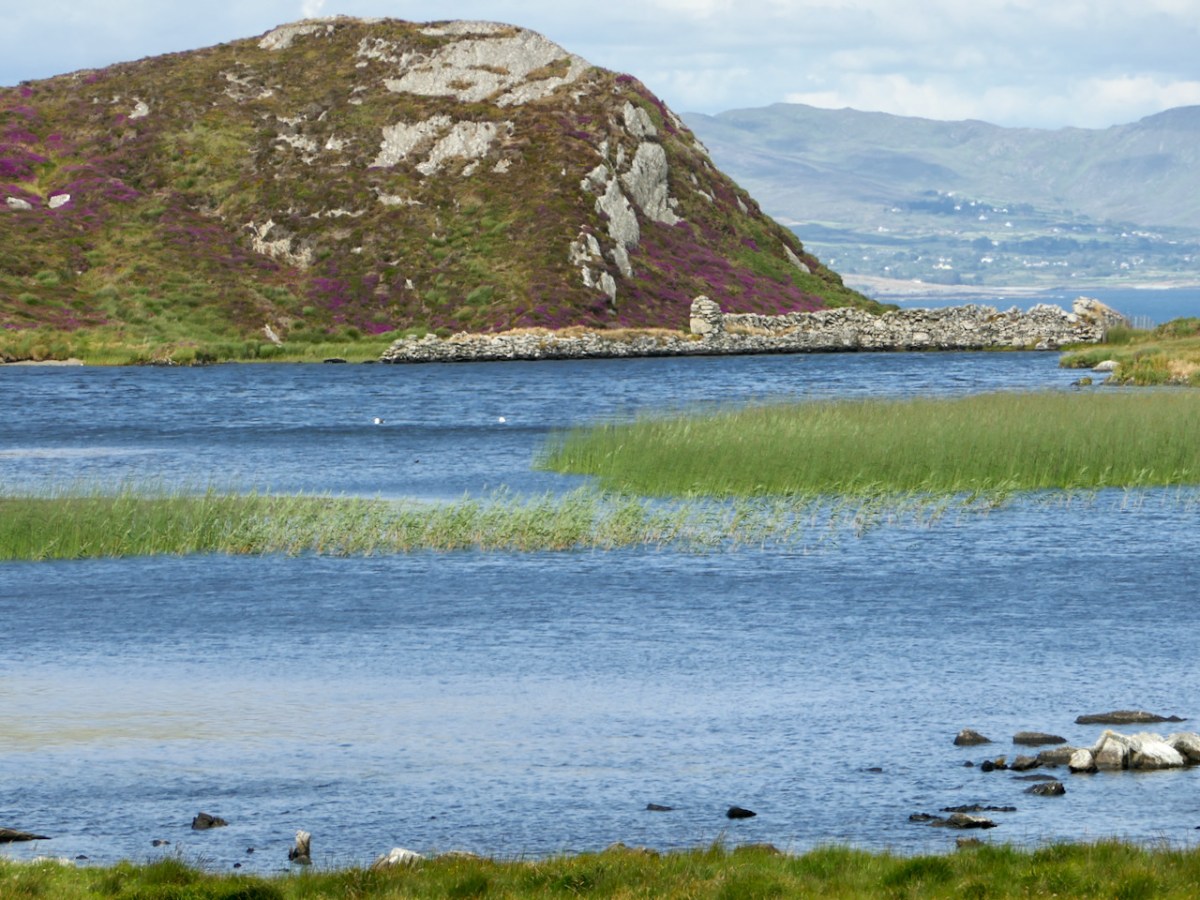
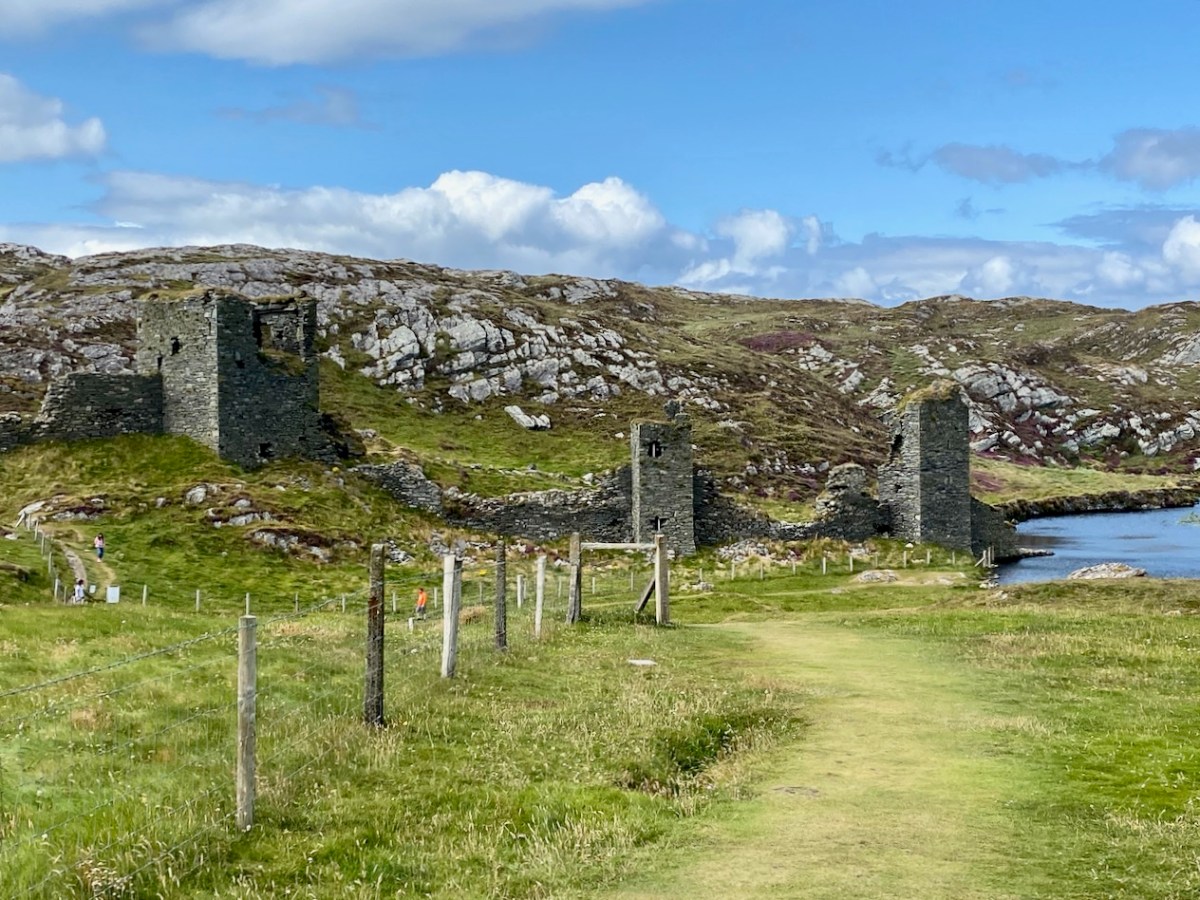
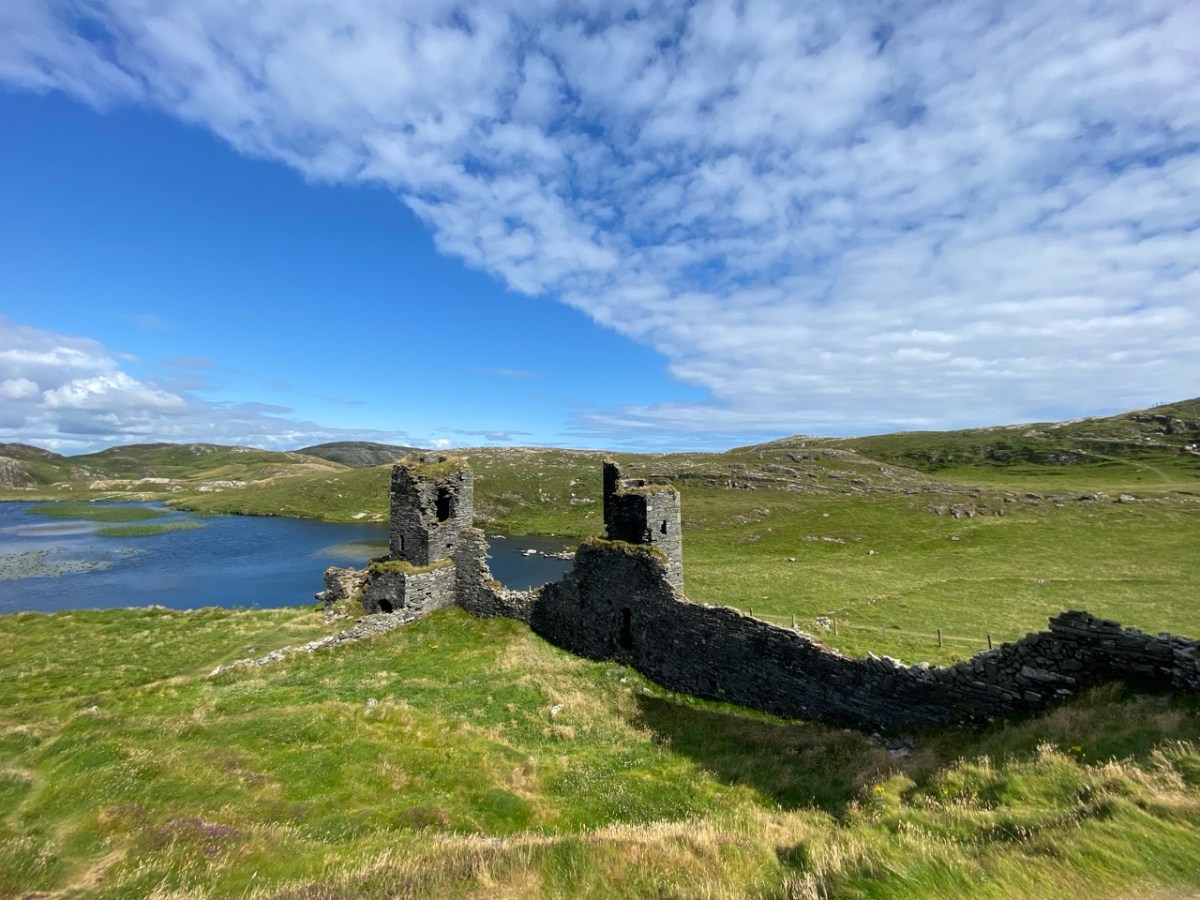
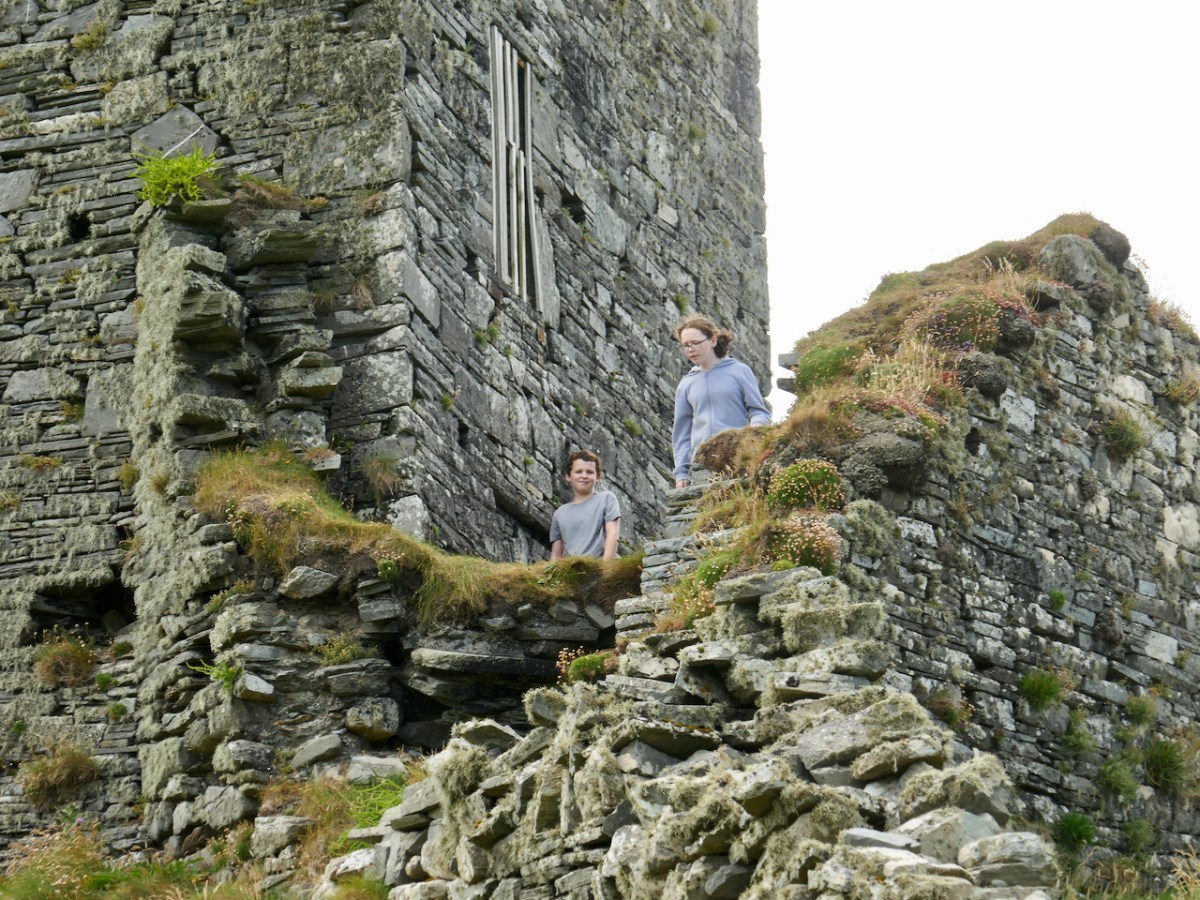
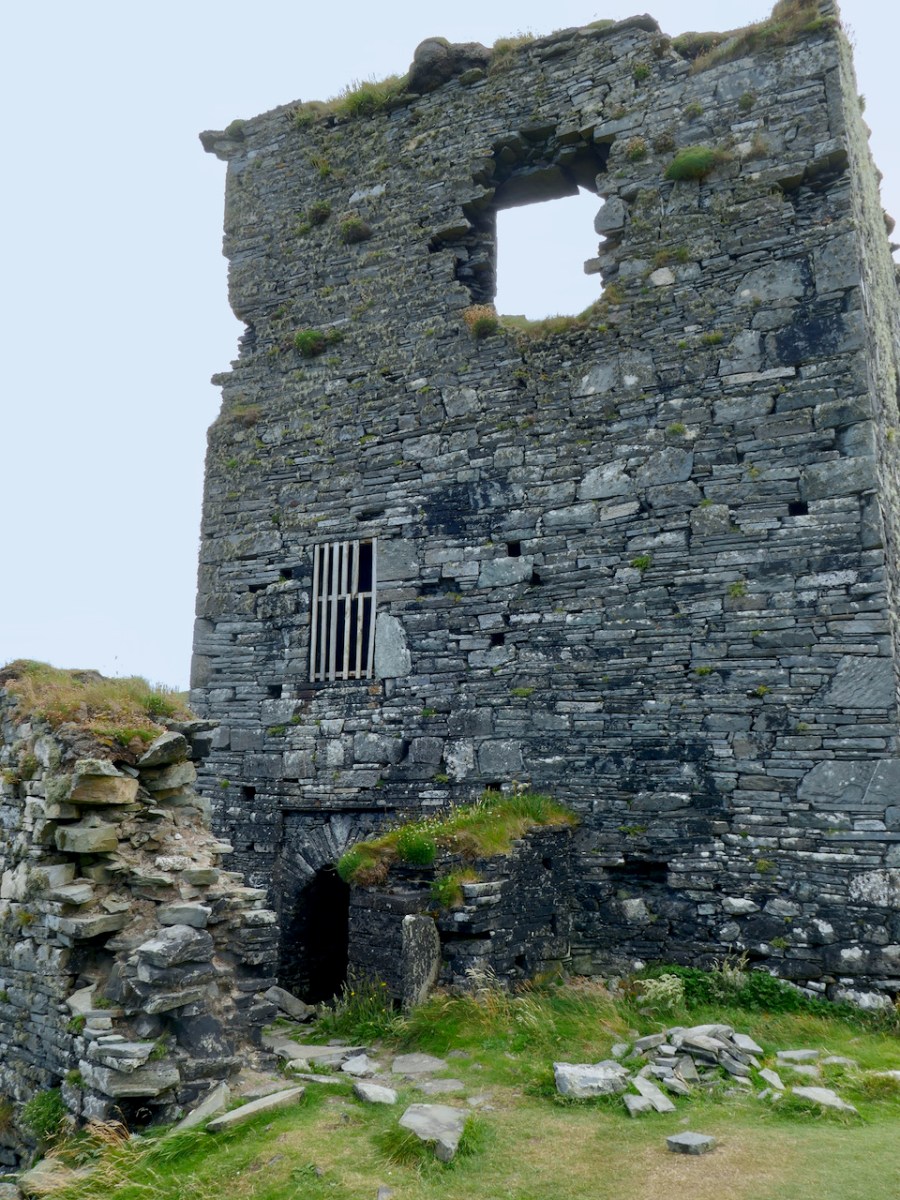
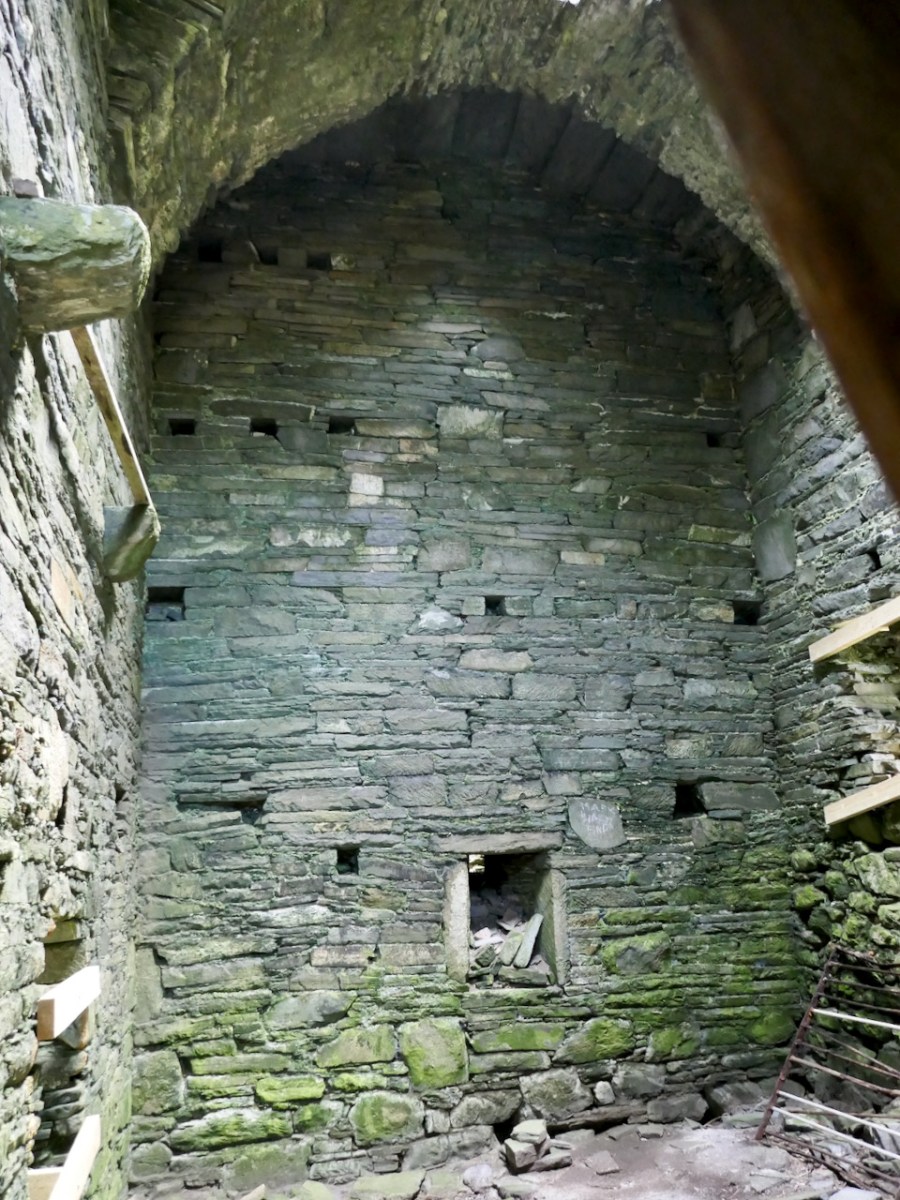
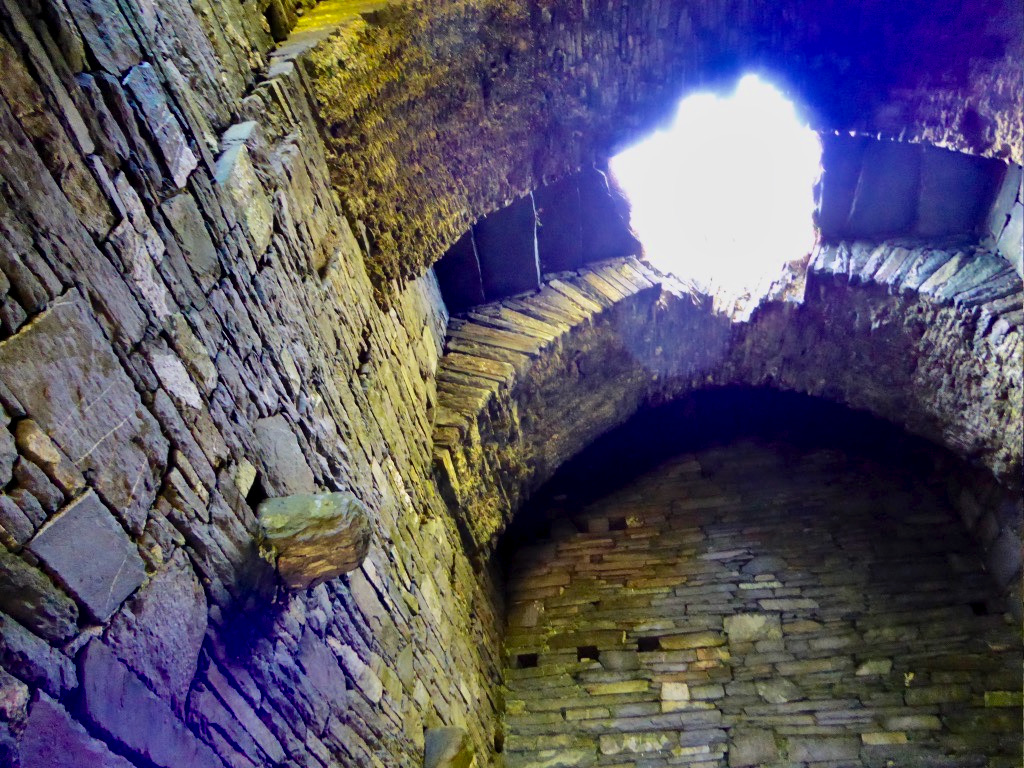
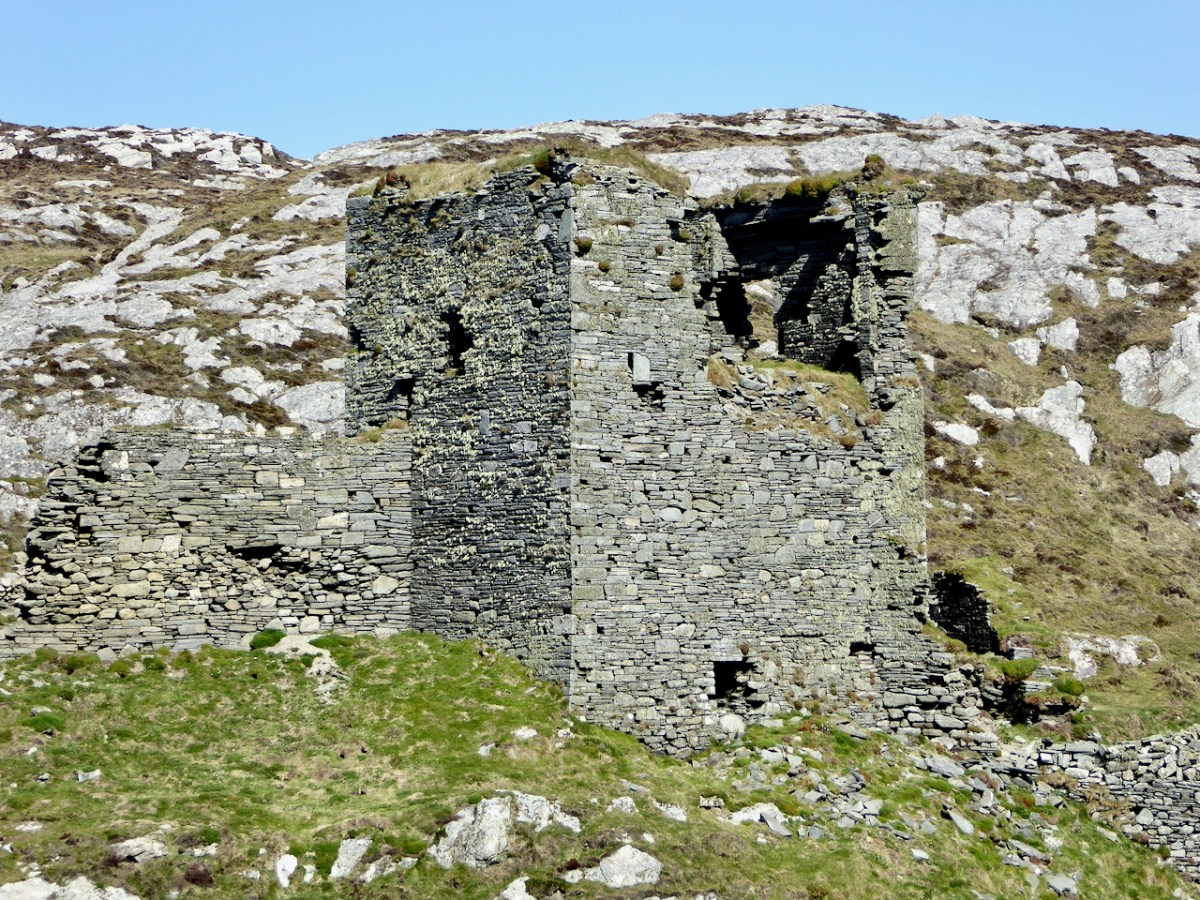
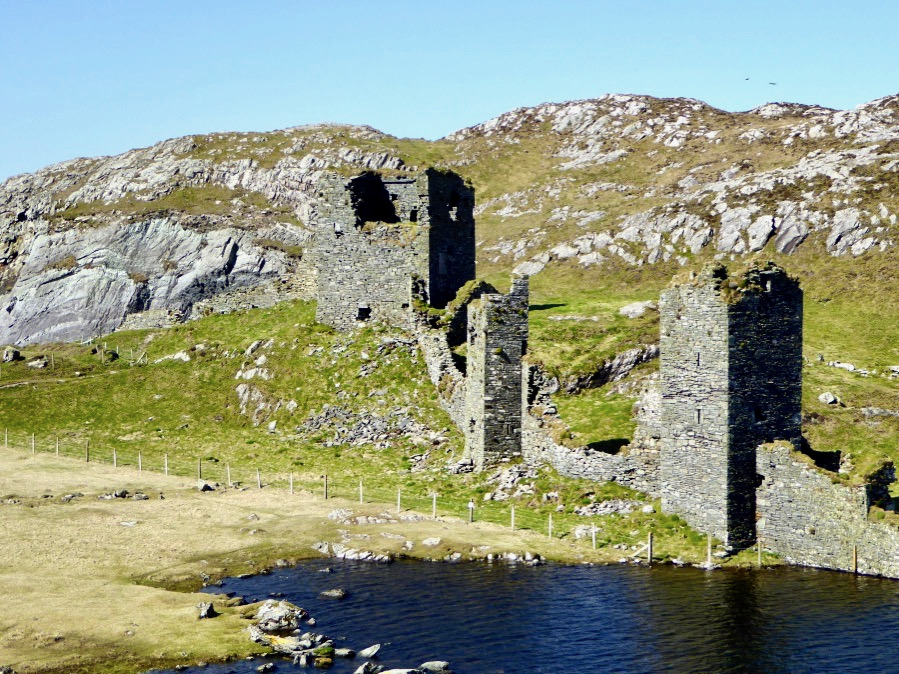
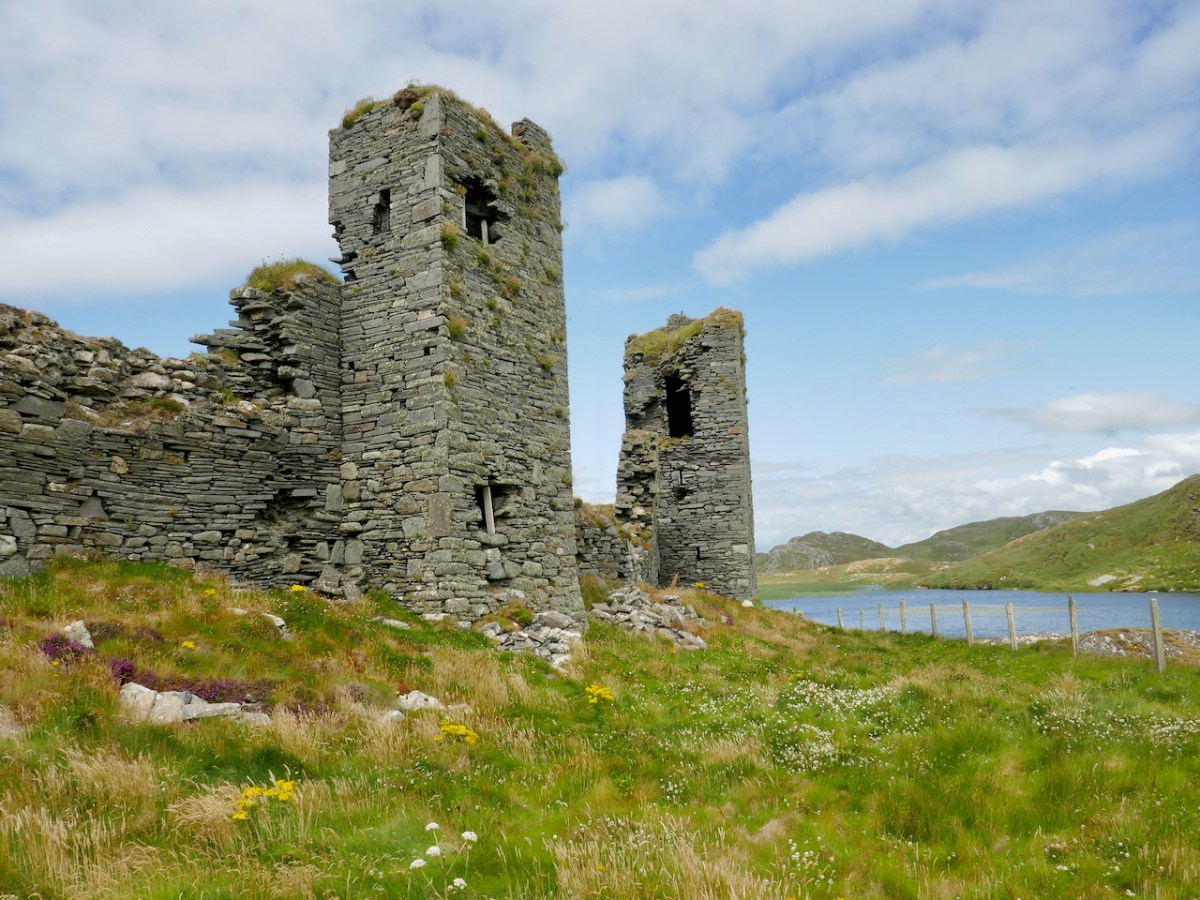
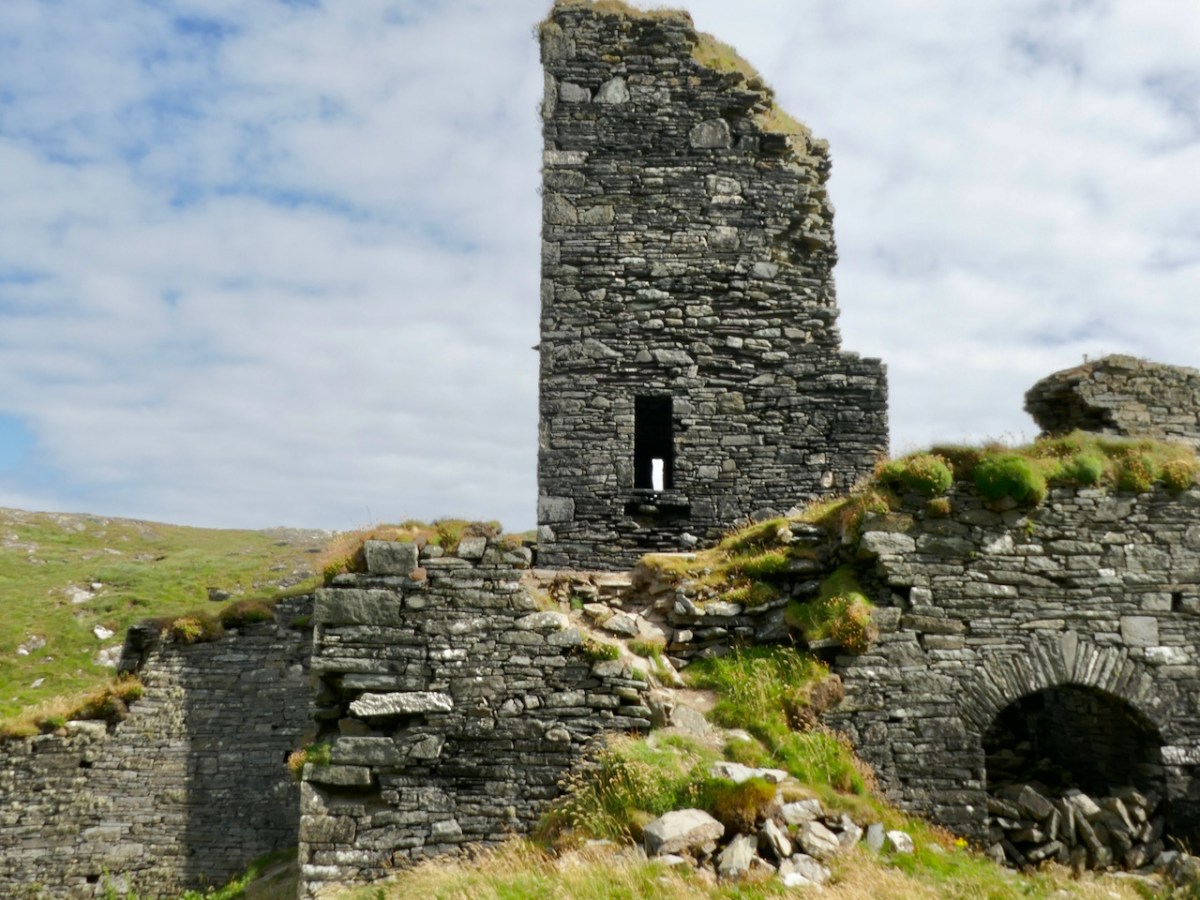
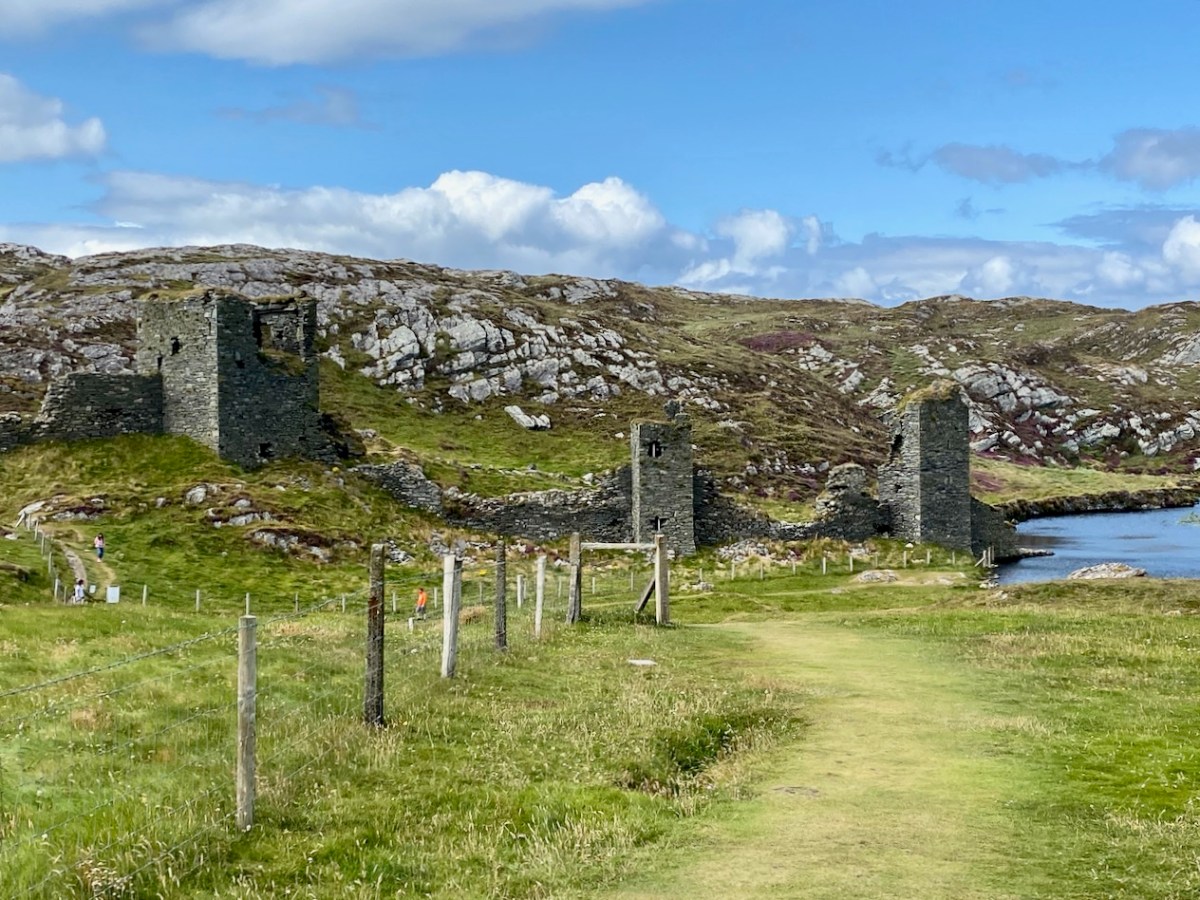
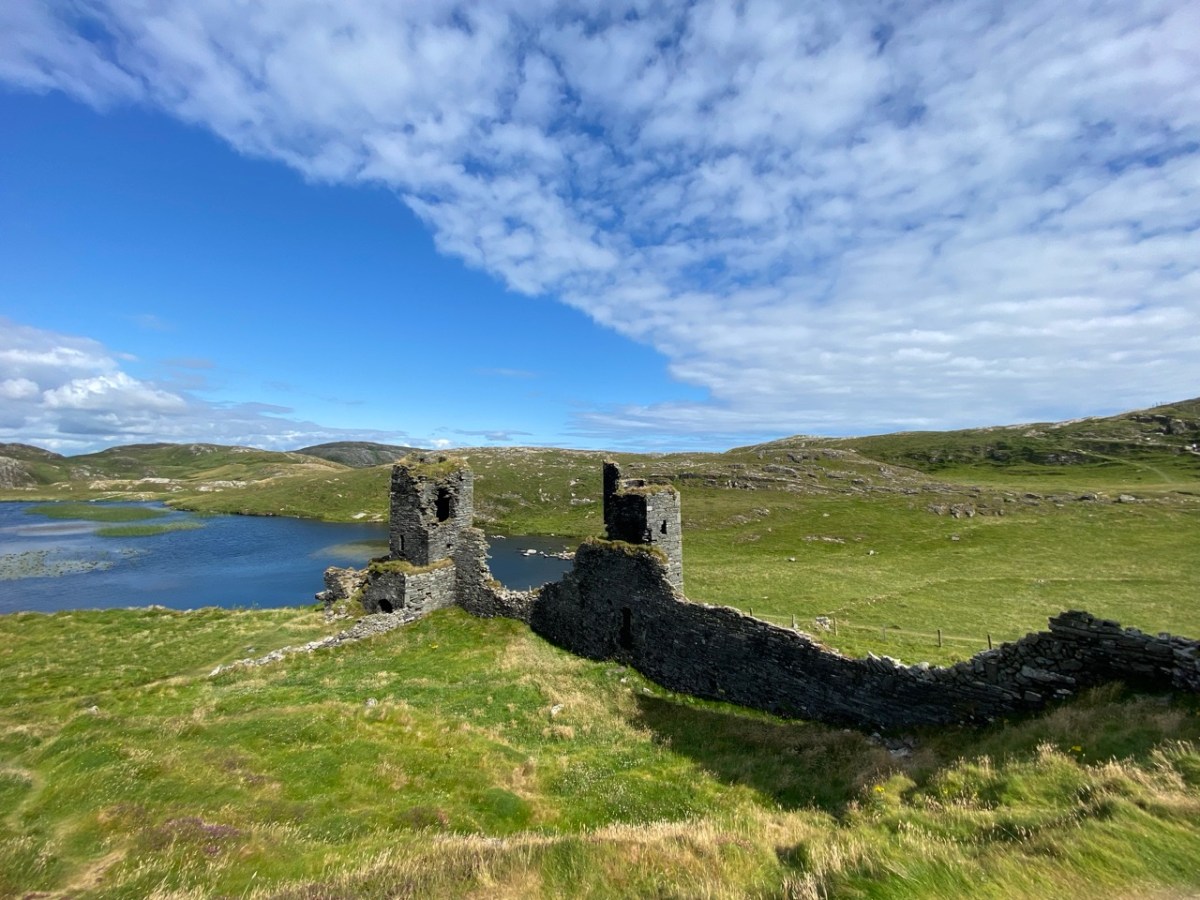
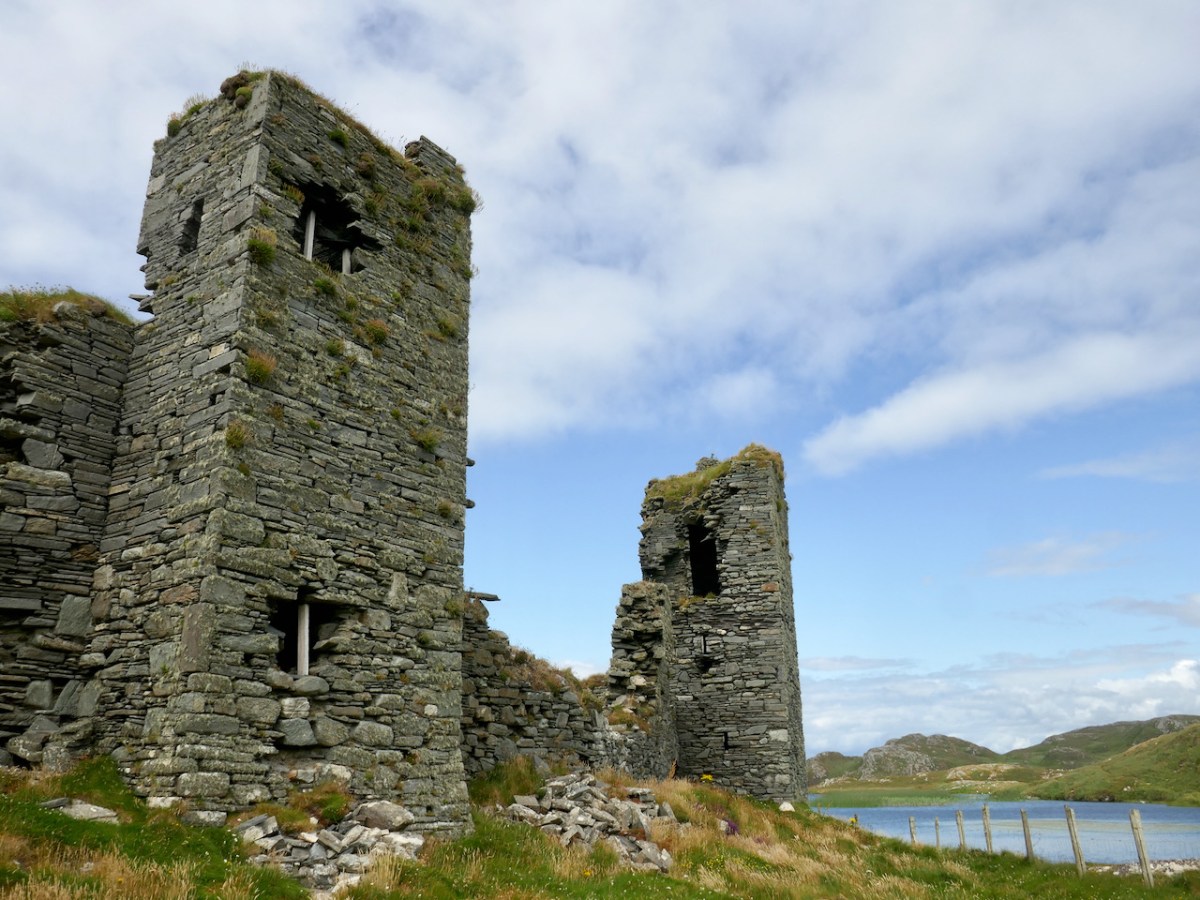
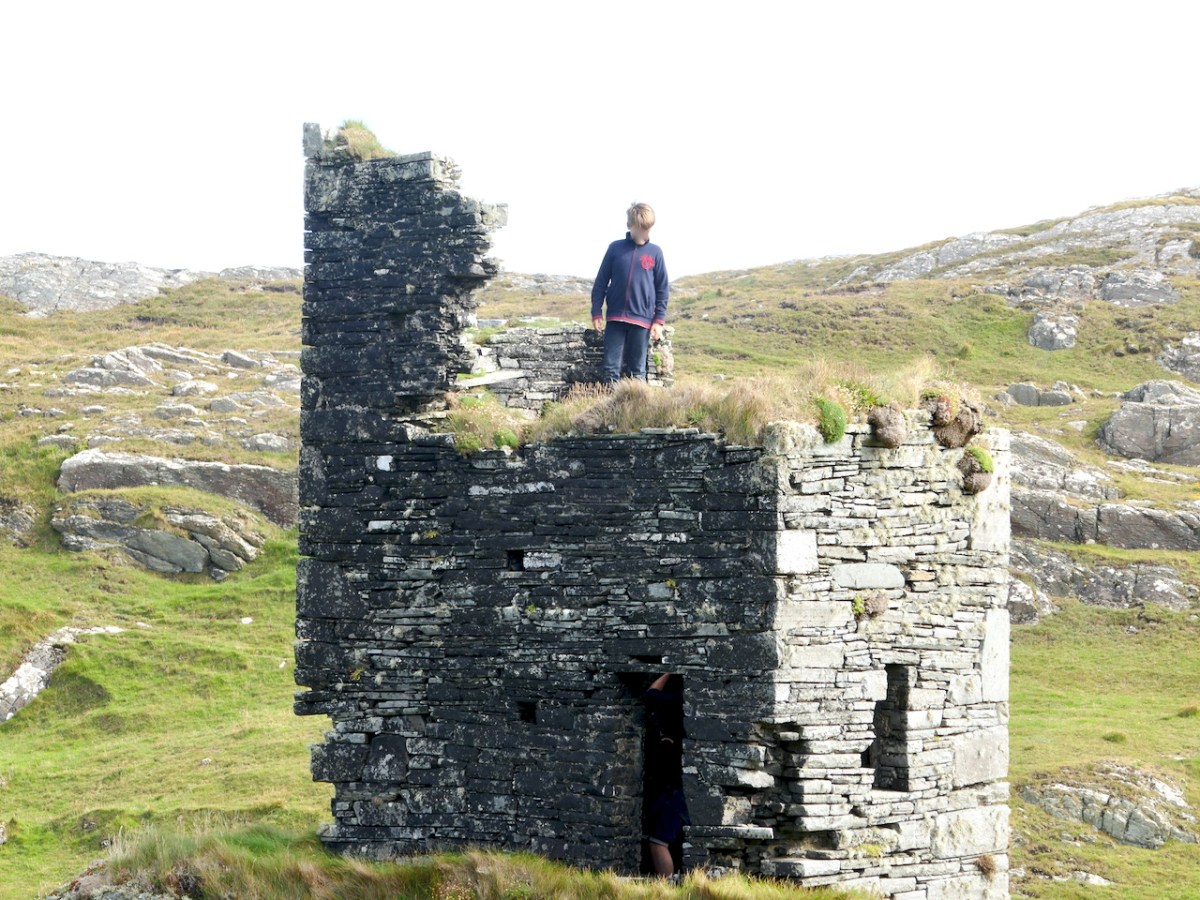
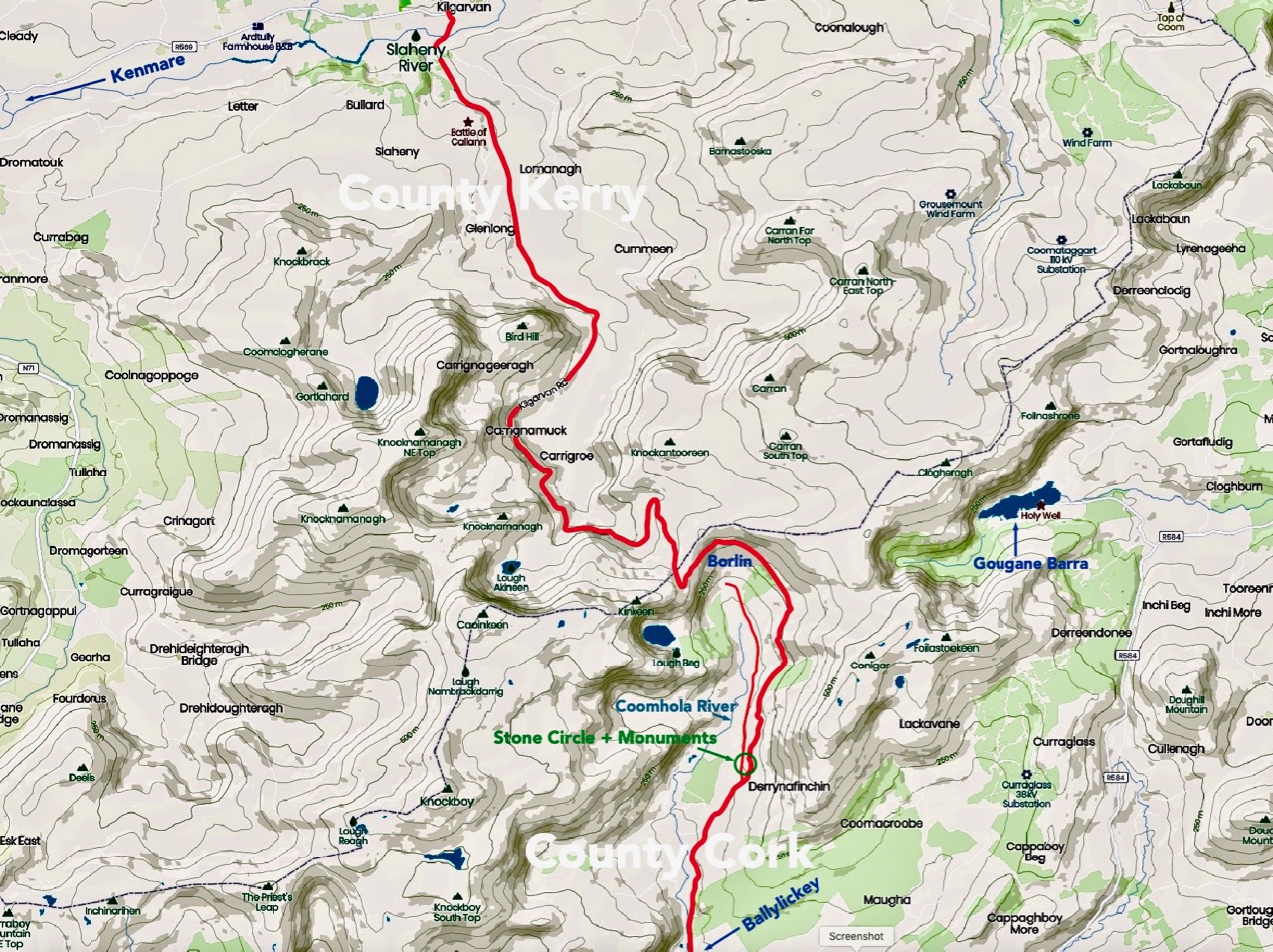
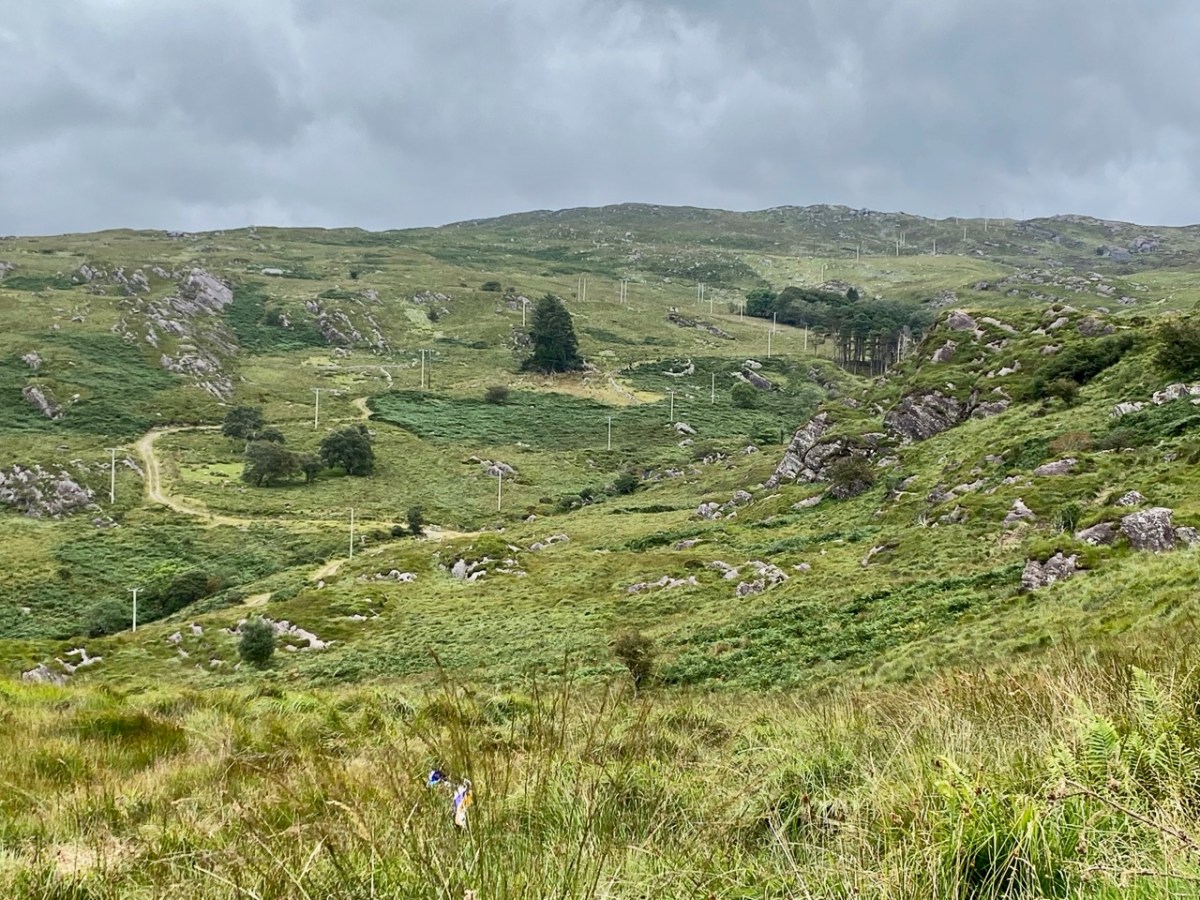
Here’s a post I published in June last year – only 15 months ago. Many of you will remember it. I’m repeating it in order to remind you of the beauty of this particularly remote corner of West Cork and Kerry. We travelled this byway again last week, and were surprised to notice how ‘raw’ the landscape seemed in places. This is partly because a new roadway has been made down through the valley to serve local property. But also I was struck by the number of power lines which go through the area.
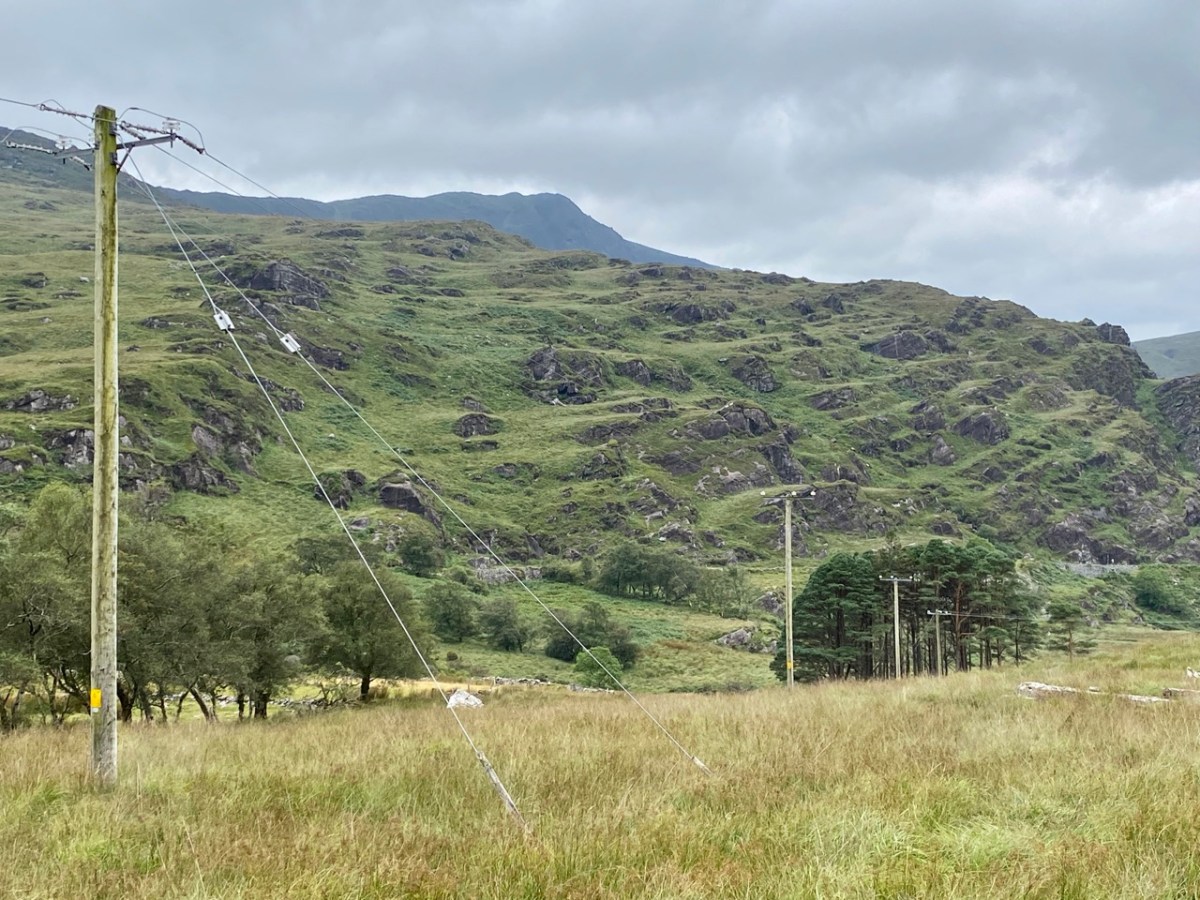
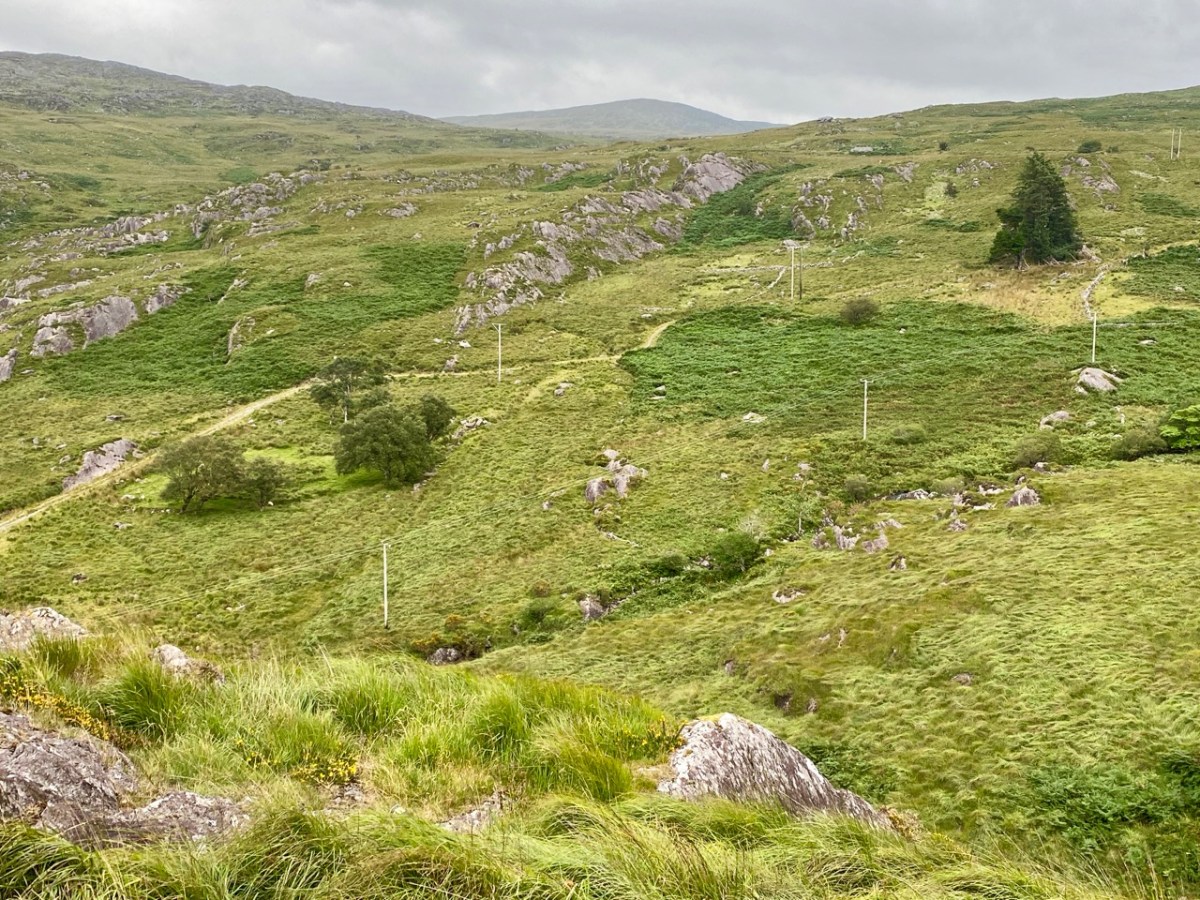
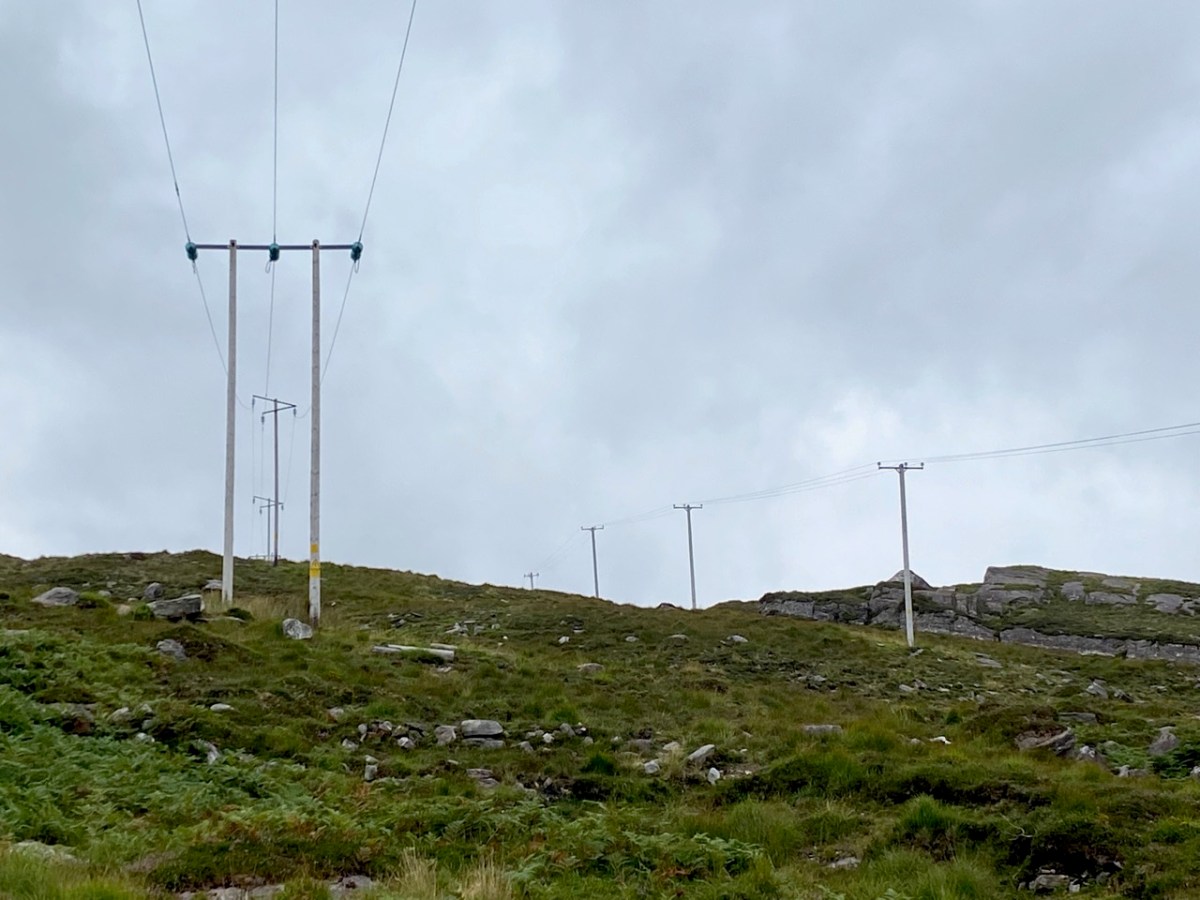




These lines were part of a programme to improve and extend the Eirgrid of Ireland – the remit of the ESB.
The distribution system delivers electricity from the transmission system to 2.3 million customers in Ireland, operating at 110kV in the Dublin area, and at 38kV, 20kV, 10kV and low voltage (LV) nationwide. In serving Ireland’s large rural population, the network length per capita is four times the European average and overhead lines outnumber underground cables 6 : 1 . . .
ESB Networks IE
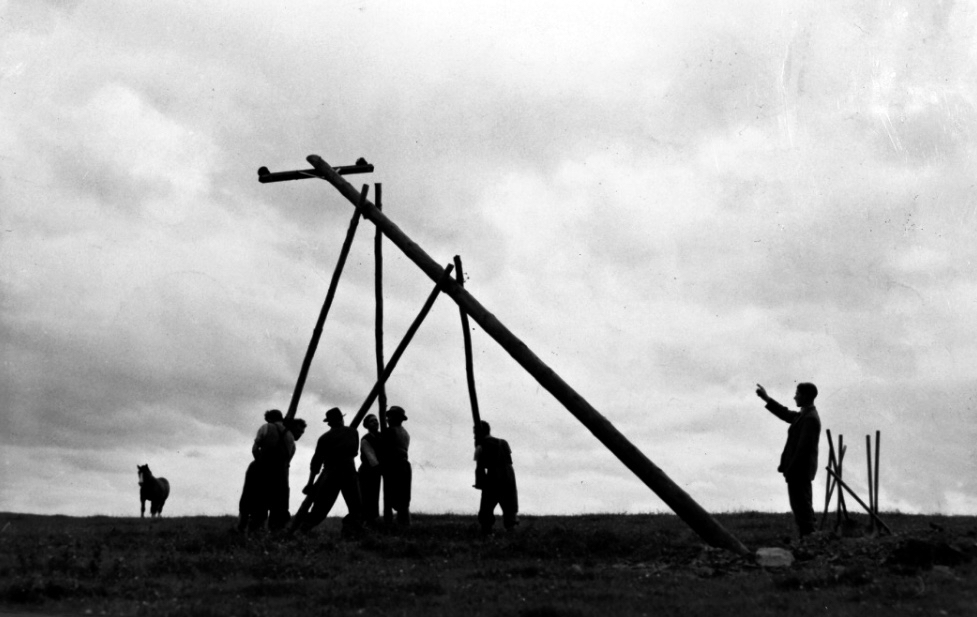
Statistics are remarkable: 2.1 million wooden poles and 150,000 km of overhead line have been used to date, along with 22,000 km of underground supply cable. Due to the Rural Electrification Scheme led by ESB, by the 1960s 80% of rural households had electricity in their homes. Now, most households are connected to the grid, and works are in progress to upgrade the system across the country. In the image below the very first pole is being erected in 1944, while under that is a photo of a PR event ten years later (both are from the ESB Archives).


Emotions are mixed as we travel through this wild country and see how power lines can affect the rural areas, while obviously also providing essential services. We were surprised that so many lines – and poles – were required to get the supply over these particular hills. A correspondent has given us the full details (thank you Justin Cremin).
. . . The bigger line on the left is a 38kv line, it goes to Kikgarvan 38kv station and originates at Ballylickey 110kv station. This supplies all of the Beara peninsula with the Kilgarvan line as an alternative “just in case”. It was built in the 1950’s at a guess and would have primarily blasted by gelignite and the poles stood manually.The line on the right is called the Hydro line. It runs over the hill to Slaheny to a small hydro and originated in Bantry 38kv where it picks up another 3 small hydro stations along the way. This Borlin leg was stood in the very early 00’s/ very late 90’s . . .
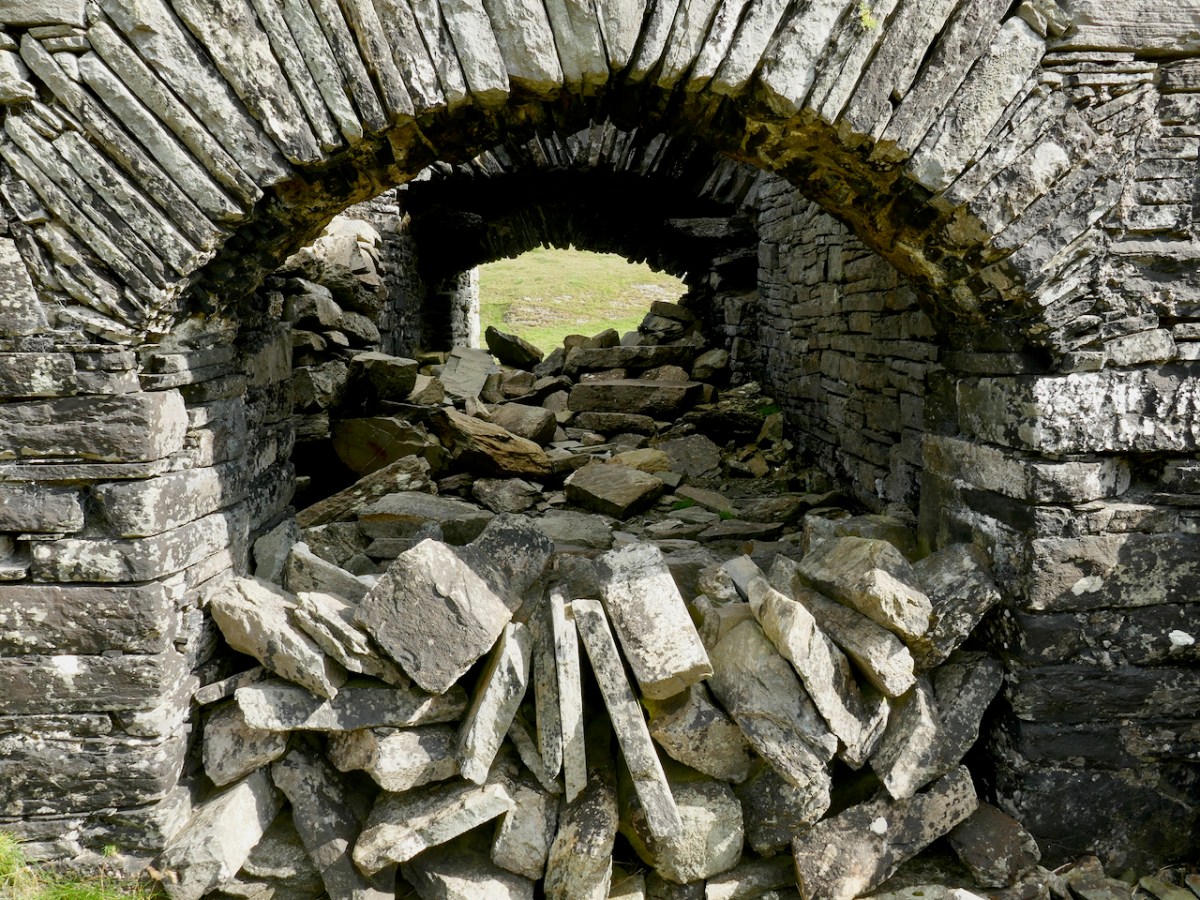
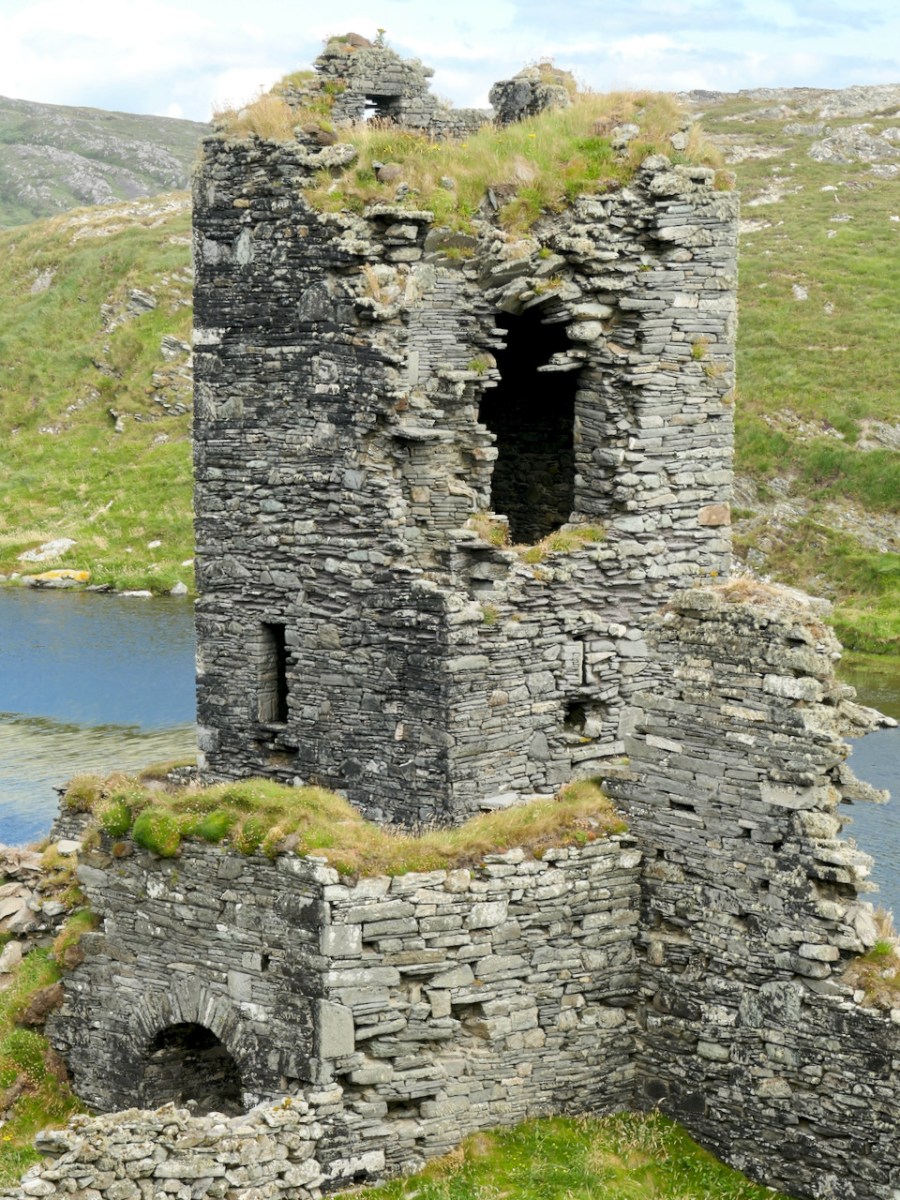
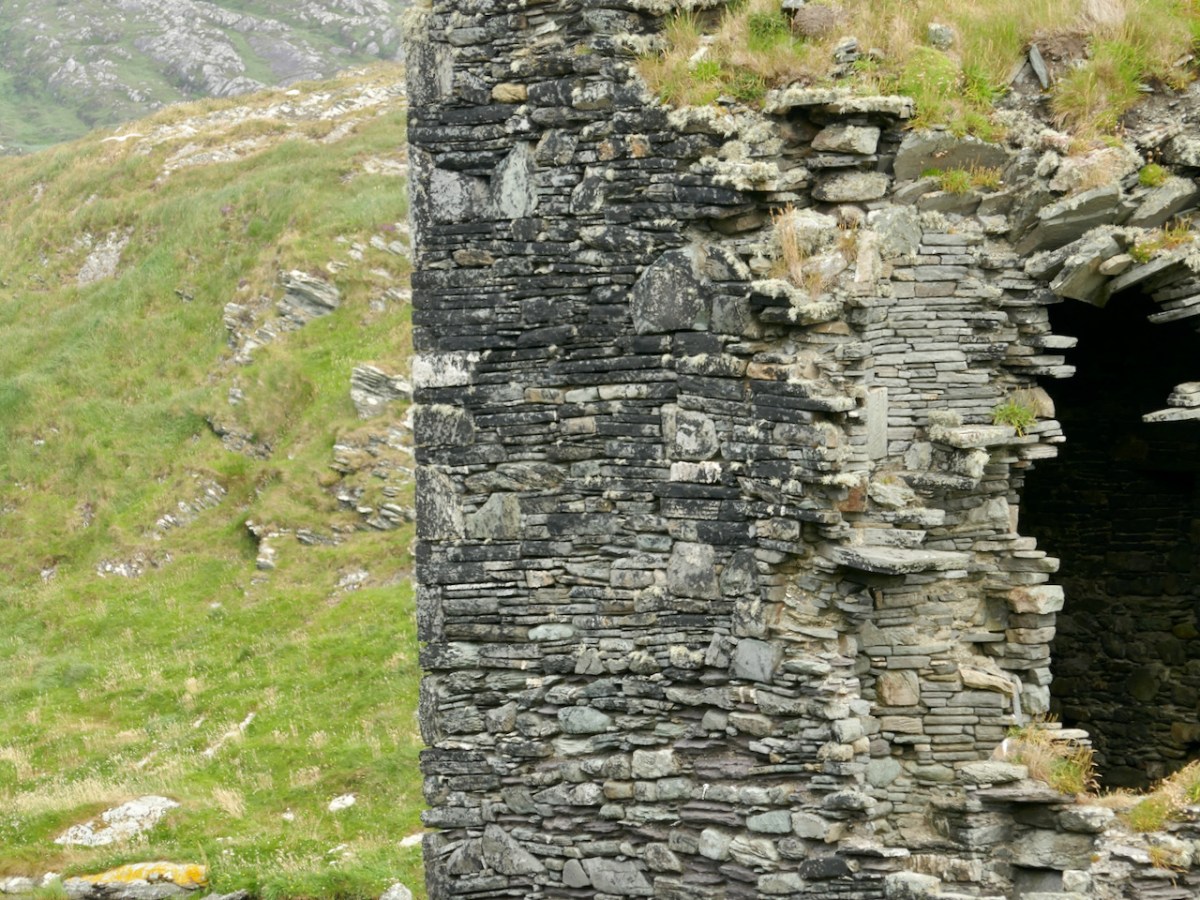
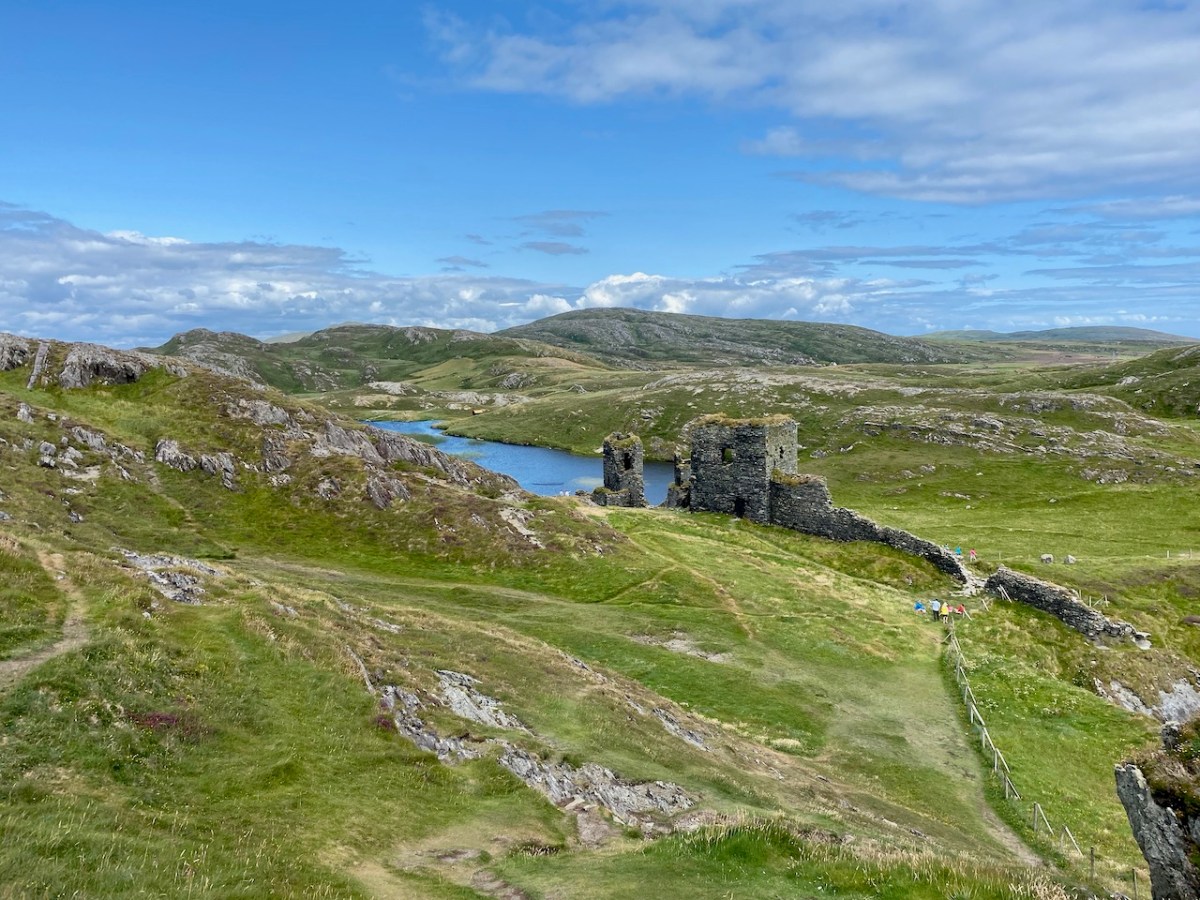
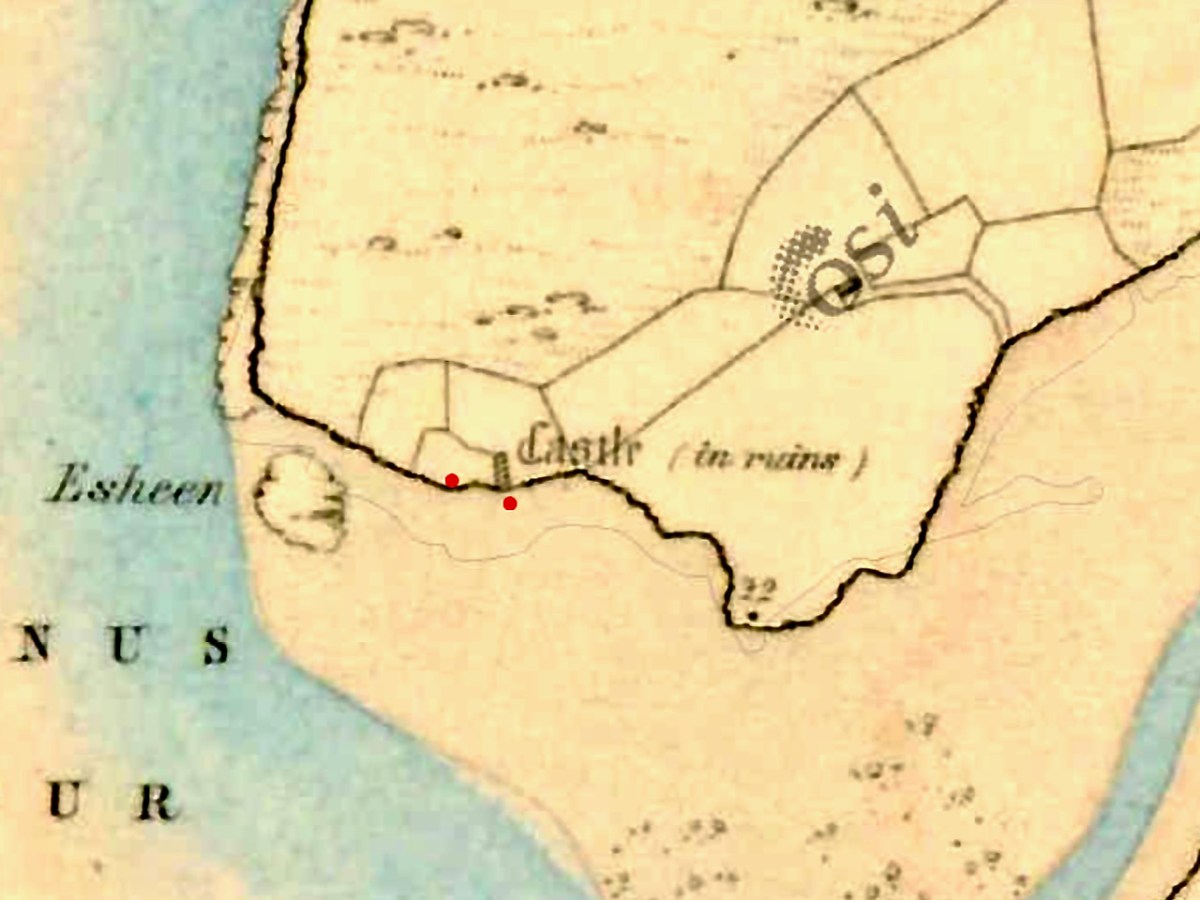
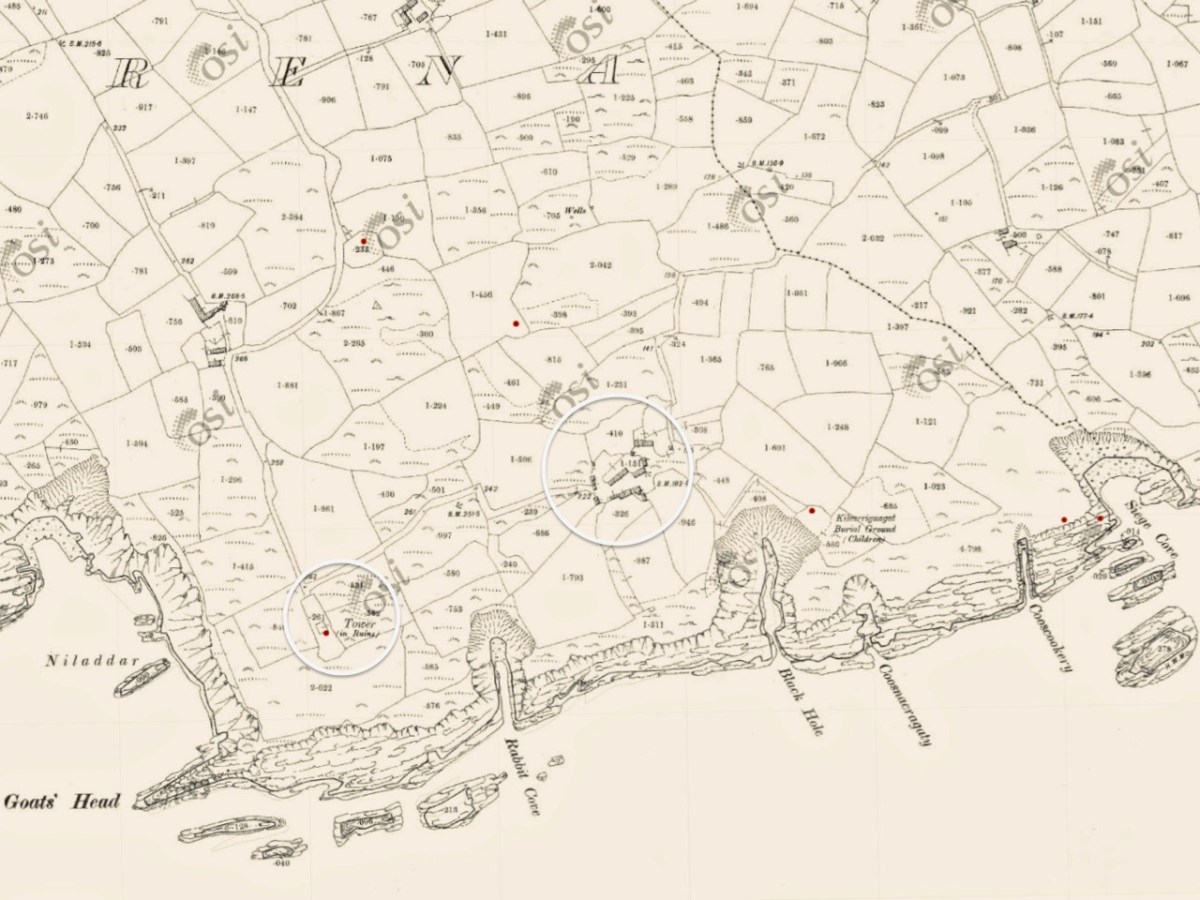
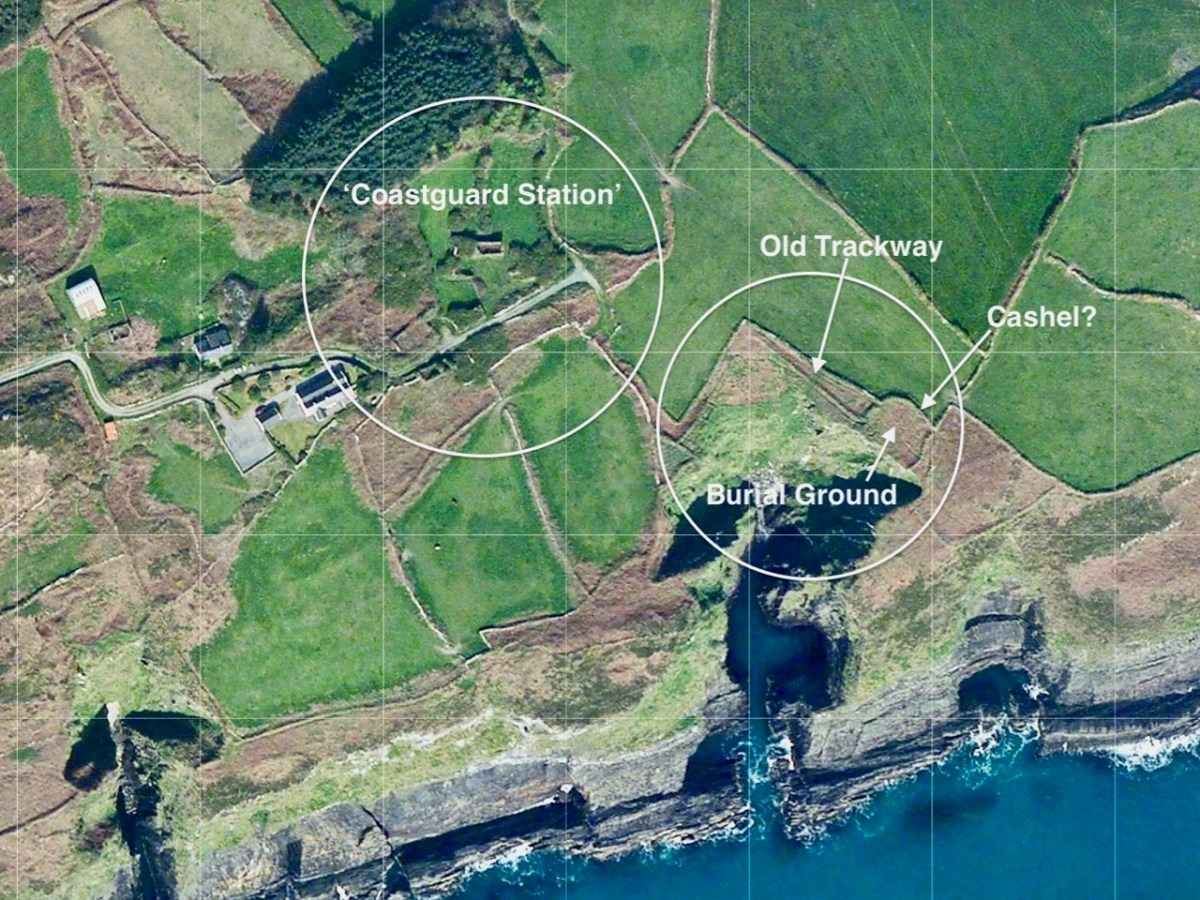
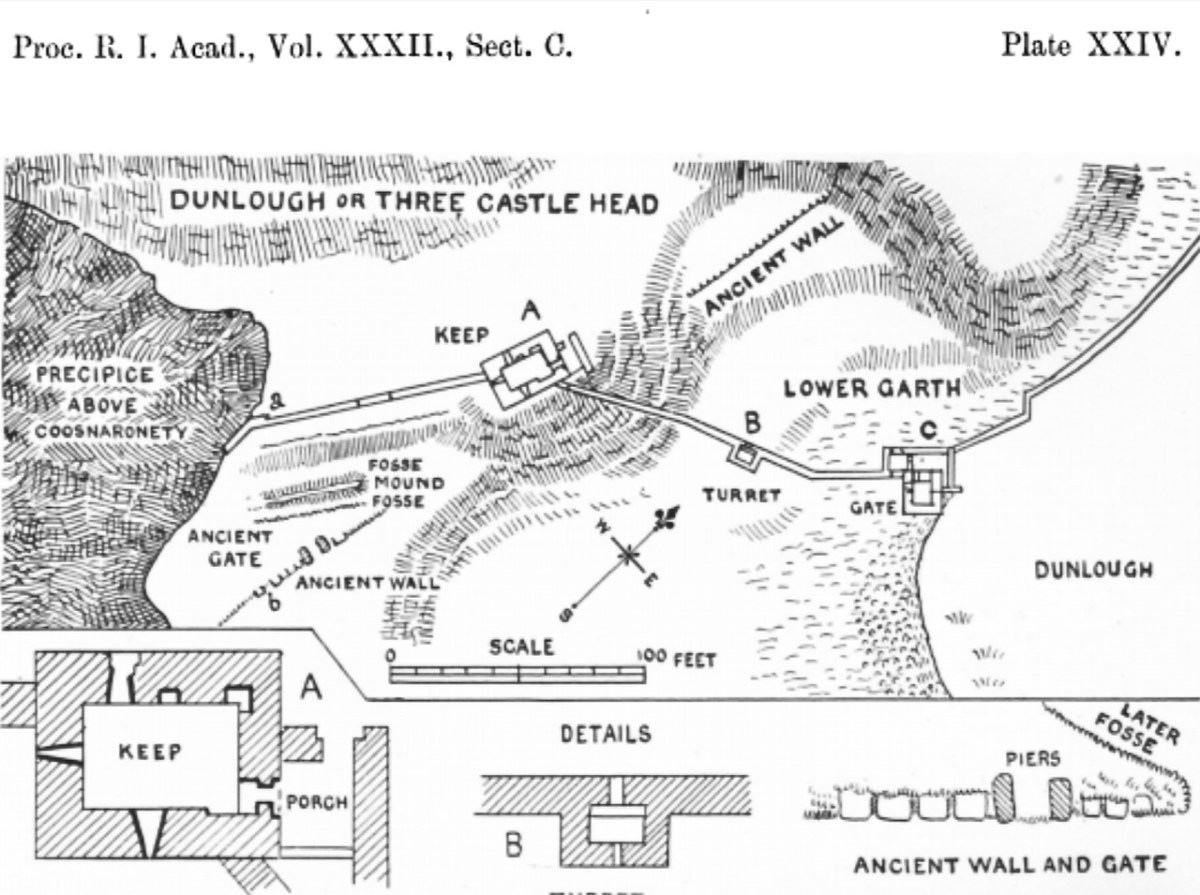
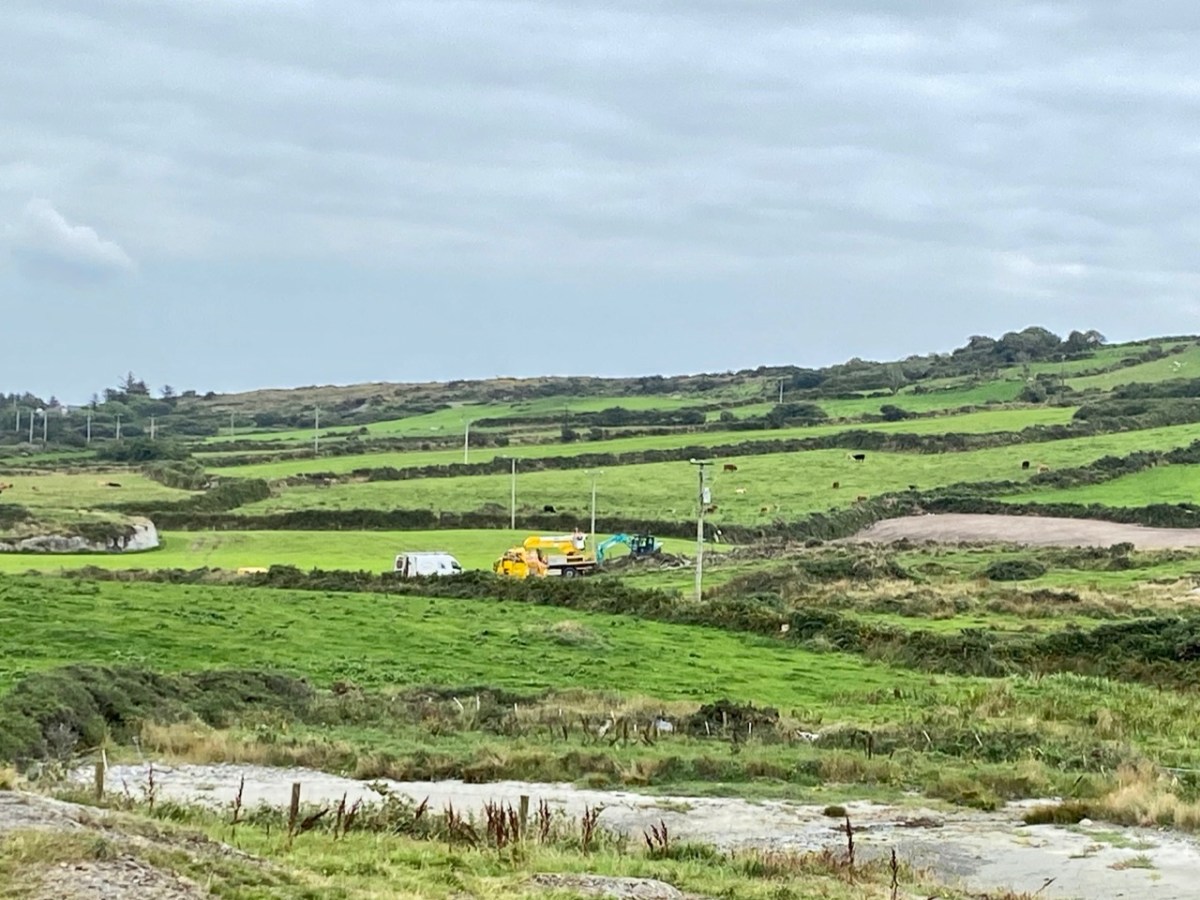
We came across further grid improvement works currently in progress on a recent trip to the environs of Dunmanus Castle:

So here – to remind you – is the Coomhola and Borlin landscape as we discovered it, and recorded it, in our post of 2020:
As the Coomhola River tumbles from Borlin to the sea, gathering tributaries, it forms many pools amongst the riffles and glides. These pools, in summer, provide leafy shelters for salmon and trout. To anyone who has fished or walked the river, each pool has its own character, and each its own name . . .
[From Hidden Gold, History and Folklore of the Coomhola and Borlin Valleys Julia Kemp: Coomhola Borlin Community Development Association 1998]
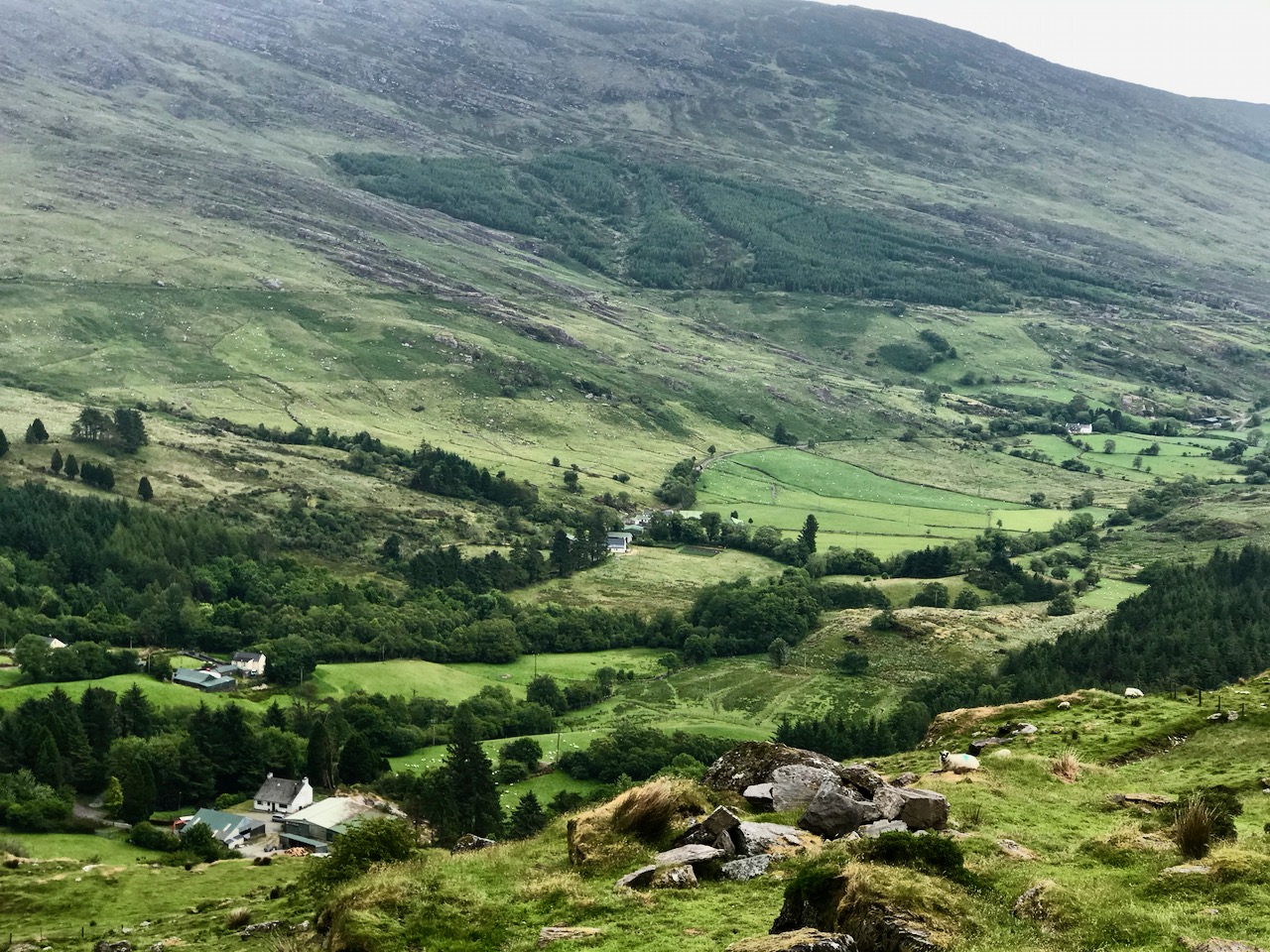
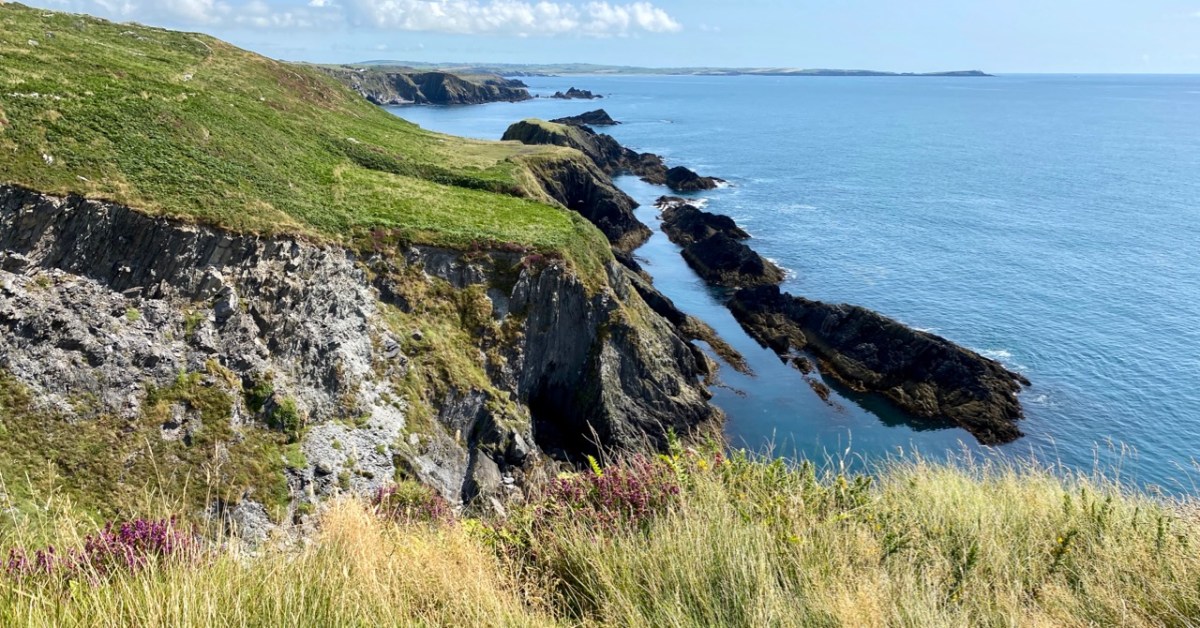
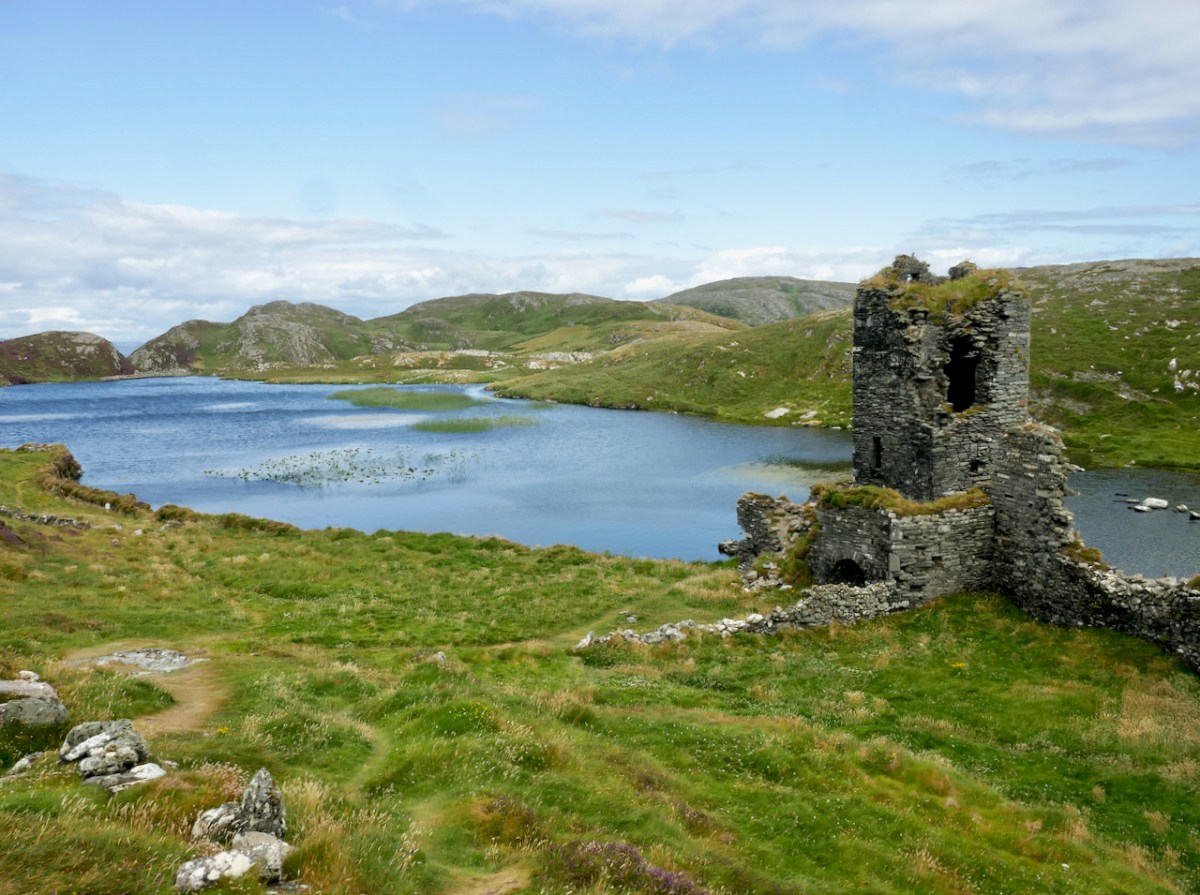
On the header is the spectacular view from Borlin, looking down the great glen where the Coomhola River finds its way through a country formed by glaciers in the Midlandian period, about 10,000 years ago. The rugged Shehy mountain range (Cnoic na Seithe in Irish, meaning Hills of the Animal Hides) with its peaks of Knockboy, Caoinkeen and Kinkeen provides some of the most dramatic scenery in West Cork, its scarred outcrops clearly showing the downward progress of the ice sheets. The contrast between the barren high land and the lush pastoral meadows laid out below evoke a beauty which is hard to match – anywhere in the world!
The Kilgarvan (Co Kerry) to Ballylickey (Co Cork) road is one of the unsung feats of Irish engineering. Until the middle of the nineteenth century it was no more than a system of ‘nearways’, providing rough, narrow access tracks to remote mountain dwellings and hard-won field systems. A famine improvement project c1846, involving metalling, a tunnel, cuttings and stone retaining walls, transformed it to the ‘through road’ which exists today – although it may seem to us no more than a boreen. It’s there for all to travel on, and will provide a breathtaking experience – but be aware that it could also deliver some hair-raising reversing episodes on the rare occasions when a vehicle is encountered coming the other way. The upper photo shows the road ‘clinging on’ to the face of a mountain outcrop, while the map gives a good idea of the circuitous route that the way takes to keep as far as possible to a level contour on its journey.
This is the country of St Finnbar. If you follow the County border east from the top of the Borlin Glen (off-road) you will very soon come to the site of his sixth century monastic settlement at Gougane Barra. This whole area was loved by the Cork born writer and illustrator Robert Gibbings, whose book Sweet Cork of Thee tells of a seven month sojourn in this mountainous region in 1949, beautifully illustrated by his woodcuts.
Mountain Road by Robert Gibbings, woodcut from Sweet Cork of Thee, published 1951
As we drove along the road beside the Inchigeelagh lakes, we could see moorhens gathering material for their nests among the taselled reeds and swans on islets, piling up dead rushes in readiness for their eggs. A corncrake was calling from a meadow. Celandines and kingcups outshone the gorse.
Mick said to me: ‘My father’s sister lived a mile to the north of us here. She married a man by the name of Scanlan. His mother came from Gougane and ’twas one evening when she was travelling west by the lake – there was no road there then, only a little bit of a track – she looked in the lake and what did she see but fields of corn and sheep and every sort of land and crop and stock. She was an old woman at the time and she knew well enough ’twas a kind of enchantment must be on the lake, so she says to herself, if I can keep an eye on it all and throw a bit of iron at it the spell will be broken. So she kept her eyes fixed on the fields and the cattle and the pigs and the hens, and all the time she was thinking where would she get a bit of iron. And the only bit she could think of was in the heel of her shoe. ‘Twould be worth it to throw in the shoe, says she. But when she went to unrip the lace wasn’t it tangled in a knot, and for the glint of a second she took her eye off the land. When she looked again ’twas all disappeared and the lake was there the same as ever.’
Our road turned south, through a wilderness of rock and bog and lilied pools . . .
[Robert Gibbings Sweet Cork of Thee, J M Dent & Sons 1951]
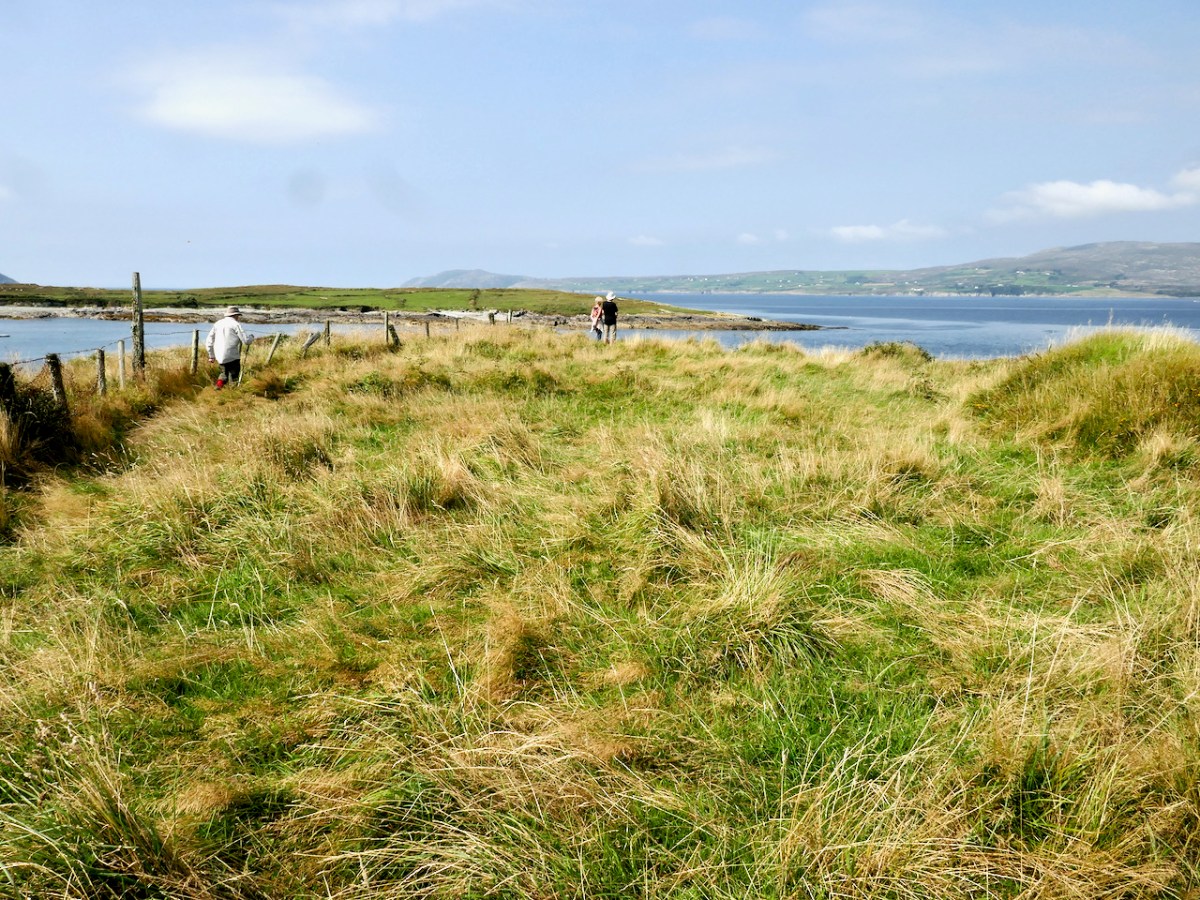
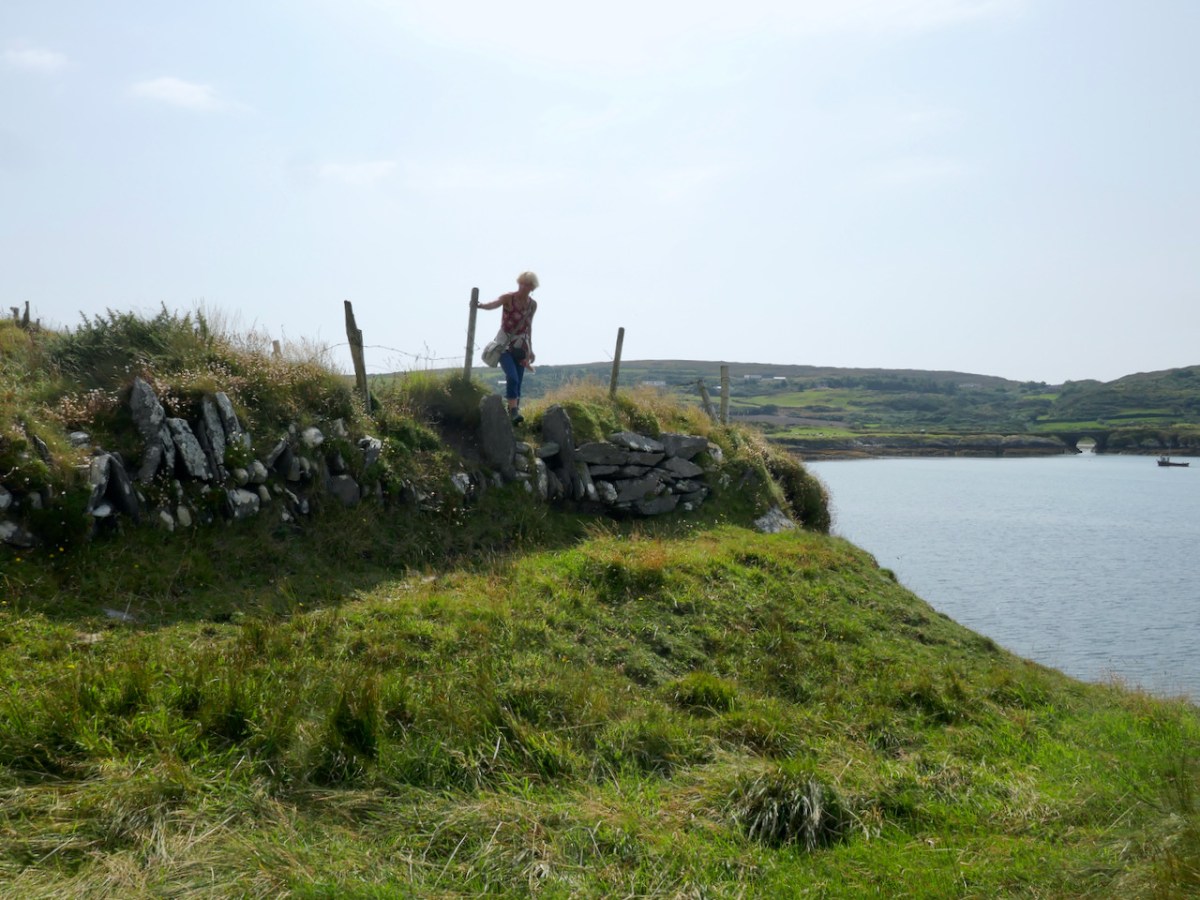
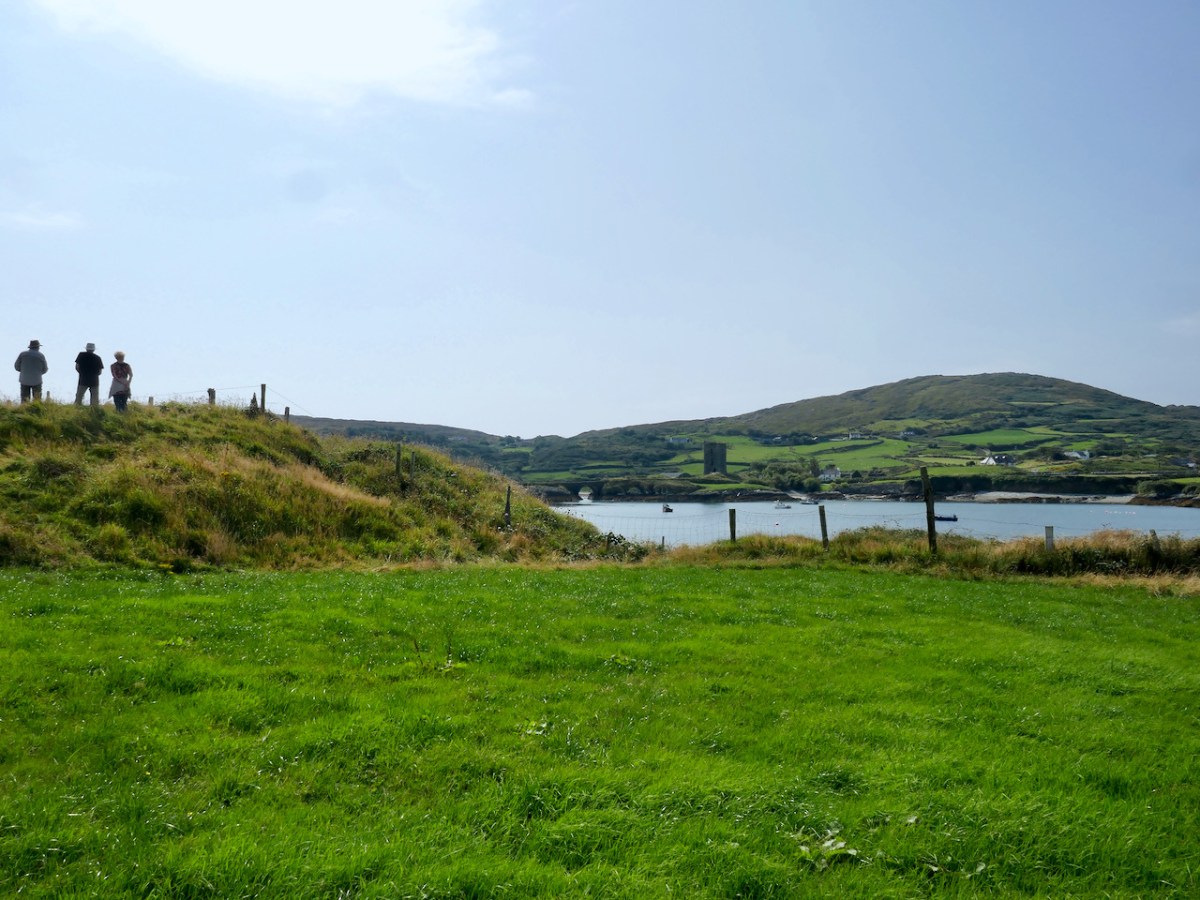
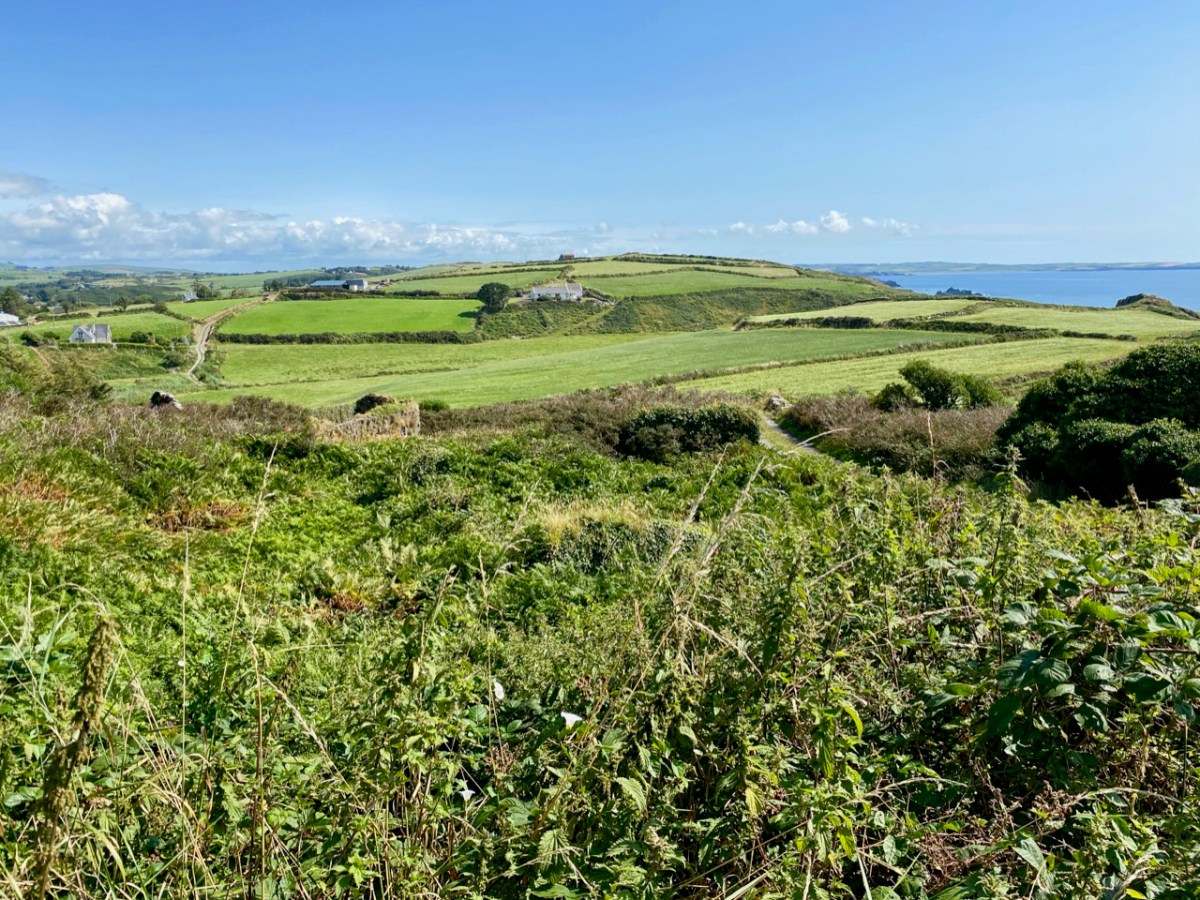
From the highest rim of Borlin Glen (upper picture), the Comhoola River valley is laid out below. Home to sheep and ravens, the scattered farmsteads emerge from rock and forest and provide a living – as they have for countless generations – to a hardy people.
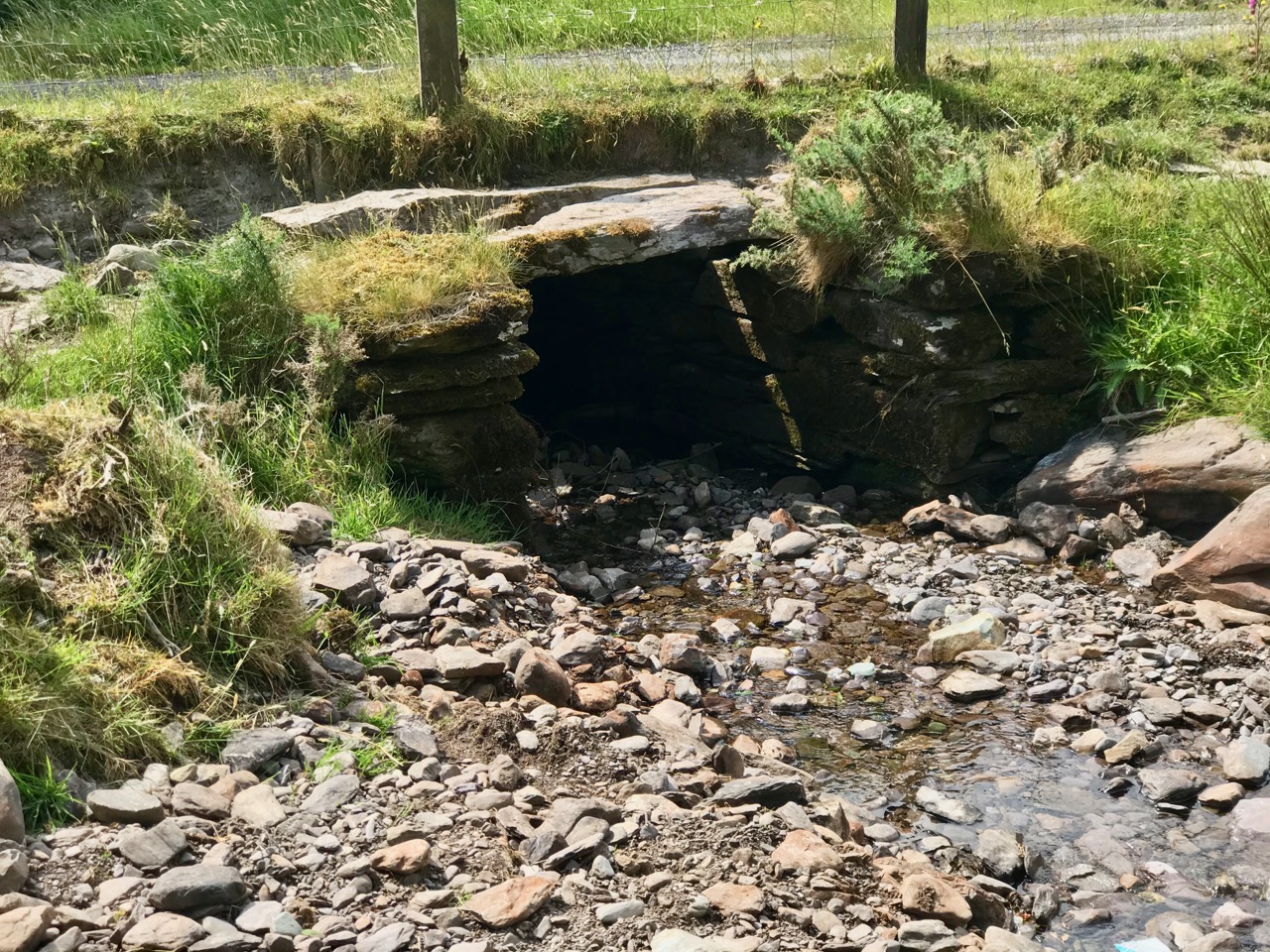
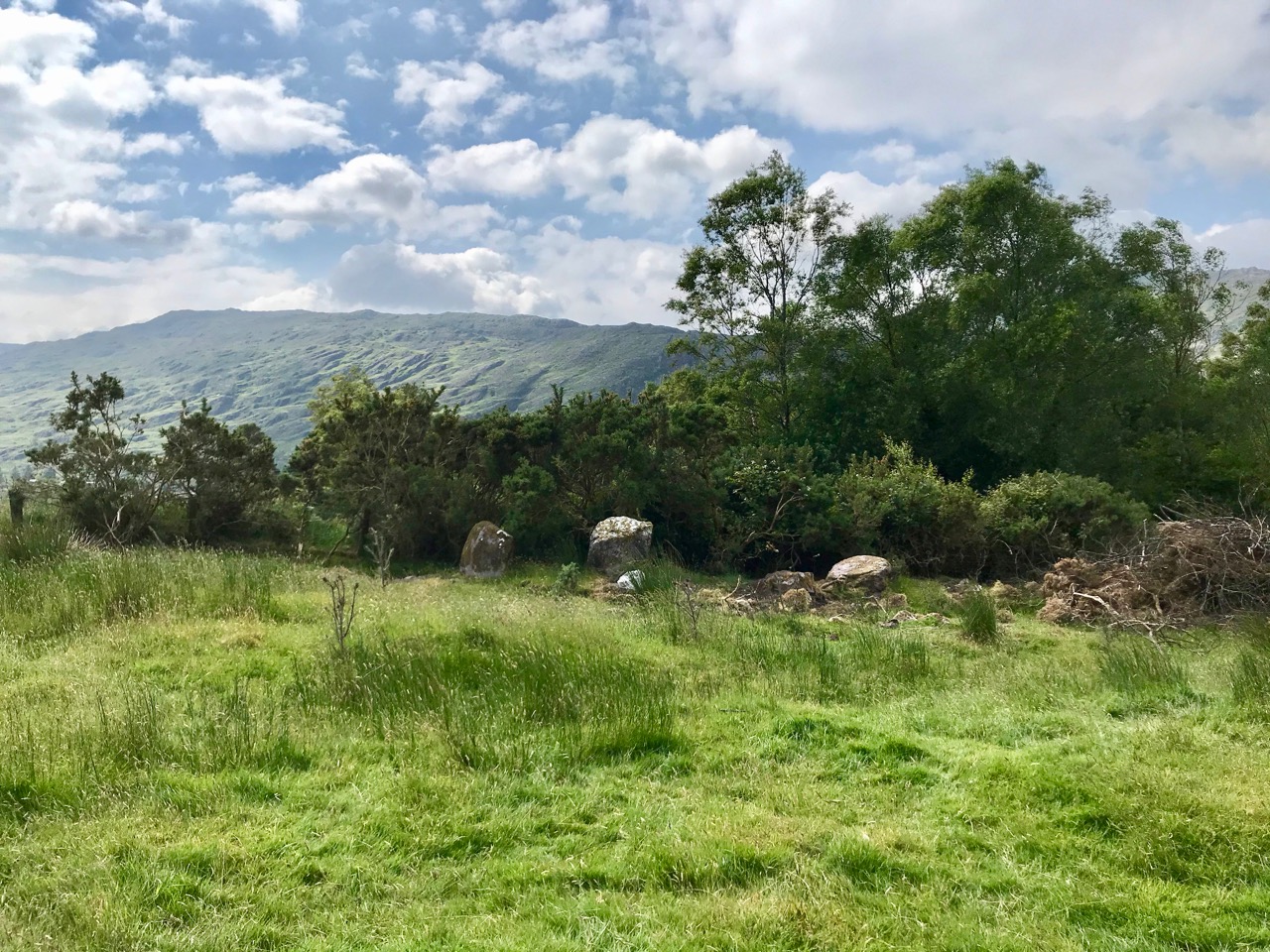
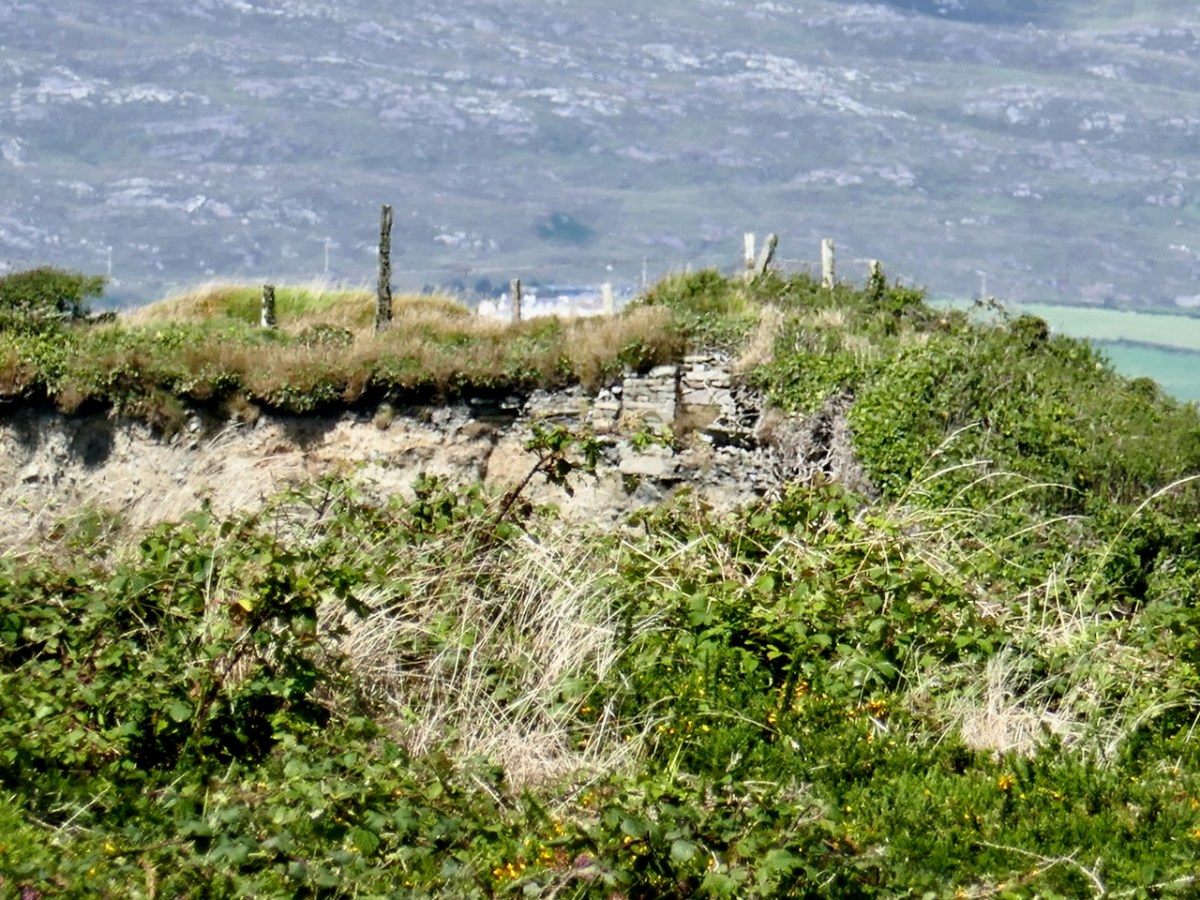
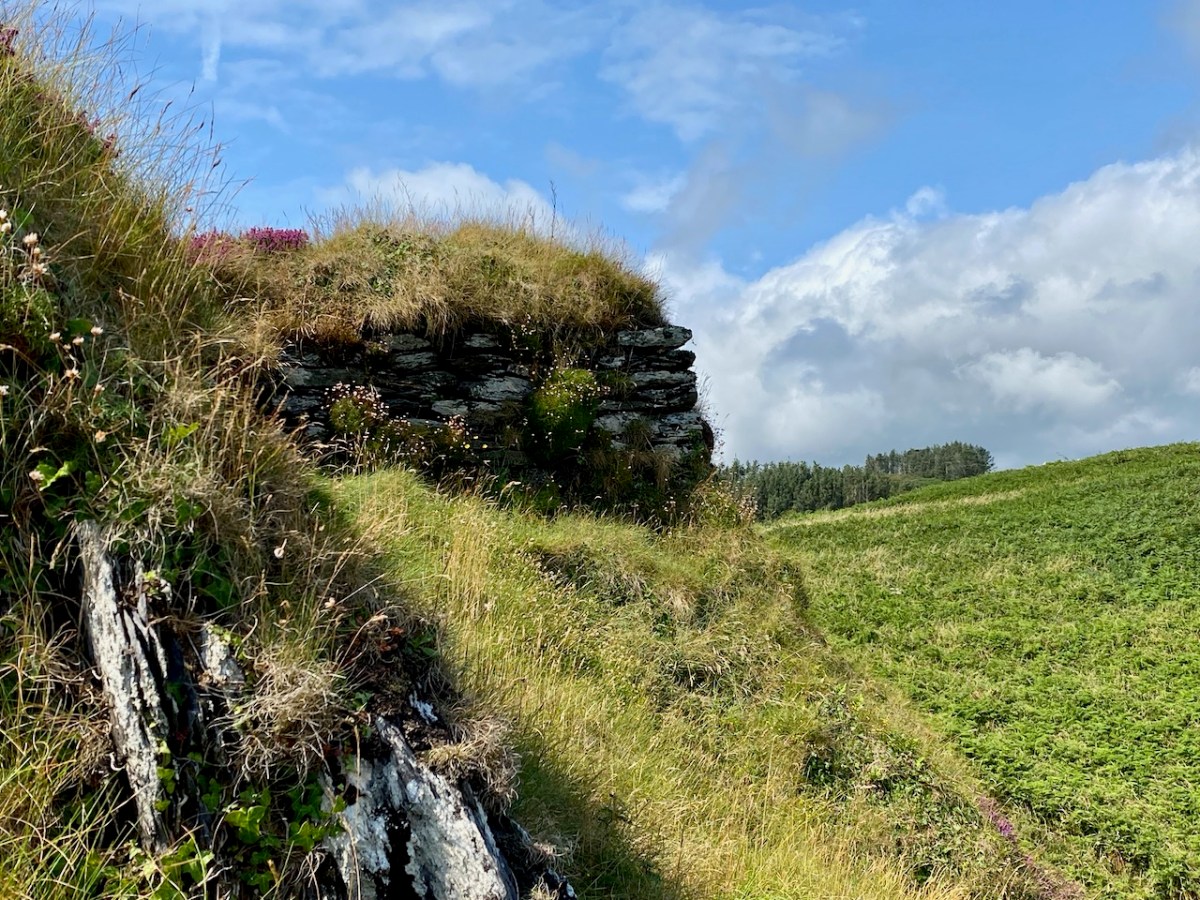
On the lush valley floor are signs of ancient activity and occupation. A stream flows through a meadow dotted with whitethorn trees (upper), while an old stone clapper bridge has been superseded by the modern boreen taking its way up to the Borlin Valley settlements (centre). Lower – a fascinating stone circle and mass rock site is interrupted by the field fence. Here, too, is a bullaun stone and cupmarked rock (below).
Let us give the last word to Johnny O’Driscoll from Snave, recorded by his grandson Sean O’Driscoll in the 1930s and featured in Julia Kemp’s Hidden Gold:
There is little gold in this area, but there is one place where it is said a crock of gold is buried. It is about a hundred yards from the Glaslough, between Coorycomade and Ardnatrush, about a mile and a half from Coomhola National School.
There is a bush growing at the exact location, and beneath the bush is a large stone which covers the hidden treasure. It belongs to a tiny dwarf, and anybody who visits the place at midnight can see this little creature on the bush above the gold.
People did go on one occasion in search of the gold, but they were unsuccessful. A little bright light is visible about midnight above the bush. I have seen it myself on several occasions . . .