…At Oldcourt a boat-building yard flourished within the walls of an old O’Driscoll castle overlooking the pier and river. Schooners and steamships used to anchor at this spot, the highest point they could travel up the river. Here their cargoes of coal and other supplies were unloaded and placed on specially built lighters with a small draught that would be poled along a further sluggish turn or two upstream to the pier at Skibbereen. In this way cargoes of cattle were brought up by islanders to be sold at the market… (description of the townland of Oldcourt from The Coast of West Cork by Peter Somerville-Large 1974)
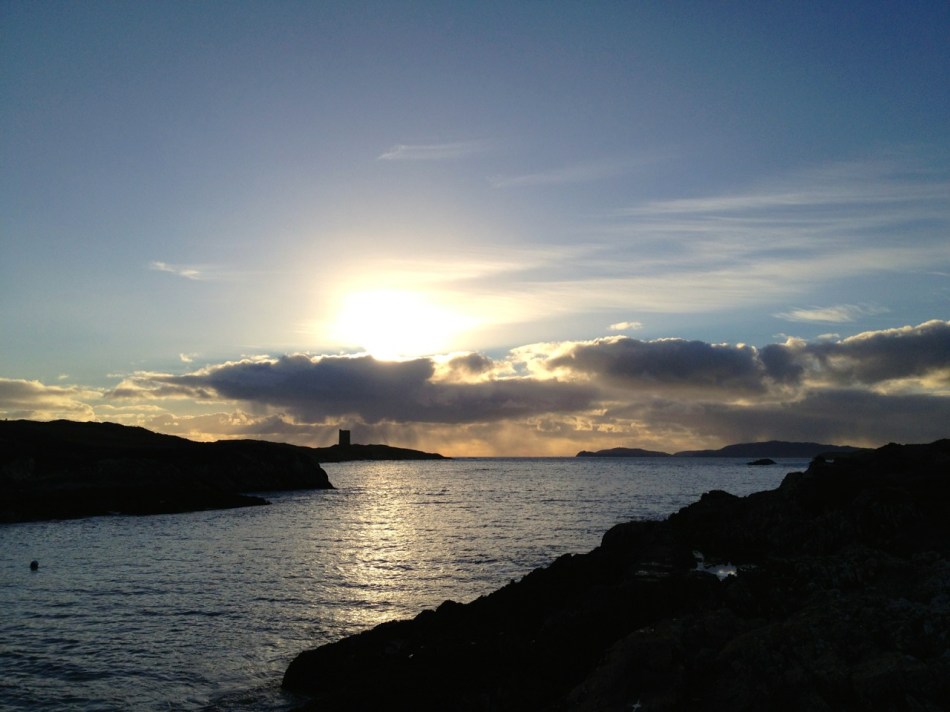
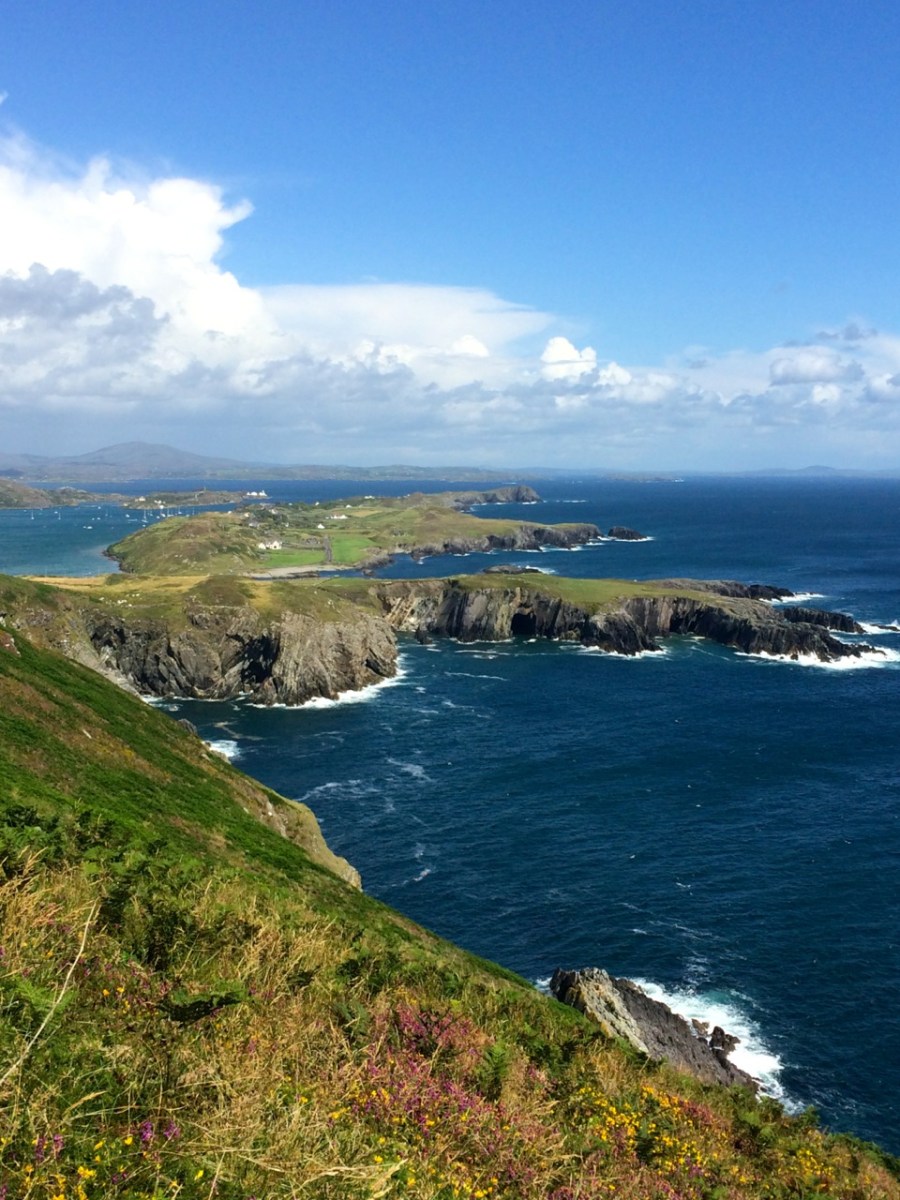
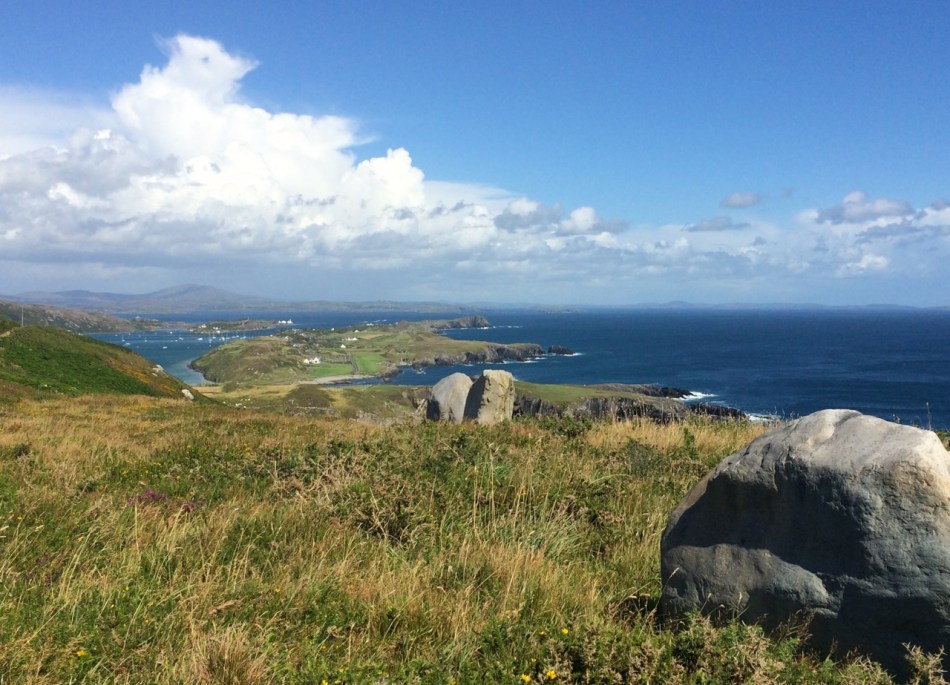
The tidal River Ilen making its lazy way out to Roaringwater Bay on a late summer evening has a melancholy beauty: it is wide and slow and – mid tide – is a perfect mirror to the sky. The sounds of Oystercatchers and Curlews coming over the water always bring thoughts of autumn: the harvest is ready to cut, the verges are brilliantly orange with the montbretia and the hedges purple-red and weighed down with fuscia.
We went down to Oldcourt to seek out history and atmosphere. We knew that it had once been a transport hub for the transhipments of goods and we wanted to see what might be visible from those earlier times. It was the river Ilen (pronounced eye-len) that gave birth to Skibbereen following a pirate raid on Baltimore in 1631. According to Skibbereen historian Gerald O’Brien …in the wake of the shock of that – the most daring pirate raid mounted against Britain or Ireland – a small number of survivors rowed upstream to resettle in the safety of the Ilen Valley. The role of this river-borne migration from Baltimore [was] a factor in the foundation of Skibbereen… (Journal of the Skibbereen and District Historical Society, Vol 7, p 91).
We found atmosphere a-plenty. On the upstream side of the wide inlet where the transhipment quays were sited is a streamlined modern boatyard where sleek yachts are wintered and serviced while, opposite and downstream, is a far more eclectic establishment surrounding and embracing the remains of the medieval castle and bawn: this is Hegarty’s – ‘…one of Ireland’s last surviving traditional boatyards…’
Our aim was to search for the old quay and the medieval buildings which had been part of the castle demesne, but we were fascinated to pick our way through boats of all kinds – classic, sailing, fishing, ferrying – and boat paraphernalia: here an old decapitated wheelhouse, there a collection of masts, everywhere ropes and tackle…
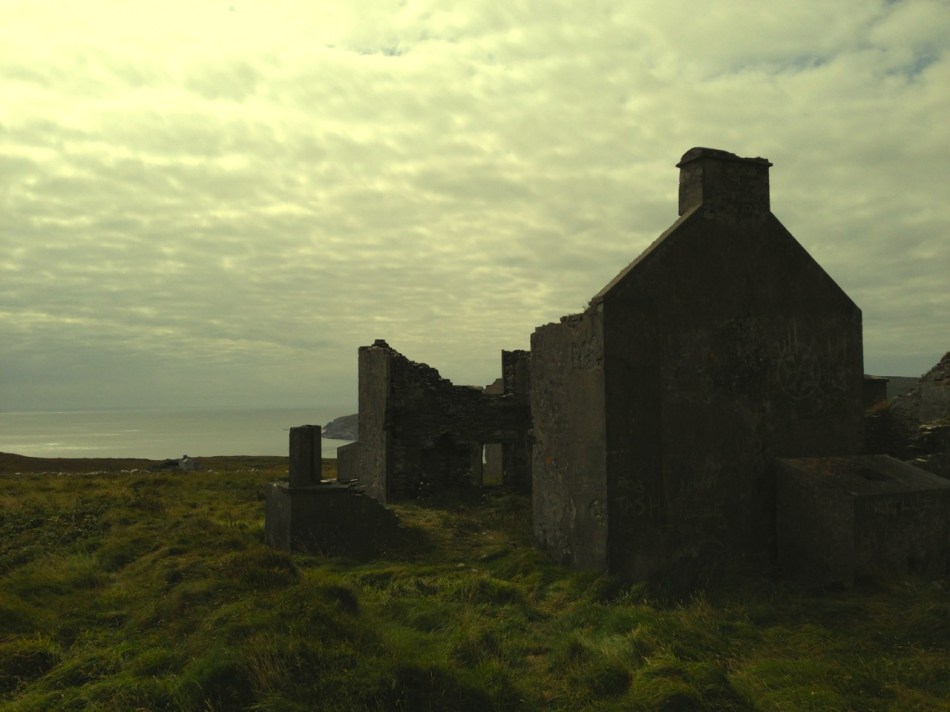
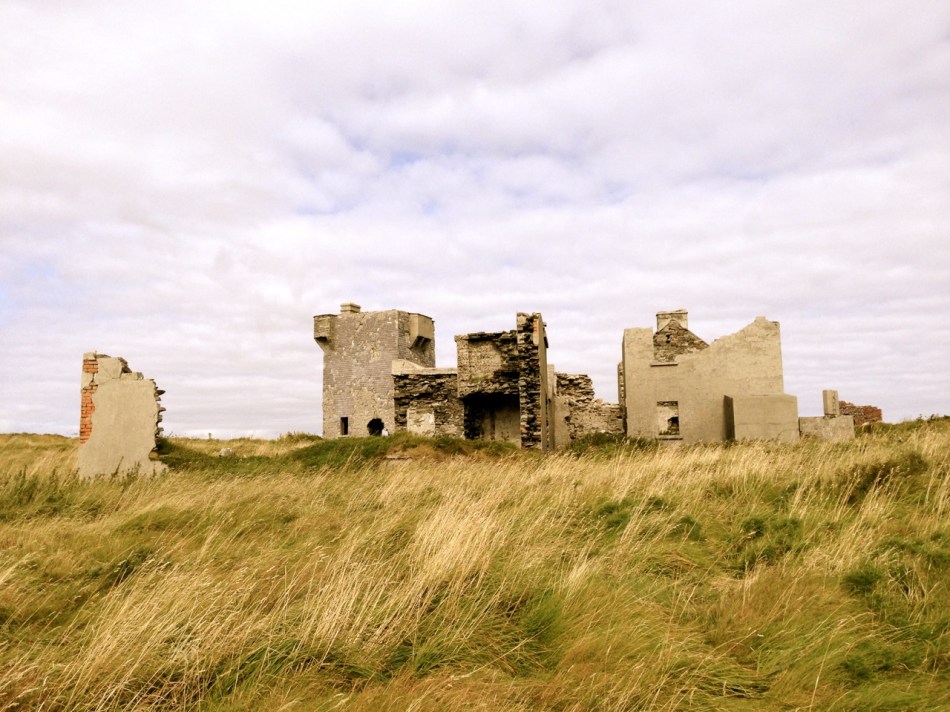
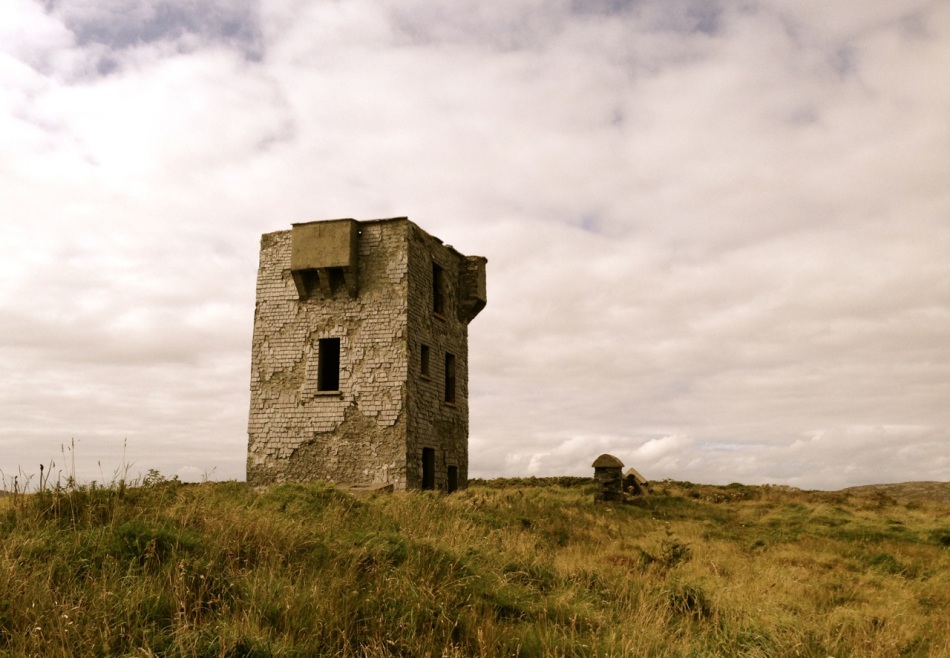
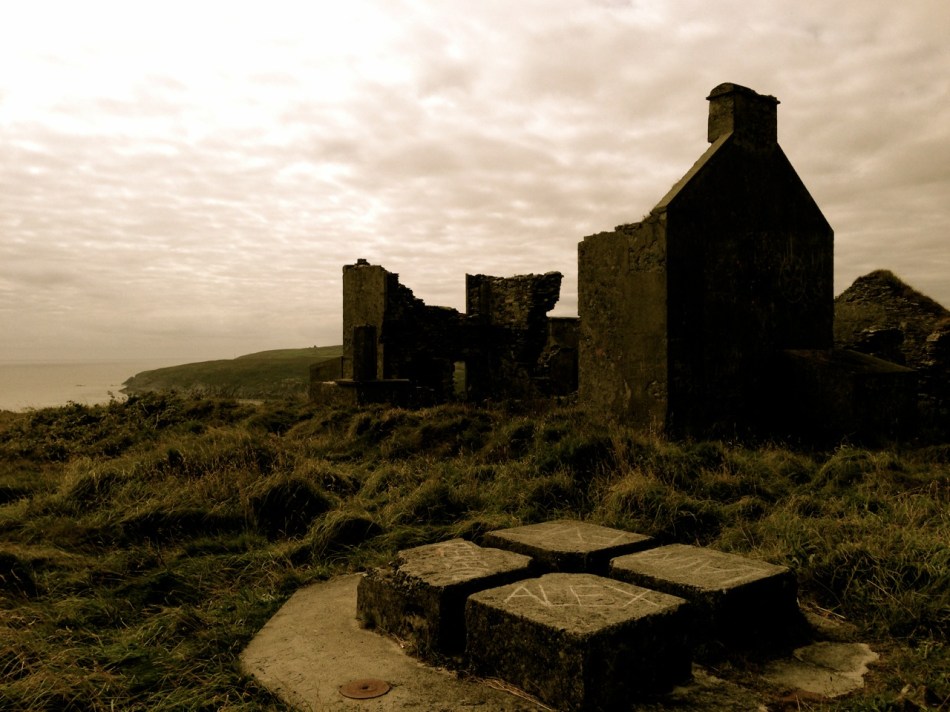
Oldcourt Castle is a tower house standing four storeys high but originally at least one storey higher, once surrounded by a bawn, some ruins of which remain. It was an O’Driscoll clan castle, probably dating from the 15th century, and was captured by English forces after the Battle of Kinsale in 1601.
Part of the castle bawn was used as a grain store up to comparatively modern times: now it houses a fascinating boat restoration. The story begins with Connor O’Brien (1880-1952) whose ketch, the Saoirse, took him on a circumnavigation of the world between 1923 and 1925. On this journey he stopped off at Port Stanley in the Falkland Islands. The islanders were so impressed at the way the Saoirse rode the waves that they asked O’Brien to arrange the building of a similar boat. This was the Ilen, named after the river and estuary and registered at the port of Skibbereen in February 1926. She was 56 feet in length overall with a beam of 14 feet and a displacement of 45 tonnes. Connor set sail in August 1926 from Cape Clear, arriving at Port Stanley in January 1927 where he handed it over to the new owners, The Falkland Islands Company, in exchange for £1,500. There she remained until the early 1990s, carrying cargoes of stores, mail, passengers and sheep. Limerick man Gary McMahon found it abandoned on one of the islands and determined that it should return to its homeland for restoration. There was great excitement when he sailed the ketch back into Baltimore in 1998. The refitting of this eighty-two year old vessel in the old bawn at Hegarty’s, Oldcourt, is now the centre of an educational project allowing people to experience first-hand the ancient skills of wooden boat building.
 The old grain store – formerly part of the Castle bawn – now houses the restoration project of the AK Ilen (above – courtesy of Roeboats)
The old grain store – formerly part of the Castle bawn – now houses the restoration project of the AK Ilen (above – courtesy of Roeboats)
Such a hive of activity at OIdcourt today… Echoes of busy days gone by when the schooners were arriving with their cargoes bound for the growing town of Skibbereen.