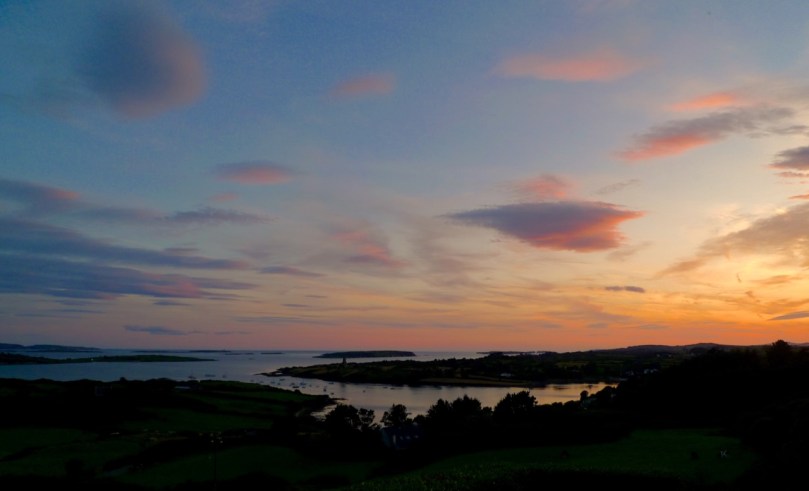
While researching for this post I picked up the excellent book by Niall Mac Coitir, Ireland’s Birds – Myths, Legends and Folklore and got diverted by a section on Eagles: why wouldn’t I, as we live up here in Nead an Iolair, Eagle’s Nest? I was delighted to discover from this book that Adam and Eve are reincarnated as Eagles and live on the island of Inishbofin, at the mouth of Killary Harbour in Galway. This adds to the list of important people of the world who have ended up in Ireland, including St Valentine in Dublin and Santa Claus (St Nicholas) who rests in Jerpoint Abbey. I’m hoping to discover many more…
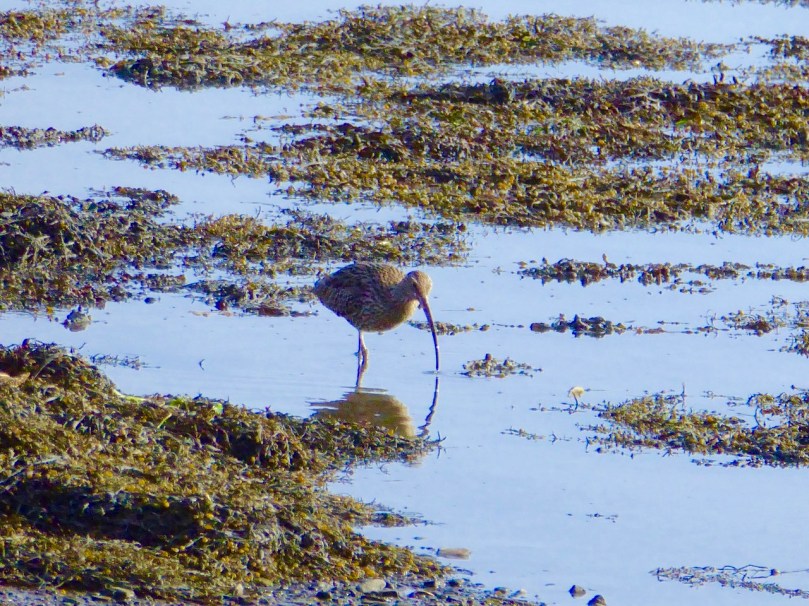
My real subject today is the Curlew: we have seen a few of them lately below us in Rossbrin Cove. They are winter visitors from Scandinavia. There is a small breeding population in Ireland, mainly centred in Galway and Mayo, but this has declined catastrophically in recent times, and the bird is now red-listed as a globally threatened species, according to Birdwatch Ireland. Every Curlew sighting, therefore, is an important one.
In Irish bird folklore, the Curlew does not come over in a good light. It has a very distinctive and haunting call, and this has probably contributed to associations with the Otherworld.
Mac Coitor says: …The Curlew was famous for its whistling and screeching calls, which were believed to foretell the arrival of rain or stormy weather… while Scottish poet Norman Alexander MacCaig (1910 – 1996) describes the Curlew’s voice:
Trailing bubbles of music over the squelchy hillside… music as desolate, as beautiful as your loved places, mountainy marshes and glistening mudflats by the stealthy sea…
Curlews fly at dusk, sometimes in groups: this has given rise to accounts of The Seven Whistlers in both Britain and Ireland. One of the earliest collectors of folkore in these islands, Jabez Allies (1787 – 1856), wrote:
…I have been informed that the country people used to talk a good deal about the ‘Seven Whistlers’ and the late John Pressdee, who lived at Cuckold’s Knoll, in Suckley, said that oftentimes, at night, when he happened to be upon the hill by his house, heard six out of the ‘Seven Whistlers’ pass over his head, but that no more than six of them were ever heard by him, or by any one else to whistle at one time, and that should the seven whistle together the world would be at an end…
Another account, from William Henderson, Folk-Lore of the Northern Counties of England and the Borders:
‘I heard ’em one dark night last winter,’ said an old Folkestone fisherman. ‘They come over our heads all of a sudden, singing “ewe, ewe,” and the men in the boat wanted to go back. It came on to rain and blow soon afterwards, and was an awful night, Sir; and sure enough before morning a boat was upset, and seven poor fellows drowned. I know what makes the noise, Sir; it’s them long-billed curlews, but I never likes to hear them.’
It’s that long, curved bill that makes the Curlew so distinct a figure down on the mud flats at low tide. The slim, pliable beak is used to probe in mud and shallow water for worms, crustaceans, and insects, and for exploring stones and shells. In flight the bird has a wonderful aerodynamism and reminds me of that beautiful aircraft – now extinct – Concorde. In my younger days, growing up in Hampshire, I watched the test flights of that plane at Farnborough, and always admired its drooping ‘Curlew’ nose.
Irish poetry has been enriched by images of the Curlew. Seamus Heaney’s From the Republic of Conscience:
When I landed in the republic of conscience
it was so noiseless when the engines stopped
I could hear a curlew high above the runway.
At immigration, the clerk was an old man
who produced a wallet from his homespun coat
and showed me a photograph of my grandfather.
The woman in customs asked me to declare
the words of our traditional cures and charms
to heal dumbness and avert the evil eye.
No porters. No interpreter. No taxi.
You carried your own burden and very soon
your symptoms of creeping privilege disappeared…
We can’t leave out W B Yeats – He reproves the Curlew:
O, CURLEW, cry no more in the air,
Or only to the water in the West;
Because your crying brings to my mind
Passion-dimmed eyes and long heavy hair
That was shaken out over my breast:
There is enough evil in the crying of wind.
Four of Yeats’ poems, including Curlew, were set to music by the eccentric English composer Philip Heseltine, who took the name Peter Warlock. The Curlew is a chamber song-cycle setting written for tenor voice, flute, cor anglais and string quartet. Heseltine spent some time in Ireland, including a period on a ‘Gaeltacht island’ (perhaps Cape Clear?) where he sought to learn the Irish language.
Heseltine / Warlock’s The Curlew brings us full circle, as the composer also spent time in Cornwall under the shadow of another Eagle’s Nest – near St Ives – in an area frequented by artists, writers and mystics including D H Lawrence, Aleister Crowley, Virginia Woolf and Patrick Heron. From Eagle’s Nest in West Cork to Eagle’s Nest in West Cornwall… The Curlew is a much-travelled bird… Be careful of the Seven Whistlers!